Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Particulate Contamination Test
Uploaded by
Oscar Obregón CamposOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Particulate Contamination Test
Uploaded by
Oscar Obregón CamposCopyright:
Available Formats
2.9.20. Particulate contamination : visible particles EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOEIA 6.
Wet the inside of the filter holder fitted with the membrane 01/2008:20920
filter with several millilitres of particle-free water R. Transfer
to the filtration funnel the total volume of a solution pool or 2.9.20. PARTICULATE
of a single unit, and apply vacuum. If needed, add stepwise
a portion of the solution until the entire volume is filtered. CONTAMINATION : VISIBLE
After the last addition of solution, begin rinsing the inner PARTICLES
walls of the filter holder by using a jet of particle-free
water R. Maintain the vacuum until the surface of the Particulate contamination of injections and infusions
membrane filter is free from liquid. Place the filter in a Petri consists of extraneous, mobile undissolved particles, other
dish and allow the filter to air-dry with the cover slightly than gas bubbles, unintentionally present in the solutions.
ajar. After the filter has been dried, place the Petri dish on The test is intended to provide a simple procedure for the
the stage of the microscope, scan the entire membrane filter visual assessment of the quality of parenteral solutions as
under the reflected light from the illuminating device, and regards visible particles. Other validated methods may be
count the number of particles that are equal to or greater used.
than 10 µm and the number of particles that are equal to
or greater than 25 µm. Alternatively, partial filter count APPARATUS
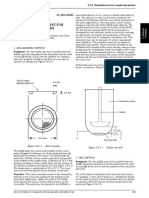
and determination of the total filter count by calculation is The apparatus (see Figure 2.9.20.-1) consists of a viewing
allowed. Calculate the mean number of particles for the station comprising :
preparation to be examined. — a matt black panel of appropriate size held in a vertical
position,
The particle sizing process with the use of the circular — a non-glare white panel of appropriate size held in a
diameter graticule is carried out by transforming mentally vertical position next to the black panel,
the image of each particle into a circle and then comparing it
— an adjustable lampholder fitted with a suitable, shaded,
to the 10 µm and 25 µm graticule reference circles. Thereby
white-light source and with a suitable light diffuser (a
the particles are not moved from their initial locations within
viewing illuminator containing two 13 W fluorescent
the graticule field of view and are not superimposed on the
tubes, each 525 mm in length, is suitable). The intensity
reference circles for comparison. The inner diameter of the
of illumination at the viewing point is maintained between
transparent graticule reference circles is used to size white
2000 lux and 3750 lux, although higher values are
and transparent particles, while dark particles are sized
preferable for coloured glass and plastic containers.
by using the outer diameter of the black opaque graticule
reference circles.
In performing the microscopic particle count test do not
attempt to size or enumerate amorphous, semi-liquid, or
otherwise morphologically indistinct materials that have the
appearance of a stain or discoloration on the membrane
filter. These materials show little or no surface relief and
present a gelatinous or film-like appearance. In such cases
the interpretation of enumeration may be aided by testing
a sample of the solution by the light obscuration particle
count test.
Evaluation
Figure 2.9.20.-1. — Apparatus for visible particles
For preparations supplied in containers with a nominal
volume of more than 100 ml, apply the criteria of test 2.A. METHOD
Remove any adherent labels from the container and wash
For preparations supplied in containers with a nominal and dry the outside. Gently swirl or invert the container,
volume of less than 100 ml, apply the criteria of test 2.B. ensuring that air bubbles are not introduced, and observe for
about 5 s in front of the white panel. Repeat the procedure in
For preparations supplied in containers with a nominal front of the black panel. Record the presence of any particles.
volume of 100 ml, apply the criteria of test 2.B.
