Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biology Reviewer: On The Origin of Species: Natural Selection
Uploaded by
Sean SheltonOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Biology Reviewer: On The Origin of Species: Natural Selection
Uploaded by
Sean SheltonCopyright:
Available Formats
Biology The Theory of Evolution
Reviewer
Evolution as a word has been used to refer to many things – from the process through which
fictional creatures known as Pokemon reach a higher level; to the reincarnation of the same
product so it can sell more.
In the context of Biology, however, we're all familiar with evolution because of the merits of one
person: Charles Darwin.
On the Origin of Species: Natural Selection.
People of Darwin's time had this conventional view of Earth and its life. Concepts dating back to
Aristotle, where species remain in fixed forms and Judeo-Christian culture enforcing literal
interpretations of biblical creation in Genesis as life being created in its present-day form, was
the prevailing notion.
Darwin’s radical thinking, coming from a fascination with nature, and subsequently, a sea
voyage, helped him frame his theory of evolution.
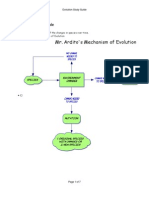
Darwin’s experience with the voyage allowed him to form his notion of evolution: “descent with
modification.” Darwin isn’t the first to propose evolution but his work provided a mechanism to
explain the process.
In the process called natural selection, individuals with certain traits will survive and reproduce
more than individuals who lack traits that fit into their living environment. Over generations,
these traits accumulate and modify the organisms to better suit their specific ways of life in their
environment. These accumulated traits and modifications are called adaptations.
To get more Biology review
materials, visit To God be the glory!
https://filipiknow.net/biology-revi
ewer/
Biology The Theory of Evolution
Reviewer
Hence, because Darwin provided strong evidence for evolution or the idea that living species
descended from ancestral species that are different from their present-day counterparts, his
peers accepted the concept as a theory. A theory is a widely accepted explanation of a
phenomenon that is broader than a hypothesis, is able to generate new hypotheses, and is
backed by a large body of evidence.
Evidence for Evolution.
During Darwin’s voyage, his observations indicated that geographic distribution or proximity is a
better predictor of relationships among organisms than the similarity of environment. For
example, plants and animals in temperate regions of South America resemble tropical species
in the continent more than those temperate living species in Europe.
He was particularly intrigued by the organisms in Galapagos Islands, located 900 km towards
the Pacific from South America, as most animal inhabitants are not found elsewhere in the world
but resemble South American species.
In addition, he witnessed how an earthquake was able to lift Chile’s coastline by a meter and
this helped him refine ideas that natural forces affect the Earth’s surface and, in turn, how life
developed. This also helped explain how he was able to find fossils of marine snails high up on
the Andes Mountain.
Fossils are remains of organisms that lived in the past. They allow us to document changes
between past and present organisms and identify many species that have become extinct.
Many fossils are found in fine-grained sedimentary rocks in layers atop another called strata.
To get more Biology review
materials, visit To God be the glory!
https://filipiknow.net/biology-revi
ewer/
Biology The Theory of Evolution
Reviewer
Paleontologists, scientists who study fossils, gain access to very old fossils when erosion carves
through the upper, younger stratum into the deeper, buried layers.
When fossils are found in the same layer/stratum, it can be assumed that they are found living
in the same point in time and this can be confirmed through dating methods. Because these
layers sort of chronicle the evolution over millions of years in the order in which fossils appear in
the rock strata, this has been referred to as the fossil record and is one of the pieces of
evidence for evolution.
Another evidence for evolution is the presence of anatomical structures that may have different
functions but are structurally similar because they come from a common ancestor.
Similarity coming from this common ancestry is called homology and these features are called
homologous structures. An example is the forelimbs of mammals. Comparing the limb of a
human to that of a whale (that has become a flipper) or that of a bat (that has been modified for
flight), the functions differ but when observed anatomically will have similarities.
This differs from analogous structures which are similar features that evolved independently for
distantly related organisms. For example, the marsupial sugar glider from Australia is able to
glide like the flying squirrel, a eutherian, because they modified their flap of skin tissues to allow
gliding. Analogous structures come to be because of convergent evolution, the independent
evolution of similar features in different lineages.
To get more Biology review
materials, visit To God be the glory!
https://filipiknow.net/biology-revi
ewer/
Biology The Theory of Evolution
Reviewer
Some homologous structures turned into remnant structures that have become marginal or
perhaps of no importance to the organism. Called vestigial structures or rudimentary structures,
these features served important functions for the ancestors of the lineage. An example in the
human body is the appendix. In ancestral species, diet is composed primarily of plant material
hence the appendix then functioned as sites where symbiotic microorganisms would help digest
cellulose from plant material.
