Professional Documents
Culture Documents
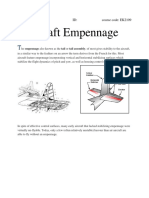
The Stabilizer Is A Fixed-Wing Section Whose Job Is To Provide Stability For The Aircraft. Controls Movement About - Axes (Taught in Chapter-6)
Uploaded by
G18 R967Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Stabilizer Is A Fixed-Wing Section Whose Job Is To Provide Stability For The Aircraft. Controls Movement About - Axes (Taught in Chapter-6)
Uploaded by
G18 R967Copyright:
Available Formats
➢ The stabilizer is a fixed-wing section whose
job is to provide stability for the aircraft.
➢ controls movement about ____ axes……
[taught in Chapter-6]
Horizontal Stabilizer (HS)
• It is a fixed or adjustable surface from which an elevator is hinged.
• In jet aircrafts, the entire horizontal stabilizer rotates & functions as an elevator. This combination is called ‘Stabilator’.
• Aircrafts with an adjustable HS have it (HS) hinged so that its setting (angle of incidence) can be altered during flight.
• The resulting stabilizer speed is known as the trim speed.
• In aircrafts with fixed HS, a trim tab on the trailing edge of the elevator is used to alter the aircraft’s trim speed.
• The F-28 Sabre first used a fixed HS & elevators with a trim tab, but later versions used adjustable HS.
• Structure:
• The internal structure consists of 2 main spars which extend the full length of the span.
• At the rear is an auxilary spar to which 4 hinges are riveted to provide for installation of the elevators.
• The principal structural members are spars & ribs.
• The outside is covered with sheet Al alloy, which transmits the loads.
Vertical Stabilizer (VS) / Fin
• VS is the section forward of the rudder.
• The construction of VS is almost similar to that of HS.
• It may be constructed as an integral part of the fuselage.
• The rear part is provided with hinges for the support of the rudder.
• The rudder is attached to the back of the VS.
➢ The rudder is attached to the back of the VS. During flight, it is used to move the nose left & right.
➢ The elevator is attached to the back of the HS. It is used to move the nose up & down.
➢ Trim tabs are small & movable portions of the trailing edge of the control surface.
➢ The trim tabs are controlled from the flight deck & these reduce control pressures.
➢ Trim tabs may be installed on ailerons/rudder/elevators.
Stabilator:
➢ In jet aircrafts, the entire horizontal stabilizer rotates & functions as an elevator. This combination is called ‘Stabilator’.
➢ It is moved using the control wheel. When the pilot pulls back on the control wheel, the stabilator pivots & so the
trailing edge moves up.
➢ This increases the aerodynamic tail load & causes the nose to move up.
➢ Stabilators have an antiservo tab extending across their trailing edge.
➢ The antiservo tab moves in the same direction as the trailing edge of the stabilator & helps make the stabilator less
sensitive.
➢ It also functions as a trim tab to relieve control pressures & helps maintain the stabilator in the desired position.
You might also like
- Aircraft General KnowledgeDocument94 pagesAircraft General KnowledgeFreddie FoxxNo ratings yet
- Flight ControlDocument139 pagesFlight ControlEthan PintoNo ratings yet
- 6 EmpennageDocument36 pages6 EmpennageAdonis MontalbanNo ratings yet
- Semana 8 Inglés Técnico 2Document22 pagesSemana 8 Inglés Técnico 2Jefferson Quispe vargasNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Flight Control SystemDocument165 pagesAircraft Flight Control SystemDamon Leong100% (5)
- Harvest TeamDocument17 pagesHarvest TeamhazvestNo ratings yet
- EmmpennageDocument14 pagesEmmpennageHarshita SobhaniNo ratings yet
- Basic Components of Aircraft: Elements of Aeronautics (13AE32) Unit-1 Part-2 Introduction To AircraftDocument16 pagesBasic Components of Aircraft: Elements of Aeronautics (13AE32) Unit-1 Part-2 Introduction To AircraftNavaneet V SreesomsonNo ratings yet
- Stability in AviationDocument13 pagesStability in AviationSyeda Azka AliNo ratings yet
- Module 11B: Piston Aeroplane Aerodynamics, Structures and SystemsDocument32 pagesModule 11B: Piston Aeroplane Aerodynamics, Structures and SystemsArjun SharmaNo ratings yet
