Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Notes - Antibiotics Table
Uploaded by
Chesmar Macapala0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views7 pagesAntibiotics
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAntibiotics
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views7 pagesNotes - Antibiotics Table
Uploaded by
Chesmar MacapalaAntibiotics
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
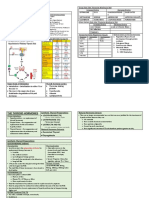
TibbsNotes – Antibacterial Table
Inhibits CLASSIFICATION ANTIBIOTICS Clinical Uses Adverse Effects Pk/Pd
Gram (+) AMPICILLIN: GI Disturbance; PENICILLIN V – Bioavaliability
- DOC: Streptococcus pyogenes (skin & soft tissue) Pseudomonas colitis impaired by food (give 1-2hrs
- DOC: Streptococcus Pneumonia (susceptible) TICARCILLIN: Hematologic before/after), low w/o food
- DOC: Non--lactamase-producing S. aureus Disturbance Excretion: Urine (Renal Dose
Garm (-) Common: Adjustment in Renal Failure),
- DOC: E. faecalis (NOT E. faecium) Hypersensitivity (cross- EXCEPT:
Crystalline/Aqueous - DOC: N. Meningitidis (NOT N. Gonorrhea) reacting) oNAFCILLIN: Bile
(IV) Atypicals Rash EBV oOXACILLIN, etc: Bile & Urine
Natural Penicillins PENICILLIN G - DOC: Treponema pallidum (Syphillis) Rare: AMOXICILLIN:
(Narrow Spectrum) - DOC: Leptospira spp Anaphylactic Shock (Tx: oNot impaired by food
C Other Uses: Epinephrine) oBiovailability higher than
E - C. tetani; Actinomyces Hemolytic Anemia Ampicillin
L - H. influenzae in high doses Interstitial Nephritis Time-Dependent Killing
L - NOT B. fragilis Others: Bactericidal
Procaine, - S. Pyogenes (Pharyngitis, prophylaxis for reinfection) Seizures (high doses)
Benzathine (IM) - T. Pallidum (Syphilis) Secondary infections
W
A Penicillins PENICILLIN V (Oral) - S. Pyogenes (Pharyngitis) (replaced by AMOXICILLIN)
L NAFCILLIN (IV) METHICILLIN - DOC: MSSA
L Anti-Staphylococcal - NOT for Enterococci & Gram (-) organisms
OXACILLIN (IV) CLOXACILLIN (Oral)
S - S. Pneumoniae (most active ORAL -lactam(
AMPICILLIN [Limited Gram (-)]
Y
- Shigella spp.
N
Amino- AMOXICILLIN )Oral) AMPICILLIN (IV) - Salmonella typhi (resistance)
T - E. coli ( NOT for other enterobacteriaceae: Klebsiella,
H Enterobacter) (UTI)
E Extended-
- Listeria monocytogenes (Pneumonia in children)
S Spectrum - Pseudomonas aeruginosa (nosocomial)
I Carboxy- TICARCILLIN CARBENICILLIN - Enterobacteriaceae (broader coverage)
S - NOT active against enterococci (ex. E. Faecalis)
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa (nosocomial)
Ureido- PIPERACILLIN (IV) - Enterobacteriaceae (broader coverage inc. Klebsiella spp.)
