Professional Documents
Culture Documents
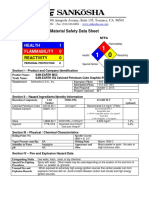
Safety Data Sheet SRPC Khaleej PC
Uploaded by
United Construction Est. TechnicalOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Safety Data Sheet SRPC Khaleej PC
Uploaded by
United Construction Est. TechnicalCopyright:
Available Formats
Safety Data Sheet Alkhalij Cement
Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) Company
Sulfate Resisting Cement (SRC)
Section 1: Product Identification
Product Name: Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC). Sulfate Resisting Portland Cement (SRC).
Product Use: Cement is used as a binder in concrete and mortars that are widely used in
construction. Cement is distributed in bags and bulk shipment.
Note: This MSDS covers Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC). Sulfate Resisting Portland Cement
(SRC).
Manufacturers Name: Alkhalij Cement Company (AKCC)
Address: Al Khalij Cement Company Doha, Qatar
P.O. Box 22504
Tel: 00974 44445900
Fax: 00974 44446900
Emergency telephone number: 44021222 (24 hours)
Cement is made from materials mined from the earth and is processed using energy
provided by fuels. Trace amounts of chemicals may be detected during chemical analysis.
For example, cement may contain trace amounts of calcium oxide (also known as free
lime or quick lime), free magnesium oxide, potassium and sodium Sulfate compounds,
chromium compounds, nickel compounds, and other trace compounds.
Section 2: Hazard Identification
Classification of the Substance or Mixture
Classification (GHS-US)
Skin Corr. 1C H314 Eye Dam. 1 H318
Skin Sens. 1 H317 Carc. 1A H350
STOT SE 3 H335
1 Revision #01 Issue Date: January 2020
Safety Data Sheet Alkhalij Cement
Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) Company
Sulfate Resisting Cement (SRC)
Label Elements:
GHS-US Labelling
Hazard Pictograms (GHS-US)
GHS05 GHS07 GHS08
Signal Word (GHS-US): Danger
Section 3: Composition / Information on Ingredients
Mixture:
Name % by weight (approx.) CAS number
Cement, Portland, chemicals 100 65997-15-1
Limestone 0-15 1317-65-3
Gypsum (Ca(SO4).2H2O) 2-10 13397-24-5
Calcium oxide 0-5 1305-78-8
Magnesium oxide (MgO) 0-4 1309-48-4
Quartz 0-0.2 14808-60-7
Cement is a solid, grey, off white, or white odorless powder. It is not combustible or explosive.
A single, short-term exposure to the dry powder presents little or no hazard. Exposure of sufficient duration to
wet cement, or to dry cement on moist areas of the body, can cause serious, potentially irreversible tissue (skin,
eye, respiratory tract) damage due to chemical (caustic) burns, including third degree burns.
2 Revision #01 Issue Date: January 2020
Safety Data Sheet Alkhalij Cement
Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) Company
Sulfate Resisting Cement (SRC)
Section 4: First Aid Measures
Eye Contact: Airborne dust may cause immediate or delayed irritation or inflammation. Eye contact with
large amounts of dry powder or with wet cement can cause moderate eye irritation, chemical
burns and blindness. Eye exposures require immediate first aid and medical attention to
prevent significant damage to the eye. Rinse eyes thoroughly with water for at least 15
minutes, including under lids, to remove all particles. Seek medical attention for abrasions
and burns.
Ingestion: Do not induce vomiting. If conscious, have person drink plenty of water. Seek medical
attention or contact poison control center immediately.
Skin Contact: Cement may cause dry skin, discomfort, irritation, severe burns, and dermatitis. Wash with
cool water and a pH neutral soap or a mild skin detergent. Seek medical attention for rash,
burns, irritation, dermatitis, and prolonged unprotected exposures to wet cement, cement
mixtures or liquids from wet cement.
Burns: Exposure of sufficient duration to wet Cement, or to dry Cement on moist areas of the body,
can cause serious, potentially irreversible damage to skin, eye, respiratory and digestive
tracts due to chemical (caustic) burns, including third degree burns. A skin exposure may
be hazardous even if there is no pain or discomfort.
Dermatitis: Cement is capable of causing dermatitis by irritation and allergy. Skin affected by dermatitis
may include symptoms such as, redness, itching, rash, scaling, and cracking.
Irritant dermatitis is caused by the physical properties of Cement including alkalinity and
abrasion.
