Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assignment 3
Uploaded by
20G062 NALVETHA BOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Assignment 3
Uploaded by
20G062 NALVETHA BCopyright:
Available Formats
18ME410 Operations Research 2019-20 (E)
Assignment 3 Inventory Models
1. State the various forms of keeping inventory.
2. Mention the different types of inventory.
3. Mention the reasons for maintaining inventory.
4. State various costs involved in inventory.
5. Define: Holding cost, Shortage cost, Set up cost.
6. State the types of variables in an inventory model.
7. Define: Lead time, Re Order level and Economic order quantity.
8. Classify deterministic inventory models.
9. State the solution factors involved in any inventory problem.
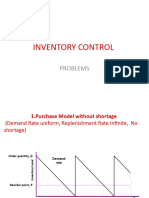
10. State Wilson’s optimal lot size formula for purchasing model with no shortages.
11. State the expressions for the operating characteristics for purchasing model with no shortages.
12. State optimal lot size formula for manufacturing model with no shortages.
13. State the expressions for the operating characteristics for manufacturing model with no shortages.
14. State optimal lot size formula for purchasing model with shortages.
15. State the expressions for the operating characteristics for purchasing model with shortages.
16. State optimal lot size formula for the operating characteristics for manufacturing model with shortages.
17. State the expressions for the operating characteristics for manufacturing model with shortages.
18. List the various criteria for the decision making under the conditions of risk.
19. Describe the news paper boy problem.
PART B
1. The annual demand for an item is 3200 units. The unit cost is Rs.6 and inventory carrying charges 25% per annum. If
the cost of one procurement is Rs.150 , determine i) Economic order quantity ii) time between two consecutive orders
iii) number of orders per year iv) the optimal total cost.
2. A manufacturing company purchases 9000 parts of a machine for its annual requirements, ordering one month usage
at a time. Each part cost Rs.20.The ordering cost per order is Rs.15. and the carrying charges are 15% of the average
inventory per year. You has been asked to suggest a more economical purchasing policy for the company. What advice
would you offer, and how much would it save the company per year?
3. A certain item costs Rs.235 per ton. The monthly requirements are 5 tons, and each time the stock is replaced, there
is a set up cost of Rs.1000.The cost of carrying inventory has been estimated at 10% of the average inventory per
year. What is the optimum order quantity?
4. For an item, the production is instantaneous. The storage cost of one item is Re one per month and the set up cost is
Rs.25 per run. If the demand is 200 units per month , find the optimum quantity to be produced per set up and hence
determine the total cost of storage and set up per month.
Dr.B.Vellaikannan Dept. of Maths TCE Madurai 15 Page 1
18ME410 Operations Research 2019-20 (E)
5. A manufacturer has to supply his customer with 600 units of his products per year. Shortages are not allowed and
storage cost amounts to 60 paise per unit per year. The set up cost is Rs.80. Find i) The economic order quantity ii)
The minimum average yearly cost iii) The optimum number of orders per year iv) The optimum period of supply per
optimum order.
6. A company uses rivets at a rate f 5000 kg per year, rivets costing Rs.2 per Kg.It costs Rs. 20 to place an order and
carrying cost of inventory is 10% per year. How frequently should the order for rivets be placed and how much?.
7. A contractor has to supply 10000 bearings per month to an automobile manufacturer. He finds that when he starts a
production run he can produce 25000 bearings per month . The cost of holding a bearing in stock for one year is Rs.2
and the set up cost of a production run is Rs. 180.How frequently should the production run be made?
8. Find the most economic batch quantity of a product on a machine if the production rate of that item on the machine is
200 pieces per day. The set up cost is Rs.200 per batch and the cost of holding one item in inventory is Rs.0.81 per
day. How will the batch quantity vary if the machine’s production rate is infinite?
9. The annual demand for a product is 100000 units The rate of production is 200000 units per year. The set up cost per
production run is rs.5000, and the variable production cost of each is Rs.10.The annual holding cost per unit is 20% of
the value of the unit. Find the optimum production lot size and the length of the production run.