01/2008:20922
Test 2.A — Solutions for infusion or solutions for injection
supplied in containers with a nominal content of more
than 100 ml 2.9.22. SOFTENING TIME
DETERMINATION OF LIPOPHILIC
The preparation complies with the test if the average number SUPPOSITORIES
of particles present in the units tested does not exceed 12 per
millilitre equal to or greater than 10 µm and does not exceed The test is intended to determine, under defined conditions,
2 per millilitre equal to or greater than 25 µm. the time which elapses until a suppository maintained in
water softens to the extent that it no longer offers resistance
Test 2.B — Solutions for infusion or solutions for injection when a defined weight is applied.
supplied in containers with a nominal content of less than
100 ml APPARATUS A
The apparatus (see Figure 2.9.22.-1) consists of a glass tube
The preparation complies with the test if the average number 15.5 mm in internal diameter with a flat bottom and a length
of particles present in the units tested does not exceed of about 140 mm. The tube is closed by a removable plastic
3000 per container equal to or greater than 10 µm and does cover having an opening 5.2 mm in diameter. The apparatus
not exceed 300 per container equal to or greater than 25 µm. comprises a rod 5.0 mm in diameter which becomes wider
302 See the information section on general monographs (cover pages)
You might also like
- Flow charts of pharmaceutical quality control tests for different dosage formsFrom EverandFlow charts of pharmaceutical quality control tests for different dosage formsNo ratings yet
- Particulate Matter in InjectionsDocument7 pagesParticulate Matter in InjectionsHernando GarayNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Industry Documents: 90 Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance Interview Questions & AnswersFrom EverandPharmaceutical Industry Documents: 90 Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance Interview Questions & AnswersNo ratings yet
- Usp 788Document3 pagesUsp 788Wesley OliveiraNo ratings yet
- 788 - Particulate Material - Usp MonographDocument6 pages788 - Particulate Material - Usp MonographVanessa CarreraNo ratings yet
- C729 11 (2016)Document6 pagesC729 11 (2016)werrteNo ratings yet
- D1795Document6 pagesD1795Ненад Кнежевић100% (2)
- Method 23Document23 pagesMethod 23Anh TuanNo ratings yet
- Usp 788Document4 pagesUsp 788AnnNo ratings yet
- Astm D 2851 - 98 R04Document3 pagesAstm D 2851 - 98 R04phaindikaNo ratings yet
- F 24 - 09 (2015) PDFDocument4 pagesF 24 - 09 (2015) PDFAzize RazamNo ratings yet
- Measuring and Counting Particulate Contamination On SurfacesDocument4 pagesMeasuring and Counting Particulate Contamination On SurfaceshopemarineNo ratings yet
- Particulate Matter in Injections StandardsDocument4 pagesParticulate Matter in Injections StandardsQC MahakamNo ratings yet
- 2.9.17. Test For Extractable Volume of Parenteral PreparationsDocument2 pages2.9.17. Test For Extractable Volume of Parenteral PreparationsG_Ranjith100% (4)
- 2130 Turbidity (2011)Document4 pages2130 Turbidity (2011)AndreaCarolinaMoraNo ratings yet
- Bresle Test Kit PDFDocument4 pagesBresle Test Kit PDFmuthukumarNo ratings yet
- AppendicesDocument169 pagesAppendicesSai PrasadNo ratings yet
- Chem 105L Lab 2 Part A PDFDocument9 pagesChem 105L Lab 2 Part A PDFTai ChanNo ratings yet
- Scope: CautionDocument7 pagesScope: CautionJavier Oswaldo Gonzalez AceroNo ratings yet
- ASTM D 1358 - 86 (Reapproved 1995) Spectrophotometric Diene Value of Dehydrated Castor OilDocument2 pagesASTM D 1358 - 86 (Reapproved 1995) Spectrophotometric Diene Value of Dehydrated Castor Oilalin2005No ratings yet
- 616 Bulk Density and Tapped Density of Powders: Method II-Measurement in A VolumeterDocument3 pages616 Bulk Density and Tapped Density of Powders: Method II-Measurement in A VolumeterDavid SRNo ratings yet
- Iso 2781 TraducidaDocument5 pagesIso 2781 TraducidaRenato Moises Rosales SaraviaNo ratings yet