Having proposed a mechanism for evolution, Darwin conceived the notion that artificial selection
– selective breeding of domesticated plants and animals to get desirable traits in their offspring
– was key to understanding change brought by evolution. By talking to farmers about livestock
breeding, he learned two essential components of artificial selection: variation and heritability.
Variation, differences among individuals in the same group, allows breeders to select animals or
plants with the most desirable combination of characters as breeding stock. Heritability,
meanwhile, refers to the transmission of a trait from parent to offspring. Despite lacking
underlying knowledge of genetics, breeders are already aware of the importance of heritability in
artificial selection.
Evolution of Populations.
In his work, The Origin of Species, Darwin provided evidence that life on Earth evolved over
time but he could not explain the cause of variation among individuals nor how these variations
are passed from parent to offspring. It was only later when Gregor Mendel wrote a
groundbreaking paper on inheritance in pea plants that the hereditary process needed to
explain natural selection was discovered. However, the significance of Mendel’s work was not
To get more Biology review
materials, visit To God be the glory!
https://filipiknow.net/biology-revi
ewer/
Biology The Theory of Evolution
Reviewer
recognized until it was rediscovered in 1900, where genetic understanding of evolution is based
upon.
Genetic Variation.
You won’t have trouble recognizing friends in a crowd (unless you have bad eyesight). This is
because each person has a unique genome reflected as phenotypic variation, the inherited
traits that are expressed in the individual such as the appearance which allows you to identify
your friends.
Of course, not all variations in a population are heritable. The phenotype is a result of the
combination of the genotype, the genetic makeup, and many influences from the environment.
For instance, having done dental work to straighten your teeth will not pass your smile to your
offspring. Only the genetic components are relevant to natural selection.
In sexually reproducing organisms, meiosis causes genetic variation since each cell undergoing
meiosis has rearranged genetic information. When fertilization thus takes place, the result is a
unique individual.
Mutation.
The mutation is the change in the genetic information encoded in DNA. Genetic information is
stored in genes that can have different versions, structures referred to as alleles, that may affect
the phenotype. When mutations of the gene occur, new alleles may form. Thus, the mutation is
the ultimate source of genetic variation that serves as a raw ingredient for evolution. In
eukaryotes, however, only mutations in cells that produce gametes can be passed and affect a
population’s genetic variability.
To get more Biology review
materials, visit To God be the glory!
https://filipiknow.net/biology-revi
ewer/
Biology The Theory of Evolution
Reviewer
Mutations can have different effects and it is up to chance whether the mutation is beneficial or
harmful. Mutation as small as a change in a single nucleotide in protein-coding genes may have
a significant effect on the phenotype such as in the case of those with sickle-cell anemia.
Some mutations may allow individuals to improve their adaptations to their environment, as in
the case of pests that develop insecticide resistance. Hence why we must be careful with the
use of antibiotics, as most pathogens are also developing resistance. Mutations of the
chromosomes, those that may alter, disrupt, or rearrange gene loci, are most certainly harmful.
All these processes may have played major roles in the evolution of a population.
Misconceptions on Evolution.
A common misconception on evolution is that individual organisms evolve during their lifetime
(some might even mistake it for metamorphosis where an individual will actually change in form
as they grow). Although it is true that natural selection acts on individuals, the impact of natural
selection becomes apparent in changes in a population of organisms over time.
To get more Biology review
materials, visit To God be the glory!
https://filipiknow.net/biology-revi
ewer/
Biology The Theory of Evolution
Reviewer
Another common example of a misconception on evolution among people is that humans came
from monkeys. To clarify this, imagine a family with two heirs--one is male and the other is
female. In the case of our culture here in the country, the more frequent occurrence is that the
male retains their last name while the female takes on her husband’s name during the marriage.
Imagine the two lines many generations later. If the ancestor male heir retains their last name,
throughout the generations they will still be related to the descendants of the female heir even if
the female heir’s lineage may have taken different last names throughout the same time span.
Evolution is like that; there was a common ancestor between monkeys and humans; not that
humans came from monkeys.
Mechanisms of Microevolution.
A population refers to a group of individuals of the same species that occupy the same area and
can reproduce with each other. In studying evolution at the population level, biologists focus on
the gene pool, which contains all copies of every allele at every locus in all members of the
population. Genes that encode for specific traits can have alleles that allow it to manifest or not.
These alleles vary in frequency in the population and when the frequency shifts over a number
of generations, evolution occurs in its smallest scale called microevolution.