- E. faecalis
COAMOXICLAV Coverage for: Klebsiella Pneumoniae, Bacteroides fragilis
Diarrhea Unreliable CNS penetration
CLAVULANIC ACID (+ Amoxicillin)
-Lactamase Inhibitors + Ticarcillin
SULBACTAM + Ampicillin
TAZOBACTAM + Piperacillin
Inhibits CLASSIFICATION ANTIBIOTICS Clinical Uses Adverse Effects Pk/Pd
- Streptococci & Staphylococci (minor skin & soft tissue infections) Common Excretion: Urine; Except
- CEFAZOLIN – DOC: Surgical Prophylaxis (NOT for colorectal Thrombophlebitis o CEFTRIAXONE (Bile)
1st Gen CEPHALEXIN (Oral) CEFAZOLIN (IV) procedure) Occasional o CEFOPERAZONE (Bile)
- E. coli (uncomplicated cystitis) (NOT Enterococci, Pseudomonas Hypersensitivity CEFOPERAZONE – DO NOT
aeruginosa, and Acinetobacter spp. Bile sludging cross BBB
CEFUROXIME (Oral) CEFUROXIME (IV) - Broader coverage: Gram (-) (inc. -actamase-producing H. CEFACLOR – Serum sickness
influenzae, Moraxella catarrhalis, Klebsiella spp. like reactions
CEFACLOR (Oral) CEFOTETAN (IV)
2nd Gen - Bacteroides fragilis (intraabdominal/pelvic infections) Hematologic disturbances
- NOT against Enterococci, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and (CEFOPERAZONE)
CEFOXITIN (IV)
Acinetobacter spp.) Disulfiram-like reaction
CEFTRIAXONE (IV) - CEFTRIAXONE, CEFOTAXIME – DOC: Meningitis by Penicillin- Metallic Taste
CEFPODOXIME (Oral) resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae Rare
CEFOTAXIME (IV) - CEFOPERAZONE, CEFTAZIDIME – Pseudomonas aeruginosa Anaphylactic Shock (cross
C
CEFOPERAZONE (IV) - Broader coverage: Enterobacteriaceae (inc. Citrobacter spp., allerginicity)
E Cephalosporins Serratia Marcescens, Providencia spp.) (Pneumonia, Pseudomembranous colitis
L Interstitial nephritis
pyelonephritis)
L - CEFTRIAXONE – DOC: N. gonorrhoeae
3rd Gen - CEFTRIAXONE – DOC: MDR Salmonella typhi
W CEFIXIME (ORAL) - CEFTAZIDIME: Burkholderia capacia
CEFTAZIDIME (IV) - CEFTAZIDIME: Empirical Treatment in neutropenic febrile
A
immunocompromised patients
L - CEFTIZOXIME: Bacteroides fraglis (Intraabdominal/Pelvic
L Infections)
- CEFIXIME, CEFTAZIDIME – NOT for Sptaphylococci & Streptococci
S - Broader coverage: Enterobacteriaceae (inc. Enterobacter spp.)
Y 4th Gen CEFEPIME CEFPIROME - Pseudomonas aeruginosa (nosocomial infections)
- NOT for Enterococci, Acinetobacter spp., and anaerobes
N
T 5th Gen CEFTAROLINE - CEFTAROLINE – NOT Pseudomonas
- Aerobic Gram (-) rods (Pneumonia, Meningitis, Sepsis) Occasional - Penetrates well in CSF
H
o Pseudomonas aeruginosa Hypersensitivity (NO - Excretion: Urine
E
Monobactam AZTREONAM (IV) o Enterobacteriaceae (inc. E. coli, Klebsiella spp., Enterobacter CROSS-ALLERGENICITY)
S spp.) Rare
I o NOT ESBLs Pseudomembranoud colitis
S No cross-allergenicity NO cross-/class-resistance
Common ERTAPENEM may be given IM
- Very broad spectrum GI Disturbance IMIPENEM – inactivated by
IMIPENEM (IV) DORIPENEM (IV) - DOC: ESBLs Occasional dehydropeptidases
- DOC: Serious mixed aerobic & anaerobic infections Hypersensitivity o CILASTATIN prolongs half-
- DOC: Enterobacter spp. Hematologic Distrubances life of IMIPENEM, maintains
Carbepenem - NOT for MRSA, Enterococci (Except IMIPENEM), and Rare therapeutic urinary
