Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Flow Diagram On The Assembly of The Extracorporeal Circuit-Group 2
Uploaded by
api-5944346640 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views1 pageThe document summarizes the key steps in managing the extracorporeal circuit during cardiovascular surgery:
1) Blood is drawn from the vena cava into the circuit through a pump and heat exchanger before exiting to an oxygenator.
2) The oxygenated blood is returned to the patient through a cannula in the aorta or femoral artery.
3) Heparin is administered before cannulation of the aorta or atrium, after which the patient is connected to the cardiopulmonary bypass machine and cardioplegia is started while the heart is arrested.
Original Description:
Original Title
flow diagram on the assembly of the extracorporeal circuit-group 2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes the key steps in managing the extracorporeal circuit during cardiovascular surgery:
1) Blood is drawn from the vena cava into the circuit through a pump and heat exchanger before exiting to an oxygenator.
2) The oxygenated blood is returned to the patient through a cannula in the aorta or femoral artery.
3) Heparin is administered before cannulation of the aorta or atrium, after which the patient is connected to the cardiopulmonary bypass machine and cardioplegia is started while the heart is arrested.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views1 pageFlow Diagram On The Assembly of The Extracorporeal Circuit-Group 2
Uploaded by
api-594434664The document summarizes the key steps in managing the extracorporeal circuit during cardiovascular surgery:
1) Blood is drawn from the vena cava into the circuit through a pump and heat exchanger before exiting to an oxygenator.
2) The oxygenated blood is returned to the patient through a cannula in the aorta or femoral artery.
3) Heparin is administered before cannulation of the aorta or atrium, after which the patient is connected to the cardiopulmonary bypass machine and cardioplegia is started while the heart is arrested.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
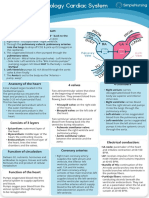
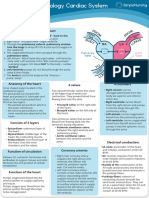
Management process of the extracorchoreal circuit
CARDIOVASCULAR
What does the perfusion professional do
GROUP # 2
Introduction
Blood from the cavas enters through the CEC
circuit. It is propelled by a pump and passes
through a heat exchanger that allows
hypothermia to be induced and the blood to be
warmed before exiting the ECC.
Subsequently, the flow passes through a
membrane or bubble oxygenator, returning to
the patient through a cannula located in the
aorta and occasionally in the femoral artery.
Extracorporeal
circuit process
Hepartin is applied to the patient and they
wait 20 minutes for coagulation, then comes
the placement of the purse strings in the
aorta, right atrium or in the root of the aorta.
When active coagulation time was
already given, the cannulation was
performed, the arterial cannula
first, followed by the venous
cannula and the third cardioplegia
cannula.
After placing the arterial cannula,
the arterial line is connected, after
placing the venous cannula, the
venous line is connected, the
cardioplegia cannula is connected,
and the line following it.
the patient enters extracorporeal
circulation, but the lung and heart
continue to function. The aorta is
occluded and cardioplegia is started.
venous blood will drain from the right
atrium directly to the venous reservoir,
then the blood enters the roller pump or
centrifugal pump, these help mobilize the
blood and send it to the oxygenator.
The emotec cools the blood and is located
in the lower part of the oxygenator, then
the oxygenated blood goes to the filter
and filters all the blood from clots and
impurities.
from the filter it goes to the arterial
cannula and from there to the circulation
as such.
