Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Deleted Portion Class XI Annual Exam Syllabus Sess - 220222 - 162416
Uploaded by
Jahida Akram0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views8 pagesOriginal Title
Deleted Portion Class XI Annual Exam Syllabus Sess_220222_162416
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views8 pagesDeleted Portion Class XI Annual Exam Syllabus Sess - 220222 - 162416
Uploaded by
Jahida AkramCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 8
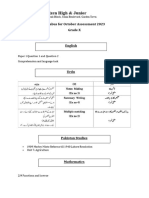
DELHI PUBLIC SCHOOL GHAZIABAD
DELETED PORTION OF SYLLABUS FOR ANNUAL EXAM
2021-22
CLASS XI
S.NO. SUBJECT NAME SYLLABUS
1. ENGLISH Writing
Classified Advertisements
Letters to the editor (giving suggestions/opinions on an issue)
Application for a job with a bio-data or résumé
Article Writing & Report Writing
Narrative Grammar
Modals
Clauses
Change of Voice
Error Correction
Editing Task
Cloze Passages
Literature
HORNBILL
• Hornbill
• Father To Son
• The Adventure
Snapshots
• The Ghat of the Only World
• The Tale of Melon City
2. PHYSICS Chapter-9 Mechanical Properties of Solids
Elastic behaviour, shear modulus of rigidity, Poisson's ratio;
elastic energy.
Chapter-11 Thermal properties matter Heat
temperature, Heat transfer-conduction, convection and
radiation
Chapter-12 Thermodynamics
Heat engine and refrigerator.
Chapter-15 Waves
fundamental mode and harmonics, Doppler effect.
3. CHEMISTRY Class XI
Portion to be Reduced
1 Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry
Nature of matter, laws of chemical combination, Dalton's
atomic
theory: concept of elements, atoms and molecules.
2 Structure of Atom Discovery of Electron, Proton and
Neutron, atomic number,
isotopes and isobars. Thomson's model and its limitations.
Rutherford's model and its limitations
3 Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties
Significance of classification, brief history of the development
of periodic table,
4 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
5 States of Matter:
Gases and Liquids liquefaction of gases, critical temperature,
kinetic energy and molecular speeds (elementary idea), Liquid
State- vapour pressure, viscosity and surface tension
(qualitative idea only, no mathematical derivations)
6 Chemical Thermodynamics Heat capacity and specific heat
capacity, Criteria for equilibrium
7 Equilibrium hydrolysis of salts (elementary idea),
Henderson Equation
8 Redox Reactions : applications of redox reactions
9 Hydrogen Preparation, properties and uses of hydrogen,
hydrogen peroxide -
preparation, reactionsand structure and use;
10 s -Block Elements Preparation and Properties of Some
Important Compounds:
Sodium Carbonate, Sodium Chloride, Sodium Hydroxide and
Sodium Hydrogen carbonate, Biological importance of
Sodium and
Potassium. Calcium Oxide and Calcium Carbonate and their
industrial uses, biological importance of Magnesium and
Calcium.
11 Some p -Block Elements
Some important compounds: Borax, Boric acid, Boron
Hydrides,
Aluminium: Reactions with acids and alkalies, uses.
Carbon: uses of some important compounds: oxides.
Important
compounds of Silicon and a few uses: Silicon Tetrachloride,
Silicones, Silicates and Zeolites, their uses.
12 Organic Chemistry:
Some basic Principles and Techniques methods of
purification, qualitative and quantitative analysis
13 Hydrocarbons free radical mechanism of halogenation,
combustion
and pyrolysis.
14 Environmental
Chemistry
Entire chapter
4. MATHEMATICS Trigonometric Functions: General Solutions of trigonometric
equations of the type sin y = sin a, cos y = cos a, and tan y =
tan a.
Permutations and Combinations: Derivation of formulae
for nPr and nCr
Straight Lines: Shifting of origin.· Equation of family of lines
passing through the point of intersection of two lines.