Allergic contact dermatitis is caused by sensitization to hexavalent chromium (chromate)
present in cement. The reaction can range from a mild rash to severe skin ulcers. Persons
already sensitized may react to the first contact with cement. Others may develop allergic
dermatitis after years of repeated contact with cement.
Inhalation (acute): Breathing dust may cause nose, throat or lung irritation, including choking, depending on
the degree of exposure. Inhalation of high levels of dust can cause chemical burns to the
nose, throat and lungs. Move person to fresh air. Seek medical attention for discomfort or if
coughing or other symptoms do not subside.
Inhalation (chronic): Risk of injury depends on duration and level of exposure.
3 Revision #01 Issue Date: January 2020
Safety Data Sheet Alkhalij Cement
Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) Company
Sulfate Resisting Cement (SRC)
Silicosis: This product contains crystalline silica. Prolonged or repeated inhalation of respirable
crystalline silica from this product can cause silicosis, a seriously disabling and fatal lung
disease. See Note to Physicians in Section 4 for further information.
Carcinogenicity: Cement is not listed as a carcinogen in general; however, cement contains trace
amounts of crystalline silica and hexavalent chromium which are classified as known human
carcinogens.
Autoimmune: Some studies show that exposure to respirable crystalline silica (without silicosis) or
Disease: that the disease silicosis may be associated with the increased incidence of
several autoimmune disorders such as scleroderma (thickening of the skin), systemic
lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis and diseases affecting the kidneys. Tuberculosis:
Silicosis increases the risk of tuberculosis.
Renal Disease: Some studies show an increased incidence of chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal
disease in workers exposed to repairable crystalline silica.
Ingestion: Do not ingest cement. Although ingestion of small quantities of cement is not known to be
harmful, large quantities can cause chemical burns in the mouth, throat, stomach, and
digestive tract.
Medical Conditions: Individuals with lung disease (e.g. bronchitis, emphysema, COPD, pulmonary disease) or
sensitivity to hexavalent chromium can be aggravated by exposure.
Most Important Symptoms and Effects Both Acute and Delayed:
General: Corrosive to eyes, respiratory system and skin. Exposure may produce an allergic reaction.
The three types of silicosis include:
9 Simple chronic silicosis – which results from long-term exposure (more than20 years) to
low amounts of respirable crystalline silica. Nodules of chronic inflammation and scarring
provoked by the respirable crystalline silica form in the lungs and chest lymph nodes. This
disease may feature breathlessness and may resemble chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
(COPD).
9 Accelerated silicosis – occurs after exposure to larger amounts of respirable crystalline silica
over a shorter period of time (5-15 years). Inflammation, scarring, and symptoms progress
faster in accelerated silicosis than in simple silicosis.
9 Acute silicosis – results from short-term exposure to very large amounts of respirable
crystalline silica. The lungs become very inflamed and may fill with fluid, causing severe
shortness of breath and low blood oxygen levels.
4 Revision #01 Issue Date: January 2020
Safety Data Sheet Alkhalij Cement
Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) Company
Sulfate Resisting Cement (SRC)
9 Progressive massive fibrosis may occur in simple or accelerated silicosis, but is more
common in the accelerated form. Progressive massive fibrosis results from severe scarring
and leads to the destruction of normal lung structures.
Section 5: Fire Fighting Measures
Extinguishing Media:
Suitable Extinguishing Media: Use extinguishing media appropriate for surrounding fire.
Unsuitable Extinguishing Media: Do not use a heavy water stream. Use of heavy stream of water may spread fire.
Special Hazards Arising from the Substance or Mixture
Fire Hazard: Not flammable.
Explosion Hazard: Product is not explosive.
Reactivity: Wet cement is alkaline and is incompatible with acids, ammonium salts and
Aluminium metal. Cement dissolves in hydrofluoric acid, producing corrosive
silicon tetrafluoride gas. Cement reacts with water to form silicates and calcium
hydroxide. Silicates react with powerful oxidizers such as fluorine, boron
trifluoride, chlorine trifluoride, manganese trifluoride, and oxygen difluoride.
Precautionary Measures Fire: Exercise caution when fighting any chemical fire.
Firefighting Instructions: Do not get water inside containers. Do not apply water stream directly at source of
leak.
Protection During Firefighting: Do not enter fire area without proper protective equipment, including respiratory
protection.
Hazardous Combustion Products: None.