- Usp c671Document4 pagesUsp c671ezygadlo6492No ratings yet
- Chemical Resistance of TilesDocument8 pagesChemical Resistance of TilesPankaaj PadmanabhanNo ratings yet
- 2130 TURBIDITY : 1. Sources and SignificanceDocument4 pages2130 TURBIDITY : 1. Sources and SignificanceNguyen Hien Duc HienNo ratings yet
- Dissolution Test For Solid Oral Dosage FormsDocument8 pagesDissolution Test For Solid Oral Dosage FormsPedro Marcelo Alva PlasenciaNo ratings yet
- Wall Wash Tests 1Document8 pagesWall Wash Tests 1Anonymous 10kxphINo ratings yet
- 616 Bulk Density and Tapped Density of Powders: Method II-Measurement in A VolumeterDocument3 pages616 Bulk Density and Tapped Density of Powders: Method II-Measurement in A VolumeterIlnus 21No ratings yet
- Penetrant Testing-III March 2009Document51 pagesPenetrant Testing-III March 2009DanielNo ratings yet
- 2 9 4 Dissolution Test For Transdermal PatchesDocument3 pages2 9 4 Dissolution Test For Transdermal Patchesapi-261124906No ratings yet
- Turbidity AWWA Standard Methods 22Document4 pagesTurbidity AWWA Standard Methods 22Marco AzambujaNo ratings yet
- IPQC Test of TabletsDocument24 pagesIPQC Test of TabletsSk Anam100% (1)
- USP 660 - 43 - Glass Grain TestDocument2 pagesUSP 660 - 43 - Glass Grain Testamitdi001_667397546No ratings yet
- Astm d3258Document2 pagesAstm d3258mynor aldanaNo ratings yet
- Adequacy of Fusion of Extruded Poly (Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Pipe and Molded Fittings by Acetone ImmersionDocument3 pagesAdequacy of Fusion of Extruded Poly (Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Pipe and Molded Fittings by Acetone ImmersionAndres Camilo BenitezNo ratings yet
- Uniform mass test for single-dose preparationsDocument3 pagesUniform mass test for single-dose preparationsSandeep KumarNo ratings yet
- D1157Document3 pagesD1157rpajaro75No ratings yet
- Revision ClassDocument44 pagesRevision ClassAjitha AzhakesanNo ratings yet
- GUID - 4 en-USDocument3 pagesGUID - 4 en-USHammam HafidzurahmanNo ratings yet
- D1725Document3 pagesD1725Ненад КнежевићNo ratings yet
- Astm C117-1995Document3 pagesAstm C117-1995Yiu Fai WongNo ratings yet
- D 1817 - 01 - Rde4mtcDocument3 pagesD 1817 - 01 - Rde4mtcDr. Ahmed Abdel-HakimNo ratings yet
- C 729 - 75 R00 QzcyoqDocument6 pagesC 729 - 75 R00 QzcyoqMarceloNo ratings yet
- UV Spectrum Analysis of EBDC CompoundsDocument29 pagesUV Spectrum Analysis of EBDC CompoundsFelipe NavarreteNo ratings yet
- D 5757 - 95 - Rdu3ntctukveDocument4 pagesD 5757 - 95 - Rdu3ntctukveDH BNo ratings yet
- Bp2018 Terms and ConditionsDocument2 pagesBp2018 Terms and ConditionsdferrierosNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Analytical Method 2.3.1 PH TestDocument9 pages2.3 Analytical Method 2.3.1 PH TestSusi MulyaniNo ratings yet
- Usp 788Document19 pagesUsp 788GRINE FaroukNo ratings yet
- ASTM D7321 Standard Test Method For Particulate Contamination of Biodiesel by Laboratory Filtration PDFDocument6 pagesASTM D7321 Standard Test Method For Particulate Contamination of Biodiesel by Laboratory Filtration PDFEdgar Fabian Diaz ArceNo ratings yet
- Materials Finer Than 75 - : Standard Test Method For M (No. 200) Sieve in Mineral Aggregates by WashingDocument3 pagesMaterials Finer Than 75 - : Standard Test Method For M (No. 200) Sieve in Mineral Aggregates by WashingLuis Alejandro Sánchez LópezNo ratings yet
- D 1766 - 01 - Rde3njyDocument2 pagesD 1766 - 01 - Rde3njyDr. Ahmed Abdel-HakimNo ratings yet
- Standard Bitumen Penetration TestDocument3 pagesStandard Bitumen Penetration TestMohammad IhsanNo ratings yet
- ASTM D 1436 - 97 (Reapproved 2002) Application of Emulsion Floor Polishes To Substrates ForDocument3 pagesASTM D 1436 - 97 (Reapproved 2002) Application of Emulsion Floor Polishes To Substrates Foralin2005No ratings yet
- D 2193 - 97 - RdixotmtotcDocument2 pagesD 2193 - 97 - RdixotmtotcRaphael CordovaNo ratings yet
- Determination of Total Suspended SolidsDocument2 pagesDetermination of Total Suspended Solidstanmay_envs100% (1)
