Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Poster - Capnografia
Uploaded by
NFSOT100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
921 views1 pageOriginal Title
Poster - capnografia
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
921 views1 pagePoster - Capnografia
Uploaded by
NFSOTCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
CMYK
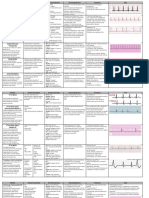
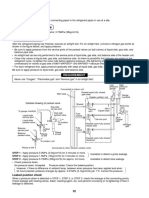
END-TIDAL CO2
Normal and Abnormal Capnogram Waveforms
Normal Capnogram Waveform
A-B: Baseline
B-C: Expiratory Upstroke
Indications: C-D: Expiratory Plateau
• ET tube is correctly positioned D: End-tidal Concentration
• Proper ventilation is occurring D-E: Inspiration
Abnormal Capnogram Waveforms
Esophageal Intubation
Observations:
• No CO2 sensed
Airway Obstruction
• Small transient waveforms Possible Causes:
• Partially kinked or occluded artificial airway
• Presence of foreign body in the airway
• Bronchospasm
Increasing EtCO2 Level - Elevated end-tidal CO2 valve
Time
- Loss of alveolar plateau
Possible Causes:
• Decrease in • Increase in
metabolic rate
respiratory rate
and/or tidal volume • Rapid rise in Decreasing EtCO2 Level
(hypoventilation) body temperature
(malignant Possible Causes:
Time • Decrease in
hyperthermia) • Increase in
metabolic rate
Leak respiratory rate
and/or tidal volume • Fall in body
(hyperventilation) temperature
Possible Causes:
Time
• ET tube cuff • Mask or Bag Mask
may be deflated Valve leak
or ruptured • Artificial airway is
• ET tube in the too small for patient
vocal cords Time
EtCO2 During Cardiac Arrest
Rebreathing EtCO2 increases significantly with
the return of effective heart function.
Possible Causes:
• Mechanical dead space Observations:
• Mechanical ventilator failure • EtCO2 drops during cardiac arrest
• As rescuer tires, a decrease in
EtCO2 is observed
Time • Increases with effective chest
compressions and heart function
Muscle Relaxants (Curare Cleft)
Possible Causes: Curare Cleft
• Patient is mechanically ventilated Real-Time Trend
Observations:
• Depth of cleft is proportional to degree
of drug activity
Time
You might also like
- Emergency Department Resuscitation of the Critically Ill, 2nd Edition: A Crash Course in Critical CareFrom EverandEmergency Department Resuscitation of the Critically Ill, 2nd Edition: A Crash Course in Critical CareNo ratings yet
- Davies Veterinary Specialists UnderstandingDocument3 pagesDavies Veterinary Specialists UnderstandingFelicity HumphreysNo ratings yet
- Capnography in ICUDocument49 pagesCapnography in ICUherbertglennyNo ratings yet
- Arterial Blood Gas Analysis - making it easyFrom EverandArterial Blood Gas Analysis - making it easyRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Capnograpy Ems Waveform Reference CardDocument2 pagesCapnograpy Ems Waveform Reference CardMayHnin Khaing100% (1)
- Anesthesiology Resident Manual of Procedures: A Step-by-Step GuideFrom EverandAnesthesiology Resident Manual of Procedures: A Step-by-Step GuideNo ratings yet
- EMS Capnography WaveformsDocument1 pageEMS Capnography Waveformsepraetorian88% (17)
- Cardiac Tamponade, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandCardiac Tamponade, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- CO2 Pocket GuideDocument2 pagesCO2 Pocket GuideDarryl Betts100% (7)
- Lung Metabolism: Proteolysis and Antioproteolysis Biochemical Pharmacology Handling of Bioactive SubstancesFrom EverandLung Metabolism: Proteolysis and Antioproteolysis Biochemical Pharmacology Handling of Bioactive SubstancesAlain JunodNo ratings yet
- Vent Modes ChartDocument1 pageVent Modes Chartladyhavocinc100% (1)
- Cardiac Dysrhythmia Chart Med Surg NUR4 PDFDocument3 pagesCardiac Dysrhythmia Chart Med Surg NUR4 PDFlml100% (1)
- ECG StripsDocument5 pagesECG StripsNursingSchoolNotes100% (1)
- RT ConsultDocument5 pagesRT ConsultRick Frea100% (2)
- ABG InterpretationDocument1 pageABG Interpretationnulall100% (18)
- Respiratory DysfunctionDocument1 pageRespiratory Dysfunctionoxidalaj100% (3)
- Tidal Volumes Cheat SheetDocument1 pageTidal Volumes Cheat SheetRick Frea100% (1)
