Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sopore Law College
Uploaded by
lone Nasir0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views7 pagesYes
Original Title
Document
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentYes
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views7 pagesSopore Law College
Uploaded by
lone NasirYes
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
Sopore law college
Name. : Nasir Bashir
Enrollment no : 17042128044 (44)
Semester : BA LLB 8th
Subject: Taxitation Law
Topic : Discuss in Detail Definitions, Nature and Scope of Service tax.
Teacher incharge : Mr. Wajid .
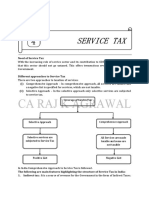
Defination of “services tax” .
Definition: Service tax is a tax levied by the government on service
providers on certain service transactions, but is actually borne by the
customers. It is categorized under Indirect Tax and came into existence
under the Finance Act, 1994.
Description: In this case, the service provider pays the tax and recovers
it from the customer. Service Tax was earlier levied on a specified list of
services, but in the 2012 budget, its scope was increased. Services
provided by air-conditioned restaurants and short term accommodation
provided by hotels, inns, etc. were also included in the list of services.
It is charged to the individual service providers on cash basis, and to
companies on accrual basis. This tax is payable only when the value of
services provided in a financial year is more than Rs. 10 lakh. This tax is
not applicable in the state of Jammu & Kashmir.
Discuss in Detail Definitions, Nature and Scope of Service tax.
Service tax is a indirect tax imposed on specific services
(taxable services) provided by a service provider
(company, individual, firm, and so on).
Service tax was first brought into force with effect from
1st July, 1994. All service providers in India, except
those in the state of Jammu and Kashmir, are required to
pay a service tax in India.
Initially only three services were brought under service
tax and the tax rate was 5%. Gradually more services
came under the ambit of service tax.
The rates currently applicable are listed below:
● Service tax - 14%
● Swachh Bharat Cess - 0.5%
● Krishi Kalyan Cess - 0.5%
Scope
Initially, service tax was chargeable on the basis of
realisation, that is, receipt of the consideration for the
services provided/to be provided (in case of advance
receipts). With effect from 1 April 2011, the Point of
Taxation Rule was introduced for the collection of
service tax.
Point of taxation refers to the point of time when a
service shall be deemed as provided.
According to this rule, the point of taxation shall be
either of the following dates, whichever is earlier:
● Date of issue of the invoice
● Date of receipt of payment
The liability of paying tax to the Government is on the
service provider, that is, the person providing the
service, and in some cases, the liability is on the service
receiver.
Example: Royal Agency provided advertising services of
Rs. 1,00,000 to SysImage. On the service amount of
Rs.1,00,000, Royal Agency is liable to pay the tax of
Rs. 12,360 @ 12.36% (12% of Service Tax, 2% of
Education Cess, 1% of Secondary Education Cess).
Applicability
Service tax is applicable on taxable services:
1. Provided and taxable in the hands of service
provider.
2. Received and taxable in the hands of service
receiver: Generally it is the service provider who is
liable to collect Service Tax from his customer/client
and pay the same to the Government. But Section
68(2) empowers the Government to notify the
services with regard to which the service receiver
would be held liable to pay Service Tax to the
Government.
For the services mentioned below, the service receiver is
liable to pay Service Tax (as per Notification 36/2004 ST
dated 31.12.2004 as amended from time to time):
● Goods Transport Agency service
● Business auxiliary service of distribution of
mutual fund by a mutual fund distributor or agent
● Sponsorship service provided to any body
corporate/firm
● Taxable services received by any person in India
from abroad
● Insurance auxiliary service by an insurance
agent
With effect from 1 July, 2012, a negative list-
based system of tax on services was introduced:
● Negative list is a list of services that are not subject
to service tax.
● All services other than those featuring in the negative
list fall under the purview of taxable services.
The definition of taxable service is different for each class
of services, for example, in case of a stock broker
agency, any service provided to an investor by buying or
selling securities listed on a recognised stock exchange
will be a taxable service.
