Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Infographic-Nestle-Fast and Efficient Brain-V2
Uploaded by
devashishOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Infographic-Nestle-Fast and Efficient Brain-V2
Uploaded by
devashishCopyright:
Available Formats
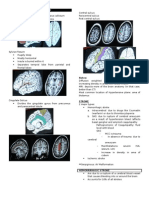
BRAIN - HOW DO YOU GET A FAST AND EFFICIENT BRAIN
Neurodevelopment largely occurs during infancy
and affects cogni�ve and behavioural pa�erns in
later years of life. Myelina�on is an important
neurodevelopmental process. Nutrients like
phospholipids contribute largely to
neurodevelopment.
Prefontral cortex
Neurogenesis
Neuronal migration
Astrogenesis
Oligodendrogenesis
Synaptogenesis
Myelination
Synaptic pruning
Adapted from Silbereis JC, et al., Neuron 2016;89:248–68
Fig 1: Timeline of key neurodevelopmental processes
EARLY STAGES OF BRAIN DEVELOPMENT STAGES OF COGNITION DEVELOPMENT
Age (Years)
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
Vision Development
Speech Development
Emo�onal Development
Math/Logic
Social A�achment & Skills
Motor Development
Peer Social Skills
Language
KEY INFLUENCING FACTORS FOR NEURODEVELOPMENT
Socio- Psycho-
cultural social risk
factors factors Sensori-
motor
CNS
develop-
ment and
func�on
Social- Cogni�ve
Biological emo�onal
Poverty risk language
factors
1 Gene 2 Environmental 3 Molecular cues guide 4 Nutri�on &
expression factors development & are Food
(nature) (nurture) dependent upon the
experiences of the
developing child
IMPORTANT NUTRIENTS FOR NEURODEVELOPMENT
DHA, Iron Certain B vitamins Choline, Lutein Phospholipids (PLs)
MYELINATION
Myelin sheaths are lipid-rich
membrane stacks
Overall ra�o of proteins to lipids Myelin Sheath
of around 1 to 186
Most part of the lipids are polar
lipids, including phospholipids and
sphingomyelin
Clinical studies show link between myelina�on and cogni�on, including
Cogni�ve Language and EFs (working Processing Sensory
ability reading memory) speed reac�vity
Sphingomyelin (SM), Phospha�dylcholine (PC) Phospha�dylethanolamine (PE) Phospha�dylserine (PS),
accounts for ~36% of dry weight
Sphingomyelin (SM) is par�cularly rich in the myelin sheath of the central nervous
SM is important for myelin integrity and func�on & supports axonal matura�on
PHOSPHOLIPIDS
Phospholipids are the most abundant lipids in In human milk, fat accounts for ~50% of the
the brain total energy contribu�on, of which 0.2–2.0%
Major components in the brain and influence: are phospholipids.
Structural membranes integrity The 5 major phospholipids are components of
Metabolic pathways related to energe�c cell membranes in neural �ssue and include:
homeostasis of the cells Phospha�dylcholine (PC)
Intracellular signaling processes / connec�ons Phospha�dylethanolamine (PE)
Found in high levels in the dendrites, myelin Phospha�dylserine (PS)
sheath, and synapses neural structures Phospha�dylinositol (PI)
Sphingomyelin (SM)
SM is par�cularly rich in
the myelin sheath of the
central nervous.
SM is important for myelin integrity and
func�on & supports axonal matura�on.
Key Takeaways
Essen�al micronutrients and macronutrients are necessary for op�mal neurodevelopmental processes.
Deficiency of these essen�al nutrients affects cogni�ve development and learning in later stages of life.
Adequate nutri�on is necessary to ensure brain development.
