Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 7: Inventories Goods Includible in Inventory
Uploaded by
AngelaMariePeñaranda0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views4 pagesThis document summarizes key concepts related to inventories. It defines different types of inventories like finished goods, work in process, and raw materials. It discusses accounting methods for valuing inventories like periodic and perpetual systems. It also outlines how to determine the cost of inventories and common adjustments for inventory shortages or overages.
Original Description:
Original Title
CHAPTER 7
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document summarizes key concepts related to inventories. It defines different types of inventories like finished goods, work in process, and raw materials. It discusses accounting methods for valuing inventories like periodic and perpetual systems. It also outlines how to determine the cost of inventories and common adjustments for inventory shortages or overages.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views4 pagesChapter 7: Inventories Goods Includible in Inventory
Uploaded by
AngelaMariePeñarandaThis document summarizes key concepts related to inventories. It defines different types of inventories like finished goods, work in process, and raw materials. It discusses accounting methods for valuing inventories like periodic and perpetual systems. It also outlines how to determine the cost of inventories and common adjustments for inventory shortages or overages.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
CHAPTER 7: INVENTORIES GOODS INCLUDIBLE IN INVENTORY
- Held for resale in the ordinary course of the - Installment contracts
business (finished goods) o Retention of the titles by the seller
- In the process of production for such sale until the selling price is fully
(work in process) collected (included in the seller)
- In the form of materials or supplies to be o Treated as a regular sale where
consumed in the production process or in income is deferred on the part of the
rendering of services (raw material and seller (excluded from the seller)
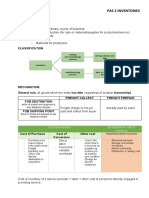
manufacturing supplies) - Goods in transit
o FOB destination where goods sold is
transferred only upon receipt of
EXAMPLE OF INVENTORIES goods (included in the seller)
o FOB shipping point where goods
- Merchandise purchased by a trading entity
sold is transferred upon shipment
and held for resale
(excluded from the seller)
- Land and other property held for sale in the
- Others
ordinary course of business
o Goods out on consignment –
- Finished goods, goods undergoing
included in the seller
production, and raw materials and supplies
o Goods consigned in – excluded from
of waiting used in the production process by
the seller
a manufacturing entity
o Goods held by customers on
approval or trial – included in the
seller
CLASSES OF INVENTORIES
- Inventories of trading or merchandising
concern FREIGHT TERMS
o An entity buys and sells the goods
Freight Term Interpretation
purchased in the same form
Freight collect Paid by the buyer
o Merchandise inventory
Freight prepaid Paid by the seller
- Inventories of manufacturing concern
FOB destination Seller is responsible for
o An entity buys goods and alter
freight
(converts) them into another form FOB shipping point Buyer is responsible for
before they are made available for freight
sale
o Raw or direct materials, work in
process, finished goods PRESENTATION
- Inventories are classified as current assets
- It shall be presented as one-line items with
TYPES OF INVENTORIES the details disclosed in the notes to the
- Finished goods – completed goods ready financial statements
for sale
- Work in process – partially completed
goods which required further or additional ACCOUNTING FOR INVENTORIES
processing before they ca be sold - Periodic system – calls for the physical