- Paint Test EquipmentDocument16 pagesPaint Test EquipmentkaleshNo ratings yet
- Rubber Closures For Containers PDFDocument2 pagesRubber Closures For Containers PDFKarla RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Wallwash Tests Astm 1722 EtcDocument4 pagesWallwash Tests Astm 1722 EtcJeet SinghNo ratings yet
- 2.9.4. Dissolution Test For Transdermal Patches PDFDocument3 pages2.9.4. Dissolution Test For Transdermal Patches PDFRani RubiyantiNo ratings yet
- 2.9.34. Bulk Density and Tapped Density of PowdersDocument4 pages2.9.34. Bulk Density and Tapped Density of PowdersPablo ParraNo ratings yet
- C27 and C32 Generator Set Engines - Troubleshooting - RENR9348-01 - Jan 2007 - CATERPILLARDocument180 pagesC27 and C32 Generator Set Engines - Troubleshooting - RENR9348-01 - Jan 2007 - CATERPILLARpevare85% (27)
- BPSM Strategic Management ProcessDocument4 pagesBPSM Strategic Management ProcessFaiyaz panchbhayaNo ratings yet
- Math Lesson on Completing PatternsDocument7 pagesMath Lesson on Completing PatternsJazmyne Obra100% (1)
- Syllabus - EU Institutions and Comparative Political System - 2023springDocument10 pagesSyllabus - EU Institutions and Comparative Political System - 2023springreif annieNo ratings yet
- Optimizing Blended Learning with Synchronous and Asynchronous TechnologiesDocument24 pagesOptimizing Blended Learning with Synchronous and Asynchronous TechnologiesAnonymous GOUaH7FNo ratings yet
- Company Profile Nadal en PDFDocument2 pagesCompany Profile Nadal en PDFkfctco100% (1)
- DepEd CI GuidebookDocument244 pagesDepEd CI Guidebookasdfg100% (4)
- Informatica Mapping ScenariosDocument81 pagesInformatica Mapping ScenariosSri Kanth SriNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Management 5th Edition Chopra Solutions ManualDocument3 pagesSupply Chain Management 5th Edition Chopra Solutions Manualdammar.jealousgvg6100% (18)
- Speed, Velocity and FrictionDocument10 pagesSpeed, Velocity and FrictionCristie Ann GuiamNo ratings yet
- Product Item Code Model Item Description MRP Count Down PricesDocument1 pageProduct Item Code Model Item Description MRP Count Down Pricesලහිරු විතානාච්චිNo ratings yet
- ARP 598, D, 2016, Microscopic SizingDocument17 pagesARP 598, D, 2016, Microscopic SizingRasoul gholinia kiviNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Synopsis & Dissertation-DefenseDocument10 pagesGuidelines For Synopsis & Dissertation-DefenseRajni KumariNo ratings yet
- Clock 38 InstructionsDocument20 pagesClock 38 InstructionsCanNo ratings yet
- Quick Start Guide - QualiPoc AndroidDocument24 pagesQuick Start Guide - QualiPoc AndroidDmitekNo ratings yet
- Other Books NewDocument136 pagesOther Books NewYashRaj ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Dream Drills for High Hardened SteelDocument8 pagesDream Drills for High Hardened SteelPuneeth KumarNo ratings yet
- Infineon IKCM30F60GD DataSheet v02 - 05 ENDocument17 pagesInfineon IKCM30F60GD DataSheet v02 - 05 ENBOOPATHIMANIKANDAN SNo ratings yet
- Econometrics IIDocument4 pagesEconometrics IINia Hania SolihatNo ratings yet
- Analyzing Reality vs Fantasy in English LessonsDocument7 pagesAnalyzing Reality vs Fantasy in English Lessonsjerico gaspanNo ratings yet
- Details of Nodal Officer - HD Officers of Other DepttDocument46 pagesDetails of Nodal Officer - HD Officers of Other DepttManoj KashyapNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4: Mean and Variance of Discrete Random Variable: Grade 11 - Statistics & ProbabilityDocument26 pagesLesson 4: Mean and Variance of Discrete Random Variable: Grade 11 - Statistics & Probabilitynicole MenesNo ratings yet
- .Design and Development of Motorized Multipurpose MachineDocument3 pages.Design and Development of Motorized Multipurpose MachineANKITA MORENo ratings yet
- Atma Bodha of Shri SankaracharyaDocument1 pageAtma Bodha of Shri SankaracharyaMerike TazaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Power PlantDocument158 pagesModule 1 Power PlantEzhilarasi NagarjanNo ratings yet
