Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Data Base and Microsoft Access - Pesa
Data Base and Microsoft Access - Pesa
Uploaded by
Sharmine Malaluan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesOriginal Title
Data Base and Microsoft Access -Pesa
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesData Base and Microsoft Access - Pesa
Data Base and Microsoft Access - Pesa
Uploaded by
Sharmine MalaluanCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
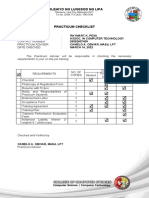
Raymart K.
Pesa
ACT 2D
A database is an organized collection of structured information, or data, typically
stored electronically in a computer system. A database is usually controlled by
a database management system (DBMS). Together, the data and the DBMS, along with
the applications that are associated with them, are referred to as a database system,
often shortened to just database.
Data within the most common types of databases in operation today is typically
modeled in rows and columns in a series of tables to make processing and data
querying efficient. The data can then be easily accessed, managed, modified, updated,
controlled, and organized. Most databases use structured query language (SQL) for
writing and querying data.
Microsoft Access is a database management system (DBMS)
from Microsoft that combines the relational Microsoft Jet Database Engine with
a graphical user interface and software-development tools. It is a member of
the Microsoft 365 suite of applications, included in the Professional and higher editions
or sold separately.
Microsoft Access stores data in its own format based on the Access Jet Database
Engine. It can also import or link directly to data stored in other applications and
databases.[2]
Software developers, data architects and power users can use Microsoft Access to
develop application software. Like other Microsoft Office applications, Access is
supported by Visual Basic for Applications (VBA), an object-based programming
language that can reference a variety of objects including the legacy DAO (Data Access
Objects), ActiveX Data Objects, and many other ActiveX components. Visual objects
used in forms and reports expose their methods and properties in the VBA
programming environment, and VBA code modules may declare and call
Windows operating system operations.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5819)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Lesson 3 Activity-Pesa, RaymartDocument2 pagesLesson 3 Activity-Pesa, RaymartSharmine MalaluanNo ratings yet
- Angkop Na Gamit NG Salita Sa PangungusapDocument2 pagesAngkop Na Gamit NG Salita Sa PangungusapSharmine MalaluanNo ratings yet
- Kolehiyo NG Lungsod NG LipaDocument3 pagesKolehiyo NG Lungsod NG LipaSharmine MalaluanNo ratings yet
- PE 5 (Malaluan, Sharmine Joy R.)Document9 pagesPE 5 (Malaluan, Sharmine Joy R.)Sharmine MalaluanNo ratings yet
- Malaluan, Sharmine Joy R. Banghay Aralin 2Document4 pagesMalaluan, Sharmine Joy R. Banghay Aralin 2Sharmine MalaluanNo ratings yet
- Malaluan, Sharmine Joy DLP BEED 3A (Physical Education)Document9 pagesMalaluan, Sharmine Joy DLP BEED 3A (Physical Education)Sharmine MalaluanNo ratings yet
- ClothingDocument5 pagesClothingSharmine MalaluanNo ratings yet
- LP IN FILIPINO (Malaluan, Sharmine Joy R.)Document11 pagesLP IN FILIPINO (Malaluan, Sharmine Joy R.)Sharmine MalaluanNo ratings yet
- Hanging ChurchDocument3 pagesHanging ChurchSharmine MalaluanNo ratings yet
- BurialDocument8 pagesBurialSharmine MalaluanNo ratings yet