- Acid-Base WorksheetDocument2 pagesAcid-Base WorksheetMayer Rosenberg100% (17)
- Capnography ExplainedDocument22 pagesCapnography ExplainedmarceloNo ratings yet
- Modes of Ventilation Chart - 1Document5 pagesModes of Ventilation Chart - 1Khamra SalahuddinNo ratings yet
- Adjusting Ventilator SettingsDocument7 pagesAdjusting Ventilator SettingsSiva RamanNo ratings yet
- Cheatsheet 5Document1 pageCheatsheet 5Rick Frea80% (5)
- STUDENT COPD Pneumonia FUNDAMENTAL - Reasoning PDFDocument8 pagesSTUDENT COPD Pneumonia FUNDAMENTAL - Reasoning PDFYeny PenaNo ratings yet
- ABG Made EasyDocument10 pagesABG Made EasyMayer Rosenberg100% (38)
- Respiratory PathophysDocument1 pageRespiratory PathophysTori IkeharaNo ratings yet
- Routine Anesthesia Set UpDocument4 pagesRoutine Anesthesia Set UpSteve Johnstone100% (2)
- Pediatric Advanced Life Support: I. PALS System Approach AlgorithmDocument19 pagesPediatric Advanced Life Support: I. PALS System Approach AlgorithmIsabel Castillo100% (1)
- DRUG TITRATION GUIDEDocument2 pagesDRUG TITRATION GUIDEEgi Munandar100% (1)
- TMCQuestions AllocationDocument2 pagesTMCQuestions AllocationMyra BuellaNo ratings yet
- Static Compliance & RSBI CheatsheetDocument1 pageStatic Compliance & RSBI CheatsheetRick FreaNo ratings yet
- Settings and Management Tip Sheet For Providers: Isp Elevated?Document1 pageSettings and Management Tip Sheet For Providers: Isp Elevated?mohamedkorieshNo ratings yet
- Drug Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesDrug Cheat SheetKeith McDonald100% (2)
- Haemodynamic Pocket GuideDocument2 pagesHaemodynamic Pocket GuideDarryl Betts85% (13)
- This Study Resource Was Shared Via: Sinus BradycardiaDocument3 pagesThis Study Resource Was Shared Via: Sinus BradycardiaPascal St Peter NwaorguNo ratings yet
- Cheatsheet 2Document1 pageCheatsheet 2Rick Frea86% (7)
- Grady EMS Drug List 2017 FINALDocument20 pagesGrady EMS Drug List 2017 FINALThomas LeachNo ratings yet
- FLASH CardsDocument3 pagesFLASH Cardsclarheena100% (2)
- Types of Assisted VentilationDocument1 pageTypes of Assisted VentilationJerry G100% (2)
- Hemodynamic Management Pocket Card PDFDocument8 pagesHemodynamic Management Pocket Card PDFjenn1722No ratings yet
- Basic EKG Interpretation Exam AnswersDocument3 pagesBasic EKG Interpretation Exam AnswerstwdroppointNo ratings yet
- Overview of Respiratory Failure & Mechanical VentilationDocument89 pagesOverview of Respiratory Failure & Mechanical VentilationsheharyarNo ratings yet
- Basics of Mechanical VentilationDocument63 pagesBasics of Mechanical VentilationDiem KhueNo ratings yet
- CapnographyReferenceHandbook OEM1220ADocument40 pagesCapnographyReferenceHandbook OEM1220Abayu_teNo ratings yet
- Mechanical VentilationDocument19 pagesMechanical VentilationDoha EbedNo ratings yet
- Emergency Room Aerosolized Medication ProtocolDocument3 pagesEmergency Room Aerosolized Medication ProtocolRick Frea67% (3)
- Vasopressors and InotropesDocument31 pagesVasopressors and InotropesReza Prakosa SedyatamaNo ratings yet
- FP-C GuideDocument107 pagesFP-C GuideJames100% (3)
- Capnography: Monitoring ETCO2 LevelsDocument1 pageCapnography: Monitoring ETCO2 LevelsAbdul RaufNo ratings yet
- CG B Ook: Rapid FindDocument25 pagesCG B Ook: Rapid FinddellaNo ratings yet
- Cheatsheet 3Document1 pageCheatsheet 3Rick Frea100% (1)
- RT Consult Form Side #2Document1 pageRT Consult Form Side #2Rick Frea100% (1)
- ECG Master Class-2Document138 pagesECG Master Class-2Shohag ID Center100% (1)
- Pediatric Mechanical VentilationDocument36 pagesPediatric Mechanical VentilationrizalNo ratings yet
- 03 Weaning, SBT and Weaning ParametersDocument48 pages03 Weaning, SBT and Weaning ParametersaryoNo ratings yet
- Inhaler LexiconDocument4 pagesInhaler LexiconRick Frea100% (2)
- Respiratory Therapy Pocket Reference: Ifnopt TriggerDocument2 pagesRespiratory Therapy Pocket Reference: Ifnopt TriggermohamedkorieshNo ratings yet
- CO2 Changes During GA: 4th Lecture / Practical Anesthesia by DR - Amassi Yakdhan 2022 - 2023Document15 pagesCO2 Changes During GA: 4th Lecture / Practical Anesthesia by DR - Amassi Yakdhan 2022 - 2023Afkir Al-HusaineNo ratings yet