Conic sections: · a point, a straight line, and a pair of
intersecting lines as a degenerated case of a conic section
5. ACCOUNTANCY Term 2
Accounting for Bills of Exchange Retirement of bill Renewal of
bill
Incomplete Records: Difference between accounts from
incomplete records and Statement of Affairs. Preparation of
Trading, Profit and Loss account and Balance Sheet
Computers in Accounting: Introduction to accounting information
system (AIS) as a part of Management Information System. Stages
in automation: (a) Accounting process in a computerized
environment; comparison between manual accounting process and
computerized accounting process, (b) Sourcing of accounting
software; generic considerations before sourcing accounting
software (c) creation of account groups and hierarchy (d)
generation of reports - trial balance, profit and loss account and
balance sheet.
6. BUSINESS STUDIES TERM 2
UNIT 7-SOURCES OF BUSINESS FINANCE-FACTORING,
LEASE FINANCING, COMMERCIAL PAPER,
INTERNATIONAL FINANCING-COMMERCIAL
BANKS,INTERNATIONAL AGENCIES, FCCB’s
Unit 8: Small Business and Entrepreneurship Development
ADMINISTRATIVE SETUP FOR THE SMALL SCALE, AGRO
AND RURAL INDUSTRIES, ROLE OF SMALL BUSINESS IN
INDIA, PROBLEMS OF SMALL BUSINESS, GOVERNMENT
ASSISTANCE TO
SMALL INDUSTRIES AND SMALL BUSINESS UNITS-
NABARD, RSBDC, SIDBI, NCEUS, RWED, WASME, SFURTI
Unit 9: Internal Trade – FIXED SHOP LARGE RETAILERS-
MAIL ORDER HOUSES, CONSUMER COOPERATIVE
STORES, SUPER MARKETS, VENDING MACHINES, ROLE
OF INDIAN CHAMBERS OF
COMMERCE AND INDUSTRY IN PROMOTION OF
INTERNAL TRADE
Unit 10: International Trade – IMPORT/EXPORT
PROCEDURE AND RELATED DOCUMENTS
7. ECONOMICS Unit: Statistical Tools and Interpretation
• Measures of Dispersion – (range, quartile deviation,
mean deviation and); (co-efficient of range, co-
efficient of quartile-deviation, co- efficient of mean
deviation,
• Correlation –Spearman’s rank correlation.
• Index Numbers – index of industrial production
Unit: Producer Behaviour and Supply
• Producer’s equilibrium-meaning and its conditions in
terms of marginal revenue-marginal cost.
Unit: Forms of Market and Price Determination under
Perfect Competition with simple applications
• Other Market Forms – monopoly, monopolistic
competition – their meaning and features
8. APPLIED MATHEMATICS Unit-10-Tax
Unit-6-Circular permutation
9. COMPUTER SCIENCE Unit I: Computer Systems and Organisation
Encoding Schemes, UTF8, UTF32, Concept of cloud computing
and cloud services (SaaS,IaaS,PaaS), cloud (public/private),
Blockchain technology
Unit II: Computational Thinking and Programming - 1
• Decomposition – concept, need for decomposing a
problem, examples of problem-solving using
decomposition. ,
• Sorting algorithm: bubble and insertion sort; count the
number of operations while sorting
10. INFORMATICS PRACTICES Unit 3: Data Handling using NumPy Data and its purpose,
importance of data, structured and unstructured data, data
processing cycle, basic statistical methods for understanding
data - mean, median, mode, standard deviation and variance.
Introduction to NumPy library, NumPy arrays and their
advantage, creation of NumPy arrays; indexing, slicing, and
iteration; concatenating and splitting array Arithmetic
operations on one Dimensional and two Dimensional arrays.
Calculating max, min, count, sum, mean, median, mode,
standard deviation, variance on NumPy arrays.