10. An item is produced at the rate of 50 items per day. The demand occurs at the rate of 25 units per day. If the set up
cost is Rs.100 per set up and holding cost is Re.0.01 per unit of item per day , find the economic lot size for one run,
assuming that shortages are not permitted. Also find the time of cycle and minimum total cost for one run.
11. A company has a demand of 12000 units per year for a item and it can produce 2000 such items per month. The cost
of one set up is Rs.400 and the holding cost per unit per month is Rs. 0.15 . Find optimum lot size, maximum
inventory, manufacturing time, total time.
12. A certain item costs Rs.250 per ton. The monthly requirements are 10 tons and each time the stock is replenished
there is a set up cost of Rs.1000.The cost of carrying inventory has been estimated as 12% of the value of the stock
per year. What is the optimal order quantity and how frequently should order be placed?
13. The demand for an item is 18000 units per year. The holding cost per unit time is Rs.1.20and the cost of shortage is
Rs.5, the production cost is Rs.400.Assuming that replacement rate is instantaneous, determine the optimal order
quantity.
14. A certain product has a demand of 25 units per month and the items are withdrawn uniformly. Each time a production
run is made , the set up cost is Rs.15.The production cost is Rs.1 per item and inventory holding cost is rs.0.30 per
item per month. If the shortage cost is Rs.1.50 per item per month, determine how often to make a production run ad
what size it should be?.
15. A dealer supplies the following information with regard to a product dealt in by him. Annual demand = 5000 units,
Buying cost = Rs.250 per order, Inventory carrying cost = 30% per year, Price= Rs.100 per unit. The dealer is
considering the possibility of allowing home back orders to occur for the product. He has estimated that the annual
cost of back ordering (allowing shortages) the product will be Rs.10 per unit. i) what should be the optimum number of
units of the product he should buy in one lot? ii) What quantity of the product should he allow to be back ordered? iii)
How much additional cost will he have to incur on inventory if he does not permit back ordering?.
Dr.B.Vellaikannan Dept. of Maths TCE Madurai 15 Page 2
18ME410 Operations Research 2019-20 (E)
16. A commodity is to be supplied at a constant rate of 200 units per day. Supplies for any amounts can be had at any
required time, but each ordering costs Rs.50 .Cost of holding commodity in inventory is Rs.2 per unit per day while
the delay in the supply of items induces a penalty of Rs.10 per unit per delay of one day. Formulate the average cost
function of this situation and find the optimal policy (q , t) where t is the reorder cycle period and q is the inventory
level after re order. What should be the best policy if the penalty cost becomes infinite?
17. A news paper boy has the following information regarding a magazine. Cost of copy of the magazine is 60 paise and
sales price is one rupee. Advise him with the help of i) EMV criterion ii) EOL Criterion to have the optimum stock and
also iii) Calculate the EVPI.
No. of Copies Sold : 10 11 12 13 14
Probability : 0.12 0.18 0.25 0.20 0.35
18. The average demand for a product is 42,000 units. The average lead time is 3 weeks. The standard deviation of
demand during the average lead time is 200 units per week .The cost of ordering is Rs.500 per order. The cost of
purchase of the product per unit is Rs.20.The cost of carrying per unit per year is 20% of the purchase price. The
maximum delay in lead time is 1 week and the probability of this delay is 0.30.Assume the service level of 0.95 .a)
What is the reorder level if the Q - system is followed b) What is the maximum inventory level if the P- System is
followed.
19. Find the optimum order quantity for a product for which the price breaks are as follows
Quantity Purchasing Cost
0<Q1<100 Rs 20 per unit
100<Q2<200 Rs 18 per unit
200<Q3 Rs 1 per unit.
The monthly demand is 400 units .The storage cost is 20 % of the unit cost of the product and the cost of ordering is Rs
25 per month.