To understand how microevolution works, let’s set up a population where evolution isn’t
occurring and thus the gene pool isn’t changing. In this population, dominant alleles would over
time become more frequent at the expense of recessive alleles.
The shuffling of alleles during sexual reproduction does not alter the genetic makeup of the
population. In other words, unless an external factor causes the genetic makeup to change, the
gene pool will remain constant. This condition is known as the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium and
for a population to be in this equilibrium, it must satisfy five main conditions:
1. The population must be large. Smaller populations are more prone to have their allele
frequencies fluctuate due to chance events or encounters, depending on the magnitude
of the event.
2. No gene flow between populations. When individuals move into or out of populations,
they add or remove alleles which alter the gene pool. Think of animal hybrids as clear
examples.
3. No mutations.
4. Random mating. As in the case of artificial selection if individuals mate preferentially,
specific traits are favored and this modifies the gene pool.
5. No natural selection.
To get more Biology review
materials, visit To God be the glory!
https://filipiknow.net/biology-revi
ewer/
Biology The Theory of Evolution
Reviewer
Deviations from the five conditions alter allele frequencies in a population. Three main causes of
evolutionary change are natural selection, genetic drift, and gene flow. Natural selection has
been discussed earlier and so we will focus on the remaining two forces.
Genetic drift refers to chance events that cause allele frequencies to fluctuate unpredictably.
Two examples of events that lead to genetic drift are the bottleneck effect and the founder
effect.
The bottleneck effect can be visualized when a catastrophe kills large numbers of individuals of
a population. The remaining population will not have the same genetic makeup as the original
population. Analogous to when shaking marbles through a bottleneck, only a few marbles will be
able to escape. These living individuals may then have specific alleles, translating to higher
allele frequency. Thus, the living population’s genetic pool becomes skewed in favor of the
increased allele.
Genetic drift also likely takes place when a few individuals colonize a new habitat referred to as
the founder effect. This small group is not representative of the genetic makeup of the original
population they left and may favor specific alleles. As such, what would otherwise be a low
allele frequency in the larger population will become more frequent in this small population.
Gene flow causes change in a population’s allele frequencies due to the migration of fertile
individuals into or out of the population or when gametes, in the case of plant pollen or fungal
spores, are transferred between populations. Gene flow tends to reduce differences between
populations but it introduces new alleles into previously isolated populations.
To get more Biology review
materials, visit To God be the glory!
https://filipiknow.net/biology-revi
ewer/
Biology The Theory of Evolution
Reviewer
Sexual Selection.
Darwin was the first to examine sexual selection, natural selection that favors individuals with
certain traits fashioned for obtaining mates. Secondary sexual characteristics, noticeable
differences not directly related to reproduction, manifest as sexual dimorphisms. These may
come in the form of size difference; but can also include forms of adornment like horns, manes,
and plumage with males usually being the showier sex, at least among vertebrates.
Sexual selection can be intrasexual or intersexual. When individuals of the same sex compete
directly for mates, this refers to the former and is usually found in species where the winning
individual acquires a harem of mates. The latter is the more common type of sexual selection
wherein individuals of one sex (usually females) are choosy in selecting mates.
Concluding Words.
There are many things to be learned about evolution and the role it plays in shaping the
diversity of life. Like a domino, factors, ranging from the smallest molecule in the DNA to
external forces that help shape the planet, shape, and form how life exists and face these
challenges.
As is the case of science, we build on the knowledge we have already gained; replacing
obsolete information with better-supported ideas and notions but in doing so, we will always
come into disagreements. Darwin did not specify that humans “evolved” in his work but anyone
could arrive at the idea.
To get more Biology review
materials, visit To God be the glory!
https://filipiknow.net/biology-revi
ewer/
Biology The Theory of Evolution
Reviewer
In his concluding lines in The Origin of Species, he stated gravity, in a subtle way that reflected
the public mindset of his time, has already been accepted as a factual natural law of the
universe. But when you compare it back to Isaac’s time, such a concept has been referred to as
“occult” and subversive of religion. As you might have noticed, evolution is an iffy subject for
some groups of people.
When the prevailing notion of the time was that of an intelligent design, that a mastermind
planned everything there is about life; Darwin helped break the mold and allowed further means
to scrutinize the knowledge we have already obtained since then.