Scope: It is leviable on taxable services ‘provided’ or ‘to be
provided’ by a service provider. The services ‘to be provided’ in
future are taxed only if payment in its respect is received in
advance.
Two separate persons required Payment to employees not
covered: For charge of service tax, it is necessary that the
service provider and service recipient should be two separate
persons acting on ‘principal to principal basis’. Services provided
by an employee to his employer are not covered service tax and,
therefore, salaries or allowances paid to them cannot be charged
to service tax.
Value: For the levy of the service tax, the value shall be computed
in accordance with section 67 read with Service Tax
(Determination of Value) Rules, 2006.
Free services not taxable : No service tax is leviable upon the
services provided free of cost.
Payment of service tax : The person providing the service (i.e.
the service provider) has to pay service tax in such manner and
within such period as is prescribed in the Service Tax Rules, 1994.
The service tax is to be paid only on the receipt of payment
towards the value of taxable services.
Procedures: Provisions have been made for registration,
assessment including self assessment, rectifications, revisions,
appeals and penalties on the service providecos
CENVAT credit: The credit of service tax and excise duty across
goods and services is allowable in accordance with the CENVAT
Credit Rules, 2004. Accordingly, output service provider (i.e.
provider of any taxable service) can avail credit not only of the
service tax paid on any input service consumed for rendering any
output service but also of the excise duty paid on any inputs and
capital goods used for rendering output service. CENVAT credit so
availed can be utilized for payment of service tax on taxable
output service.
Services provided by an unincorporated association/body
to its members also taxable
Explanation to Sec. 65] : ‘Taxable service’ includes any taxable
service provided or to be provided by any unincorporated
association or body of persons to a member thereof, for
cash, deferred payment or any other valuable consideration.
Hence, the services (falling under any category of taxable
service) provided or to be provided by any unincorporated
association/body to member thereof shall be liable to service tax.
This provision is an exception to the ‘principle of mutuality’.
Performance of statutory activities/duties, not ’service’: An
activity performed by a sovereign /public authority under
provisions of law does not constitute provision of taxable service
to a person and, therefore, no service tax is leviable on such
entities.
Import/Export of services: While import of services is
chargeable to tax u/s 66A, the export of services has been made
exempt from tax. Import/export provisions are discussed
separately.
You might also like
- Service TaxDocument7 pagesService TaxmurusaNo ratings yet
- Service Tax: Aiaims Mms-ADocument31 pagesService Tax: Aiaims Mms-AAbbas Haider NaqviNo ratings yet
- Tax on Services in India: Introduction, Concepts, and Governing ProvisionsDocument11 pagesTax on Services in India: Introduction, Concepts, and Governing Provisionsnishantjain95No ratings yet
- SERVICE TAX: INDIRECT TAX ON SERVICESDocument24 pagesSERVICE TAX: INDIRECT TAX ON SERVICESfaraznaqvi100% (1)
- Indirec TaxDocument8 pagesIndirec TaxSubashNo ratings yet
- Provisons On Service TaxDocument37 pagesProvisons On Service TaxSunita NitinNo ratings yet
- Final Tax Sem 4PAYMENT, REGISTRATION AND RETURNS OF SERVICE TAXDocument32 pagesFinal Tax Sem 4PAYMENT, REGISTRATION AND RETURNS OF SERVICE TAXkarthika kounderNo ratings yet