11 PSYCHOLOGY Chapter 6 Learning-
Concept Learning, Transfer of Learning, Learning Styles, Applications
of Learning Principles
Chapter 7 Human Memory-
Knowledge Representation and Organization in Memory
Chapter 8- Entire Chapter
Chapter 9- Entire Chapter
12. LEGAL STUDIES Unit-5: iv. Children
vi. Property, Inheritance and succession
13. FINE ARTS Unit 3: Rock cut Temples- Sculpture- Ravana shaking mountain
Kailash
14. BANKING No Deletion in Banking in any unit.
15. BIOLOGY Under Unit 1: Diversity of Living Organisms
Chapter-1: The Living World
• taxonomy and systematics; tools for study of taxonomy-
museums, zoological parks, herbaria, botanical gardens,
keys for identification.
Chapter-3: Plant Kingdom
• Angiospermae; Angiosperms - classification up to class,
characteristic features and examples.
Under Unit-II Structural Organization in Animals and Plants
Chapter-5: Morphology of Flowering Plants
• Morphology and modifications: Morphology of different
parts of flowering plants: root, stem, leaf, fruit and seed.
Description of families: - Fabaceae
Chapter-6: Anatomy of Flowering Plants
• Anatomy and functions of different tissues and tissue
systems in dicots and monocots. Secondary growth.
Chapter-7: Structural Organisation in Animals
• Morphology, Anatomy and functions of different systems
(digestive, circulatory, respiratory, nervous and
reproductive) of an insect (cockroach), (a brief account
only)
Under Unit-IV Plant Physiology
Chapter-11: Transport in Plants
• Movement of water, gases and nutrients; cell to cell
transport, diffusion, facilitated diffusion, active transport;
plant-water relations, imbibition, water potential, osmosis,
plasmolysis; long distance transport of water - Absorption,
apoplast, symplast, transpiration pull, root pressure and
guttation; transpiration, opening and closing of stomata;
Uptake and translocation of mineral nutrients - Transport
of food, phloem transport, mass flow hypothesis.
Chapter-12: Mineral Nutrition
• Essential minerals, macro- and micronutrients and their
role; deficiency symptoms; mineral toxicity; elementary
idea of hydroponics as a method to study mineral
nutrition; nitrogen metabolism, nitrogen cycle, biological
nitrogen fixation.
Chapter-15: Plant - Growth and Development
• Seed germination; phases of plant growth and plant
growth rate; conditions of growth; differentiation,
dedifferentiation and redifferentiation; sequence of
developmental processes in a plant cell; Seed dormancy;
vernalisation; photoperiodism
Under Unit-V Human Physiology
Chapter-16: Digestion and Absorption
• Alimentary canal and digestive glands, role of digestive
enzymes and gastrointestinal hormones; Peristalsis,
digestion, absorption and assimilation of proteins,
carbohydrates and fats; calorific values of proteins,
carbohydrates and fats; egestion; nutritional and digestive
disorders - PEM, indigestion, constipation, vomiting,
jaundice, diarrhoea.
Chapter-20: Locomotion and Movement
• Types of movement - ciliary, flagellar, muscular; Skeletal
system and its functions; joints; disorders of muscular and
skeletal systems - myasthenia gravis, tetany, muscular
dystrophy, arthritis, osteoporosis, gout.