Stenotrophomonas maltophila Seizures concentration, and
- Used for meningitis o IMIPENEM: Most decreases nephrotoxicity
MEROPENEM (IV) ERTAPENEM (IV) - Anaerobic: Aspiration pneumonia, intraabdominal infections epileptogenic High urinary concentration
- Use with bacteria resistant to other drugs o DORIPENEM: Least Excretion: Urine
epileptogenic
Hallucination
Inhibits CLASSIFICATION ANTIBIOTICS Clinical Uses Adverse Effects Pk/Pd
Common Binds to d-ala-d-ala terminus, inhibiting transglycosylase
- DOC: MRSA (Pneumonia, Bacteremia, Endocarditis, & for Prophylaxis) Red Man/Neck Syndrome TELAVANCIN: disrupts bacterial cell membrane potential
VANCOMYCIN - DOC: Coagulase-negative staphylococci (Prosthetic device infections, CSF (Due to histamine release, Passes through inflamed meninges
shunt infections, catheter-related infections infusion related flushing Time-dependent killing
- Broad-Spectrum Gram (+) Phlebitis Excretion: Urine (Glomerular Filtration)
Glycopeptides - Others: Occasional o Check serum levels
o Enterococci Ototoxicity
TEICOPLANIN TELAVANCIN* o Penicillin-resistant S. pneumoniae (Meningitis) Nephrotoxicity
(IV, IM) o Metronidazole-resistant C. difficile (colitis)
Cell Membrane
Function Muscle Toxicity (Myopathy) Ca-dependent insertion of its lipid tail to the cell
- DOC: VRSA
membrane, depolarizing it with K+ efflux
- MRSA alternative
Lipopeptides DAPTOMYCIN (IV) - NOT meningitis
Little penetration in CSF
INACTIVATED BY LUNG SURFACTANT
- NOT FOR PNEUMONIA
Concentration-dependent Killing
- Multidrug-resistant organisms (Pneumonia, Skin & tissue infections, Common Attach and disrupt cell membrane (cationic agent)
Polymixin B (SC) Intraabdominal infections, Bacteremia) Nephrotoxicity Penetrates CSF
Polymixins - Opposite of VANCOMYCIN/DAPtOMYCIN Occasional Excretion: Urine
- Broad Gram (-) coverage Neurotoxicity Concentration-dependent Killing
Polymixin E (COLISTIN) (IV) - NOT as monotherapy Rare - Hypersensitivity
Common Mechanisms of Resistance
OTOTOXICITY Transferase Enzymes
Nephrotoxicity Impaired entry
STREPTOMYCIN AMIKACIN - Serious Infections: Combination w/ -lactam Abs Pregnancy: Ototoxicity Ribosomal protection
o Gram (-) septicemia (irreversible) Pk/Pd
o GENTAMYCIN, STREPTOMYCIN: Staphylococcal & enterococcal Rare Excretion (given oral): Feces (poor absorption)
endicarditis Hypersensitivity,
Aminoglycosides - NOT MONOTHERAPY: P. aeruginosa (pneumonia) (although it HAS
Excretion (IV): Urine
anaphylaxis Poorly absorbed in tissue EXCEPT in neonates (large size,
coverage) Neuromuscular Blockare polycationinc charge, lipid insolubility)
o Poor penetration to infected lung tissue due to low O2 (Antidote: Calcium
GENTAMYCIN TOBRAMYCIN - NOT MRSA
SYNERGISM with -lactam Abs
Gluconate) Antagonism with other bacteriostatic agents
Concentration-dependent killing
o Better efficacy: single large dose
Inhibition
TETRACYCLINE - Coverage for atypicals Common Pk
of Protein 30S - DOC: Ricketssiae Permanent teeth Hydrophobic
Synthesis DOXYCYCLINE - Other Uses: Atypicals discoloration Impaired by food (Except Doxy & Minocycline), antacids,
o Mycoplasma pneumoniae Bone deformity etc.