- Liability of Service TaxDocument7 pagesLiability of Service TaxkasiriverNo ratings yet
- Reverse Charge Mechanism by Bimal Jain Tax ExpertDocument4 pagesReverse Charge Mechanism by Bimal Jain Tax ExpertYogesh ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- Service Tax BasicsDocument5 pagesService Tax BasicsKiran RaviNo ratings yet
- Servicetaxandvat 130420194223 Phpapp01Document65 pagesServicetaxandvat 130420194223 Phpapp01Ram ShiralkarNo ratings yet
- Service Tax1Document8 pagesService Tax1Suman pendharkarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1. Overview of Service Tax: Constitutional Validity and ConceptsDocument38 pagesChapter 1. Overview of Service Tax: Constitutional Validity and ConceptsPrateek UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Service TaxDocument17 pagesService Taxvenky_1986100% (2)
- Service Tax - 1.1Document18 pagesService Tax - 1.1Arun ChopraNo ratings yet
- Payment of Service Tax Under Reverse Charge - A Comprehensive StudyDocument13 pagesPayment of Service Tax Under Reverse Charge - A Comprehensive Studyav_meshramNo ratings yet
- 9Th Semester: Taxation LawDocument7 pages9Th Semester: Taxation LawHena khanNo ratings yet
- Indian Service TaxDocument13 pagesIndian Service Taxanon_993677No ratings yet
- 2 Service TaxDocument10 pages2 Service TaxArchana ThirunagariNo ratings yet
- Concept of Service TaxDocument47 pagesConcept of Service TaxSrinivas ReddyNo ratings yet
- Service Tax Report on Key Provisions and ComplianceDocument19 pagesService Tax Report on Key Provisions and CompliancemayankkrishnaNo ratings yet
- Service Tax - Based On Negative List ApproachDocument22 pagesService Tax - Based On Negative List ApproachRajavati NadarNo ratings yet
- Indian Indirect Tax Laws-A Brief Guide: Shammi Kapoor Vishal Kumar Purva JunejaDocument33 pagesIndian Indirect Tax Laws-A Brief Guide: Shammi Kapoor Vishal Kumar Purva Junejavijay9514No ratings yet
- Service Tax: Concept, Definition and ImpositionDocument16 pagesService Tax: Concept, Definition and Impositionsantosh lakhmaniNo ratings yet
- Constitutional & Legal Provisions Behind Levy of Service Tax in IndiaDocument15 pagesConstitutional & Legal Provisions Behind Levy of Service Tax in Indiasrinath121No ratings yet
- Service TAXDocument27 pagesService TAXSamiya KhanNo ratings yet
- Final Project On Service Tax 2017Document21 pagesFinal Project On Service Tax 2017ansh patelNo ratings yet
- Service TaxDocument3 pagesService Taxapi-3822396No ratings yet
- Service Tax: Some of The Major Services That Come Under The Ambit of Service Tax AreDocument7 pagesService Tax: Some of The Major Services That Come Under The Ambit of Service Tax AreChetan ShivankarNo ratings yet
- New Rules for Service Tax Valuation & ReimbursementDocument5 pagesNew Rules for Service Tax Valuation & Reimbursementkrazy_kuki2000No ratings yet
- Answer 4: Custom DutyDocument3 pagesAnswer 4: Custom DutyAshlee RobertsNo ratings yet
- Service Tax Structure in India: By: Vardah SaghirDocument18 pagesService Tax Structure in India: By: Vardah SaghirBhagavatheeswaran HariharanNo ratings yet
- FM 302: Management of Direct and Indirect TaxesDocument15 pagesFM 302: Management of Direct and Indirect Taxesjainsuman11No ratings yet
- Presentation On Service Tax AmendmentsDocument19 pagesPresentation On Service Tax AmendmentsSmriti KhannaNo ratings yet
- Variant 3 REVISED Jan13 LDocument96 pagesVariant 3 REVISED Jan13 LGopakumar PNo ratings yet
- Taxes in IndiaDocument6 pagesTaxes in IndiaRAJIV MURALNo ratings yet
- Ovw1 1 - ST Ataglance 19may16Document4 pagesOvw1 1 - ST Ataglance 19may16Sanjog DewanNo ratings yet