Chapter-21: Neural Control and Coordination
• reflex action; sensory perception; sense organs;
elementary structure and functions of eye and ear
16. BIOTECH Under Unit I: Biotechnology: An Overview o Chapter 1
Biotechnology: An Overview: Public Perception of Biotechnology,
Biotechnology in India and Global Trends
Under Unit II: Molecules of Life • Chapter 1 Bio-molecules-
Building Blocks: Sphingosine, Biochemical Transformations
Under Unit III:Genetics and Molecular Biology • Chapter 1:
Concepts of Genetics Gene Interaction, Sex-Linked Inheritance,
Extra nuclear Inheritance, Quantitative Inheritance, Genes at the
Population Level • Chapter 2: Genes and Genomes: Structure and
Function Regulation of Gene Expression, DNA Repair, Genome
Organization
Under Unit IV: Cells and Organisms o Chapter 1: The Basic Unit
of Life Tissues and Organs, Stem Cells, Biodiversity • Chapter 2:
Cell Growth and Development Gaseous Exchange, Internal
Transport, Maintaining the Internal Environment, In
vitroFertilization, Animal and Plant, Development, Programmed
Cell Death, Defense Mechanisms in Plants
17. MUSIC Hindustani Unit-1 Brief study of Nibaddha- Aniboddha Gan, Swarmalika,
Lakshan Geet.
Uni-2 Brief study of various Gharanas
Unit-3 Brief study of Brihaddeshi
Unit-4 Description of Prescribed Talas along with Tala Notation
with Thah, Dugun and Chaugun Dadra, Keharwa ,Sultaal
Uni-5 Writing in notation the compositions of prescribed Ragas
Raag-Jaunpur
18. PHYSICAL EDUCATION No deleted portion
19. SOCIOLOGY
1.Social Structure, Stratification And Social Processes In
Society
2. Environment and Society
.20. POL. SCIENCE A-Political Theory
1. Citizenship
2. Nationalism
3. Secularism
4. Peace
B- Indian Constitution at Work
1. Federalism
2.Chapter -2 (Rights in the Indian Constitution), Chapter –9 (
Constitution-As a Living Document) ,Chapter-10 (The philosophy of
the Constitution ) are merged with Chapter –1 ( Constitution-why
and How )
21. FASHION STUDIES Nothing is deleted from the syllabus
22. HOME SCIENCE Ch 13: Care and Education
Ch 18: Perspectives in Communication
Ch 19: Individual Responsibilities and Rights
23. ENTREPRENEURSHIP Chapter 1 – No change
Chapter 2 – No change
Chapter 3 – Self assessment of qualities, skills, resources and dreams = 4
marks
Chapter 4 – Risk taking- concept and types = 4 marks
Chapter 5 – No change
Chapter 6 - Income statement = 2 marks and Cash Flow Projection
= 3marks
Chapter 7 – Estimating financial resources requirement; Methods of
meeting financial requirements; Size and capital – based
classification= 8 marks
24. GEOGRAPHY Fundamental of Physical Geography Ch-12 World climate and
Climate change
India Physical Environment Ch-7 Natural Hazards and Disasters
25. GEOSPATIAL Nothing is deleted from the syllabus
26. HISTORY Theme-1 From Beginning of Time
Theme5- Nomadic Empire
Theme –8 Confrontation of Cultures
27. NCC National Integration - Freedom Struggle and Nationalist
Movement in India, Religions, culture, traditions and customs
of India
Unity in Diversity
Drill – Drill without arms, Ceremonial Drill
Weapon training - Short range firing, aiming and alteration of
sight
Personality Development and Leadership - Effects of
leadership with historical examples, Conflict motives –
resolution, Values/code of ethics
Social Awareness - Traffic control organisation and anti-
drunken driving