- AC21 Aircraft Structure-IDocument36 pagesAC21 Aircraft Structure-Irupalikuchekar17No ratings yet
- Parts of An AircraftDocument7 pagesParts of An Aircraftkothapalli21No ratings yet
- Parts of Airplane - Part 1Document2 pagesParts of Airplane - Part 1Atheer AlghamdiNo ratings yet
- Fin - Vertical Stabilizer & Trimmable Horizontal StabilizerDocument2 pagesFin - Vertical Stabilizer & Trimmable Horizontal StabilizersaifkhanptpNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Flight Control SystemDocument187 pagesAircraft Flight Control SystemTahnia AyshiNo ratings yet
- Basic Components of An AircraftDocument40 pagesBasic Components of An AircraftKruthika K CNo ratings yet
- Flight Control SurfacesDocument7 pagesFlight Control Surfacesmani kvr0% (1)
- Flight Control System: AEROLAB Pre-Finals TermDocument59 pagesFlight Control System: AEROLAB Pre-Finals TermSantos MaineNo ratings yet
- Structure-Basico B-727Document103 pagesStructure-Basico B-727Nicolas PrietoNo ratings yet
- Air Planes: Parts & Their Functions: Elias Hossain BiplobDocument7 pagesAir Planes: Parts & Their Functions: Elias Hossain BiplobChandru ChristurajNo ratings yet
- Eo M331.01Document30 pagesEo M331.01EknoorNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Motion and ControlDocument35 pagesAircraft Motion and ControlAbazer ElfakiNo ratings yet
- Elevator ArmDocument9 pagesElevator ArmhaziqsajjadNo ratings yet
- Compasison Leaf Spring - Plastic SpringDocument21 pagesCompasison Leaf Spring - Plastic Springpippo233No ratings yet
- 11Document5 pages11ccoyureNo ratings yet
- Airplane Control SurfacesDocument3 pagesAirplane Control SurfacesAndroid OneNo ratings yet
- Theory of FlightDocument67 pagesTheory of FlightARQUAM WAHAJNo ratings yet
- Control Surfaces Notes PDFDocument12 pagesControl Surfaces Notes PDFSubash DhakalNo ratings yet
- Akbar English 3123Document2 pagesAkbar English 3123Iskandar MudaNo ratings yet
- BAA AGK Lesson 1 - 3-StabilizersDocument61 pagesBAA AGK Lesson 1 - 3-StabilizersReece BhaveNo ratings yet
- Ase305 Unit 06Document52 pagesAse305 Unit 06Alok MishraNo ratings yet
- Prey Ent AreDocument1 pagePrey Ent AreValentin ConduracheNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Structures and Flight ControlsDocument46 pagesAircraft Structures and Flight Controlssanjay MariyanNo ratings yet
- AVIA122 Ch13Document46 pagesAVIA122 Ch13이용일No ratings yet
- Flight Controls: Center of GravityDocument1 pageFlight Controls: Center of GravityValentin ConduracheNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Systems - Flight ControlsDocument27 pagesAircraft Systems - Flight ControlsFelipe PanNo ratings yet
- Basicaircraftstructure 110325070203 Phpapp02Document36 pagesBasicaircraftstructure 110325070203 Phpapp02yinkaakins2001No ratings yet
- Parts of An Airplane FuselageDocument4 pagesParts of An Airplane Fuselagevorontsovsky11No ratings yet
- Aircraft StructuresDocument3 pagesAircraft StructuresVarun Karthikeyan ShettyNo ratings yet
- Assignment AircraftDocument12 pagesAssignment Aircraftaliabbas007200No ratings yet
- Basicaircraftstructure 110325070203 Phpapp02Document36 pagesBasicaircraftstructure 110325070203 Phpapp02Kv PavanNo ratings yet
- Helicopter PPT 1Document18 pagesHelicopter PPT 1Sunil PanwarNo ratings yet
- 8 Vocabulary AviationDocument16 pages8 Vocabulary AviationHisyam KamilNo ratings yet
- Chap 4 Flight Controls 1Document8 pagesChap 4 Flight Controls 1ismain.niniNo ratings yet
- 017Document8 pages017mino eatineNo ratings yet
- Aircraft KnowledgeDocument94 pagesAircraft KnowledgeJoey GemsNo ratings yet
- Airplane AxesDocument4 pagesAirplane AxesbnolascoNo ratings yet
- 017Document8 pages017mino eatine100% (1)
- Airfoil: American English British English Wing Propeller Screw Sail Fluid Lift Downforce CamberDocument27 pagesAirfoil: American English British English Wing Propeller Screw Sail Fluid Lift Downforce Cambermanoj chauhanNo ratings yet
- AKD20503 - 1 Teory of Flight (Fixed Wing) Jan12Document82 pagesAKD20503 - 1 Teory of Flight (Fixed Wing) Jan12Atiqah Nabilah RazaliNo ratings yet