Section 6: Accidental Release Measures
General: Personal Precautions, Protective Equipment and Emergency Procedures. Place
spilled material into a container. Avoid actions that cause the cement to become
airborne. Avoid inhalation of cement and contact with skin. Wear appropriate
protective equipment as described in PPE Section below. Scrape wet cement and
place in container. Allow material to dry or solidify before disposal. Do not wash
cement down sewage and drainage systems or into bodies of water (e.g. streams).
5 Revision #01 Issue Date: January 2020
Safety Data Sheet Alkhalij Cement
Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) Company
Sulfate Resisting Cement (SRC)
Waste Disposal Method: Dispose of cement according to Federal, State, Provincial and Local Regulations,
Section 7: Handling Storage and Usage
General: Keep bulk and bagged cement dry until used. Stack bagged material in a secure manner to
prevent falling. Bagged cement is heavy and poses risks such as sprains and strains to the
back, arms, shoulders and legs during lifting and mixing. Handle with care and use
appropriate control measures.
Engulfment hazard: To prevent burial or suffocation, do not enter a confined space, such as
a silo, bin, bulk truck, or other storage container or vessel that stores or contains cement.
Cement can build up or adhere to the walls of a confined space. The cement can release,
collapse or fall unexpectedly.
Properly ground all pneumatic conveyance systems. The potential exists for static build-up
and static discharge when moving cement powders through a plastic, non- conductive, or
non-grounded pneumatic conveyance system. The static discharge may result in damage to
equipment and injury to workers.
Cutting, crushing or grinding hardened cement, concrete or other crystalline silica-
bearing materials will release respirable crystalline silica. Use all appropriate measures of
dust control or suppression, and Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) described below.
Housekeeping: Avoid actions that cause the cement to become airborne during clean-up such as dry
sweeping or using compressed air. Use HEPA vacuum or thoroughly wet with water to
clean-up dust. Use PPE described below.
Storage Temperature: Below 120 ºC
Storage Pressure: Unlimited.
Clothing: Promptly remove and launder clothing that is dusty or wet with cement. Thoroughly
wash skin after exposure to dust or wet cement.
6 Revision #01 Issue Date: January 2020
Safety Data Sheet Alkhalij Cement
Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) Company
Sulfate Resisting Cement (SRC)
Section 8: Usage Exposure Controls/Personal Protection
Engineering Controls: Use local exhaust or general dilution ventilation or other suppression methods to maintain
dust levels below exposure limits.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
Under ordinary conditions no respiratory protection is required.
Wear a NIOSH Protection: approved respirator that is properly fitted and is in good
condition when exposed to dust above exposure limits.
Eye Protection: Wear approved glasses or safety goggles when handling dust or wet cement to prevent
contact with eyes. Wearing contact lenses when using cement, under dusty conditions, is not
recommended.
Skin Protection: Wear gloves, boot covers and protective clothing impervious to water to prevent skin
contact. Do not rely on barrier creams, in place of impervious gloves. Remove clothing and
protective equipment that becomes saturated with wet cement and immediately wash
exposed areas.
Section 9: Physical and Chemical Properties
Physical State: Solid
Appearance: Gray, off white or white powder
Odor: Odorless
Odor Threshold: Not available
pH: 12 - 13 (in water)
Relative Evaporation Rate (butylacetate=1): Not available
Melting Point: Not available
Freezing Point: Not available
7 Revision #01 Issue Date: January 2020
Safety Data Sheet Alkhalij Cement
Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) Company
Sulfate Resisting Cement (SRC)
Boiling Point: > 1000 °C (> 1832 °F)
Flash Point: Not available
Auto-ignition Temperature: Not available
Decomposition Temperature: Not available
Flammability (solid, gas): Not available
Lower Flammable Limit: Not available
Upper Flammable Limit: Not available
Vapor Pressure: Not available
Viscosity: None, solid.
Specific Gravity: 3.15
Solubility in Water: Slightly (0.1 - 1.0%)
Explosion Data:
Sensitivity to Mechanical Impact:
Not expected to present an explosion hazard due to mechanical impact.
Explosion Data – Sensitivity to Static Discharge:
Not expected to present an explosion hazard due to static discharge.
Section 10: Stability and Reactivity
Stability: Stable. Keep dry until use. Avoid contact with incompatible materials.
Incompatibility: Wet cement is alkaline and is incompatible with acids, ammonium salts and Aluminium
metal. Cement dissolves in hydrofluoric acid, producing corrosive silicon tetra fluoride
gas. Cement reacts with water to form silicates and calcium hydroxide. Silicates react
with powerful oxidizers such as fluorine, boron trifluoride, chlorine trifluoride,
manganese trifluoride, and oxygen difluoride.