Disaster management - Civil defence organization and NDMA
Health and hygiene – wounds and fractures, Causes and
prevention of HIV AIDS, Structure and function of the human
body
Adventure training – Rock climbing, slithering
Armed forces -Task and role of fighting arms
Map reading - Relief, contours and gradients, Map to ground
and ground to map
Field craft - Types of knots and lashings
Military History – War movies
Communication – Basic RT procedures
You might also like
- Engineering Chemistry NotesDocument125 pagesEngineering Chemistry NotesDulce DeNo ratings yet
- Permabond Adhesive Guide: - Our Science... Your SuccessDocument28 pagesPermabond Adhesive Guide: - Our Science... Your SuccessU4 CreationZNo ratings yet
- Determination of Volatile Fatty Acid in Enviromental Aqueos Samples PDFDocument6 pagesDetermination of Volatile Fatty Acid in Enviromental Aqueos Samples PDFNierza Alfiannur100% (1)
- Introduction to Dynamic Programming: International Series in Modern Applied Mathematics and Computer Science, Volume 1From EverandIntroduction to Dynamic Programming: International Series in Modern Applied Mathematics and Computer Science, Volume 1No ratings yet
- DR Engp M II p1 1.1 R.5grifadoDocument176 pagesDR Engp M II p1 1.1 R.5grifadoleo100% (1)
- Hipot Cable TestingDocument13 pagesHipot Cable Testingsofyan_shah100% (4)
- 05 Fiber - Reinforced Polymers Processes and ApplicationsDocument470 pages05 Fiber - Reinforced Polymers Processes and ApplicationsarivumaniNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For Annual Exam - XI (2023-24) - 1Document3 pagesSyllabus For Annual Exam - XI (2023-24) - 1Harshit GargNo ratings yet
- 2nd Holiday Assignment SS2 2018 FOR 3rd Term2 PDFDocument21 pages2nd Holiday Assignment SS2 2018 FOR 3rd Term2 PDFBukola RotimiNo ratings yet
- Class XII Second Terminal SyllabusDocument5 pagesClass XII Second Terminal Syllabussampannkhanna21No ratings yet
- B.Tech. Electrical Engineering SyllabusDocument40 pagesB.Tech. Electrical Engineering Syllabussaurabh1116No ratings yet
- Xi Ansyllabus 2023 24Document15 pagesXi Ansyllabus 2023 24khanuja.mkNo ratings yet
- Class Xi Deleted PortionDocument8 pagesClass Xi Deleted PortionHACKER CHAUDHARYNo ratings yet
- GXI Syllabus & DS For PT4 FinalAsessment 2023-24Document8 pagesGXI Syllabus & DS For PT4 FinalAsessment 2023-24aayush.verma2105No ratings yet
- Ix - Syllabus For Eoy Exams 2023Document3 pagesIx - Syllabus For Eoy Exams 2023tahira mujahidNo ratings yet
- Term - Wise Syllabus Session-2019-20 Class - XII Subject: Chemistry (Code: 043)Document4 pagesTerm - Wise Syllabus Session-2019-20 Class - XII Subject: Chemistry (Code: 043)Naeem RehmanNo ratings yet
- Term - Wise Syllabus Session-2019-20 Class - XII Subject: Chemistry (Code: 043)Document4 pagesTerm - Wise Syllabus Session-2019-20 Class - XII Subject: Chemistry (Code: 043)Tushar YadavNo ratings yet
- Delhi Public School: Term-2 (Final Examination) - Syllabus - 2021-2022Document3 pagesDelhi Public School: Term-2 (Final Examination) - Syllabus - 2021-2022lasyaNo ratings yet
- Syl 11148490932Document3 pagesSyl 11148490932Uma ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Semster 1 & 2Document12 pagesSemster 1 & 2ASHYOUTUBE 10No ratings yet
- 2nd Holiday Assignment SS1 2018 FOR 3RD TERM2Document22 pages2nd Holiday Assignment SS1 2018 FOR 3RD TERM2Franca OkechukwuNo ratings yet
