Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Long Exam 2 - Photosynthesis vs. Cellular Respiration
Uploaded by
Krizel LagundiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Long Exam 2 - Photosynthesis vs. Cellular Respiration
Uploaded by
Krizel LagundiCopyright:
Available Formats
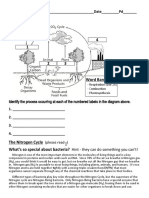
PHOTOSYNTHESIS CELLULAR RESPIRATION
● Anabolic ● Catabolic
● Equation: ● Equation:
6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy → C6H12O6 + 6O2 C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy
○ Energy in the form of light ○ Energy in the form of ATP
○ CO2 is from cellular respiration ○ O2 is from photosynthesis
● Reactants: Carbon dioxide & Water ● Reactants: Glucose & Oxygen
● Products: Glucose & Oxygen ● Products: Carbon dioxide & Water
● Captures energy from sunlight & ● Captures energy from glucose &
releases energy in the form of glucose releases energy in the form of ATP
● Used ONLY in plant cells ● Used in ALL eukaryotes (primarily
animal)
● Occurs ONLY in organisms that make
their own food (autotrophs) ● Occurs in all living cells of an alive
organism (autotrophs & heterotrophs)
● Occurs in the chloroplast
○ Light rxn: thylakoid ● Occurs in the cytoplasm &
○ Dark rxn: stroma mitochondria
○ Glycolysis: cytoplasm
● Steps: ○ Krebs Cycle: matrix
○ ETC: inner membrane
○ Light-dependent reactions ● Steps:
■ Photolysis
(breakdown of H2O)
○ Calvin Cycle ○ Glycolysis
(Light-independent reactions) ○ Krebs Cycle
○ Oxidative Phosphorylation
● Factors affecting the rate of ■ Electron Transport
photosynthesis: Chain (ETC)
○ Water ■ Chemiosmosis
○ Temperature
○ Light intensity ● Factors affecting cellular respiration:
○ Temperature
● Final Electron Acceptor: NADP+ ○ Molecular Oxygen
○ Carbon dioxide concentration
○ State of hydration
○ Age & Type of tissues
● Final Electron Acceptor: O2
PHOTOSYNTHESIS:
6 turns of Calvin cycle + 18 ATP + 12 NADPH
= 1 glucose
also
6 CO2 = 2 G3P (Calvin cycle) = 1 glucose
CELLULAR RESPIRATION:
1 glucose = 2 pyruvate; 2 acetyl CoA; 36 ATP
also
1 glucose = 6 H2O & 6 CO2
CHLOROPLAST MITOCHONDRIA
● Site for photosynthesis ● Site for cellular respiration
● Found in plant and algae cells ● Found in all aerobic eukaryotic cells
● Foldings in inner membrane form ● Foldings in inner membrane form
stromules cristae
● Convert light energy (photons) into ● Convert glucose into chemical energy
glucose (ATP)
● 2 compartments: thylakoid & stroma ● 2 compartments: cristae & matrix
● Pigments are present ● No pigments are present
● Use CO2 and H2O to build glucose ● Break down glucose to CO2 and H2O
● Uses light energy ● Produces chemical energy
PHOTOSYNTHESIS
PHOTOSYSTEM 1 PHOTOSYSTEM 2
● Location: outer surface of the ● Location: inner surface of the
thylakoid membrane thylakoid membrane
● Photocenter is P700 ● Photocenter is P680
● Pigments absorb longer wavelengths ● Pigments absorb shorter wavelengths
of light (≈700) of light (≈680)
○ Accepts lower energy ○ Accepts higher energy
● Involved in BOTH cyclic and ● Involved ONLY in non-cyclic
non-cyclic photophosphorylation photophosphorylation
● No photolysis of water occurs ● Photolysis of water occurs
● Main function is ATP synthesis ● Main function is O2, ATP, & NADPH
synthesis
LIGHT RXN DARK RXN
● Takes place in the thylakoid ● Takes place in the stroma
membranes
● Use ATP and NADPH to convert CO 2
● Convert light energy to ATP and to the sugar G3P
NADPH
● Return ADP, P(i), & NADP + to the light
● Split H2O and release O2 rxn
C4 CAM
● Found in hot and moist environments ● Found in hot, dry, and very cold
environments
● 15% of plants
● 5% of plants
● Divides photosynthesis spatially:
Mesophyll cells & Bundle sheath ● Separate photosynthesis in time:
Night & Day
● Light rxn: mesophyll cells
● Dark rxn: bundle sheath ● Light rxn: during the day
● Dark rxn: when CO2 is present
● Malate as Malic acid is the source of
CO2 ● Malate as Malic acid is the source of
CO2
● Pathway:
○ PEP accepts CO2 ● Pathway:
○ PEP + CO2 = Oxaloacetate ○ Stomata open at night & CO2
○ Oxaloacetate → Malate enters
○ Malate moves to bundle ○ CO2 → Malate → Malic acid
sheath & releases CO2 ○ Stomata close at day & CO2 is
○ RuBP accepts CO2 released from Malic acid
○ Calvin cycle occurs ○ RuBP accepts CO2
○ Calvin cycle occurs
C3
● Found in hot and moist environments
● 80% of plants
● Dark rxn: spongy mesophyll cells
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5806)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Carbon Cycle Nitrogen Cycle DiagramsDocument2 pagesCarbon Cycle Nitrogen Cycle DiagramsEdward OllingerNo ratings yet