o Chlamydia pneumoniae & C. psittuaci Pregnancy Risk Category D NO CSF penetration
Tetracyclines o NOT recommended for LEGIONELLA Occasional Excretion: Bile & Urine; except DOXYCYCLINE (Bile)
o GONOCOCCAL DISEASE (+ CEFtRIAXONE) Photosensitivity CAN CROSS PLACENTE, EXCRETED IN MILK
MINOCYCLINE Rare
o Leptospira spp. (Mild infection, prophylaxis) Pd: Time-dependent killing
o Vibrio spp. (Cholera) Fanconi Syndrome
o Borellia burgdorferi (Lime Disease) Interstitial Nephritis
o Plasmodium falciparum (Prophylaxis)
- Infections caused by multidrug-resistant organisms (Skin & soft tissue Same as tetracycline No cross-resistance with 2nd or 1st gen tetracyclines
Glycycyclines TIGECYCLINE infections; intraabdominal infections) Alteration of GI flora NO CSF penetration
(IV) (3rd Gen Tetracycline) - NOT recommended as 1st line drug for pneumonia (treatment faillure) Excretion: Bile and Urine
- NOT recommended for bacteremia
Inhibits CLASSIFICATION ANTIBIOTICS Clinical Uses Adverse Effects Pk/Pd
- DOC: ATYPICAL PNEUMONIA – Legionella pneumoniae, Chlamydophila Common Absorption impaired by food
pneumoniae, Chlamydophila spp. GI Disturbance (due to MOTILIN) NO CSF penetration
- DOC: Corynebacterium spp. (Diphteria) Occasional Excretion: Bile
Acute cholestatic hepatitis (estolate) Crosses placenta; excreted in Milk
ERYTHROMYCIN - DOC: Bordetella pertussis
Stomatitis
- Other: Inhibitor of CYP 450
Rare
o Chlamydia trachomatis Infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis
Time-dependent killing
o Penicillin substitute for S. pyogenes with penicillin-allergy QT interval prolongation
Macrolides Less GI disturbance Less affected by food
Excretion: Urine
CLARITHROMYCIN - Most active against H. influenzae & Myobacterium avium complex Time-dependent killing
Inhibitor of CYP 450
Less GI disturbance Absorption impaired by food
AZITHROMYCIN - DOC: Bartonella henselae (Cat Scratch Disease) Concentration-dependent killing
Does not inhibit CYP 450
Common Absorption not affected by food
- DOC: Community Acquired MRSA (skin and soft tissue infection)
GI Distrubance NO CSF penetration
o NOT for Hospital Acquired MRSA
Occasional Can penetrate abscesses
Inhibition Lincosamide CLINDAMYCIN o NOT for bacteremia & meningitis Toxic Megacolon Excretion: Bile & Urine
- Anaerobic infections ABOVE THE DIAPHARGM (eg. lung abscess) EXCEPT CNS Rare:
of Protein 50S Crosses placenta
- Alternative for Staphylococcal infections Esophageal ulceration
Synthesis Time-dependent killing
Common Prodrug
Dose-related Anemia o Oral produces higher livel of free drug than IV
- Alternative drug for -lactam for treatment of meningitis
Gray Baby Syndrome CSF penetration
- Other uses:
Occasional Metabolized in the liver (glucuronic acid conjugation)
CHLORAMPHENICOL o Salmonella typhi GI disturbance Excretion: Urine & bile
o Shigella spp. Rare Crosses placenta; excreted in milk
o Ricketsia spp. Aplastic Anemia CYP 450 inhibitor
Optic Neuritis Time-dependent killing
Common BACTERIOSTATIC but BACTERICIDAD AGAINST
- Infections caused by Multidrug-resistant Gram (+) cocci (MRSA, VRA)
Hematologic disturbances STREPTOCOCCI
o Skin and soft tissue infections
Occasional 100% bioavailability in oral
Oxazolidinone LINEZOLID o Pneumonia
Lactic Acidosis CSF penetration
- Not recommended for MRSA bacteremia Serotonin Syndrome Excretion: Urine
