Professional Documents
Culture Documents
4 Safety and Infection Control
Uploaded by
Rossiene Airos0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views3 pagesThis document defines key terms related to nosocomial infections and outlines procedures to prevent their transmission. Common types of nosocomial infections include urinary tract and respiratory infections. Hand hygiene, personal protective equipment (PPE), isolation protocols, and disinfection/sterilization help break the chain of infection. Proper donning and doffing of PPE is also described.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document defines key terms related to nosocomial infections and outlines procedures to prevent their transmission. Common types of nosocomial infections include urinary tract and respiratory infections. Hand hygiene, personal protective equipment (PPE), isolation protocols, and disinfection/sterilization help break the chain of infection. Proper donning and doffing of PPE is also described.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views3 pages4 Safety and Infection Control
Uploaded by
Rossiene AirosThis document defines key terms related to nosocomial infections and outlines procedures to prevent their transmission. Common types of nosocomial infections include urinary tract and respiratory infections. Hand hygiene, personal protective equipment (PPE), isolation protocols, and disinfection/sterilization help break the chain of infection. Proper donning and doffing of PPE is also described.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
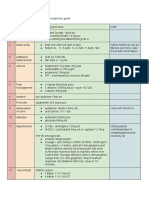
Safety and Infection Control Nosocomial/ Healthcare Acquired Infections
Nosocomial Infection: used to designate an
infection acquired by a patient during hospital
Definition of Terms
stay
Biological Hazards: substance that poses a threat o Common Nosocomial Infections
to the health of living organisms, primarily humans Urinary Tract Infections: catheter associated
Respiratory Pneumonia: ventilator associated
Infection Control: procedures to control and o Common Pathogens Associated in N.I.
monitor infections occurring within their facilities Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas
aeruginosa, Escherichia coli, Acinetobacter
Chain of Infection: requires a continuous link baumanii, C. difficile and coagulase-negative
between 6 components staphylococcus
Healthcare-acquired Infection: an infection
Six Components of Chain of Infection acquired by a patient as a result of healthcare
procedure that may or may not require a hospital
Infectious Agent stay
o bacteria, fungi, parasites and viruses
o breaking the chain: early detection and Transmission Prevention Procedures
treatment of infectious agents
Reservoir preventing transmission of microorganisms from
o a place where infectious agents can live and infected reservoirs to susceptible hosts is critical
possibly multiply like humans, animals, in controlling the spread of infection
equipment and soiled objects
Procedures used to prevent transmission
o breaking the chain: disinfecting work
hand hygiene
areas
wearing of PPE
Portal of Exit isolation of highly infective or highly susceptible
o phlebotomist provides a portal of exit when they patients
collect blood
proper disposal of contaminated materials
o breaking the chain: disposing of needles and
strict adherence to the guidelines published by
lancets in sealed, sharp containers and other
Center for Disease Control and the
contaminated materials in biohazard containers
Occupational Safety and Health Administration
and keeping tubes and sample containers
sealed Hand Hygiene
Means of transmission
o infectious agent has a way to reach a includes both hand washing and the use of
susceptible host through: alcohol-based cleansers
direct contact: unprotected host is touched alcohol-based cleansers are recommended
by the reservoir after contact with spore-forming bacteria
droplet: host inhales material from reservoir including Clostridum difficle (major cause of
such as aerosol droplets from infected person HAI) and Bacillus sp.
airborne: inhalation of dried aerosol nuclei
circulating on air currents or attached to dust
particles
vehicle: ingestion of contaminated food or
water
vector: parasites such as malaria transmitted
by a mosquito bite
o breaking the chain: hand washing, Standard
Precautions and Transmission-based
Precautions
Portal of Entry
o portal entry can be the same as portal of exit
(mouth, mucous membranes, and open
wounds)
o breaking the chain: disinfection and
sterilization, and strict adherence to Standard
Precautions and Transmission-based
Precautions
Susceptible Host
o can be the patient or the health care provider
o may be: patients undergoing chemotherapy,
immunocompromised patients, newborns (0-2
months old), infants (2 months- 1 year old),
senior citizens Best time to do Hand Washing?