- State Properties: Molecular Weight, Compositions, Density, Vapor Pressure Etc. ForDocument34 pagesState Properties: Molecular Weight, Compositions, Density, Vapor Pressure Etc. ForParth BrahmbhattNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument101 pagesSyllabusSubburaj KarthickNo ratings yet
- S No Unit Portion To Be Reduced: CHEMISTRY (043) Class XIDocument4 pagesS No Unit Portion To Be Reduced: CHEMISTRY (043) Class XIA.Mohammad idhrisNo ratings yet
- Sem 4 SyllabusDocument6 pagesSem 4 SyllabusTushar RathiNo ratings yet
- Periodic Test 2 - GR-11Document5 pagesPeriodic Test 2 - GR-11Red AsusNo ratings yet
- NDA Syllabus 2019 For Mathematics: Topic-Wise Distribution of Questions in MathsDocument4 pagesNDA Syllabus 2019 For Mathematics: Topic-Wise Distribution of Questions in Mathsrohit champNo ratings yet
- Annual Examination Syllabus Class 11Document9 pagesAnnual Examination Syllabus Class 11aakashga68No ratings yet
- 9IG-Syllabus 2024Document2 pages9IG-Syllabus 2024abhijayg02No ratings yet
- Organisational Behaviour PDFDocument2 pagesOrganisational Behaviour PDFANIRBAN BHULNo ratings yet
- Course-Structure-Syllabi-BCom 1-101-140Document40 pagesCourse-Structure-Syllabi-BCom 1-101-140Ram YadavNo ratings yet
- Xi - Annual Syllabus - 24TH Jan - 240125 - 091613-1Document4 pagesXi - Annual Syllabus - 24TH Jan - 240125 - 091613-1GenNo ratings yet
- Amie Syllabus Sec B ChemicalDocument6 pagesAmie Syllabus Sec B ChemicalArunkumarNo ratings yet
- EOY Syllabus: Cambridge Campus Gulshan Class X Beaconhouse School System End of Year Examination (EOY)Document2 pagesEOY Syllabus: Cambridge Campus Gulshan Class X Beaconhouse School System End of Year Examination (EOY)amnaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For Yea 20232024 Grade 11Document6 pagesSyllabus For Yea 20232024 Grade 11yash saravgiNo ratings yet
- Syl 51782814928Document10 pagesSyl 51782814928shreyayadav8818No ratings yet
- Lecture # 1&2 - Week # 1-2Document45 pagesLecture # 1&2 - Week # 1-2Sufyan KhanNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Science Syllabus 2023-24 (Revised) PDF DownloadDocument5 pagesCBSE Class 10 Science Syllabus 2023-24 (Revised) PDF Downloadrawatshashwat70No ratings yet
- 10 Science Eng 2024 25Document3 pages10 Science Eng 2024 25gipsmanishNo ratings yet
- Y10 Portions - End of The Year AssessmentDocument8 pagesY10 Portions - End of The Year AssessmentInsightful TutorsNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Annual Exam SyllabusDocument7 pagesClass 11 Annual Exam SyllabusManju BansalNo ratings yet
- Grade X SyllabusDocument8 pagesGrade X SyllabusHPlayzNo ratings yet
- S No Unit Portion To Be Reduced: CHEMISTRY (043) Class XIDocument2 pagesS No Unit Portion To Be Reduced: CHEMISTRY (043) Class XIDivyansh BishtNo ratings yet
- Unit No. Unit: MarksDocument5 pagesUnit No. Unit: MarksSajayanKSNo ratings yet
- CLASS XII (2020-21) (Theory) Total Periods (Theory 98 + Practical 36) Time: 3 Hours 70 Marks Unit No. Title No. of Periods MarksDocument3 pagesCLASS XII (2020-21) (Theory) Total Periods (Theory 98 + Practical 36) Time: 3 Hours 70 Marks Unit No. Title No. of Periods MarksAlok RajNo ratings yet