- Model Aircraft: Weight Wings LiftDocument3 pagesModel Aircraft: Weight Wings LiftGCVishnuKumarNo ratings yet
- PropellersDocument13 pagesPropellerstatomhNo ratings yet
- Landing Gear b777 OverviewDocument15 pagesLanding Gear b777 OverviewAzwan Aziz100% (1)
- 1) Trim TabDocument13 pages1) Trim TabPramod GowdaNo ratings yet
- 1 - BasicAircraftStructure Ver2007 - 2017-18 PDFDocument49 pages1 - BasicAircraftStructure Ver2007 - 2017-18 PDFAndhika Prahasta Djaya100% (2)
- Introduction To AircraftDocument19 pagesIntroduction To AircraftVikash PalNo ratings yet
- Flight Control SurfacesDocument28 pagesFlight Control Surfacesjan paul de leonNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Notes - FundamentalsDocument19 pagesPreliminary Notes - Fundamentalssarathkumar sebastinNo ratings yet
- Texte Colocviu AeroDocument5 pagesTexte Colocviu AeroDiana PuiuNo ratings yet
- Intermediate 4 Final ExamDocument4 pagesIntermediate 4 Final ExamWilliam Fernando Mendoza Romero100% (1)
- IRITS0615079Pullstar Heavy Air FlyerDocument4 pagesIRITS0615079Pullstar Heavy Air FlyerShubham JainNo ratings yet
- SS Marine JumperDocument2 pagesSS Marine JumperKevin HockerNo ratings yet
- Asme CodesDocument14 pagesAsme CodesSaidFerdjallahNo ratings yet
- MSA5T0726A161934 Headlight Beam Leveler System PDFDocument1 pageMSA5T0726A161934 Headlight Beam Leveler System PDFMishu MishuNo ratings yet
- Fireman Lift NoteDocument3 pagesFireman Lift Notesoumya garaiNo ratings yet
- Air Brakes Module 1Document49 pagesAir Brakes Module 1Rodel SampeloNo ratings yet
- EXCW Hyndai R140W-9SDocument10 pagesEXCW Hyndai R140W-9SImron RosyadiNo ratings yet
- MandateDocument3 pagesMandateGabor FarkasNo ratings yet
- Pilatus PC-12 NGX Specifications, Cabin Dimensions, PerformanceDocument1 pagePilatus PC-12 NGX Specifications, Cabin Dimensions, PerformanceAndres LealNo ratings yet
- Emanage Ultimate Installation ManualDocument40 pagesEmanage Ultimate Installation Manualdcc jempolNo ratings yet
- Installation Notice: All Right ReservedDocument46 pagesInstallation Notice: All Right ReservedPaul CollinsNo ratings yet
- Inventory Management MaterialDocument18 pagesInventory Management Material719 Sowmiya. SNo ratings yet
- Train Setv2 18 (Vande Bharat)Document76 pagesTrain Setv2 18 (Vande Bharat)Mercy ClaraNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis From The Drivers SeatDocument101 pagesDiagnosis From The Drivers Seatabul hussain100% (1)
- PcodesDocument1,572 pagesPcodesdiegoNo ratings yet
- Delsan Transport v. CA (2001)Document2 pagesDelsan Transport v. CA (2001)Gigi LucilleNo ratings yet
- Product Information: Molygen New Generation 5W-30Document2 pagesProduct Information: Molygen New Generation 5W-30Vinicius Vilbert RodriguesNo ratings yet
- MR SolomonDocument6 pagesMR SolomonMarcusNo ratings yet
- STANDARD BBS FORMAT FOR 2-L (With Cushion)Document10 pagesSTANDARD BBS FORMAT FOR 2-L (With Cushion)Sreedhar BhuduruNo ratings yet
- Sandvik 533: Technical Specification 533-Revision 2 1/9Document9 pagesSandvik 533: Technical Specification 533-Revision 2 1/9ricardoNo ratings yet
- Jamitons: Phantom Traffic JamsDocument9 pagesJamitons: Phantom Traffic Jamsapt917228393No ratings yet
- Grade 7 - 15 Minute Test - Semester 2Document6 pagesGrade 7 - 15 Minute Test - Semester 2Nguyên NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Importing GuidelinesDocument3 pagesImporting GuidelinesRandall YlaganNo ratings yet
- Taxiing: Preflight: PreflightDocument8 pagesTaxiing: Preflight: PreflightSamson Hailu KNo ratings yet
- Cat Electronic Technician 2019C v1.0 Product Status ReportDocument17 pagesCat Electronic Technician 2019C v1.0 Product Status ReportAndy A.S.No ratings yet
- PCM Products GeneralDocument6 pagesPCM Products Generalvenugopalan srinivasanNo ratings yet
- Odyssey RB3 Radio WiringDocument38 pagesOdyssey RB3 Radio WiringLevisrabak Rabak100% (1)
- VOLVO EW160B-0 GeneralDocument17 pagesVOLVO EW160B-0 GeneralPIKO MOB100% (1)
- Udyam Registration CertificateDocument4 pagesUdyam Registration CertificateAvinash TiwariNo ratings yet