o breaking the chain: observation of special o before patient contact
precautions when working in the nursery and in o when gloves are removed
isolation rooms (ICU patients or oncology dept.) o before leaving the work area
o at any time when they have been knowingly
contaminated
o before going to designated break areas
o before and after using bathroom facilities
Handwashing Technique
o antimicrobial soap, paper towels, running water, Transmission-Based Precautions
and waste container
o (1) Wet hands with warm water; don’t touch the guidelines for isolation practices and have been
sink periodically revised
o (2) Apply soap can find these guidelines regarding PPE posted
o (3) Rub hands. Thoroughly clean between on the outside doors to isolation rooms
fingers and under fingernails at least 20 secs;
include thumbs and wrists in cleaning Classifications
o (4) Rinse hands with water in a downward Airborne precautions: when microorganisms
position can remain infective while being carried through
o (5) Dry hands thoroughly with a single use the air on the dried residue of a droplet or on a
towel dust particle
o (6) Turn off faucet using used towel Droplet precautions: for persons infected with
microorganisms that can be transmitted on moist
Personal Protective Equipment particles (coughing and sneezing)
Contact precautions: for infections that can be
Gloves: worn to protect hands from transmitted by direct skin-skin contact or by
contamination indirect contact
o Latex Allergy: reaction to latex include irritant
contact dermatitis (dry, itchy irritation on Phlebotomy Procedures in Isolation
hands); replace with nitrile or vinyl gloves
Delayed Hypersensitivity: resembles poison samples taken from the room should be cleaned
ivy of any blood contamination and placed in plastic
True Immediate Hypersensitivity: often bags located near or just outside the door
characterized by respiratory difficulty
Gowns: worn to protect clothing and skin; Protective/ Reverse Isolation
fluid-resistant gowns should be worn when
the possibility of encountering splashes is may be required for severely burned patients,
anticipated patients receiving chemotherapy, and organ and
Masks: worn to protect against inhalation of bone marrow transplant patients and in the
droplets containing microorganisms from nursery
infective patients PPE worn by phlebotomists: gowns, gloves, and
Goggles: worn to protect mucous masks
membranes of mouth, nose, and eyes
Biohazard
Face Shields: protect mucous membranes
from splashes; additional layer of protection
expose an unprotected individual to bacteria,
Respirators: required when collecting blood viruses, parasites, or other biological entities that
from patients who have airborne diseases can result in injury
exposure occurs from ingestion, inoculation,
Donning PPE tactile contamination, or inhalation of infectious
(1) Handwashing/Hand rubbing material
(2) Put on inner gloves contaminated equipment and supplies must be
(3) Put on the gown, first tied at the neck and disposed in containers clearly marked with the
waist. biohazard symbol or red or yellow color coding
(4) Put on mask urine can be poured out in the lab sink; disinfect
(5) Put on face shield nondisposable equipment with 1:10 dilution of
(6) Put on outer gloves sodium hypochlorite prepared weekly in a plastic
bottle
Doffing PPE
(1) Hand hygiene Chemical Hazards
(2) Remove outer gloves
(3) Hand hygiene
may come in contact while accessioning or
(4) Untie and remove gown processing samples in the lab and preparing
(5) Hand hygiene containers for urie samples
(6) Remove face shield chemicals should never be mixed together unless
(7) Hand hygiene specified and must be added in the order
(8) Remove inner gloves specified (acid into water)
(9) Hand hygiene all chemicals and reagents containing hazardous
(10) Remove mask ingredients in concentration >1% are required to