- Class XI (NEW) Syllabus 3rd AugustDocument46 pagesClass XI (NEW) Syllabus 3rd AugustSandipan ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Scheme & Syllabus of Examination of Part-I For Post No. 4 Assistant Account Officer Grade-IiDocument4 pagesScheme & Syllabus of Examination of Part-I For Post No. 4 Assistant Account Officer Grade-IiVikash SinghNo ratings yet
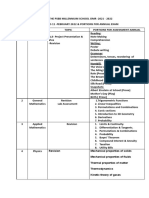
- Class 11 - Portions - FEBRUARY 2022Document3 pagesClass 11 - Portions - FEBRUARY 2022Amit JNo ratings yet
- RGPV 1st Year (Sy) 1st & 2nd SemDocument17 pagesRGPV 1st Year (Sy) 1st & 2nd Semsaurabhrai160290No ratings yet
- Corrigendum/ Addendum in Syllabus: + GommerceDocument7 pagesCorrigendum/ Addendum in Syllabus: + GommerceNilambar SahuNo ratings yet
- Circular 181 22 5902 2Document5 pagesCircular 181 22 5902 2Hemang ChoubeyNo ratings yet
- Nehru Smaraka Vidyalaya Portion List For Grade 11Document3 pagesNehru Smaraka Vidyalaya Portion List For Grade 11Sanjeev KumarNo ratings yet
- GBU Syllabus First SemDocument16 pagesGBU Syllabus First SemAnonymous ZUMyVoNo ratings yet
- REVISED SR SEC Chemistry 2020 21Document8 pagesREVISED SR SEC Chemistry 2020 21jacobNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: Chemical Engineering (05) Subject CodeDocument4 pagesGujarat Technological University: Chemical Engineering (05) Subject CodeMayank PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Revised Chemistry Syllabus 2020 21Document8 pagesCBSE Class 12 Revised Chemistry Syllabus 2020 21Arsh AhmadNo ratings yet
- Approved Syllabus For Analyst GradeII - 02022024Document5 pagesApproved Syllabus For Analyst GradeII - 02022024viswanath SomanchiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry CourseDocument4 pagesChemistry CourseanilstaffNo ratings yet
- Shahu EntranceDocument7 pagesShahu Entrancessd22.11.7No ratings yet
- Syllabus & Details About CETEE (Lab) Facility: Energy Management (2019 - 2020)Document14 pagesSyllabus & Details About CETEE (Lab) Facility: Energy Management (2019 - 2020)SukujuNo ratings yet
- Syllabus UG2001ch5to8Document46 pagesSyllabus UG2001ch5to8harikrishnan86100% (3)
- Cbse Grades 12 Curriculum Overview - 2022-23Document8 pagesCbse Grades 12 Curriculum Overview - 2022-23prasanthiNo ratings yet
- Science Subjects I Year 30 PercentDocument12 pagesScience Subjects I Year 30 Percentp. sashankNo ratings yet
- A Basic Introduction to Pollutant Fate and Transport: An Integrated Approach with Chemistry, Modeling, Risk Assessment, and Environmental LegislationFrom EverandA Basic Introduction to Pollutant Fate and Transport: An Integrated Approach with Chemistry, Modeling, Risk Assessment, and Environmental LegislationNo ratings yet
- Class 10 UT 3 2021Document3 pagesClass 10 UT 3 2021Jahida AkramNo ratings yet
- Power SharingDocument6 pagesPower Sharingspecial kavitasNo ratings yet
- Periodic Classification of Elements VerifiedDocument12 pagesPeriodic Classification of Elements VerifiedHIMNISH SHARMANo ratings yet
- Class XI Annual Exam Syllabus Session 2021-22-21Document10 pagesClass XI Annual Exam Syllabus Session 2021-22-21Jahida AkramNo ratings yet
- Revised End Term Exam Date Sheet Class XIDocument1 pageRevised End Term Exam Date Sheet Class XIJahida AkramNo ratings yet
- Internal Assessment - Ii Class Xi Stndard MathematicsDocument2 pagesInternal Assessment - Ii Class Xi Stndard MathematicsJahida AkramNo ratings yet
- Kelm403 PDFDocument33 pagesKelm403 PDFSoniya SahuNo ratings yet
- Sika Top Seal - 107 ElasticDocument2 pagesSika Top Seal - 107 Elasticislam ashrafNo ratings yet