Hazardous Polymerization: None.
Hazardous Decomposition: None.
8 Revision #01 Issue Date: January 2020
Safety Data Sheet Alkhalij Cement
Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) Company
Sulfate Resisting Cement (SRC)
Section 11: Toxicological Information
Information on Toxicological Effects – Product
Acute Toxicity: Not classified
LD50 and LC50 Data: Not available
Skin Corrosion/Irritation: Causes severe skin burns and eye damage. pH: 12 - 13 (in water)
Serious Eye Damage/Irritation: Causes serious eye damage. pH: 12 - 13 (in water)
Respiratory or Skin Sensitization: May cause an allergic skin reaction.
Germ Cell Mutagenicity: Not classified
Teratogenicity: Not available
Carcinogenicity: May cause cancer (Inhalation).
Specific Target Organ Toxicity (Repeated Exposure): Not classified
Reproductive Toxicity: Not classified
Specific Target Organ Toxicity (Single Exposure): May cause respiratory irritation.
Aspiration Hazard: Not classified
Symptoms/Injuries after Inhalation: The three types of silicosis include:
1) Simple chronic silicosis: which results from long-term exposure (more than 20 years) to low amounts of
respirable crystalline silica. Nodules of chronic inflammation and scarring provoked
by the respirable crystalline silica form in the lungs and chest lymph nodes. This
disease may feature breathlessness and may resemble chronic obstructive pulmonary
disease (COPD).
2) Accelerated silicosis: Occurs after exposure to larger amounts of respirable crystalline silica over a
shorter period of time (5-15 years).
3) Acute silicosis: Results from short-term exposure to very large amounts of respirable crystalline
silica. The lungs become very inflamed and may fill with fluid, causing severe
shortness of breath and low blood oxygen levels. Inflammation, scarring, and
symptoms progress faster in accelerated silicosis than in simple silicosis.
Progressive massive fibrosis may occur in simple or accelerated silicosis, but is
more common in the accelerated form.
9 Revision #01 Issue Date: January 2020
Safety Data Sheet Alkhalij Cement
Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) Company
Sulfate Resisting Cement (SRC)
Progressive massive fibrosis results from severe scarring and leads to the
destruction of normal lung structures. Some studies show that exposure to
respirable crystalline silica (without silicosis) or that the disease silicosis may be
associated with the increased incidence of several autoimmune disorders such as
scleroderma (thickening of the skin), systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid
arthritis and diseases affecting the kidneys. Silicosis increases the risk of
tuberculosis. Some studies show an increased incidence of chronic kidney disease
and end-stage renal disease in workers exposed to respirable crystalline silica.
Corrosive to the respiratory tract.
Symptoms/Injuries after Skin Contact: Cement may cause dry skin, discomfort, irritation, severe burns, and dermatitis.
Exposure of sufficient duration to wet cement, or to dry cement on moist areas of
the body, can cause serious, potentially irreversible damage to skin, eye,
respiratory and digestive tracts due to chemical (caustic) burns, including third
degree burns. A skin exposure may be hazardous even if there is no pain or
discomfort. Cement is capable of causing dermatitis by irritation and allergy. Skin
affected by dermatitis may include symptoms such as, redness, itching, rash,
scaling, and cracking. Irritant dermatitis is caused by the physical properties of
cement including alkalinity and abrasion. Allergic contact dermatitis is caused by
sensitization to hexavalent chromium (chromate) present in cement. The reaction
can range from a mild rash to severe skin ulcers. Persons already sensitized may
react to the first contact with cement. Others may develop allergic dermatitis after
years of repeated contact with cement.
Symptoms/Injuries after Eye Contact: Airborne dust may cause immediate or delayed irritation or inflammation. Eye
contact with large amounts of dry powder or with wet cement can cause moderate
eye irritation, chemical burns and blindness. Eye exposures require immediate
first aid and medical attention to prevent significant damage to the eye.
Symptoms/Injuries after Ingestion: May cause burns or irritation of the linings of the mouth, throat, and
gastrointestinal tract.
Chronic Symptoms: If dust is generated, repeated exposure through inhalation may cause cancer or
lung disease.