- In The Customs Excise & Service Tax Appellate Tribunal West Block No.2, R. K. Puram, New Delhi-110066Document10 pagesIn The Customs Excise & Service Tax Appellate Tribunal West Block No.2, R. K. Puram, New Delhi-110066Dipesh Chandra BaruaNo ratings yet
- Valuation of Taxable ServicesDocument25 pagesValuation of Taxable Servicessites1650No ratings yet
- Group 15 - Legal and Accounting ReportDocument14 pagesGroup 15 - Legal and Accounting ReportG51Mamatha PatlollaNo ratings yet
- Cenvat Credit PDFDocument38 pagesCenvat Credit PDFsaumitra_mNo ratings yet
- Material - Mr. A. R. Krishnan - 21.8.2013Document29 pagesMaterial - Mr. A. R. Krishnan - 21.8.2013mld2017No ratings yet
- Service TaxDocument55 pagesService Taxtushar vatsNo ratings yet
- Background: It Is Very Common Practice in The Construction or Infrastructure Related Industries That TheDocument10 pagesBackground: It Is Very Common Practice in The Construction or Infrastructure Related Industries That TheViral BakhadaNo ratings yet
- Service Tax Qick RevisionDocument91 pagesService Tax Qick RevisiongouthamNo ratings yet
- Newsletter Vol3 - 2014 PDFDocument11 pagesNewsletter Vol3 - 2014 PDFrahul422No ratings yet
- Law of TaxationDocument9 pagesLaw of TaxationShailesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Liability of Co-Operative Housing Societies To Service TaxDocument3 pagesLiability of Co-Operative Housing Societies To Service TaxShirishNo ratings yet
- ST WbsebDocument2 pagesST Wbsebapi-3822396No ratings yet
- GST Unit 3Document61 pagesGST Unit 3SANSKRITI YADAV 22DM236No ratings yet
- Template Service AgreementDocument19 pagesTemplate Service Agreementshivangi.bharadwajNo ratings yet
- GST BILL Highlights of Draft Model GST LawDocument6 pagesGST BILL Highlights of Draft Model GST LawS Sinha RayNo ratings yet
- What Is Service Tax ?Document15 pagesWhat Is Service Tax ?Nawab SahabNo ratings yet
- Stax ManualDocument97 pagesStax ManualSamartha Raj SinghNo ratings yet
- Service Tax on Air TravelDocument15 pagesService Tax on Air TravelvijaykoratNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document5 pagesChapter 4Prem ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- Service Tax AssignmentDocument9 pagesService Tax AssignmentRahat AdenwallaNo ratings yet
- 1040 Exam Prep Module III: Items Excluded from Gross IncomeFrom Everand1040 Exam Prep Module III: Items Excluded from Gross IncomeRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- 1040 Exam Prep Module XI: Circular 230 and AMTFrom Everand1040 Exam Prep Module XI: Circular 230 and AMTRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Textbook of Urgent Care Management: Chapter 21, Employment Contracts and CompensationFrom EverandTextbook of Urgent Care Management: Chapter 21, Employment Contracts and CompensationNo ratings yet
- Appointment of receivers under CPCDocument5 pagesAppointment of receivers under CPClone NasirNo ratings yet
- Before The Honorable Court of Sessions Judge, New DelhiDocument14 pagesBefore The Honorable Court of Sessions Judge, New Delhilone NasirNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis Of: Sondur Gopal Vs Sondur Rajini On 15 July, 2013 Bench: Chandramauli Kr. Prasad, V. Gopala GowdaDocument6 pagesCase Analysis Of: Sondur Gopal Vs Sondur Rajini On 15 July, 2013 Bench: Chandramauli Kr. Prasad, V. Gopala Gowdalone NasirNo ratings yet
- Sopore Law College Name: Zubair Manzoor Enrollment No: 17042128023 (23) Semester: BA LLB 8Document3 pagesSopore Law College Name: Zubair Manzoor Enrollment No: 17042128023 (23) Semester: BA LLB 8lone NasirNo ratings yet
- Loan Amortization Schedule3Document9 pagesLoan Amortization Schedule3devanand bhawNo ratings yet
- India CIO All Data SalesDocument177 pagesIndia CIO All Data Salesbharat50% (2)
