Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Estimated Voltage Drop Calculator 1.1 - SIEMENS
Uploaded by
Cipri RengleCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Estimated Voltage Drop Calculator 1.1 - SIEMENS
Uploaded by
Cipri RengleCopyright:
Available Formats
Project Name
Firm Name
Date
Engineer
Feeder Data
Estimated Voltage Drop Calculator
Input
Load Voltage 120 V 1Ø
Conductor Size 12
Conductor Type Cu Al
Number of Sets 1
Distance (one way) Feet
Load (A) A
Output
Unity Power Factor 85% PF
Voltage Drop (V) 0.0 V 0.0 V
Voltage Drop (%) 0.0 % 0.0 %
Voltage at Load 120.0 V 120.0 V
Minimum Conductor Size for 3% VD
Minimum Conductor Size for 5% VD
Voltage Drop Summary
Project Name:
Engineer:
Date:
Feeder Designation Source Panel Source Circuit Vd (V) Vd (%)
Information
Information
This voltage drop calculator is based on public domain formulae and will provide an approximate value for use in
project design. The National Electrical Code™ Articles 210.19(A)(1) FPN No.4 and 215.2(A)(3) FPN No.2 suggest
that a design with no more than 3% voltage drop for feeders and no more than a total of 5% voltage drop in branch
circuits to the farthest outlet will "provide reasonable efficiency of operation".
Even though FPN's (fine print notes) in this case are not code requirements but recommendations, it is still good
engineering practice to closely follow these guidelines, and indeed exceed them where needed. In fact, Section
647, Sensitive Electronic Equipment, requires (not an FPN) that voltage drop for feeders and branches shall not
exceed 1.5% and 2.5%, respectively, and shall not exceed 1% and 2% respectively for cord-connected equipment.
Fire pumps have additional maximum voltage drop requirements and these are outlined in Section 695.
If you do increase the size of your conductors to accommodate for voltage drop, remember to check if the new
conductor size is compatible with the lugs to which they will be attached. The circuit breaker manufacturers make
available the acceptable conductor sizes, and in some cases offer optional larger lugs for this purpose. Also,
Article 250 requires that if the conductors are upsized, the grounding conductor must also be upsized
proportionately.
The unity power factor section of this program is based on the approximate voltage drop formula Vd = (2 K Q I D) /
CM for single phase and Vd = (1.732 K Q I D) / CM for three phase where K equals 12.9 for Copper and 21.2 for
Aluminum, Q is the ratio of Rac/Rdc for conductors larger than 2/0 (this takes into account skin effect at larger
conductor sizes), I is the current in amperes, D is the one-way circuit distance in feet, and CM is the conductor
cross section in circular mils. This equation assumes a power factor of 1.0, conductor temperature of 75°C,
and individual conductors run in steel conduit. The 85% power factor section is based on NEC™ Chapter 9,
Tables 8 and 9.
Printing - When printing the Voltage Drop Calculator sheet, go to File/Print Preview and select "black & white"
from the Print options.
You might also like
- Log in Register 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Next LastDocument3 pagesLog in Register 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Next LastCipri RengleNo ratings yet
- Garlic Soup 100x Stronger Than MedicineDocument2 pagesGarlic Soup 100x Stronger Than MedicineCipri RengleNo ratings yet
- ANEXA 2 - Dimensiunile Şi Secţiunile Conductoarelor Rotunde Din CupruDocument1 pageANEXA 2 - Dimensiunile Şi Secţiunile Conductoarelor Rotunde Din CupruCipri RengleNo ratings yet
- Crono 75 RG Motorhacke BJ 2011 AlpinaDocument7 pagesCrono 75 RG Motorhacke BJ 2011 AlpinaCipri RengleNo ratings yet
- When A Transport Tycoon Hard Game Begins (Or Open TTD) ... Early Survival TipsDocument5 pagesWhen A Transport Tycoon Hard Game Begins (Or Open TTD) ... Early Survival TipsCipri RengleNo ratings yet