(11) Hand hygiene have a Material Safety Data Sheet on file
(12) Wear new mask
Sharp Hazards
Standard Precautions
exposure to bloodborne pathogen due to
developed by CDC by combining the accidental puncture
recommendations of Universal Precautions and never recap a needle
Body Substance Isolation procedures
Bloodborne Pathogens: HIV, HBV, HCV,
assume that every person in the healthcare
syphilis, malaria, other viral diseases
setting is potentially infected
o HIV: attacks human immune system by infecting the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA)
and destroying the T-lymphocyte subset CD4; classifies fire according to type of burning
can progress from HIV to AIDS material and the fire extinguisher used to control
o HBV: attacks the liver causing mild to severe them
chronic disorders; may develop jaundice Multipurpose ABC fire extinguishers: most
o HCV: also attacks the liver and now the leading common but label should always be checked
bloodborne pathogen cause of chronic liver before using
disease progressing to cirrhosis and liver o PASS: Pull, Aim, Squeeze, Sweep
cancer
Enforcement Procedure for the Occupational Types of fire and Fire Extinguishers
Exposure to Bloodborne Pathogen Standard:
placed emphasis on the use of engineering
controls to prevent accidental exposure to
bloodborne pathogens
Postexposure Prophylaxis: initiated within 24
hours of accidental exposure to blood
Components of the OSHA Bloodborne
Pathogen Standard
Engineering Controls: sharp disposal containers;
discarding of needles w/ activated safety device
and holder attached; proper labelling
Work Practice Controls: practice Standard
Precautions; no eating, drinking, smoking, etc.;
daily disinfection
PPE: provide PPE for employees
Medical: immunizations; medical follow-up to
employees
Documentation: annual training in safety
standards; evaluation & implementation of safety Physical Hazards
devices; involve employees in selection &
evaluation of new devices; maintain sharps injury agent, factor or circumstance that can cause
log harm with contact
classified as type of occupational hazard or
Radioactive Hazards environmental hazard
Avoid running in rooms and hallways
while drawing blood from patients in the radiology Be alert for wet floors
dept. or from patients receiving radioactive Bend the knees when lifting heavy objects or
treatments and, in the lab patients
exposure to radiation is dependent on the Keep long hair tied back and removed dangling
combination of time, distance and shielding jewelry
persons working in a radioactive environment Wear comfortable, closed-toes shoes with
wear measuring devices to determine amount of nonskid soles
radiation they are accumulating; they also wear Maintain a clean, organized work area.
LED gown/aprons
Electrical Hazards
healthcare setting contains a large amount of
electrica
l equipment with which phlebotomists are in
contact
electrical equipment are closely monitored by
designated hospital personnel but phlebotomist
should always be observant for any dangers
Fire/Explosive Hazards
Joint Commission requires that all healthcare
institutions have posted evacuation routes and
detailed plans to follow
Initial Steps to follow
o Rescue anyone in immediate danger
o Alarm: activate institutional fire alarm system
o Contain: close all doors to potentially affected
areas
o Extinguish/ Evacuate: extinguish fire if
possible, or evacuate, closing the door
You might also like
- Prepration of The Isolation UnitDocument43 pagesPrepration of The Isolation UnitGayatri MudliyarNo ratings yet
- John Hudson's How to Survive a Pandemic: Life Lessons for Coping with Covid-19From EverandJohn Hudson's How to Survive a Pandemic: Life Lessons for Coping with Covid-19No ratings yet
- AUBF - Chapter 1Document7 pagesAUBF - Chapter 1Kristin SoquilloNo ratings yet