20. Find the optimal order quantity for the following. The annual demand =3600 units.Order cost is Rs.50.Cost of storage
is 20% of the unit cost. The price Break is 0<Q1<100 Rs.20
100> Q2 Rs.18
********
Dr.B.Vellaikannan Dept. of Maths TCE Madurai 15 Page 3
You might also like
- CBT QuestionsDocument20 pagesCBT Questionsmohammed amjad ali100% (1)
- SCM Numerical 2011Document13 pagesSCM Numerical 2011arvindpmNo ratings yet
- PROBLEM SHEET ON INVENTORY CONTROL OPTIMIZATIONDocument3 pagesPROBLEM SHEET ON INVENTORY CONTROL OPTIMIZATIONNavneeth KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Pom Inventory ProblemsDocument8 pagesPom Inventory ProblemsSharath Kannan0% (2)
- C7,8 - ExercisesDocument31 pagesC7,8 - ExercisesTÂM MAI0% (1)
- Cyber Security 2017Document8 pagesCyber Security 2017Anonymous i1ClcyNo ratings yet
- Inventory Optimization Problems and FormulasDocument6 pagesInventory Optimization Problems and FormulasShreya GanguliNo ratings yet
- Practice questions on deterministic inventory modelsDocument3 pagesPractice questions on deterministic inventory modelsSabir Ali0% (2)
- Operations Research Tutorial ProblemDocument4 pagesOperations Research Tutorial ProblemAjitsingh JagtapNo ratings yet
- Inventory ProblemsDocument2 pagesInventory ProblemsKhaja MohiddinNo ratings yet
- Material Management & Inventory Control QuestionsDocument41 pagesMaterial Management & Inventory Control QuestionsArun HariharanNo ratings yet
- Inventory 1Document5 pagesInventory 1Kim Ivy May FabunanNo ratings yet
- Material Costing CalculationsDocument11 pagesMaterial Costing CalculationsAnimeshSahaNo ratings yet
- Inventory control EOQ calculations and solutionsDocument3 pagesInventory control EOQ calculations and solutionsहुमागाँई शिशिर0% (3)
- Operations Research Assignments 4Document1 pageOperations Research Assignments 4Deepak Agrawal0% (2)
- Optimal inventory ordering policy for raw materialsDocument5 pagesOptimal inventory ordering policy for raw materials19R21A05C0 19 - CSE BNo ratings yet
- Mem 720 - QBDocument10 pagesMem 720 - QBJSW ENERGYNo ratings yet
- Operations Management QuestionsDocument2 pagesOperations Management QuestionsSyed QutubuddinNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5 PDFDocument2 pagesAssignment 5 PDFranjeet singhNo ratings yet
- MATERIALS Costing Handouts FinalDocument16 pagesMATERIALS Costing Handouts FinalLegends CreationNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Questions Operations Management (Iet204)Document3 pagesTutorial Questions Operations Management (Iet204)Jagajith Sathis Chandran NairNo ratings yet
- BIT Pilani II Semester 2012-13 Operations Research Assignment 2Document1 pageBIT Pilani II Semester 2012-13 Operations Research Assignment 2Prathamesh BahetiNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2023-24 MEE1024 TH VL2023240105926 2023-10-06 Reference-Material-VDocument14 pagesFALLSEM2023-24 MEE1024 TH VL2023240105926 2023-10-06 Reference-Material-Vjayfulewar23No ratings yet
- EOQ QuestionsDocument3 pagesEOQ QuestionshhaiderNo ratings yet
- Problems On Material CostingDocument9 pagesProblems On Material CostingROHIT TANETINo ratings yet
- Practice Set EOQ ModelDocument1 pagePractice Set EOQ ModelBhaswar ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Practice Session ThreeDocument3 pagesPractice Session ThreeKUMAR ABHISHEKNo ratings yet