- Raw materials – goods to be used in counting of goods on hand at the end of the
production accounting period to determine quantities
- Direct materials – goods that are already o The quantities at the end of the
issued in production period are multiplies by its unit cost
- Factory or manufacturing supplies – are raw to determine the inventory value of
material issued t production financial statement purposes
o Do not form a part of the finished o Used when inventory have small
product peso investment and are fast
o If they form part of the finished moving
product, they cannot be - Perpetual system – requires the
economically, directly or easily maintenance of stock cards that shows the
identifiable or that their cost is running balance of the inventory including
insignificant its movements
o An inventory count is conducted at period
the end of the period to verify
quantities reflected in the records
COST OF INVENTORY
o It is used for inventory items with a
relatively large peso investment - Purchase cost, purchase price, import
o The inventory quantity and value is duties, non-happy refundable or non-
known at any time recoverable purchased assets, and
transport, handling and other costs directly
attributable to the acquisition of the
INVENTORY SHORTAGE/OVERAGE inventory
o Trade discounts are directly
- The difference between the physical
deducted
inventory and amount recorded in the stock
o Foreign exchange gains or loss are
records is accounted for as inventory short
excluded
or over which requires an adjustment to the
o The difference between the
inventory account
purchase price for normal credit
o Inventory shortage – physical
terms and the amount paid is
inventory is less than the amount
recognized as interest expense
recorded in the books
- Conversion cost refers to the costs
o Inventory overage – physical
necessary in converting raw materials into
inventory is greater than the amount
finished goods which included direct labor
recorded in the books
and production overhead
- Other costs are necessary in bringing the
inventories to their present location and
INVENTORY DISCOUNTS
condition
- Trade discounts – deductions from the list - Abnormal amounts of waste material, labor
or catalog prices in order to arrive at the or other production costs
invoice prices which is the amount - Storage costs, unless this costs are
chargeable to the buyer necessary in the production process before
o Trade discounts are not recorded a further production stage
o Its purpose is to encourages trading - Administrative overhead that do not
or increase sales contribute to bringing inventory so their
o It suggests the price at which the present location and condition
goods may be resold - Selling costs
- Cash discounts – deductions from the
invoice price when payment is made within
the discount period COST OF INVENTORIES OF A SERVICE PROVIDER
o Its purpose is to encourage prompt
- Includes primarily of the labor and other
payment or early payment of costs of personnel directly engaged in
account providing the service (supervisory personnel
o Purchase discount/sales discount and overhead)
METHOD OF RECORDING PURCHASES - Generally, they are classified as work in
progress
- Gross method – both the purchase and - Labor and other costs relating to sales and
account payable are recorded at gross general administrative personnel are
(100%) excluded (classified as expense)
- Net method – both the purchases and
accounts payable are recorded at net of
discount COST FORMULAS
Transaction Gross Net - Cost formulas deal with the computation of
Purchase Purchase and Purchase and cost of inventories that are charged as
AP at gross AP at net
expense and when the related revenue is
Payment AP Accounts
recognized as well as the cost of unsold
withing the Cash payable and
inventories at the end of the period that are
discount Purchase cash at net
period Discount recognized as an asset
Payment Accounts AP o Specific identification – specific