I will finish this text by sharing with you a passage from Richard Dawkins, a confirmed atheist,
with the intent of sharing other perspectives on the nature of life than the preconceived notions
we already have. In his work The Blind Watchmaker, Dawkins recounted when he tried to find a
queen among a colony of army ants. He wrote the following:
“I never did glimpse the queen, but somewhere inside that boiling ball she was, the central data
bank, the repository of the master DNA of the whole colony. Those gaping soldiers were
prepared to die for the queen, not because they loved their mother, not because they had been
drilled in the ideals of patriotism, but simply because their brains and their jaws were built by
genes stamped from the master die carried in the queen herself. They behaved like brave
soldiers, because they had inherited the genes of a long line of ancestral queens whose lives,
and whose genes, had been saved by soldiers as brave as themselves.”
Remember, knowledge is everywhere. How we handle, filter, and make use of that knowledge,
which has become so much easier for us to grasp, ultimately rests on our hands.
To get more Biology review
materials, visit To God be the glory!
https://filipiknow.net/biology-revi
ewer/
You might also like
- The Shape of Life: Genes, Development, and the Evolution of Animal FormFrom EverandThe Shape of Life: Genes, Development, and the Evolution of Animal FormNo ratings yet
- Concept of Evolution: What Is Natural Selection?Document25 pagesConcept of Evolution: What Is Natural Selection?Adikwu SimonNo ratings yet
- EC Notes - 1Document8 pagesEC Notes - 1Christian AdepojuNo ratings yet
- Science 10: 10 - Amaziah/Week 5Document35 pagesScience 10: 10 - Amaziah/Week 5Alice KrodeNo ratings yet
- Biolec NotesDocument5 pagesBiolec Notesouie ouieNo ratings yet
- Evo Bio Midterm Notes ExplainedDocument21 pagesEvo Bio Midterm Notes ExplainedShareeze GomezNo ratings yet
- Evidences of EvolutionDocument9 pagesEvidences of EvolutionNobisuke NobiNo ratings yet
- Position Paper About Evolution 1Document3 pagesPosition Paper About Evolution 1Johnryl AraosNo ratings yet
- Unit8L1-4 SCIENCEDocument8 pagesUnit8L1-4 SCIENCEKhrysNo ratings yet
- Evolution and Extinction: Life's Changes Over Millions of YearsDocument7 pagesEvolution and Extinction: Life's Changes Over Millions of YearsMarkdanielRamiterreNo ratings yet
- AP Bio TermsDocument12 pagesAP Bio TermsMina NagibNo ratings yet
- EvolutionDocument56 pagesEvolutionKristhia Cyra RiveraNo ratings yet
- BiologyIIforNonMajorsII 02Document69 pagesBiologyIIforNonMajorsII 02GERONA GABRYLE MARCNo ratings yet
- Ace Tutorial GST 112 - 023048Document27 pagesAce Tutorial GST 112 - 023048Uteh AghoghoNo ratings yet
- MWL E1 Ovth B6 JFJJQ 1 J0 Yrvphoxy JESt TT 9 KQ 6 o 6 WDocument64 pagesMWL E1 Ovth B6 JFJJQ 1 J0 Yrvphoxy JESt TT 9 KQ 6 o 6 Wy972918No ratings yet
- Evolution As A Way of Seeing The Natural WorldDocument49 pagesEvolution As A Way of Seeing The Natural WorldShimi OcidoNo ratings yet
- Descent with Modification: The Development of Evolutionary ThoughtDocument5 pagesDescent with Modification: The Development of Evolutionary ThoughtEvangelene Esquillo SanaNo ratings yet
- Darwin's Theory of Evolution ?Document13 pagesDarwin's Theory of Evolution ?Dark mayersNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - Relevance, Mechanisms, Evidence/Bases, and Theories of EvolutionDocument5 pagesWeek 1 - Relevance, Mechanisms, Evidence/Bases, and Theories of EvolutionDharyn Khai100% (2)
- Sources of Evidence in The Study of EvolutionDocument25 pagesSources of Evidence in The Study of EvolutionSidney MendozaNo ratings yet
- EvolutionDocument105 pagesEvolutiontemesgen abebeNo ratings yet
- YasminDocument21 pagesYasminYasmin AseriosNo ratings yet
- Darwin's TheoryDocument7 pagesDarwin's TheoryAbdelrahman MohamedNo ratings yet
- Bio ProjectDocument12 pagesBio ProjectCadine DavisNo ratings yet
- Darwin Natural Selection 1xwxo3eDocument41 pagesDarwin Natural Selection 1xwxo3eHamza MunirNo ratings yet