References
1. Silbereis JC, et al., Neuron 2016;89:248–68
2. Thompson RA and Nelson CA. Am Psychol. 2001;56(1):5–15; 2. Martorell R, et al. J Nutr. 2010;140:348–354.
3. Walker S.P. et al, The Lancet, 2007
4. Kullenberg D, Taylor LA, Schneider M, Massing U. Health effects of dietary phospholipids. Lipids Health Dis. 2012;11:3-16
5. Schmitt et al. Biochemica et Biophysica Acta, 2015
6. O’Brian et al. Journal of Lipid Reasearch, 1965
7. Morell, 2012
8. Spiegel I and Peles E, 2002
9. Don et al. 2014
10. Ledesma, 1999
11. Janssen et al. 1981
You might also like
- Myelination - Newsletter - v5.0Document4 pagesMyelination - Newsletter - v5.0devashishNo ratings yet
- WHO - Micronutrient DeficienciesDocument2 pagesWHO - Micronutrient DeficienciesdevashishNo ratings yet
- WHO - Conclusions and Recommendations - 2006Document11 pagesWHO - Conclusions and Recommendations - 2006devashishNo ratings yet
- NIH Public Access: Author ManuscriptDocument9 pagesNIH Public Access: Author ManuscriptdevashishNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Aguilar 2018Document13 pagesAguilar 2018Mario Manuel Fiorentino FerreyrosNo ratings yet
- Trigger Point Dry Needling An Evidence and Clinical Based Approach 1st Edition Ebook PDF VersionDocument58 pagesTrigger Point Dry Needling An Evidence and Clinical Based Approach 1st Edition Ebook PDF Versionbernice.hickman158100% (38)
- Daoist Concept of Alarm Points in Medical AcupunctureDocument12 pagesDaoist Concept of Alarm Points in Medical AcupunctureHambos PahatouridisNo ratings yet
- Code Stroke & Hyperacute Stroke TreatmentDocument35 pagesCode Stroke & Hyperacute Stroke TreatmentSitti Fatwan NisakNo ratings yet
- The Psychopath MagnetizedDocument9 pagesThe Psychopath MagnetizedAvengingBrainNo ratings yet
- Lab 03 Reflexes Referred PainDocument14 pagesLab 03 Reflexes Referred PainViraj TatikondaNo ratings yet
- Ashton Manual English PDFDocument58 pagesAshton Manual English PDFMalissa Bowen100% (2)
- Aimc-2019 - Aimc-2019-Ssh-611Document9 pagesAimc-2019 - Aimc-2019-Ssh-611Yovan P. PutraNo ratings yet
- PMC National MDCAT Syllabus 2020 19-10-2020Document46 pagesPMC National MDCAT Syllabus 2020 19-10-2020Mughees AhmedNo ratings yet
- Boost Your Practice With Brain Health CoachingDocument4 pagesBoost Your Practice With Brain Health CoachingClint RumboltNo ratings yet
- Science 8 PDFDocument172 pagesScience 8 PDFaftab khanNo ratings yet
- Approach To A Child With HemiplegiaDocument5 pagesApproach To A Child With HemiplegiaBeenish IqbalNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Contusions and LacerationDocument5 pagesCerebral Contusions and LacerationVithaa'TetaaNo ratings yet
- Theory of First Language Acquisition (Language Acquisition Device) (WEEK 8) Mind MAPDocument7 pagesTheory of First Language Acquisition (Language Acquisition Device) (WEEK 8) Mind MAPlopobhia noobyteNo ratings yet
- Pshcology AssignmentDocument5 pagesPshcology AssignmentAbdul MoizNo ratings yet
- Biopsychology 9th Edition Pinel Test BankDocument25 pagesBiopsychology 9th Edition Pinel Test BankCameronAllenmtwei100% (64)
- Institute of Neurosciences Kolkata (Schedule) PDFDocument2 pagesInstitute of Neurosciences Kolkata (Schedule) PDFpvkdasaNo ratings yet
- Script When Presenting About Listening and HearingDocument3 pagesScript When Presenting About Listening and HearingGladyss PunzalanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plansarah hanaNo ratings yet
- Escalas de Valoracion PediatricaDocument4 pagesEscalas de Valoracion PediatricaSebastian MantillaNo ratings yet
- Praktikum Faal - PhysioEx Fisiologi Otot PDFDocument5 pagesPraktikum Faal - PhysioEx Fisiologi Otot PDFFeri AlmanaNo ratings yet
- CHP 7 Class 10Document13 pagesCHP 7 Class 10sourabh nuwalNo ratings yet
- GOALS Partnership-Occupational Therapist and Other Health ProfessionalsDocument5 pagesGOALS Partnership-Occupational Therapist and Other Health ProfessionalsarvinNo ratings yet
- Biology Capsule for Defence ExamsDocument15 pagesBiology Capsule for Defence ExamsShubhneetNo ratings yet
- 1 - Action & Graded Potentials LecDocument21 pages1 - Action & Graded Potentials LecMohamedHossamNo ratings yet
- NeuroradiologyDocument11 pagesNeuroradiologysarguss14100% (2)
- The Wisdom of Trauma Booklet - FinalDocument11 pagesThe Wisdom of Trauma Booklet - FinalAdela100% (2)
- Taste Buds & Taste ReceptorsDocument6 pagesTaste Buds & Taste ReceptorsMissz WazeeNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Parkinsons Pre TestDocument4 pagesGroup 1 Parkinsons Pre TestAyman NabilNo ratings yet
- Brain TumorsDocument30 pagesBrain TumorsDagmawi BahiruNo ratings yet