0% found this document useful (0 votes)
95 views3 pagesGout Management and Fracture Types
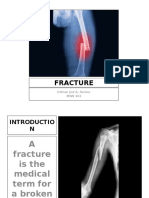
This document discusses fracture nursing management. It describes the types of fractures including close/simple fractures where the skin is intact and open/complex fractures where the bone protrudes through the skin. It outlines nursing priorities for close fractures such as health teaching and monitoring for pain relief and for open fractures such as preventing infection, promoting healing, and assessing neurological status. Surgical management options like open reduction open fixation using titanium plates and closed reduction manipulating fractures manually are mentioned. Potential early complications of fractures include hypovolemic shock and fat embolism. Fracture healing depends on the individual and typically takes 3-12 weeks in children and 6 months or more in adults.
Uploaded by
Nurse NotesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
95 views3 pagesGout Management and Fracture Types
This document discusses fracture nursing management. It describes the types of fractures including close/simple fractures where the skin is intact and open/complex fractures where the bone protrudes through the skin. It outlines nursing priorities for close fractures such as health teaching and monitoring for pain relief and for open fractures such as preventing infection, promoting healing, and assessing neurological status. Surgical management options like open reduction open fixation using titanium plates and closed reduction manipulating fractures manually are mentioned. Potential early complications of fractures include hypovolemic shock and fat embolism. Fracture healing depends on the individual and typically takes 3-12 weeks in children and 6 months or more in adults.
Uploaded by
Nurse NotesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.