outside the Payable and PD costs are attributed to identifies
discount cash at gross Cash items of inventory
Characteristics: multiplied with the
The cost of inventory inventory quantity on
is determined by hand to arrive at the
multiplying the units cost of the ending
on hand by their inventory
actual unit cost It is relatively easy to
This should be used apply, especially with
for inventories that the use of computers
are not ordinarily It produces inventory
interchangeable and valuation that
those that are approximates current
segregated for value if there is rapid
specific projects turn over of inventory
The flow of inventory There may be
corresponds with the considerable lag
actual physical flow between current cost
It is very costly to and inventory
implement valuation since it
includes early
purchases
o First-in, First-out – it is assumed that In rising prices,
inventories that were purchased or inventory valuation
produced first are sold first or issued will be less than
to production current cost
Characteristics
The costs of sales
represent costs from Moving average – the terms
earlier purchases used in computing the
The cost of ending weighted average unit cost of
inventory represents inventory under the perpetual
costs from the most method
recent purchases A new weighted
It favors balance average cost per unit
sheet presentation is computed after
There is improper every purchase or
matching of costs purchase return
against revenue
because the COGS is
stated as an earlier NET REALIZABLE VALUE
purchase price
- Inventories shall be measured at lower cost
In rising prices, FIFI
and net realizable value
produces the highest
- Net realizable value refers to the estimated
net income
selling price in the ordinary course of
o Weighted average – the cost of sales
business less the estimated cost of
and ending inventory are determined
completion and the estimated costs
based on the weighted average cost
necessary to make the sale
of beginning inventory and all
- Assets shall not be carried in excess of
inventories purchase or produced
amounts expected to realized from their
during the period
sale or use
Characteristics
The weighted average
unit cost is computed
UNRECOVERABLE INVENTORIES
by dividing the total
costs available for - If the inventories are damaged, wholly or
sale by the total partially obsolete, or if the selling prices
number of units have declined
available for sale - If the estimated cost of completion or the
The weighted average estimated cost of disposal has increased
unit costs is
DETERMINATION OF NET REALIZABLE VALUE made – loss (other expense) is recorded in
the period of the price decline
- Inventories are written down to net
- Entry:
realizable value on an item per item or
o Loss on purchase commitment
individual basis
Estimated liability for
- It is not appropriate to write down
purchase commitment
inventories based on classification of
- If the market price rises at the time of the
inventory (finished goods or all inventories
purchase – gain on purchase commitment
in a particular industry or geographical
is recorded that is limited to the loss on the
segment)
purchase commitment previously recorded
- Materials and other supplies for production
are not written down to NRV if the related
finished products are expected to be sold at
or above cost
- If the price of the material and other
supplies declines and the cost of the related
finished products exceeds NRV, the material
and other supplies are written down to NRV
using its replacement cost
ACCOUNTING FOR INVENTORY WRITEDOWN
- If the cost is lower than NRV – no
adjustment
- If the NRV is lower than cost – inventory is
measured at NRV
o Direct method or the COGS method
– the inventory is recorded at lower
of cost or NRV
Any loss on inventory write-
down is not accounted for
separately but absorbed or
buried in the COGS
Ending inventory is recorded
opposite the income and
expense summary account at