- Infection ControlDocument16 pagesInfection ControlMohamed AbdelkaderNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan On Hospital Acquired InfectionDocument17 pagesLesson Plan On Hospital Acquired InfectionRadha Sri100% (1)
- Infection Control PracticesDocument5 pagesInfection Control PracticesMaryNo ratings yet
- Hap Lo5Document8 pagesHap Lo5cjNo ratings yet
- Definition of InfectionDocument27 pagesDefinition of InfectionRenit AntoNo ratings yet
- Asepsis and Infection Control SkillsDocument26 pagesAsepsis and Infection Control SkillsDominic SantosNo ratings yet
- Communicable Disease Nursing TermsDocument269 pagesCommunicable Disease Nursing Termsmatrixtrinity100% (1)
- Handwashing and Infection ControlDocument23 pagesHandwashing and Infection ControlLiane BartolomeNo ratings yet
- Module 2 INFECTION CONTROL, SAFETY, FIRST AID AND PERSONAL WELLNESSDocument61 pagesModule 2 INFECTION CONTROL, SAFETY, FIRST AID AND PERSONAL WELLNESSYesha Marie FanoNo ratings yet
- HostDocument21 pagesHostJoanna DagohoyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Infection Control LecDocument45 pagesChapter 2 Infection Control LecRhea CarinoNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Safety in The Clinical Microscopy SectionDocument6 pagesLaboratory Safety in The Clinical Microscopy SectionFarida WongNo ratings yet
- Urinalysis and Other Body FluidsDocument64 pagesUrinalysis and Other Body FluidsJahre Mark ToledoNo ratings yet
- Hospital Infection (Laundry) PDFDocument39 pagesHospital Infection (Laundry) PDFSumantri KasmadiNo ratings yet
- OUTFOXCDCStandardPrecautions PDFDocument2 pagesOUTFOXCDCStandardPrecautions PDFmorris_tyoNo ratings yet
- Infection Control: IntroductionDocument17 pagesInfection Control: Introductionsuman gupta100% (1)
- Lec 5 Surgical AsepsisDocument52 pagesLec 5 Surgical Asepsisshahnaz AyasrahNo ratings yet
- I Infection ControlDocument11 pagesI Infection ControlTuTitNo ratings yet
- Dr. Nadia Aziz C.A.B.C.M Baghdad Medical CollegeDocument39 pagesDr. Nadia Aziz C.A.B.C.M Baghdad Medical CollegeMazinNo ratings yet
- AUBF Lec - Lab Safety - QADocument12 pagesAUBF Lec - Lab Safety - QALeinard ClaveroNo ratings yet
- Lec 11 PDFDocument8 pagesLec 11 PDFFlorida ManNo ratings yet
- Standard Precautions 1Document34 pagesStandard Precautions 1Melody LandichoNo ratings yet
- Infection ControlDocument24 pagesInfection ControlMuhammad UmairNo ratings yet
- INFECTION PREVENTION AND SAFETY MEASURESDocument19 pagesINFECTION PREVENTION AND SAFETY MEASURESSopan ShindeNo ratings yet
- Infection Prevention and Safety Measures Including HivDocument37 pagesInfection Prevention and Safety Measures Including HivRipunjoy KalitaNo ratings yet
- Infection Control in PediatricDocument13 pagesInfection Control in PediatricToka HessenNo ratings yet
- MODULE 7 Infection ControlDocument43 pagesMODULE 7 Infection ControlBitoy AlarconNo ratings yet
- Universal PrecautionsDocument4 pagesUniversal PrecautionsRasheena Alaja JainalNo ratings yet
- Aseptics, Antiseptics, Hospital Infections, WasteDocument16 pagesAseptics, Antiseptics, Hospital Infections, WasteYemuuuNo ratings yet
- Isolation PrecautionsDocument13 pagesIsolation Precautionsmalyn1218No ratings yet
- Workplace Biohazards & Standard PrecautionsDocument9 pagesWorkplace Biohazards & Standard Precautionsjacob marinasNo ratings yet
- Infection Prevention in Health Care Systems by Incorporation of Well-Equipped and Designed Isolation RoomsDocument8 pagesInfection Prevention in Health Care Systems by Incorporation of Well-Equipped and Designed Isolation RoomsInternational Journal of Arts, Humanities and Social Studies (IJAHSS)No ratings yet
- Nasocomial Infection Presentation-WPS OfficeDocument30 pagesNasocomial Infection Presentation-WPS Officerithikkumars2020No ratings yet
- PMLS2 2Document45 pagesPMLS2 2john dale duranoNo ratings yet
- Principles of Asepsis and Sterile TechniquesDocument4 pagesPrinciples of Asepsis and Sterile Techniquesjgcriste93% (14)