- GUILLAIN BARRE SYNDROME CASE STUDY (Group)Document28 pagesGUILLAIN BARRE SYNDROME CASE STUDY (Group)Kylie Golindang100% (7)
- Tom Kenyon - ImmunityDocument9 pagesTom Kenyon - ImmunityDren Hoti100% (2)
- Forensic Mycology - The Use of Fungi in Criminal Investigations.Document11 pagesForensic Mycology - The Use of Fungi in Criminal Investigations.Carlos MolinaNo ratings yet
- Tam1726834776305969 - RLS 4Document16 pagesTam1726834776305969 - RLS 4Rahul GNo ratings yet
- Dr. John Stuart ReidENDocument2 pagesDr. John Stuart ReidEN刘育楠100% (1)
- FCA (SA) Part I Past Papers - 2020 1st Semester 27 3 2020 PDFDocument75 pagesFCA (SA) Part I Past Papers - 2020 1st Semester 27 3 2020 PDFdchunNo ratings yet
- ID#120 - Bhbio Bachelor of Science in Human BiologyDocument1 pageID#120 - Bhbio Bachelor of Science in Human BiologyKrizel LagundiNo ratings yet
- (HSO) Medical Examination FormDocument1 page(HSO) Medical Examination FormKrizel LagundiNo ratings yet
- Botany Notes PDFDocument21 pagesBotany Notes PDFKrizel LagundiNo ratings yet
- De La Salle University: Department of BiologyDocument8 pagesDe La Salle University: Department of BiologyKrizel LagundiNo ratings yet
- Story:: Mystery Case Title: The Stolen CupcakeDocument2 pagesStory:: Mystery Case Title: The Stolen CupcakeKrizel LagundiNo ratings yet
- Parasitism, Commensalism, and Mutualism: Exploring The Many Shades of SymbiosesDocument9 pagesParasitism, Commensalism, and Mutualism: Exploring The Many Shades of SymbiosesBen OusoNo ratings yet
- Gauk 1 Picture1 PDFDocument1 pageGauk 1 Picture1 PDFIshak Ika KovacNo ratings yet
- Molluscan Shellfish Aquaculture and ProductionDocument8 pagesMolluscan Shellfish Aquaculture and ProductionAnonymous xv5fUs4AvNo ratings yet
- Rescorla & Wagner 1972Document18 pagesRescorla & Wagner 1972Víctor Eduardo FuentesNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Chemistry II CBSGS Semester VI Pratik BarveDocument4 pagesPharmaceutical Chemistry II CBSGS Semester VI Pratik BarvePt.Govind BhardawajNo ratings yet
- Family Dynamics and Assessment Tools: Dr. Oryzati Hilman Agrimon, MSC - CMFM, PHD (C)Document40 pagesFamily Dynamics and Assessment Tools: Dr. Oryzati Hilman Agrimon, MSC - CMFM, PHD (C)Ther Ray100% (1)
- Mind Does Really Matter: Evidence From Neuroimaging Studies of Emotional Self-Regulation, Psychotherapy, and Placebo EffectDocument19 pagesMind Does Really Matter: Evidence From Neuroimaging Studies of Emotional Self-Regulation, Psychotherapy, and Placebo Effectseagoddess_simoNo ratings yet
- Physical Science: Quarter 1 - Module 4: Biological MacromoleculesDocument25 pagesPhysical Science: Quarter 1 - Module 4: Biological MacromoleculesSansay SaylonNo ratings yet
- Medical Imaging and Pattern RecognitionDocument49 pagesMedical Imaging and Pattern RecognitionworkshoppeNo ratings yet
- Viral Oncogenesis DR - Fokam-JosephDocument31 pagesViral Oncogenesis DR - Fokam-JosephRosemary FuanyiNo ratings yet
- CANITA - 3PTC - Piaget - S Stages of Cognitive DevelopmentDocument14 pagesCANITA - 3PTC - Piaget - S Stages of Cognitive Developmentim. EliasNo ratings yet
- All Subjects Worksheets Class 4th 1Document48 pagesAll Subjects Worksheets Class 4th 1DrSyed ShujauddinNo ratings yet
- Titin ProteinDocument40 pagesTitin ProteinAlexanderNo ratings yet
- Dividual SubjectivationsDocument12 pagesDividual SubjectivationslukasNo ratings yet
- Taste Buds: Name: Dronadula, Prasanna Kumar Clinical Clerk Amec-BccmDocument10 pagesTaste Buds: Name: Dronadula, Prasanna Kumar Clinical Clerk Amec-BccmroarmikeNo ratings yet
- Virtual Laboratory Worksheet-Cellular Transport MechanismDocument2 pagesVirtual Laboratory Worksheet-Cellular Transport MechanismKeizzhia Alleonah T. CastilloNo ratings yet
- Botox Nation: Because People MatterDocument16 pagesBotox Nation: Because People MatterBPMStaffNo ratings yet
- DNA StructureDocument4 pagesDNA StructureMG - 11CJ 972501 Cawthra Park SSNo ratings yet
- CSAT General Mental AbilityDocument10 pagesCSAT General Mental AbilityDishani SarkarNo ratings yet
- The Mystery of A Flower.Document11 pagesThe Mystery of A Flower.Cillar Chipo JuniorNo ratings yet
- APTTDocument2 pagesAPTTApril Lady Faith P. PaundogNo ratings yet
- 2016 Black Soldier Fly WartazoaDocument11 pages2016 Black Soldier Fly WartazoaghotamaNo ratings yet
- Organa Brands Dream TeamDocument3 pagesOrgana Brands Dream TeamMichael_Lee_RobertsNo ratings yet