Information on Toxicological Effects - Ingredient(s): LD50 and LC50 Data:
Calcium oxide (1305-78-8)
ATE CLP (oral) 500.000 mg/kg
Quartz (14808-60-7)
LD50 Oral Rat > 5000 mg/kg
Quartz (14808-60-7)
IARC Group 1
National Toxicity Program (NTP) Status Known Human Carcinogens.
10 Revision #01 Issue Date: January 2020
You might also like
- Concrete Safety GuideDocument35 pagesConcrete Safety GuideKimmy LyonsNo ratings yet
- MM - 9E Planetary Axle Wheel EndsDocument41 pagesMM - 9E Planetary Axle Wheel EndsPablo Rodriguez100% (1)
- WSH guidelines diagnose manage occupational diseasesDocument106 pagesWSH guidelines diagnose manage occupational diseasesmediaaprina100% (1)
- Dr. S.K. Haldar's Lectures On Industrial Health For AFIH Students - Occu. Lung Dis Asbestosis Silicosis ByssinosisDocument26 pagesDr. S.K. Haldar's Lectures On Industrial Health For AFIH Students - Occu. Lung Dis Asbestosis Silicosis ByssinosisDr. Prakash Kulkarni100% (2)
- Secoroc RotaryDocument84 pagesSecoroc RotaryElgi Zacky ZachryNo ratings yet
- Kvetoslav R Spurny Editor Analytical Chemistry of Aerosols ScienceDocument499 pagesKvetoslav R Spurny Editor Analytical Chemistry of Aerosols ScienceShibu Arjunan100% (1)
- Safety Data Sheet ConcreteDocument6 pagesSafety Data Sheet ConcreteItalo RicardoNo ratings yet
- Cement MSDS Provides Safety InformationDocument21 pagesCement MSDS Provides Safety Informationkalang kaboetNo ratings yet
- MSDS Cement ITPDocument6 pagesMSDS Cement ITPbobby birowoNo ratings yet
- MSDS Portland Cement Safety DataDocument8 pagesMSDS Portland Cement Safety Dataariowintono nurNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet: November 2012 Page 1 of 7Document7 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet: November 2012 Page 1 of 7malaya tripathyNo ratings yet
- MSDS Portland Cement PDFDocument5 pagesMSDS Portland Cement PDFMohamad TaufikNo ratings yet
- Flyash MSDSDocument6 pagesFlyash MSDSManuel CardosoNo ratings yet
- Concrete MSDS 1 PDFDocument5 pagesConcrete MSDS 1 PDFmanil_5100% (1)
- Lafarge Ready Mix ConcreteDocument6 pagesLafarge Ready Mix ConcreteazerNo ratings yet
- Portland Cement: Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS)Document6 pagesPortland Cement: Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS)eslam sokaNo ratings yet
- MSDS Portland CementDocument5 pagesMSDS Portland CementMonali VarpeNo ratings yet
- MSDS DiamondDocument4 pagesMSDS DiamondVishwakarma VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Sds Portland CementDocument11 pagesSds Portland Cementkwame fosterNo ratings yet
- Holcim PremixedConcrete SDSDocument7 pagesHolcim PremixedConcrete SDSameliasulistianiNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet Portland Cement Kiln Dust: Section 1: IdentificationDocument19 pagesSafety Data Sheet Portland Cement Kiln Dust: Section 1: Identificationomar rahmounNo ratings yet
- Cemento Portland Hoja de Seguridad (38 charactersDocument4 pagesCemento Portland Hoja de Seguridad (38 charactersWilly MendozaNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet: Portland and Blended CementDocument6 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet: Portland and Blended CementBoo Mark DusalNo ratings yet
- Extra Rapid Cement Msds 231018bDocument12 pagesExtra Rapid Cement Msds 231018bSiti KhotimahNo ratings yet
- Portland Cement: Safety Data SheetDocument11 pagesPortland Cement: Safety Data Sheetanon_381289007No ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet Ambuja Hirise CementDocument7 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet Ambuja Hirise CementMukesh KatarnavareNo ratings yet
- 2015-06-01 Sds Portland Cement Clinker Engelsk PDFDocument13 pages2015-06-01 Sds Portland Cement Clinker Engelsk PDFrjay216No ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet For Blended CementDocument8 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet For Blended Cementshahrilzainul77No ratings yet