- Chapter 1 Personal Finance Planning in Action - StudentDocument25 pagesChapter 1 Personal Finance Planning in Action - StudentHân NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Sajjan Precision Castings: Terms & ConditionsDocument1 pageSajjan Precision Castings: Terms & ConditionsHarpal SinghNo ratings yet
- V B V V B.: Chapter 17: Capital Structure: Limits To The Use of Debt Questions and Problems: 17.1aDocument16 pagesV B V V B.: Chapter 17: Capital Structure: Limits To The Use of Debt Questions and Problems: 17.1aEhsan MohitiNo ratings yet
- Fake Credit Card StatementDocument17 pagesFake Credit Card Statementvishal sharmaNo ratings yet
- Valuing Wal Mart 2010 SolutionDocument8 pagesValuing Wal Mart 2010 SolutionAaron OrogNo ratings yet
- Acting Pricey: Some Stocks' Rich Valuations Are Sticky, Irrespective of The Market's Exuberance or TurmoilDocument92 pagesActing Pricey: Some Stocks' Rich Valuations Are Sticky, Irrespective of The Market's Exuberance or TurmoilhariNo ratings yet
- Autority To Sell of Real PropertyDocument2 pagesAutority To Sell of Real PropertyBblabsLlamera100% (1)
- Introduction IFRS17Document9 pagesIntroduction IFRS17Ruben Perez Espinoza100% (1)
- The Statement of Financial PositionDocument17 pagesThe Statement of Financial Positionlouielyn candidoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Sesi 1 2022 2023Document42 pagesChapter 3 - Sesi 1 2022 2023黄勇添No ratings yet
- Q1. Cadila Co. Has Three Production Departments A, B and C and Two ServiceDocument5 pagesQ1. Cadila Co. Has Three Production Departments A, B and C and Two Servicemedha surNo ratings yet
- Investment Policy Statement ExampleDocument12 pagesInvestment Policy Statement ExampleCheeseong LimNo ratings yet
- Financial RatiosDocument35 pagesFinancial RatiosLetsah Bright100% (1)
- Statement of Cash FlowsDocument33 pagesStatement of Cash Flowslove_abhi_n_22No ratings yet
- Book Value Assets Total Unsecured Realizable ValueDocument9 pagesBook Value Assets Total Unsecured Realizable ValueJPNo ratings yet
- Wood Chipper Machinery Proforma InvoiceDocument2 pagesWood Chipper Machinery Proforma InvoiceAlvaro Espino RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Best Practices With Lean Principles in Furniture Green ManufacturingDocument10 pagesBest Practices With Lean Principles in Furniture Green ManufacturingJeevanandhamNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain ManagementDocument2 pagesSupply Chain Managementsuraj rouniyarNo ratings yet
- Final Pyramid of Ratios: Strictly ConfidentialDocument3 pagesFinal Pyramid of Ratios: Strictly ConfidentialaeqlehczeNo ratings yet
- InventoryDocument8 pagesInventoryDianna DayawonNo ratings yet
- LOPEZ, ELLA MARIE - QUIZ 2 FinAnaRepDocument4 pagesLOPEZ, ELLA MARIE - QUIZ 2 FinAnaRepElla Marie LopezNo ratings yet
- OA315 - Prelim Modules Module 2Document4 pagesOA315 - Prelim Modules Module 2John EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- ICICI BankDocument17 pagesICICI BankMehak SharmaNo ratings yet
- SKF Intelligent Clean Strategy MR 0Document29 pagesSKF Intelligent Clean Strategy MR 0Andres Elias Fernandez PastorNo ratings yet
- Autodesk Invoice #9122128059 1.255,60Document1 pageAutodesk Invoice #9122128059 1.255,60Rambabu kNo ratings yet
- Water Bottling AgreementDocument8 pagesWater Bottling AgreementAshish RaiNo ratings yet
- Sl. No. Grade Cement Ggbfs Micro Filler CA FA Admixture Name of Lab Date Status RemarksDocument1 pageSl. No. Grade Cement Ggbfs Micro Filler CA FA Admixture Name of Lab Date Status Remarksmahesh naikNo ratings yet
- Business Plan For EntrepreneurDocument10 pagesBusiness Plan For EntrepreneurMary Joyce Camille ParasNo ratings yet