End
You might also like
- Simple Nursing Medical Surgical - CompletoDocument157 pagesSimple Nursing Medical Surgical - CompletoRenato Bandeira100% (5)
- Nursing Simplified SheetsDocument14 pagesNursing Simplified Sheetssao sl78% (9)
- Pharmacology SummaryDocument32 pagesPharmacology Summaryminikatiting95% (22)
- Circulatory SystemDocument25 pagesCirculatory SystemadnanNo ratings yet
- The Lord of The Rings Real HistoryDocument2 pagesThe Lord of The Rings Real HistoryDUNCAN0420No ratings yet
- Application For A Social Security Card Applying For A Social Security Card Is Free!Document5 pagesApplication For A Social Security Card Applying For A Social Security Card Is Free!Edward McNattNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology Cardiac SystemDocument1 pageAnatomy & Physiology Cardiac SystemTori RolandNo ratings yet
- Operations Management Assignment 1Document10 pagesOperations Management Assignment 1Muhammad SajidNo ratings yet
- Case Study of Benign Hand TremorsDocument7 pagesCase Study of Benign Hand TremorsLupa Ingatan100% (1)
- Cardiac Physio TRANS 2Document8 pagesCardiac Physio TRANS 2Kyle MañiboNo ratings yet
- Care of Mother and Child at Risk or With ProblemsDocument87 pagesCare of Mother and Child at Risk or With ProblemsQueen Jyil100% (1)
- Individual Report EMTC 55 (Mohamad Azim Bin Mohd Adam)Document40 pagesIndividual Report EMTC 55 (Mohamad Azim Bin Mohd Adam)Azim Adam83% (23)
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument10 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDarel Joy A. Simon95% (19)
- VariableDocument10 pagesVariableReizel Joy Borja RasonaNo ratings yet
- CVS FullDocument32 pagesCVS FullLianne PalinsadNo ratings yet
- PEDIA - Cardio (Esguerra) PDFDocument9 pagesPEDIA - Cardio (Esguerra) PDFMedisina101No ratings yet
- Perfusion SystemDocument52 pagesPerfusion Systemprafilaash100% (1)
- Cymbalta (Duloxetine)Document1 pageCymbalta (Duloxetine)Cassie50% (2)
- Pre-Installation Manual: Standard Frequency Series GeneratorsDocument20 pagesPre-Installation Manual: Standard Frequency Series GeneratorsLuis Fernando Garcia SNo ratings yet
- 21stCenturyLiteratureLesson1 LabiganLeidenDocument10 pages21stCenturyLiteratureLesson1 LabiganLeidenAnonymousNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Critical Success Factors For Construction Projects in PakistanDocument13 pagesAssessment of Critical Success Factors For Construction Projects in PakistanAbdul Qayoom Memon100% (1)
- Heart and PericardiumDocument26 pagesHeart and PericardiumpalNo ratings yet
- Nursing Responsibilities After CCDocument5 pagesNursing Responsibilities After CCSofia P. PanlilioNo ratings yet
- Resumen Article IcDocument14 pagesResumen Article Icapi-689165620No ratings yet
- Cardiac Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument2 pagesCardiac Anatomy and PhysiologyKarina YurchenkoNo ratings yet
- 4944 D 5 CBD 50 C 12 F 36 FfaDocument22 pages4944 D 5 CBD 50 C 12 F 36 Ffaapi-725606760No ratings yet
- Caso Clinico Reemplazo Valvular AorticoDocument15 pagesCaso Clinico Reemplazo Valvular Aorticoapi-683975964No ratings yet
- Lecture 2: The Heart: Prof. Magidah Alaudi, M.SCDocument62 pagesLecture 2: The Heart: Prof. Magidah Alaudi, M.SCMonicaNo ratings yet
- Session 5Document41 pagesSession 5tazebNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology SummaryDocument31 pagesPharmacology Summarydesshe09No ratings yet
- Myocardical RevascularizationDocument11 pagesMyocardical Revascularizationjuliana sachicaNo ratings yet