- Cemex Panama Msds ConcretoDocument8 pagesCemex Panama Msds ConcretoJulio PerezNo ratings yet
- SDS No. CASDS01 | Cement Safety Data SheetDocument6 pagesSDS No. CASDS01 | Cement Safety Data SheetMatt LNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet - SAN EARTHDocument3 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet - SAN EARTHPaulo CLNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet Msds For White Masonry Cement (Complies With Osha Hazard Communication Standard, 29 CFR 1910 1200)Document7 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet Msds For White Masonry Cement (Complies With Osha Hazard Communication Standard, 29 CFR 1910 1200)Praful E. PawarNo ratings yet
- MSDS for ConcreteDocument5 pagesMSDS for Concretegamms upNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet of Porland Cement HolcimDocument6 pagesSafety Data Sheet of Porland Cement HolcimRisma cahya putriNo ratings yet
- FDS Clinker CEMEX Rev7 InglesDocument16 pagesFDS Clinker CEMEX Rev7 InglesJackson VuNo ratings yet
- Cement - API Oilwell Cement, Class 'G', Moderate Sulphate Resistant - Lehigh Cement Limited 2014 PDFDocument6 pagesCement - API Oilwell Cement, Class 'G', Moderate Sulphate Resistant - Lehigh Cement Limited 2014 PDFAMSNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet: MSDS: Limestone and DolomiteDocument6 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet: MSDS: Limestone and DolomiteMisr RaymondNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: Portland Cement ClinkerDocument11 pagesSafety Data Sheet: Portland Cement ClinkerJuan HenaoNo ratings yet
- MSDS for cement materialsDocument6 pagesMSDS for cement materialsMade YennyNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: SupplierDocument6 pagesSafety Data Sheet: SupplierShahid BhattiNo ratings yet
- MSDS-2017 Ca (Oh) 2Document6 pagesMSDS-2017 Ca (Oh) 2mayaNo ratings yet
- Rapid Set Repair MaterialDocument7 pagesRapid Set Repair Materialsam damsNo ratings yet
- MSDS Ready Mix Concrete 2016 09 12Document10 pagesMSDS Ready Mix Concrete 2016 09 12ibrahim syedNo ratings yet
- UZIN Plaster: Safety Data Sheet Wall PlasteringDocument2 pagesUZIN Plaster: Safety Data Sheet Wall PlasteringMon ToonNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet: MSDS: Lafarge Portland CementDocument6 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet: MSDS: Lafarge Portland Cementazer100% (1)
- Msds 4 Cement - LafargeDocument11 pagesMsds 4 Cement - LafargeMahmoud AhmedNo ratings yet
- READYMIX Safety Data SheetDocument9 pagesREADYMIX Safety Data Sheetalbarajeel forwarding001No ratings yet
- Msds p500 NagpurDocument7 pagesMsds p500 NagpurAnkur BarsainyaNo ratings yet
- Conforms to HazCom 2012/United States Safety Data SheetDocument12 pagesConforms to HazCom 2012/United States Safety Data SheetJaphet Charles Japhet MunnahNo ratings yet
- Concrete Ready Mix 2017Document11 pagesConcrete Ready Mix 2017albarajeel forwarding001No ratings yet
- Odessa Portland Cement CoDocument7 pagesOdessa Portland Cement Cosaa6383No ratings yet
- Cement Safety Data Sheet: SECTION 1: Identification of The Substance/mixture and of The Company/ UndertakingDocument27 pagesCement Safety Data Sheet: SECTION 1: Identification of The Substance/mixture and of The Company/ UndertakingjaymarNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet Blended Cement FinalDocument14 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet Blended Cement FinalAndrea Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Low Heat Bagged Cement - Safety Data SheetDocument6 pagesLow Heat Bagged Cement - Safety Data SheetLily ShubinaNo ratings yet
- CemexDocument2 pagesCemexdaniel878787No ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet For CementDocument6 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet For Cementjohan tindiNo ratings yet
- Health and Safety Data Sheet For Common Cements and Cement ProductsDocument6 pagesHealth and Safety Data Sheet For Common Cements and Cement Productsjack21abNo ratings yet