the lower of cost or NRV
o Allowance method – the inventory is
recorded at cost and any loss is
accounted for separately
Gain or loss in inventory
write-down is recorded as an
adjustment to the COGS
Allowance for inventory
write-down is a reduction in
the cost of the inventory
PURCHASE COMMITMENTS
- Obligations of the entity to acquire certain
goods sometime in the future at a fixed
price and fixed quantity
o When purchase commitments are
significant or unusual – disclosure is
required
o Losses from firm and non-
cancellable commitments shall be
recognized
- Decline in the purchase price after a non-
cancellable purchase commitment has been
You might also like
- Cfas - InventoriesDocument6 pagesCfas - InventoriesYna SarrondoNo ratings yet
- Chap 10 and 11Document5 pagesChap 10 and 11Mary Claudette UnabiaNo ratings yet
- Materials and Supplies Awaiting Use in The Production ProcessDocument3 pagesMaterials and Supplies Awaiting Use in The Production ProcessMizumi IshiharaNo ratings yet
- Intacc 1 Notes Part 4Document10 pagesIntacc 1 Notes Part 4Crizelda BauyonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10: InventoriesDocument39 pagesChapter 10: InventoriesCarl Aaron LayugNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - Inventories: Maritime Shipping TermsDocument4 pagesModule 5 - Inventories: Maritime Shipping TermsAva RodriguesNo ratings yet
- INVENTORIESDocument28 pagesINVENTORIESLourdios EdullantesNo ratings yet
- ACC 203 Module 4 PAS 2 Inventories PAS 41 Biological AssetsDocument15 pagesACC 203 Module 4 PAS 2 Inventories PAS 41 Biological AssetsKirsty SicamNo ratings yet
- FINACC1 Inventories PDFDocument6 pagesFINACC1 Inventories PDFJerico DungcaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 16-Inventories: Far SummaryDocument3 pagesCHAPTER 16-Inventories: Far SummaryFuturamaramaNo ratings yet
- Subsequent Measurement:: Differ in Inventory ValueDocument4 pagesSubsequent Measurement:: Differ in Inventory ValueCharina Jane PascualNo ratings yet
- 1 Inventories Pas 2 Reviewer Intermediate AccountingDocument5 pages1 Inventories Pas 2 Reviewer Intermediate AccountingDalia ElarabyNo ratings yet
- 1010 2. InventoriesDocument9 pages1010 2. Inventorieslizie elizaldeNo ratings yet
- Inventories Basic PrinciplesDocument7 pagesInventories Basic PrinciplesSandia EspejoNo ratings yet
- Intacc ReviewerDocument2 pagesIntacc ReviewerCassandra CeñidoNo ratings yet
- INVENTORIESDocument64 pagesINVENTORIESLuisa Janelle BoquirenNo ratings yet
- INVENTORIESDocument89 pagesINVENTORIESLuisa Janelle BoquirenNo ratings yet
- IA 1 - 5 InventoriesDocument8 pagesIA 1 - 5 InventoriesVJ MacaspacNo ratings yet
- Inventories: Financial Accounting and ReportingDocument6 pagesInventories: Financial Accounting and ReportingcolNo ratings yet
- Accounting NotesDocument12 pagesAccounting NotesKrystelle JalemNo ratings yet
- InventoriesDocument9 pagesInventoriesDon John David100% (2)
- Chapter 10: Inventories: CustomersDocument4 pagesChapter 10: Inventories: CustomersireneNo ratings yet
- Pas 2 Inventories: Nature: DefinitionDocument3 pagesPas 2 Inventories: Nature: DefinitionKristalen ArmandoNo ratings yet
- 161 12 PAS 2 InventoriesDocument2 pages161 12 PAS 2 InventoriesRegina Gregoria SalasNo ratings yet
- Inventories: PERIODIC SYSTEM-physical Counting of Goods OnDocument4 pagesInventories: PERIODIC SYSTEM-physical Counting of Goods OnGirl Lang AkoNo ratings yet
- Inventories: Classes of Inventories ConsignmentDocument3 pagesInventories: Classes of Inventories ConsignmentJonathan NavalloNo ratings yet
- Inventories HandoutDocument4 pagesInventories HandoutRoselle Jane LanabanNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Audit of Inventories and Cost of SalesDocument2 pages4.1 Audit of Inventories and Cost of SalesNavsNo ratings yet
- Far Notes For QualiDocument10 pagesFar Notes For QualiMergierose DalgoNo ratings yet
- 121 Prelims ReviewerDocument6 pages121 Prelims Reviewerjohnmichaelaspe1234No ratings yet