- The Circulation of Blood: 1A RtuDocument3 pagesThe Circulation of Blood: 1A RtuGiffari MuslihNo ratings yet
- B 45377 D 66 Acdfdfa 2 Ca 4Document24 pagesB 45377 D 66 Acdfdfa 2 Ca 4api-725875845No ratings yet
- WEEK 7 - PERFUSION TECHNOLOGY v2Document44 pagesWEEK 7 - PERFUSION TECHNOLOGY v2Marc Jeff GabasaNo ratings yet
- Lectura - CorazónDocument11 pagesLectura - CorazónFabrizioNo ratings yet
- What Is CPB CircuitDocument4 pagesWhat Is CPB CircuitkhanNo ratings yet
- Heart Covering and WallsDocument2 pagesHeart Covering and WallsZein MjNo ratings yet
- B 56 A 6 Be 8 D 6526826 B 68 FDocument23 pagesB 56 A 6 Be 8 D 6526826 B 68 Fapi-725875845No ratings yet
- Askep Ps DGN Tindakan Invasif & INB KD 2021Document91 pagesAskep Ps DGN Tindakan Invasif & INB KD 2021gayuspatarru123No ratings yet
- Presentation 5Document5 pagesPresentation 5mahnoorcollection20No ratings yet
- Circulatory System HandoutsDocument4 pagesCirculatory System HandoutsCzarae VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- D 54 Ed 270648 C 442 DF 2 e 9Document23 pagesD 54 Ed 270648 C 442 DF 2 e 9api-725606760No ratings yet
- Clinical Case 4 RVMDocument13 pagesClinical Case 4 RVMapi-654112138No ratings yet
- Physiology DES: Biruk A. (Balemaye@sgu - Edu) & Sami Ahmed. (Sahmed10@sgu - Edu)Document56 pagesPhysiology DES: Biruk A. (Balemaye@sgu - Edu) & Sami Ahmed. (Sahmed10@sgu - Edu)Joseph KimNo ratings yet
- 272 F 80 e 4 BF 329 Ca 1 Fee 2Document16 pages272 F 80 e 4 BF 329 Ca 1 Fee 2api-684047665No ratings yet
- Clinical Case Perfusion March 8 2024 Isis Daniela RojasDocument19 pagesClinical Case Perfusion March 8 2024 Isis Daniela Rojasapi-725651063No ratings yet
- Structure and Function of The Cardiovascular System PDFDocument9 pagesStructure and Function of The Cardiovascular System PDFteuuuuNo ratings yet
- ArrythmiasDocument26 pagesArrythmiasValeria MolinaNo ratings yet
- Cardiac SurgeryDocument27 pagesCardiac SurgeryReeti Singh100% (1)
- Circulatory SystemDocument15 pagesCirculatory SystemaggyNo ratings yet
- Extracorporeal MachineDocument7 pagesExtracorporeal Machineapi-594276188No ratings yet
- Af 49 D 0509 F 90 D 75 B 3 A 50Document23 pagesAf 49 D 0509 F 90 D 75 B 3 A 50api-725875845No ratings yet
- Clinical Case "Aortic Valve Replacement"Document10 pagesClinical Case "Aortic Valve Replacement"Andrea OrtizNo ratings yet
- Reviewer 2 Health AssessmentDocument13 pagesReviewer 2 Health AssessmentchristinejeancenabreNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document28 pagesChapter 9Jill ZabalaNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing: Anatomy HeartDocument8 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing: Anatomy HeartRoyce Vincent TizonNo ratings yet
- Heart and CirculationDocument12 pagesHeart and CirculationEizelle Zabyne VerzosaNo ratings yet
- Quiz Reviewer 2Document1 pageQuiz Reviewer 2NER CARLO SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Components of The Cardiovascular SystemDocument23 pagesComponents of The Cardiovascular SystemMr. DummyNo ratings yet
- (H.a.) Chapter 12 - Heart & Neck VesselsDocument9 pages(H.a.) Chapter 12 - Heart & Neck VesselsLevi Sebastian T. CabiguinNo ratings yet
- Body Fluids & CirculationDocument29 pagesBody Fluids & CirculationAyaan AshrafNo ratings yet
- Physiology of HeartDocument74 pagesPhysiology of Heartmadeha goharNo ratings yet
- Problem Based Learning Discussion (Recovered)Document44 pagesProblem Based Learning Discussion (Recovered)Priya Nair MenonNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument26 pagesCirculatory SystemJeus BatadlanNo ratings yet