- Other use: M. tuberculosis Optic & peripheral neuropathy Time-dependent killing
QUINUPRISTIN - Infections caused by Multidrug-resistant Gram (+) cocci (EXCEPT Enterococcus Direct Hyperbilirubinemia QUIINUPRISTIN-DALFOPRISTIN (30:70 ratio)
faecalis) Arthralgia-Myalgia Syndrome NO CSF penetration
(STREPTOGRAMIN B)
Streptogramin o Skin and soft tissue infections Excretion: Feces
DALFOPRISTIN o Pneumonia CYP 3A4 inhibitor
(STREPTOGRAMIN A) o Bacteremia Concentration-dependent killing
Inhibits CLASSIFICATION ANTIBIOTICS Clinical Uses Adverse Effects Pk/Pd
- DOC: Stenotrophomonas maltophila SMX: Photosensitivity, Rash Individually bacteriostatic, together, bactericidal
- DOC: Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia (PCP) Occasional Mechanism of Resistance
SULFAMETH - May be used for prostatitis (prostate penetration) Hematologic Disturbances o SMX
Sulfonamides - NOR for empiric therapy for pneumonia o SMX: Aplastic Anemia, Hemolytic Overproduction of PABA
-OXAZOLE Overproduction of duhydropteroate
- Other: anemia (G6PD deficiency(
COTRIMO- o TMP: Megaloblastic Anemia, etc Impaired entry
Folic Acid o Susceptible MRSA
Synthesis XAZOLE o Burholderia capacia Kernicterus o TMP
(TMP-SMX) Overproduction of DHFR
o Salmonella typhi Urinary Tract Disturbances
Impaired entry into the cell
DHFR TRIMETHO- o Shigella spp (REMEMBER: Penetrates prostate)
CSF penetration, distributed in prostate & vaginal fluid
o Nocordia spp. Rare
Inhibitors PRIM SMX: Stevens-Johnson Syndrome
Metabolized in liver
Inhibition o Alternaive treatment for Toxoplasma gondii encephalitis (DOC: Excretion: urine
PYRIMETHEMINE-SULFADIAZINE) Lupus-like Syndrome Time-dependent killing
of Nucleic
CIPROFLOXACIN - CIPROFLOXACIN: most active for gram (-); Pseudomonas coverage Hyperglycemia Inhibit bacterial topoisomerase II (DNA Gyrase) &
Acid
- Active against atypical organisms Arthropathy Topoisomerase IV
Synthesis - Good against N. gonorrhoeae Damages growing cartilage CSF penetration and prostate penetration
- CIPROFLOXACIN, LEVOFLOXACIN: Oral step-down therapy for Pseudomonas RETINAL DETACHMENT (Rare) Excretion: Urine; EXCEPT:
aeruginosa QT prolongation, torsades de pointed o GEMIFLOXACIN (Bile and urine)
- Other Uses: o MOXIFLOXACIN (Bile)
DNA Topo- Fluoro- o Salmonella typhi
Concentration-dependent killing
iso-merases quinolones LEVOFLOXACIN o Shigella spp.
o E. coli (Cystitis, Pyelonephritis)
o N. meningitidis (Post-exposure prophylaxis)
- NOT for N. gonorrhoeae
- Others:
o MDR M. tuberculosis
- Only coverage: Anaerobes inc. B. fragilis & Clostridium difficile Metallic taste MOA only achieved in anaerobes
- DOC: Clostridium difficile colitis Dry mouth Loss of helical DNA structure and strand breakage
Nitro Group - Anaerobic infections BELOW THE LEVEL OF THE DIAPHRAGM (eg. intraabdominal Urethral bleeding CSF penetration
infection) Darkening of urine Excretion: Urine & Feces
Chemically
- Brain abscess Peripheral & optic neutopathy Penetrate abscesses
Reduced METRONIDAZOLE - Other: Concentration-dependent killing
(DNA o Clostridium tetani
Damage) o Entamoeba histolytica
o Trichomonas vaginalis
Others
o Giardia lamblia
Synthesis of - Urinary antiseptic (uncomplicated acute cystitis) Hemolytic anemia
DNA, RNA, NITROFURANTOIN - NOT during renal failure Pulmonaryinfiltration, fibrosis