- Accounting For INVENTORIESDocument4 pagesAccounting For INVENTORIESMeludyNo ratings yet
- InventoriesDocument3 pagesInventoriesNikki RañolaNo ratings yet
- Inventories and Cost of Sales What Is Inventory?: Financial Accounting For BusinessDocument19 pagesInventories and Cost of Sales What Is Inventory?: Financial Accounting For BusinessĐàm Quang Thanh TúNo ratings yet
- Inventories 2024Document27 pagesInventories 2024Charish Ann SimbajonNo ratings yet
- JPIAN - S Digest - InventoriesDocument12 pagesJPIAN - S Digest - InventoriesMyrrh ErosNo ratings yet
- IntAcc 2 Midterm NotesDocument93 pagesIntAcc 2 Midterm NotesAlmaera CeninaNo ratings yet
- GROUP 2 - PAS 2 InventoriesDocument7 pagesGROUP 2 - PAS 2 InventoriesNhicoleChoiNo ratings yet
- TM 10 InventoriesDocument91 pagesTM 10 Inventories2310111212No ratings yet
- Inventories P1Document8 pagesInventories P1Shane CalderonNo ratings yet
- Cfas Lesson 3 Pas 2 (Activity)Document3 pagesCfas Lesson 3 Pas 2 (Activity)Michelle CabezoNo ratings yet
- Scope: Allocation of Fixed Production OverheadsDocument8 pagesScope: Allocation of Fixed Production OverheadsjayveeNo ratings yet
- Inventories: Assertions Audit Objectives Audit Procedures I. Existence/ OccurrenceDocument4 pagesInventories: Assertions Audit Objectives Audit Procedures I. Existence/ OccurrencekrizzmaaaayNo ratings yet
- Intermediate-Accounting Handout Chap 10Document4 pagesIntermediate-Accounting Handout Chap 10Joanne Rheena BooNo ratings yet
- C7 Inventories (MT)Document2 pagesC7 Inventories (MT)Cyril Grace DedumoNo ratings yet
- Pas 2 InventoriesDocument12 pagesPas 2 InventoriesLETIGIO, RHEANA ROSE M.No ratings yet
- InventoryDocument20 pagesInventoryE.D.J33% (3)
- CH 08Document54 pagesCH 08Jessie jorgeNo ratings yet
- CH 8 - AnswerDocument58 pagesCH 8 - Answer金沛霓No ratings yet
- UFAS2Document4 pagesUFAS2Romylen De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- InventoriesDocument8 pagesInventoriesangel ciiiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Intermediate AccountingDocument4 pagesChapter 10 - Intermediate AccountingPrincess PriyaNo ratings yet
- PDF Warren SM ch07 Final - CompressDocument20 pagesPDF Warren SM ch07 Final - CompressBerliana MustikasariNo ratings yet
- InventoriesDocument3 pagesInventoriesZance JordaanNo ratings yet
- Accounting For A Merchandising BusinessDocument3 pagesAccounting For A Merchandising BusinessAngelique Faye CalucinNo ratings yet
- Inventories: Inventories Net Sales FormulaDocument6 pagesInventories: Inventories Net Sales Formulagab camonNo ratings yet
- Inventories NotesDocument7 pagesInventories NotesJessel Ann MontecilloNo ratings yet
- Presentation4.1 - Audit of Inventories, Cost of Sales and Other Related AccountsDocument37 pagesPresentation4.1 - Audit of Inventories, Cost of Sales and Other Related AccountsRoseanne Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Inventory Lecture NotesDocument15 pagesInventory Lecture NotesMinh ThưNo ratings yet
- Week Five:: Reporting andDocument38 pagesWeek Five:: Reporting andIzham ShabdeanNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Accounting 3Document10 pagesIntermediate Accounting 3AngelaMariePeñarandaNo ratings yet
- 2019 IntAcc Vol 3 CH 5 AnswersDocument9 pages2019 IntAcc Vol 3 CH 5 AnswersAngelaMariePeñarandaNo ratings yet
- Code of Conduct or Employee ManualDocument6 pagesCode of Conduct or Employee ManualAngelaMariePeñarandaNo ratings yet
- Income TaxesDocument37 pagesIncome TaxesAngelaMariePeñarandaNo ratings yet
- Financial ManagementDocument96 pagesFinancial ManagementAngelaMariePeñarandaNo ratings yet
- CFAS - Biological Assets, Intangibles, and InvestmentsDocument8 pagesCFAS - Biological Assets, Intangibles, and InvestmentsAngelaMariePeñarandaNo ratings yet
- CFAS Chapter 5 - Accounts ReceivableDocument6 pagesCFAS Chapter 5 - Accounts ReceivableAngelaMariePeñarandaNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Framework and Accounting StandardsDocument14 pagesConceptual Framework and Accounting StandardsAngelaMariePeñarandaNo ratings yet