- Six Elements of InfectionDocument18 pagesSix Elements of InfectionAlhadzra AlihNo ratings yet
- Hospital Acquired Infections PDFDocument4 pagesHospital Acquired Infections PDFMuhammad Mohsin Ali DynamoNo ratings yet
- Chain of InfectionDocument24 pagesChain of Infectionnanakwame5769No ratings yet
- INFECTION PREVENTION BMW MANAGEMENTDocument9 pagesINFECTION PREVENTION BMW MANAGEMENTDipti PunjalNo ratings yet
- 2chain of DiseaseDocument43 pages2chain of Diseaseyuuki konno100% (1)
- Prepared By: Mr. Val L. Ramilo RNDocument65 pagesPrepared By: Mr. Val L. Ramilo RNMilk CoNo ratings yet
- Seminar ON: Infection Prevention (Including Hiv) and Standard Safety Measures, Bio - Medical Waste ManagementDocument24 pagesSeminar ON: Infection Prevention (Including Hiv) and Standard Safety Measures, Bio - Medical Waste ManagementTHONDYNALUNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Healthcare EpidemiologyDocument10 pagesChapter 12 Healthcare EpidemiologyRegiena Tamargo100% (1)
- SAFETY-CONTROL (Copy)Document9 pagesSAFETY-CONTROL (Copy)PD CisnerosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Medical and Surgical AsepsisDocument31 pagesChapter 6 - Medical and Surgical AsepsisAbegail ListancoNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument11 pagesUntitledAkash HalsanaNo ratings yet
- PMLS-2-LESSON-2 NoDocument6 pagesPMLS-2-LESSON-2 NoVoid MelromarcNo ratings yet
- Infection ControlDocument24 pagesInfection Controlمحمد العراقيNo ratings yet
- Standard PrecautionsDocument4 pagesStandard PrecautionsEthel May AlabastroNo ratings yet
- Clinical Bacteriology Lab (W01)Document7 pagesClinical Bacteriology Lab (W01)nicholehernandez05No ratings yet
- Infection Control: Evangeline H, SKPDocument49 pagesInfection Control: Evangeline H, SKPEvangeline HutabaratNo ratings yet
- Module 8-NSTP 1-Health Program, Common Illness & Their PreventionDocument46 pagesModule 8-NSTP 1-Health Program, Common Illness & Their PreventionDCRUZNo ratings yet
- Module 8-NSTP 1-Health Program, Common Illness & Their PreventionDocument46 pagesModule 8-NSTP 1-Health Program, Common Illness & Their PreventionLalaine AlonNo ratings yet
- Infection and Prevention Control-2Document14 pagesInfection and Prevention Control-2NIKHIL RAJNo ratings yet
- Isolation Precautions: Personal Protective Equipment: Extended TextDocument13 pagesIsolation Precautions: Personal Protective Equipment: Extended TextIonut ChicinasNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Living - Summer 2016Document108 pagesDiabetic Living - Summer 2016Lohrasp Suraliwala100% (2)
- Bennett2007 PDFDocument8 pagesBennett2007 PDFMirza RisqaNo ratings yet
- Construction Manpower SafetyDocument25 pagesConstruction Manpower SafetyFritz BalasabasNo ratings yet
- St. Paul University PhilippinesDocument4 pagesSt. Paul University PhilippinesAshley DayagNo ratings yet
- Medicinal plants guide with uses and preparationsDocument6 pagesMedicinal plants guide with uses and preparationsCaroline Kim100% (1)
- BrightDocument279 pagesBrightfernando100% (1)
- Plasticity of Macrophage 2019 ReviewDocument9 pagesPlasticity of Macrophage 2019 ReviewKudelko MatNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan Ineffective Tissue Perfusionderic83% (29)
- Magic Items of The UnderdarkDocument4 pagesMagic Items of The UnderdarkAndré Rodrigues Mano0% (1)
- AsbestosDocument4 pagesAsbestoskoketsoNo ratings yet
- Acute Abdomen CausesDocument5 pagesAcute Abdomen CausesSheetal DherangeNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document5 pagesAssignment 3Samantha PargadNo ratings yet
- Journal Club: DR Meera Nandan 3 Year MD ClinicalyogaDocument54 pagesJournal Club: DR Meera Nandan 3 Year MD ClinicalyogaMeera NandanNo ratings yet
- Marjo S. Van Der Knaap MD, PHD, Jacob Valk MD, PHD Auth. Magnetic Resonance of Myelin, Myelination, and Myelin DisordersDocument570 pagesMarjo S. Van Der Knaap MD, PHD, Jacob Valk MD, PHD Auth. Magnetic Resonance of Myelin, Myelination, and Myelin Disordersali tidaNo ratings yet
