Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Coupling
Coupling
Uploaded by
Harsh Koshti0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views5 pagesCoupling rxn
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCoupling rxn
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views5 pagesCoupling
Coupling
Uploaded by
Harsh KoshtiCoupling rxn
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
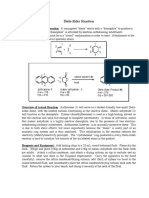
Stille Coupling
oe ests Pd(0) or
The Stille cross—coupling is the palladium catalyzed
reaction between stannanes and halides to generate
a C-C bond.
halides
x x
fF fx Cr a*
Alkynyl Alkenyl hy Allyl
Mechanism
x
Pd(0)Ln Cw
Oxidative
Reductive Addition
Elimination
Phy
xoPallLn
hy
el Pally ee Retr
LL Ph ‘ Ph Transmetalation
wh, SE, X-Sn'Bu3
1. Oxidative addition of an organic halide to Pd(0) to form Pd(Il).
2. Transmetalation between Pd(Il) and the organotin reagent.
3. Reductive elimination to form the C-C sigma bond and regeneration
of the catalyst.
@LluisLlorens
CS)
Kumada Coupling
RigX pal
ax or Se
R-LI Solvent / Ligand
The Kumada Cross—coupling is the transition metal-catalyzed
carbon-carbon bond forming reaction of alkenyl or aryl halides
and organomagnesium or organolithium reagents.
Mechanism
Pd catalyzed
LnPd®)
oxidative addition
l=]
elimination UZ Xo
Ppa _ Cee
C encaniis
1. Initially, the electron-rich Pd(0) catalyst inserts into the R-X bond of the
organic halide. This oxidative addition forms an organo-Pd(II}-complex.
2. Subsequent transmetalation with the Grignard or the organolithium
reagent forms a hetero-organometallic complex.
3. Before the next step, isomerization is necessary to bring the organic
ligands next to each other into cis positions.
4. Finally, reductive elimination leads to the formation of a C-C bond and
releases the cross coupled product while regenerating the Pd(0) catalyst.
Ni-catalyzed
LNIO% oy
2R-MgX
2. XMgX
: ~S XMgX
Ri Revi,
Ni Ly
R-X “ eosinaton_
@lluisLlorens
Heck Coupling
Pd(0)
Be SR
CS Ligand, base
The Heck Reaction is the cross—coupling between
an unsaturated halide or triflate and an alkene in the
presence of a base and a palladium catalyst.
Mechanism
Q
a HY Br Br
Pit sid 2 Pd(O)L, C
— Ae: (OLn Oxidative
ecoordination pf era Addition
Elimination
Jf Pata
B-hydride
elimination 4, H~scoome
ee
complex
ft formation
Migratory Es
insertion
1. Oxidative addition of an organic halide to Pd(0) to form Pail).
2. Pd forms a TT complex with the alkene.
3. Migratory insertion: the alkene inserts in the Pd—C bond in a syn
addition step.
3. B-hydride elimination leads to the m complex.
4. Decoordination of the complex followed by reductive elimination
to regenerate the catalyst.
8 oer .
AY CooEt
erat rr
Br Syn elimination
Yo Ph
Yoet Woooet
Dat
Hace
Br
@luisLlorens
é ) Named Reactions in Organic Chemistry ao
Negishi Coupling
X 2.Znx Pd oR
ar Um or Ni R
Sonogashira Coupling
Pd(0) BZ
oto
Cul, ccalan
The Sonogashira cross—coupling is the copper-palladium
catalyzed reaction of terminal alkynes with aryl or
vinyl halides.
Mechanism
Pd(O)L2 (
Oxidative
Addition
Reductive
Elimination
Ph,
wm yPatiNLe
Transmetalation
SSE Et)NH*X:
Ae a
1. Oxidative addition of an organic halide to Pd(0) to form Pd(I!).
2. Deprotonation of the alkyne and formation of copper acetylide.
3. Transmetalation between Pd(Il) and the acetylide.
4. Reductive elimination to form the C-C sigma bond and regeneration
of the catalyst.
@LluisLlorens
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5810)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (346)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Drugs and Receptors: DG Lambert BSC (Hons) PHDDocument4 pagesDrugs and Receptors: DG Lambert BSC (Hons) PHDHarsh KoshtiNo ratings yet
- Diels AlderDocument3 pagesDiels AlderHarsh KoshtiNo ratings yet
- FutureChemistry AppNote3.4 FlowStart Paal-KnorrDocument4 pagesFutureChemistry AppNote3.4 FlowStart Paal-KnorrHarsh KoshtiNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Anticancer Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics 2004Document623 pagesHandbook of Anticancer Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics 2004Harsh KoshtiNo ratings yet
- Biogenesis of TerpinoidsDocument67 pagesBiogenesis of TerpinoidsHarsh KoshtiNo ratings yet
- Analytical Methods OriDocument18 pagesAnalytical Methods OriHarsh KoshtiNo ratings yet
- Article No 8Document19 pagesArticle No 8Harsh KoshtiNo ratings yet
- Stereochemistry OC101 MC130Document19 pagesStereochemistry OC101 MC130Harsh KoshtiNo ratings yet
- Cocaine Benzoyl Thioester: Synthesis, Kinetics of Base Hydrolysis, and Application To The Assay of Cocaine EsterasesDocument7 pagesCocaine Benzoyl Thioester: Synthesis, Kinetics of Base Hydrolysis, and Application To The Assay of Cocaine EsterasesHarsh KoshtiNo ratings yet
- USFDA Regulatory Toxicology OverviewDocument100 pagesUSFDA Regulatory Toxicology OverviewHarsh KoshtiNo ratings yet