- Gran Slag Properties PDFDocument4 pagesGran Slag Properties PDFROWHEITNo ratings yet
- MSDS DECON Beton InstanDocument5 pagesMSDS DECON Beton InstanMuhammad RidwanNo ratings yet
- SOTACIB-Material Safety Data Sheet - Juillet 2017Document10 pagesSOTACIB-Material Safety Data Sheet - Juillet 2017lindaNo ratings yet
- Steelmaking Drop Out Door Dust SDSDocument7 pagesSteelmaking Drop Out Door Dust SDSmoath.m.h.alzNo ratings yet
- Fire Barrier 135 Msds PDFDocument8 pagesFire Barrier 135 Msds PDFE Hammam El MissiryNo ratings yet
- Safety Information: Ready-Mixed ConcreteDocument6 pagesSafety Information: Ready-Mixed ConcreteJAVIERA FRANCIS BUSTOS PEREZNo ratings yet
- Saran Untuk Caleg Yang Asal NgomongDocument1 pageSaran Untuk Caleg Yang Asal NgomongUnited Construction Est. TechnicalNo ratings yet
- Strategi Caleg Yang Asal NgomongDocument3 pagesStrategi Caleg Yang Asal NgomongUnited Construction Est. TechnicalNo ratings yet
- 5 Langkah Strategi Caleg MilenialDocument3 pages5 Langkah Strategi Caleg MilenialUnited Construction Est. TechnicalNo ratings yet
- National Paint Qatar Dealer AuthDocument3 pagesNational Paint Qatar Dealer AuthUnited Construction Est. TechnicalNo ratings yet
- Kedudukan Arbitrase Adalah Di Jakarta, Indonesia.Document3 pagesKedudukan Arbitrase Adalah Di Jakarta, Indonesia.United Construction Est. TechnicalNo ratings yet
- The Path Forward An Implementation Plan: Prepared by The American Forest & Paper Association 1999Document32 pagesThe Path Forward An Implementation Plan: Prepared by The American Forest & Paper Association 1999United Construction Est. TechnicalNo ratings yet
- Safety Materials JNPDocument2 pagesSafety Materials JNPUnited Construction Est. TechnicalNo ratings yet
- Strategi Calon Legislatif Baru Menghadapi PemiluDocument15 pagesStrategi Calon Legislatif Baru Menghadapi PemiluUnited Construction Est. TechnicalNo ratings yet
- Nvironmental Ampaign LAN: N T E ISO 14001 YDocument10 pagesNvironmental Ampaign LAN: N T E ISO 14001 YUnited Construction Est. TechnicalNo ratings yet
- JNP Trading Company: Your Local Partner Serving QatarDocument2 pagesJNP Trading Company: Your Local Partner Serving QatarUnited Construction Est. TechnicalNo ratings yet
- The Study of Minority Communities and The Waste Stream: October 2002Document100 pagesThe Study of Minority Communities and The Waste Stream: October 2002United Construction Est. TechnicalNo ratings yet
- M Aterial Submittal For Domestic Water System DisinfectionDocument4 pagesM Aterial Submittal For Domestic Water System DisinfectionUnited Construction Est. TechnicalNo ratings yet
- City of Gastonia Wastewater Treatment DivisionDocument14 pagesCity of Gastonia Wastewater Treatment DivisionLee OngNo ratings yet
- SRPC Khaleej PCDocument2 pagesSRPC Khaleej PCUnited Construction Est. TechnicalNo ratings yet
- TerramDocument5 pagesTerramAlle LunagNo ratings yet
- Mining-Contract-Negotiations-For-Developing-Countries-Volume-1 - Iisd-HandbookDocument69 pagesMining-Contract-Negotiations-For-Developing-Countries-Volume-1 - Iisd-HandbookUnited Construction Est. TechnicalNo ratings yet
- Contractual Arrangement - Uranium Te - 0468Document142 pagesContractual Arrangement - Uranium Te - 0468United Construction Est. TechnicalNo ratings yet
- Fruit Culligan 4Document4 pagesFruit Culligan 4United Construction Est. TechnicalNo ratings yet
- Area Culligan 2Document6 pagesArea Culligan 2United Construction Est. TechnicalNo ratings yet
- You Can Give Your Customers Culligan WaterDocument2 pagesYou Can Give Your Customers Culligan WaterUnited Construction Est. TechnicalNo ratings yet
- Sopra: Product Data SheetDocument2 pagesSopra: Product Data SheetUnited Construction Est. TechnicalNo ratings yet
- Kids Culligan 3Document4 pagesKids Culligan 3United Construction Est. TechnicalNo ratings yet
- Culligan in the Middle East Provides Water SolutionsDocument10 pagesCulligan in the Middle East Provides Water SolutionsUnited Construction Est. TechnicalNo ratings yet