- Awareness On Proper Waste Disposal in Barangay Tawantwan Mlang North CotabatoDocument16 pagesAwareness On Proper Waste Disposal in Barangay Tawantwan Mlang North CotabatoRap Rap100% (1)
- Documentation On Medicinal Plants Sold I PDFDocument9 pagesDocumentation On Medicinal Plants Sold I PDFGbadeyanka O WuraolaNo ratings yet
- COVID Toes, Rashes: How The Coronavirus Can Affect Your SkinDocument6 pagesCOVID Toes, Rashes: How The Coronavirus Can Affect Your SkinlittlemisseeeNo ratings yet
- Master Drug ChartDocument22 pagesMaster Drug ChartMahadhir AkmalNo ratings yet
- Bulky Uterus Fibroids Ovarian Cyst Cured HomoeopathyDocument9 pagesBulky Uterus Fibroids Ovarian Cyst Cured HomoeopathyPriyakrishnaVasamsettiNo ratings yet
- Blood Lesson Planning and AssessmentDocument10 pagesBlood Lesson Planning and Assessmentapi-364329432No ratings yet
- Colds and Their BenefitsDocument105 pagesColds and Their BenefitsAlmiranteAckbarNo ratings yet
- 2015 Khairallah Et AlDocument9 pages2015 Khairallah Et AlAnifo Jose AntonioNo ratings yet
- Nutrition - TPN (Basics)Document37 pagesNutrition - TPN (Basics)Giorgi BradNo ratings yet
- BT-740 OP Manual (740-ENG-OPM-EUR-R02) PDFDocument50 pagesBT-740 OP Manual (740-ENG-OPM-EUR-R02) PDFJaneth Pariona SedanNo ratings yet
- Malnutrition e BD 12Document51 pagesMalnutrition e BD 12dr.vichiayorinaNo ratings yet
- Jared Griffin Care PlanDocument14 pagesJared Griffin Care PlanKarina Rodriguez100% (4)
- 101 Ways To Reduce StressDocument11 pages101 Ways To Reduce StressStephen Comee100% (1)
- NCP - LeprosyDocument3 pagesNCP - LeprosyKevin DareNo ratings yet
- Key Acupoints PDFDocument6 pagesKey Acupoints PDFthouartu50% (2)
- Cabbage & CauliflowerDocument19 pagesCabbage & CauliflowerramNo ratings yet
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionFrom EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (402)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (14)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (78)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsFrom EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo ratings yet
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsFrom EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (169)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeNo ratings yet
- Techniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementFrom EverandTechniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (40)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (42)
- The Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesFrom EverandThe Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (34)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- The Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingFrom EverandThe Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- The Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsFrom EverandThe Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsNo ratings yet
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessFrom EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (327)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeFrom EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (253)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (33)
- Daniel Kahneman's "Thinking Fast and Slow": A Macat AnalysisFrom EverandDaniel Kahneman's "Thinking Fast and Slow": A Macat AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (130)
- Summary: It Didn't Start with You: How Inherited Family Trauma Shapes Who We Are and How to End the Cycle By Mark Wolynn: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: It Didn't Start with You: How Inherited Family Trauma Shapes Who We Are and How to End the Cycle By Mark Wolynn: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)