- Text EditorDocument2 pagesText EditorVarunNo ratings yet
- Design Steel Concrete Composite StructuresDocument1 pageDesign Steel Concrete Composite StructuresDinuSkyNo ratings yet
- Otimizar Windows 8Document2 pagesOtimizar Windows 8ClaudioManfioNo ratings yet
- Nature and Scope of History as a Social ScienceDocument14 pagesNature and Scope of History as a Social SciencejustadorkyyyNo ratings yet
- Lamosa CatalogoDocument51 pagesLamosa CatalogoSofi SamareitesNo ratings yet
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (33)
- Alex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessFrom EverandAlex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessNo ratings yet
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseFrom EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (69)
- Fire Season: Field Notes from a Wilderness LookoutFrom EverandFire Season: Field Notes from a Wilderness LookoutRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (142)
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildFrom EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (44)
- Wayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldFrom EverandWayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionFrom EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (811)
- The Other End of the Leash: Why We Do What We Do Around DogsFrom EverandThe Other End of the Leash: Why We Do What We Do Around DogsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (63)
- Eels: An Exploration, from New Zealand to the Sargasso, of the World's Most Mysterious FishFrom EverandEels: An Exploration, from New Zealand to the Sargasso, of the World's Most Mysterious FishRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (30)
- The Revolutionary Genius of Plants: A New Understanding of Plant Intelligence and BehaviorFrom EverandThe Revolutionary Genius of Plants: A New Understanding of Plant Intelligence and BehaviorRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (137)
- Why Fish Don't Exist: A Story of Loss, Love, and the Hidden Order of LifeFrom EverandWhy Fish Don't Exist: A Story of Loss, Love, and the Hidden Order of LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (699)
- When You Find Out the World Is Against You: And Other Funny Memories About Awful MomentsFrom EverandWhen You Find Out the World Is Against You: And Other Funny Memories About Awful MomentsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (13)
- The Secret Life of Lobsters: How Fishermen and Scientists Are Unraveling the Mysteries of Our Favorite CrustaceanFrom EverandThe Secret Life of Lobsters: How Fishermen and Scientists Are Unraveling the Mysteries of Our Favorite CrustaceanNo ratings yet
- World of Wonders: In Praise of Fireflies, Whale Sharks, and Other AstonishmentsFrom EverandWorld of Wonders: In Praise of Fireflies, Whale Sharks, and Other AstonishmentsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (221)
- Winged Obsession: The Pursuit of the World's Most Notorious Butterfly SmugglerFrom EverandWinged Obsession: The Pursuit of the World's Most Notorious Butterfly SmugglerRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (67)
- The Mind of Plants: Narratives of Vegetal IntelligenceFrom EverandThe Mind of Plants: Narratives of Vegetal IntelligenceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (11)
- Spoiled Rotten America: Outrages of Everyday LifeFrom EverandSpoiled Rotten America: Outrages of Everyday LifeRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (19)
- The Big, Bad Book of Botany: The World's Most Fascinating FloraFrom EverandThe Big, Bad Book of Botany: The World's Most Fascinating FloraRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (10)
- The Hidden Life of Trees: What They Feel, How They CommunicateFrom EverandThe Hidden Life of Trees: What They Feel, How They CommunicateRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1002)