- Problems On Inventory ManagementDocument1 pageProblems On Inventory ManagementPrasenjit ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- 2 Material PracticleDocument13 pages2 Material PracticleUdaykiran BheemaganiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 (BBA & BBIS) SUB: OM Inventory Management: EOQ 200 Units & ROL 40 L, L Lead TimeDocument3 pagesAssignment 1 (BBA & BBIS) SUB: OM Inventory Management: EOQ 200 Units & ROL 40 L, L Lead Timesajal koiralaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document2 pagesTutorial 2Puvithera A/P GunasegaranNo ratings yet
- Assignment-04 Inventory Control Models: DSC 3346 Advanced Operations ResearchDocument3 pagesAssignment-04 Inventory Control Models: DSC 3346 Advanced Operations ResearchSupun jayathungeNo ratings yet
- CMA Inventory Management New HandoutDocument10 pagesCMA Inventory Management New HandoutahmedNo ratings yet
- IE 323 Study Set 2 Optimal Inventory SolutionsDocument5 pagesIE 323 Study Set 2 Optimal Inventory SolutionsMehmet ŞahinNo ratings yet
- Work Sheet 1Document6 pagesWork Sheet 1Sourabh PatidarNo ratings yet
- Material CostingDocument8 pagesMaterial CostingJash SanghviNo ratings yet
- Problems On Inventory ManagementDocument1 pageProblems On Inventory ManagementPrasenjit ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Assignment - material controlDocument2 pagesAssignment - material controlkevin75108No ratings yet
- Questions of Recorded Lectures Material Costing: Prof. Bhambwani'S Reliable ClassesDocument6 pagesQuestions of Recorded Lectures Material Costing: Prof. Bhambwani'S Reliable ClassesVishesh GuptaNo ratings yet
- MHA F2 KitDocument113 pagesMHA F2 KitMenaal UmarNo ratings yet
- Inventory ModelsDocument9 pagesInventory ModelsSayiram GNo ratings yet
- 2 Break-Even Analysis - AssignmentDocument2 pages2 Break-Even Analysis - AssignmentNamanNo ratings yet
- Working CapitalDocument5 pagesWorking Capitalchanchal shahiNo ratings yet
- Operations Management Assignment-IiDocument1 pageOperations Management Assignment-IiRaju YadavNo ratings yet
- Inventory ManagementDocument2 pagesInventory Managementpranay639No ratings yet
- Assignment 1 OM PDFDocument3 pagesAssignment 1 OM PDFSuman ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- CH 16Document4 pagesCH 16Riya Desai100% (5)
- 6091fd8f6f2df151707cb223 1620184992 Big Picture C Inventory ManagementDocument7 pages6091fd8f6f2df151707cb223 1620184992 Big Picture C Inventory ManagementChi BellaNo ratings yet
- IIT Guwahati ME421 Assignment on EOQ and EPQ modelsDocument1 pageIIT Guwahati ME421 Assignment on EOQ and EPQ modelsBishal Raj GayanNo ratings yet
- Winter Exam-2012: Management AccountingDocument4 pagesWinter Exam-2012: Management AccountingSamina IrshadNo ratings yet
- Inventory Control and EOQ CalculationsDocument2 pagesInventory Control and EOQ CalculationsDhairya MudgalNo ratings yet
- Inventory MGMT ComprehensiveDocument4 pagesInventory MGMT ComprehensivebigbaekNo ratings yet
- 3rd Sem Cost AccountingDocument3 pages3rd Sem Cost AccountingkapilchandanNo ratings yet
- Deterministic Inventory Control Model Formulas RushabhDocument6 pagesDeterministic Inventory Control Model Formulas RushabhVijay ShekhawatNo ratings yet
- Strategic Capacity Planning for Products and ServicesDocument3 pagesStrategic Capacity Planning for Products and ServicesNazifa Sultana 1831133030No ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 - Inventory Control ModelsDocument1 pageTutorial 2 - Inventory Control ModelsMUSA AHMED ABDULLAHI ALINo ratings yet
- Calculate EOQ and savings from adopting EOQ model for herbal tea importerDocument4 pagesCalculate EOQ and savings from adopting EOQ model for herbal tea importerJahanzaib ButtNo ratings yet