- C19 SPACE ToolKit ChecklistsDocument8 pagesC19 SPACE ToolKit ChecklistsAdrian BălanNo ratings yet
- Cap No GraphyDocument41 pagesCap No GraphyCheryls RajuNo ratings yet
- Enviando Por Email 10.1016@j.bja.2019.11.033Document10 pagesEnviando Por Email 10.1016@j.bja.2019.11.033Sérgio Mariano ZuazoNo ratings yet
- LactateDocument10 pagesLactateRodrigo PrestesNo ratings yet
- Articulo - Anestesia CX UrologicaDocument5 pagesArticulo - Anestesia CX UrologicaNFSOTNo ratings yet
- CR 3 - Score Relajacion ResidualDocument10 pagesCR 3 - Score Relajacion ResidualNFSOTNo ratings yet
- CR 4 - CalabadionDocument26 pagesCR 4 - CalabadionNFSOTNo ratings yet
- Artículo - Bloqueo CostoclavicularDocument8 pagesArtículo - Bloqueo CostoclavicularNFSOTNo ratings yet
- Manejo de Parto PretérminoDocument8 pagesManejo de Parto PretérminoDinahNo ratings yet
- Example of Thesis in PhilippinesDocument5 pagesExample of Thesis in PhilippinesNeedHelpWritingMyPaperCleveland100% (2)
- MCE 244 Course OutlineDocument1 pageMCE 244 Course OutlineKaren DavisNo ratings yet
- 11 - NRG - Cathodic Protection DesignDocument15 pages11 - NRG - Cathodic Protection DesignBalan100% (1)
- TX AsiaDemandForecast 2018Document12 pagesTX AsiaDemandForecast 2018Muhammad AsadNo ratings yet
- Current CalendarDocument393 pagesCurrent CalendarAmar BenAmarNo ratings yet
- Nomothetic Vs IdiographicDocument9 pagesNomothetic Vs IdiographicBhupesh ManoharanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Psychological Assessment and PsychodiagnosisDocument75 pagesIntroduction To Psychological Assessment and PsychodiagnosisNishesh AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Igcse Chemistry Topic 13 Carbonates AnsDocument7 pagesIgcse Chemistry Topic 13 Carbonates AnsCClfourNo ratings yet
- 2016 CMCDocument536 pages2016 CMCStefan WeissNo ratings yet
- PLC ProjectsDocument7 pagesPLC ProjectsshakirNo ratings yet
- Cs Lab Manual 31.05.14Document195 pagesCs Lab Manual 31.05.14sravanNo ratings yet
- Big Data Maturity ModelDocument6 pagesBig Data Maturity Modelkatherine976No ratings yet
- 2011 2012 Machinery SubsidyDocument130 pages2011 2012 Machinery SubsidyanbugobiNo ratings yet
- eGr13OM BioResoBookDocument137 pageseGr13OM BioResoBookJanath AnthonyNo ratings yet
- Inside Earth's LayersDocument2 pagesInside Earth's Layersansh parasharNo ratings yet
- GOLDEN DAWN 3 8 Highlights of The Fourth Knowledge LectureDocument7 pagesGOLDEN DAWN 3 8 Highlights of The Fourth Knowledge LectureF_RCNo ratings yet
- ) Perational Vlaintena, Nce Manual: I UGRK SeriesDocument22 pages) Perational Vlaintena, Nce Manual: I UGRK Seriessharan kommiNo ratings yet
- Acer LCD x193hq Sm080904v1 Model Id Ra19waanuDocument36 pagesAcer LCD x193hq Sm080904v1 Model Id Ra19waanuFrancis Gilbey Joson ArnaizNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Crops - D.Tay-2Document27 pagesEvolution of Crops - D.Tay-2liam peinNo ratings yet
- Alice Through The Looking Glass Movie Review (Great Books)Document2 pagesAlice Through The Looking Glass Movie Review (Great Books)Maria Kara Alexir CalambaNo ratings yet
- Living ThingsDocument12 pagesLiving ThingsangelcealoNo ratings yet
- V-Qa Full Final (PART-B) PDFDocument104 pagesV-Qa Full Final (PART-B) PDFKoushik DeyNo ratings yet
- User Manual Servo Driver SZGH-302: (One Driver To Control Two Motors Simultaneously)Document23 pagesUser Manual Servo Driver SZGH-302: (One Driver To Control Two Motors Simultaneously)Zdeněk HromadaNo ratings yet
- PSD SiemensDocument45 pagesPSD Siemensbrijendra2185% (13)
- Theosophical Quarterly v23 1925-1926Document424 pagesTheosophical Quarterly v23 1925-1926Joma SipeNo ratings yet
- Concepts - Essential Elements of Theories PDFDocument5 pagesConcepts - Essential Elements of Theories PDFKarlHeinrichNo ratings yet
- My ResumeDocument2 pagesMy ResumeSathanandhNo ratings yet
- Copper Pipe Leak Test and VacuumDocument2 pagesCopper Pipe Leak Test and Vacuumalone160162l100% (1)
- Lecture 1 (Production, Trade, Losses, & Causes)Document12 pagesLecture 1 (Production, Trade, Losses, & Causes)Ana Mae AquinoNo ratings yet