and Proteins - NOT for upper tract infection (pyelonephritis)
Cell Wall Inhibit enilpyruvate transferase
Synthesis - Uncomplicated acute cystitis Exxcretion: Urine
FOSFOMYCIN - NOT for 1st line treatment for MDR infections
(Very Early
Stage)
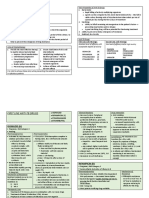
Inhibits CLASSIFICATION ANTIBIOTICS
Crystalline/Aqueous (IV)
Natural Penicillins PENICILLIN G
Procaine, Benzathine (IM)
(Narrow Spectrum)
PENICILLIN V (Oral)
NAFCILLIN (IV) METHICILLIN
C Penicillins Anti-Staphylococcal
E OXACILLIN (IV) CLOXACILLIN (Oral)
L Amino- AMOXICILLIN )Oral) AMPICILLIN (IV)
L Extended-Spectrum Carboxy- TICARCILLIN CARBENICILLIN
Ureido- PIPERACILLIN (IV)
W COAMOXICLAV
A CLAVULANIC ACID (+ Amoxicillin)
L -Lactamase Inhibitors + Ticarcillin
L SULBACTAM + Ampicillin
TAZOBACTAM + Piperacillin
S 1st Gen CEPHALEXIN (Oral) CEFAZOLIN (IV)
Y CEFUROXIME (Oral) CEFUROXIME (IV)
N 2nd Gen CEFACLOR (Oral) CEFOTETAN (IV)
T CEFOXITIN (IV)
H CEFTRIAXONE (IV)
Cephalosporins CEFPODOXIME (Oral)
E CEFOTAXIME (IV)
3rd Gen
S CEFOPERAZONE (IV)
CEFIXIME (ORAL)
I CEFTAZIDIME (IV)
S 4th Gen CEFEPIME CEFPIROME
5th Gen CEFTAROLINE
Monobactam AZTREONAM (IV)
IMIPENEM (IV) DORIPENEM (IV)
Carbepenem
MEROPENEM (IV) ERTAPENEM (IV)
VANCOMYCIN
Glycopeptides
TEICOPLANIN (IV, IM) TELAVANCIN*
Cell Membrane Function Lipopeptides DAPTOMYCIN (IV)
Polymixin B (SC)
Polymixins
Polymixin E (COLISTIN) (IV)
STREPTOMYCIN AMIKACIN
Aminoglycosides
GENTAMYCIN TOBRAMYCIN
TETRACYCLINE
30S Tetracyclines DOXYCYCLINE
MINOCYCLINE
Glycycyclines TIGECYCLINE
(IV) (3rd Gen Tetracycline)
Inhibition of Protein ERYTHROMYCIN
Synthesis
Macrolides CLARITHROMYCIN
AZITHROMYCIN
Lincosamide CLINDAMYCIN
50S
CHLORAMPHENICOL
Oxazolidinone LINEZOLID
QUINUPRISTIN (STREPTOGRAMIN B)
Streptogramin
DALFOPRISTIN (STREPTOGRAMIN A)
TibbsNotes – Antibacterial Table
You might also like
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Notes - Thyroid Hormones & Anti-Thyroid DrugsDocument7 pagesNotes - Thyroid Hormones & Anti-Thyroid DrugsChesmar MacapalaNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Notes - Lec 20 - Antimycobacterial AgentsDocument14 pagesNotes - Lec 20 - Antimycobacterial AgentsChesmar MacapalaNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Contraction of Whole MuscleDocument7 pagesContraction of Whole MuscleAli UyNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Skeletal System Pics PDFDocument9 pagesSkeletal System Pics PDFIris AndalNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Post Lab. Exs. 8-35 PhyanaDocument33 pagesPost Lab. Exs. 8-35 PhyanaChesmar Macapala100% (7)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- C 8 TabletsDocument3 pagesC 8 Tabletschizms_1234No ratings yet
- Therapeutic and Toxic Blood Levels of Over 800 DrugsDocument28 pagesTherapeutic and Toxic Blood Levels of Over 800 DrugsAndreia AndreiutzaNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- PHA 070 Dispensing 2 P1 REVIEWER From QuizzizDocument6 pagesPHA 070 Dispensing 2 P1 REVIEWER From Quizzizjenet soleilNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- 00 History of Indonesian Medicine & GarutDocument34 pages00 History of Indonesian Medicine & Garutacep sopianNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- BactobanDocument1 pageBactobanSrkocherNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Atthapu Niper Hyderabad Faculty Selection List For InterviwDocument4 pagesAtthapu Niper Hyderabad Faculty Selection List For InterviwAtthapu ThirupathaiahNo ratings yet