- MSDS Malaysia Kahf Humbling Forest Eau de ToiletteDocument4 pagesMSDS Malaysia Kahf Humbling Forest Eau de ToiletteyeniNo ratings yet
- Ointment PrepDocument12 pagesOintment PrepRoland GealonNo ratings yet
- Citrosteril Disinfectant 101Document2 pagesCitrosteril Disinfectant 101Darnel Perino CabañingNo ratings yet
- Dividing Wall Technology in Distillation ColumnsDocument5 pagesDividing Wall Technology in Distillation ColumnsAmda AmdaNo ratings yet
- Fluid SaturationDocument14 pagesFluid SaturationHarry JakeNo ratings yet
- RBSA Indian Steel Industry AnalysisDocument45 pagesRBSA Indian Steel Industry AnalysisVasiliy GuryevNo ratings yet
- 8.0 Series IBR 20/21/25/26 To 588 PSI, IBR 35/36 To 235 PSI: Fig.7.1: ITABAR IBR-25 For Pipe Size ID 5.76 InchesDocument7 pages8.0 Series IBR 20/21/25/26 To 588 PSI, IBR 35/36 To 235 PSI: Fig.7.1: ITABAR IBR-25 For Pipe Size ID 5.76 InchesarfanNo ratings yet
- Aldehyde and Ketone Madam GanDocument3 pagesAldehyde and Ketone Madam GannursyahirahNo ratings yet
- Propellant Ignition and Flame PropagationDocument31 pagesPropellant Ignition and Flame PropagationOsvaldo BenitezNo ratings yet
- Ultima X Series Instruction Manual - enDocument141 pagesUltima X Series Instruction Manual - enStefano EsmNo ratings yet
- Tube Erosion PDFDocument9 pagesTube Erosion PDFktjayakumar3878No ratings yet
- Thiruppathiajan R - CVDocument4 pagesThiruppathiajan R - CVThiruppathirajanNo ratings yet
- Kris Arvid BerglundDocument40 pagesKris Arvid BerglundckleinnikeNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Combined Science 0653/51Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Combined Science 0653/51Paca GorriónNo ratings yet
- Influence of Vegetable Based Cutting Fluids On Cutting Force and Vibration Signature During Milling of Aluminium Metal Matrix CompositesDocument17 pagesInfluence of Vegetable Based Cutting Fluids On Cutting Force and Vibration Signature During Milling of Aluminium Metal Matrix CompositesNima FakherNo ratings yet
- Magnet Recycling: Rethinking Scrap Collection and SeparationDocument16 pagesMagnet Recycling: Rethinking Scrap Collection and SeparationBerk GülörtenNo ratings yet
- Paper+Cutting+Knives+englDocument23 pagesPaper+Cutting+Knives+englbelan_80No ratings yet
- Strength and Transport Characteristics of Volcanic Pumice Powder Based High Strength Concrete - Zeyad Tayeh YusufDocument11 pagesStrength and Transport Characteristics of Volcanic Pumice Powder Based High Strength Concrete - Zeyad Tayeh Yusufseth HernanNo ratings yet
- BS 434-2-1984 Code of Practice For Use of Bitumen Road EmulsiDocument22 pagesBS 434-2-1984 Code of Practice For Use of Bitumen Road EmulsianjanaNo ratings yet
- Rocks PDFDocument5 pagesRocks PDFfatwa27No ratings yet
- Sheet Metal - WikipediaDocument10 pagesSheet Metal - WikipediaDhamo_55No ratings yet
- CHAPTER - BOOK - Fundición A Presión (Molde Permanente)Document10 pagesCHAPTER - BOOK - Fundición A Presión (Molde Permanente)JimyVillaNo ratings yet
- Parameter Study of Melt Spun Polypropylene Fibers by Centrifugal SpinningDocument16 pagesParameter Study of Melt Spun Polypropylene Fibers by Centrifugal SpinningAnonymous PHCzwD8eAONo ratings yet
- Bronze Trolley Wire: Standard Specification ForDocument6 pagesBronze Trolley Wire: Standard Specification ForAhmed BilalNo ratings yet