- Me AND kID 8Document2 pagesMe AND kID 8United Construction Est. TechnicalNo ratings yet
- Area Culligan 2Document6 pagesArea Culligan 2United Construction Est. TechnicalNo ratings yet
- Jotafloor Easy Painting Guide For Concrete Floors - tcm40 5703 PDFDocument8 pagesJotafloor Easy Painting Guide For Concrete Floors - tcm40 5703 PDFaljarrah84No ratings yet
- Jotafloor Industrial Brochure - tcm132-91542Document16 pagesJotafloor Industrial Brochure - tcm132-91542United Construction Est. TechnicalNo ratings yet
- Merino Panel Products ISO 14001:2015 Certification ComplianceDocument1 pageMerino Panel Products ISO 14001:2015 Certification ComplianceUnited Construction Est. TechnicalNo ratings yet
- General Specification of Mainlaying Materials - 2005Document77 pagesGeneral Specification of Mainlaying Materials - 2005babmech6007No ratings yet
- Dust and Mirrors' or Corruption Is in The Eye of The Beholder'Document2 pagesDust and Mirrors' or Corruption Is in The Eye of The Beholder'nadir adelNo ratings yet
- Nitotile XS GroutDocument33 pagesNitotile XS GroutAhmad SamyNo ratings yet
- Welcome To The Presentation: Dust Survey and Free Silica AnalysisDocument21 pagesWelcome To The Presentation: Dust Survey and Free Silica AnalysisMS RajuNo ratings yet
- Hot Mix Asphalt: Section 1: IdentificationDocument11 pagesHot Mix Asphalt: Section 1: Identificationfathul syaafNo ratings yet
- Fosroc Renderoc FC: Safety Data SheetDocument8 pagesFosroc Renderoc FC: Safety Data Sheetusman khalidNo ratings yet
- Effect of Particulate Matter On Human Health, Prevention, and Imaging Using Pet or SpectDocument13 pagesEffect of Particulate Matter On Human Health, Prevention, and Imaging Using Pet or SpectViet Bui DucNo ratings yet
- Natural Gypsum MSDS 2017Document6 pagesNatural Gypsum MSDS 2017Beautty Rahma ThikaNo ratings yet
- Hoja de Seguridad Alginato TropicalginDocument14 pagesHoja de Seguridad Alginato TropicalginNINI SUAREZNo ratings yet
- Manual de Filtro de Aire 1028600Document12 pagesManual de Filtro de Aire 1028600Ayme AlcazarNo ratings yet
- Msds-016 Conbextra GP - Sds11813 - enDocument5 pagesMsds-016 Conbextra GP - Sds11813 - enjoker batmanNo ratings yet
- Fosroc Conbextra GBDocument9 pagesFosroc Conbextra GBVinith KumarNo ratings yet
- Asbestos companies' ethical dilemmaDocument5 pagesAsbestos companies' ethical dilemmaAster DemissieNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet: S100 70/140-Mesh Sand S100Document7 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet: S100 70/140-Mesh Sand S100sajad gohariNo ratings yet
- The Year in U.S. Occupational Health & Safety 2015Document64 pagesThe Year in U.S. Occupational Health & Safety 2015Celeste MonfortonNo ratings yet
- Rammer 333 Operators Manual 414Document64 pagesRammer 333 Operators Manual 414SerkanAlNo ratings yet
- Dust and FumesDocument3 pagesDust and FumesPavaloaie Marian ConstantinNo ratings yet
- 3M ANZ Disposable Respirators Brochure 2019Document20 pages3M ANZ Disposable Respirators Brochure 2019MartinLukNo ratings yet
- E 133 Thermo LyneDocument48 pagesE 133 Thermo LyneJITENDRA KUMAR SHARMANo ratings yet
- Diagnosis of PneumoconiosisDocument55 pagesDiagnosis of PneumoconiosiselsaNo ratings yet
- Economic and Political Weekly - MAY 28Document91 pagesEconomic and Political Weekly - MAY 28Ajay KarthikNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - Mine DustDocument63 pagesLecture 4 - Mine DustBial100% (1)
- 11 Training OSHA Silica Presentation 3-31-10 Larry Joswial MPHDocument26 pages11 Training OSHA Silica Presentation 3-31-10 Larry Joswial MPHABCDNo ratings yet
- Killer Jeans Report FinalDocument11 pagesKiller Jeans Report FinalRuthwick GowdaNo ratings yet
- Insta CSP23T1Q SubjectDocument23 pagesInsta CSP23T1Q SubjectMessy MessyNo ratings yet
- Respirable Crystalline Silica and Total Dust StandardDocument47 pagesRespirable Crystalline Silica and Total Dust StandardJunaid MazharNo ratings yet