- Service Manual Aiwa NSX-R37Document55 pagesService Manual Aiwa NSX-R37Zoran ProkicNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Traction - PKPattanaik-2019Document7 pagesTraction - PKPattanaik-2019Guru MishraNo ratings yet
- Sunny Tripower 20000Tl / 25000TlDocument2 pagesSunny Tripower 20000Tl / 25000TlnooralhudNo ratings yet
- VFD Harmonic MitigationDocument17 pagesVFD Harmonic Mitigationbirmaduu100% (1)
- Effects of Voltage Sag Due To Starting of Induction Motor-Ed2Document14 pagesEffects of Voltage Sag Due To Starting of Induction Motor-Ed2Mohd Amzary JamaludinNo ratings yet
- Blaw Emm ElectricityDocument18 pagesBlaw Emm ElectricityCommence NkomoNo ratings yet
- Cir Vision enDocument32 pagesCir Vision enJuan Manuel GelminiNo ratings yet
- KVAR RegulationDocument2 pagesKVAR Regulationwagner_guimarães_1No ratings yet
- VF A7 ManualDocument249 pagesVF A7 ManualzlatkozdihanNo ratings yet
- Multi Pulse With RectifireDocument17 pagesMulti Pulse With RectifireDix TandelNo ratings yet
- Power Quality in Electrical Systems - SoftwareDocument6 pagesPower Quality in Electrical Systems - Softwareb33lawNo ratings yet
- PSBD Unit 3 Page No 95Document8 pagesPSBD Unit 3 Page No 95Vishal BhatNo ratings yet
- Upgrading The ProtectionDocument4 pagesUpgrading The ProtectionMukesh KumarNo ratings yet
- BTech CSE Syllabus 2018 PDFDocument156 pagesBTech CSE Syllabus 2018 PDFShashank NadakuditiNo ratings yet
- SMA - Sunny Central Storage 500 1000 - enDocument6 pagesSMA - Sunny Central Storage 500 1000 - enJayapavidranNo ratings yet
- A Three Phase Integrated On-Board Charger For Plug in Electric VehiclesDocument18 pagesA Three Phase Integrated On-Board Charger For Plug in Electric VehiclesUdu KumarNo ratings yet
- 3 Phase Power Analyzer: ISO-9001, CE, IEC1010Document2 pages3 Phase Power Analyzer: ISO-9001, CE, IEC1010Mathías Huillca CameronNo ratings yet
- Synchronous MotorsDocument25 pagesSynchronous MotorsJan Edward L. SuarezNo ratings yet
- A Novel AC To AC Wireless Power Transfer SystemDocument6 pagesA Novel AC To AC Wireless Power Transfer Systemarunkumarmurugesan88No ratings yet
- CP2000 Quick Start - English PDFDocument5 pagesCP2000 Quick Start - English PDFNghiaNguyentrungNo ratings yet
- Lutron DW-6092 PDFDocument61 pagesLutron DW-6092 PDFedyyurisNo ratings yet
- KEB R6 S Rev 2D ManualDocument42 pagesKEB R6 S Rev 2D ManualTeoNo ratings yet
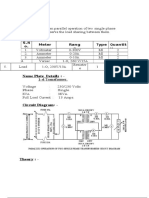
- A I M:-Appar Atus:-: S.N O. Meter Rang e Type Quantit yDocument4 pagesA I M:-Appar Atus:-: S.N O. Meter Rang e Type Quantit yTapobroto ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- P-192-94 WAPDA SPECIFICATION For 132kV CAPACITOR BANKSDocument12 pagesP-192-94 WAPDA SPECIFICATION For 132kV CAPACITOR BANKSHasnain AwanNo ratings yet
- Manual Iq Dataplus IIDocument47 pagesManual Iq Dataplus IIArmando HuarayaNo ratings yet
- PowerLogic PM800 Series - PM870MGDocument3 pagesPowerLogic PM800 Series - PM870MGJose TomassettiNo ratings yet
- Thyne500 - 600 Model Rev10Document25 pagesThyne500 - 600 Model Rev10Giovani Scarpati100% (1)
- Wet Transformer? Dry It On-Line No Stops: Now Wet Transformers Can Be Dehydrated Without Being Taken Out of Service!Document2 pagesWet Transformer? Dry It On-Line No Stops: Now Wet Transformers Can Be Dehydrated Without Being Taken Out of Service!Vishwas KaleNo ratings yet
- Annamacharya Institute of Technology and Sciences Rajampet (An Autonomous Institution)Document2 pagesAnnamacharya Institute of Technology and Sciences Rajampet (An Autonomous Institution)Aravind KumarNo ratings yet
- Tmda Inverter Catalog Update 20220610Document24 pagesTmda Inverter Catalog Update 20220610monozone789No ratings yet
- Air Cooled Screw Chillers - McEnergy Mono - Rev. 7.0 PDFDocument40 pagesAir Cooled Screw Chillers - McEnergy Mono - Rev. 7.0 PDFHung Tran100% (1)