- Growth Hormone Deficiency Treatment with NorditropinDocument5 pagesGrowth Hormone Deficiency Treatment with NorditropinCaralee Nelson HarpsøeNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- AG Harris Draft Guidelines - April 2011Document21 pagesAG Harris Draft Guidelines - April 2011harris6553No ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- ECA Efficient Batch Record Design ReviewDocument4 pagesECA Efficient Batch Record Design ReviewMina Maher MikhailNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Process Validation Protocol For Ketofast 10 TabletDocument26 pagesProcess Validation Protocol For Ketofast 10 TabletShagorShagor100% (6)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Naplex Mpje Bulletin 011714Document46 pagesNaplex Mpje Bulletin 011714amzeidanNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Injectable DrugDocument5 pagesInjectable DrugMaria SinggihNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Autism From No Harm FoundationDocument35 pagesAutism From No Harm FoundationKaren JordanNo ratings yet
- 25021Document18 pages25021Reena Singh SheoranNo ratings yet
- Antihelminticos, Antiprotozoos, AntimicoticosDocument6 pagesAntihelminticos, Antiprotozoos, AntimicoticosEylin Yarely Flores Cruz100% (1)
- Drug Study: West Visayas State University La Paz, Iloilo CityDocument3 pagesDrug Study: West Visayas State University La Paz, Iloilo CityBALOGO TRISHA MARIENo ratings yet
- D Angelo Et Al., 2016Document43 pagesD Angelo Et Al., 2016Caio Bonfim MottaNo ratings yet
- Dimension Xpand Plus/Rxl Max Integrated Chemistry Systems: Global Test MenuDocument2 pagesDimension Xpand Plus/Rxl Max Integrated Chemistry Systems: Global Test Menujyoti ranjanNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- PQRI - Biosimilar USADocument27 pagesPQRI - Biosimilar USANgoc Sang HuynhNo ratings yet
- Review Factors Contributing To Medication Errors: A Literature ReviewDocument9 pagesReview Factors Contributing To Medication Errors: A Literature Reviewsoul_0602No ratings yet
- Formoterol FumarateDocument3 pagesFormoterol Fumarateapi-3797941100% (1)
- Phytochemical Screening and CharacterizationDocument5 pagesPhytochemical Screening and CharacterizationyamunaraviNo ratings yet
- Flox Report Rev 11Document253 pagesFlox Report Rev 11azpam100% (1)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Education Regulations, 1991Document28 pagesEducation Regulations, 1991Latest Laws TeamNo ratings yet
- Atorvastatin 10 MGDocument7 pagesAtorvastatin 10 MGmohit_jindal_24No ratings yet
- FDA SilicaDocument77 pagesFDA SilicaBryan396No ratings yet
- Doctors in North CebuDocument15 pagesDoctors in North CebuericNo ratings yet
- Research Output 12Document42 pagesResearch Output 12Anna H. Navarro100% (1)
- AaaaaDocument32 pagesAaaaarats clusterNo ratings yet
- How To Make Delicious Weed FirecrackersDocument8 pagesHow To Make Delicious Weed FirecrackersRegina Zagala100% (1)
- Anderson & Townsend Preventing High-Alert Medication Errors in Hospitalized PatientsDocument6 pagesAnderson & Townsend Preventing High-Alert Medication Errors in Hospitalized PatientsCG0% (1)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)