- Review of Cardiovascular SystemDocument20 pagesReview of Cardiovascular SystemVăn ĐứcNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Markers-It Is An Enzyme That Increases If You Have Cardiac Muscle Injury. We NeedDocument5 pagesCardiac Markers-It Is An Enzyme That Increases If You Have Cardiac Muscle Injury. We Needcamile buhanginNo ratings yet
- Script of Kidney DissectionDocument3 pagesScript of Kidney DissectionmeryjuvelhNo ratings yet
- Overview of The Entire Cardiovascular SystemDocument10 pagesOverview of The Entire Cardiovascular SystemSpuipt PanagtasanNo ratings yet
- WEEK 1 MEDSURG AsynchDocument12 pagesWEEK 1 MEDSURG AsynchLeigh Angelika Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Coronary Artery BypassDocument3 pagesCoronary Artery Bypassapi-349547787No ratings yet
- CardioplegiaDocument1 pageCardioplegiaapi-594434664No ratings yet
- Diagnostic Methods - Cardiovascular: Which Are? Non-Invasive InvasiveDocument1 pageDiagnostic Methods - Cardiovascular: Which Are? Non-Invasive Invasiveapi-594434664No ratings yet
- Decree 4725 of 2005Document2 pagesDecree 4725 of 2005api-594434664No ratings yet
- Development of Venous SystemDocument2 pagesDevelopment of Venous Systemapi-594434664No ratings yet
- 44 FlowchartDocument2 pages44 Flowchartapi-594434664No ratings yet
- Crossword - History of The Cardiovascular SurgeryDocument1 pageCrossword - History of The Cardiovascular Surgeryapi-594434664No ratings yet
- Course Hero 41Document5 pagesCourse Hero 41Maria Helen MarcelinoNo ratings yet
- MA Thesis - Reinhoudt - Translating and Subtitling Wordplay in Disney SongsDocument102 pagesMA Thesis - Reinhoudt - Translating and Subtitling Wordplay in Disney SongsLaura Alzieu100% (1)
- When Learning CeasesDocument2 pagesWhen Learning CeasesMaryrose CastilloNo ratings yet
- Sample Exam COMP 9444 NEURAL NETWORKS PDFDocument7 pagesSample Exam COMP 9444 NEURAL NETWORKS PDFAlshabwani SalehNo ratings yet
- Factors of Individual Behavior in An Organization and Its Performance at WorkDocument6 pagesFactors of Individual Behavior in An Organization and Its Performance at WorkImpact JournalsNo ratings yet
- DocDocument5 pagesDocYour Materials33% (3)
- 5th Ed Ch12 QCDocument3 pages5th Ed Ch12 QCsepepebinNo ratings yet
- Chap3.3 HexCrystal DirectionsDocument6 pagesChap3.3 HexCrystal DirectionsJeonghun LeeNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument85 pagesUntitledR e t n oNo ratings yet
- Dysphagia in Cerebral Palsy: Annamaria Salghetti, Andrea MartinuzziDocument6 pagesDysphagia in Cerebral Palsy: Annamaria Salghetti, Andrea MartinuzziCristina Sánchez CastilloNo ratings yet
- BBM11411 Final Exam 2022 S1Document5 pagesBBM11411 Final Exam 2022 S1bonaventure chipetaNo ratings yet
- Theory Matrix 2Document2 pagesTheory Matrix 2api-654837218No ratings yet
- Prehistory Lecture NotesDocument21 pagesPrehistory Lecture Notesconnor odonnellNo ratings yet
- Hsyallx: Tutorial Letter 301/3/2023Document32 pagesHsyallx: Tutorial Letter 301/3/2023Lebohang MalauNo ratings yet
- Effect of Audit Findings and Audit RecommendationDocument25 pagesEffect of Audit Findings and Audit RecommendationDwi Puspita SariNo ratings yet
- Adaptive Teaching Guide TemplateDocument11 pagesAdaptive Teaching Guide TemplateAni Pearl PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Q1-M2 Genres of ViewingDocument41 pagesQ1-M2 Genres of ViewingChristine LlantoNo ratings yet
- 1 G.R. No. 205657Document11 pages1 G.R. No. 205657Jenely Joy Areola-TelanNo ratings yet
- Apartheid - WikipediaDocument55 pagesApartheid - WikipediaMunawir Abna NasutionNo ratings yet