- CFAS Chapter 4 - Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument3 pagesCFAS Chapter 4 - Cash and Cash EquivalentsAngelaMariePeñarandaNo ratings yet
- Star BucksDocument3 pagesStar BucksRoger YoungNo ratings yet
- Compare and Contrast The Industrial Organisation Approach To The ResourceDocument3 pagesCompare and Contrast The Industrial Organisation Approach To The ResourceMarvin AlleyneNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 HBS Case 1 ValuationDocument15 pagesAssignment 3 HBS Case 1 ValuationqrpiotrNo ratings yet
- CRM - Future Group Big BazaarDocument25 pagesCRM - Future Group Big BazaarAadit ShahNo ratings yet
- FSA Case Study SolutionDocument6 pagesFSA Case Study SolutionConnor CooperNo ratings yet
- Pdiso-Ts 55010-2019 (E)Document50 pagesPdiso-Ts 55010-2019 (E)Pedro Pastrana SocorroNo ratings yet
- RAJNEESH AWASTHI MINI PROJECT Final - RAJNEESH AWASTHI MBA 1st Semester RSMTDocument37 pagesRAJNEESH AWASTHI MINI PROJECT Final - RAJNEESH AWASTHI MBA 1st Semester RSMTrajawasthi7133No ratings yet
- Foreign Collaboration and Joint Venture-Key Ppts-2020Document70 pagesForeign Collaboration and Joint Venture-Key Ppts-2020najiath mzeeNo ratings yet
- Ebook Accounting Information For Business Decisions 4Th Australian Edition PDF Full Chapter PDFDocument67 pagesEbook Accounting Information For Business Decisions 4Th Australian Edition PDF Full Chapter PDFgina.letlow138100% (27)
- Sol. Man. Chapter 8 Acctg For Franchise Operations Franchisor 2021 EditionDocument11 pagesSol. Man. Chapter 8 Acctg For Franchise Operations Franchisor 2021 EditionkoyNo ratings yet
- CH 21 No.4-6Document2 pagesCH 21 No.4-6adeline ikofaniNo ratings yet
- EntreprDocument112 pagesEntreprmeow meowwNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: BUSINESS 9609/32Document4 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: BUSINESS 9609/32Fatema NawrinNo ratings yet
- Maria HernandezDocument6 pagesMaria Hernandezchtbox1039No ratings yet
- Deepwater Well Project and Risk Management DR-TC3-NXT17530Document1 pageDeepwater Well Project and Risk Management DR-TC3-NXT17530GUILLERMONo ratings yet
- SCML 200: - Supply Chain Management & OperationsDocument25 pagesSCML 200: - Supply Chain Management & OperationsHello WorldNo ratings yet
- Sravan Digital Marketing ResumeDocument2 pagesSravan Digital Marketing ResumeRavi RanjanNo ratings yet
- B2B Marketing and Sales - OrangeDocument62 pagesB2B Marketing and Sales - OrangeMuhammad UsmanNo ratings yet
- Prosultative Selling - Mike PilcherDocument119 pagesProsultative Selling - Mike PilcherMike PilcherNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document8 pagesChapter 1Rizalyn Jo YanosNo ratings yet
- Need For The StudyDocument7 pagesNeed For The StudyKalyan RagampudiNo ratings yet
- Top SupermarketsDocument3 pagesTop SupermarketsAvinash GowdaNo ratings yet
- Business Model Canvas For 'The Vanity Fur' - Pet Care StartupDocument2 pagesBusiness Model Canvas For 'The Vanity Fur' - Pet Care StartupVedant KarnatakNo ratings yet
- Accounting Techniques For Decision MakingDocument24 pagesAccounting Techniques For Decision MakingRima PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Ias 8Document7 pagesIas 8Jan Joshua Paolo GarceNo ratings yet
- B. Com (CA) SyllabusDocument70 pagesB. Com (CA) SyllabusBhaskar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Operations Management: Emin IlyasDocument24 pagesOperations Management: Emin IlyasAsifIsmayilovNo ratings yet
- Million Dollar BrandDocument13 pagesMillion Dollar BrandkyleNo ratings yet
- Assignment 20 09 20Document9 pagesAssignment 20 09 20Sherwin AuzaNo ratings yet
- Comparing Alternative Approaches To Calculating Long-Run Incremental CostDocument20 pagesComparing Alternative Approaches To Calculating Long-Run Incremental CostCore ResearchNo ratings yet