- Quiz 3 QuestionsDocument1 pageQuiz 3 Questionsmahnoor javaidNo ratings yet
- EOQ Problems: Economic Order Quantity SolutionsDocument4 pagesEOQ Problems: Economic Order Quantity SolutionsGhilman HabibNo ratings yet
- Unit - 4 (Inventory Management)Document5 pagesUnit - 4 (Inventory Management)Anukriti DhawanNo ratings yet
- Total Relevant Cost (TRC)Document7 pagesTotal Relevant Cost (TRC)LinhThùyNo ratings yet
- Cost & Managerial Accounting II EssentialsFrom EverandCost & Managerial Accounting II EssentialsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- BCRW Course - Answer-Booklet PDFDocument18 pagesBCRW Course - Answer-Booklet PDFSarah ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- United Airlines Case Study: Using Marketing to Address External ChallengesDocument4 pagesUnited Airlines Case Study: Using Marketing to Address External ChallengesSakshiGuptaNo ratings yet
- Friction, Gravity and Energy TransformationsDocument12 pagesFriction, Gravity and Energy TransformationsDaiserie LlanezaNo ratings yet
- PAPERBOARD QUALITYDocument8 pagesPAPERBOARD QUALITYaurelia carinaNo ratings yet
- LogDocument119 pagesLogcild MonintjaNo ratings yet
- Moon Fast Schedule 2024Document1 pageMoon Fast Schedule 2024mimiemendoza18No ratings yet
- Year 10 Maths PlaneDocument62 pagesYear 10 Maths Planehal wangNo ratings yet
- Biamp Vocia Catalog Apr2020Document24 pagesBiamp Vocia Catalog Apr2020Mahavir Shantilal DhokaNo ratings yet
- Themes in Romeo and JulietDocument7 pagesThemes in Romeo and JulietChiosa AdinaNo ratings yet
- Answer Questions Only: Chemical Engineering DeptDocument2 pagesAnswer Questions Only: Chemical Engineering DepthusseinNo ratings yet
- ClientsDocument7 pagesClientsLiane PanahacNo ratings yet
- Sonigra Manav Report Finle-Converted EDITEDDocument50 pagesSonigra Manav Report Finle-Converted EDITEDDABHI PARTHNo ratings yet
- spl400 Stereo Power Amplifier ManualDocument4 pagesspl400 Stereo Power Amplifier ManualRichter SiegfriedNo ratings yet
- 13Document47 pages13Rohan TirmakheNo ratings yet
- Admission Procedure For International StudentsDocument8 pagesAdmission Procedure For International StudentsAndreea Anghel-DissanayakaNo ratings yet
- BOQ - Hearts & Arrows Office 04sep2023Document15 pagesBOQ - Hearts & Arrows Office 04sep2023ChristianNo ratings yet
- Telephone Triggered SwitchesDocument22 pagesTelephone Triggered SwitchesSuresh Shah100% (1)
- College of Physical Therapy Produces Skilled ProfessionalsDocument6 pagesCollege of Physical Therapy Produces Skilled ProfessionalsRia Mae Abellar SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Gen EconDocument10 pagesWeek 4 Gen EconGenner RazNo ratings yet
- Omobonike 1Document13 pagesOmobonike 1ODHIAMBO DENNISNo ratings yet
- SS1c MIDTERMS LearningModuleDocument82 pagesSS1c MIDTERMS LearningModuleBryce VentenillaNo ratings yet
- Polygenic InheritanceDocument13 pagesPolygenic InheritanceSandeep Kumar RaghuvanshiNo ratings yet
- Presentation of Urban RegenerationsDocument23 pagesPresentation of Urban RegenerationsRafiuddin RoslanNo ratings yet
- Useful Relations in Quantum Field TheoryDocument30 pagesUseful Relations in Quantum Field TheoryDanielGutierrez100% (1)
- Apps Tables Excel FRMTDocument4 pagesApps Tables Excel FRMTSunil ReddyNo ratings yet
- TNTCL Cost Data 2021 22Document95 pagesTNTCL Cost Data 2021 22Akd DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- The Unbounded MindDocument190 pagesThe Unbounded MindXtof ErNo ratings yet
- Stellar Structure and EvolutionDocument222 pagesStellar Structure and Evolutionjano71100% (2)