- Darwin EvolutionDocument34 pagesDarwin Evolutionadelfasilapan57No ratings yet
- Topic 4 Theory of Evolution by Charles DarwinDocument29 pagesTopic 4 Theory of Evolution by Charles DarwinLyka Jane BucoNo ratings yet
- The TIES Middle School Evolution Presentation 1Document37 pagesThe TIES Middle School Evolution Presentation 1Thirdymon PundeNo ratings yet
- Darwin EvolutionDocument54 pagesDarwin EvolutionRenz Junyll ApigoNo ratings yet
- Pieces of Evidence For EvolutionDocument27 pagesPieces of Evidence For EvolutionLovely AC HalconNo ratings yet
- Assignment: Theophilus Sahr MorsayDocument6 pagesAssignment: Theophilus Sahr MorsayKomba KangbaiNo ratings yet
- Evolution WriteupDocument33 pagesEvolution WriteupShipra SinghNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Living Things: Darwin's TheoryDocument35 pagesEvolution of Living Things: Darwin's TheoryPhatgoblinkayeNo ratings yet
- Biology 101Document5 pagesBiology 101KC AngelineNo ratings yet
- 6.1 Darwin's Theory of Evolution: Why and How Have Organisms Changed Over Time???Document35 pages6.1 Darwin's Theory of Evolution: Why and How Have Organisms Changed Over Time???Diya SaherNo ratings yet
- Spiritual Scientist - Evolution TSSDocument31 pagesSpiritual Scientist - Evolution TSSKrishal BhattaraiNo ratings yet
- Evolution: A Historical Perspective: Evidence For Evolution Comes From The Fields ofDocument5 pagesEvolution: A Historical Perspective: Evidence For Evolution Comes From The Fields ofRolandcare BurdeosNo ratings yet
- Summary DarwinDocument3 pagesSummary DarwinAhmad BadrusNo ratings yet
- General ScienceDocument30 pagesGeneral SciencepapayaoffcNo ratings yet
- Evolution - Part 1Document29 pagesEvolution - Part 1Wei Zhang100% (1)
- Evolution of Life: Biology Document Explains Key ConceptsDocument32 pagesEvolution of Life: Biology Document Explains Key ConceptsHaruka NanaseNo ratings yet
- Theory of EvolutionDocument2 pagesTheory of EvolutionhomamunfatNo ratings yet
- Bio ProjectDocument17 pagesBio ProjectSpectra DragneelNo ratings yet
- Biology Reviewer Biological DiversityDocument23 pagesBiology Reviewer Biological DiversityAndrea Grace Bayot AdanaNo ratings yet
- Evolution MdcatDocument32 pagesEvolution MdcatMuhammad Saad TariqNo ratings yet
- 5 Learnings in The Videos of Zoology LectureDocument2 pages5 Learnings in The Videos of Zoology LectureCaitlyn FerrerNo ratings yet
- Evidences and Bases of EvolutionDocument21 pagesEvidences and Bases of EvolutionArlynKaren VargasNo ratings yet
- Evidence of Evolution - DNA, Fossils, Embryos & BiogeographyDocument4 pagesEvidence of Evolution - DNA, Fossils, Embryos & BiogeographyCheena Francesca LucianoNo ratings yet
- Evolution: Darwinism and The Fact of EvolutionDocument15 pagesEvolution: Darwinism and The Fact of EvolutionnaveenajaykumarNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science Q2 Module 8 EvolutionDocument19 pagesEarth and Life Science Q2 Module 8 EvolutionMarc Joseph NillasNo ratings yet
- Biological EvolutionDocument54 pagesBiological EvolutionMa. Krizia Tiny ParconNo ratings yet
- Theory of Evolution PDFDocument2 pagesTheory of Evolution PDFAnonymous gKzRMGjNo ratings yet
- Darwin and Wallace's Theory ExplainedDocument33 pagesDarwin and Wallace's Theory ExplainedMorita Pelaéz RamírezNo ratings yet
- Evolution Study GuideDocument7 pagesEvolution Study Guidegmanb5100% (3)
- EvolutionDocument65 pagesEvolutionJaeden AnsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Outline 3Document3 pagesChapter 10 Outline 3Zarri bradshawNo ratings yet
- Misconceptions of Evolution ExplainedDocument6 pagesMisconceptions of Evolution ExplainedNicole PauigNo ratings yet
- Natural Selection ReviewDocument27 pagesNatural Selection Reviewapi-290100812No ratings yet
- EvolutionDocument35 pagesEvolutionGabriel LanceNo ratings yet
- DetailsDocument3 pagesDetailsNurse NotesNo ratings yet
- Dev Psych - Midterm ExamDocument1 pageDev Psych - Midterm ExamSean SheltonNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of the AbdomenDocument38 pagesAnatomy of the AbdomenSean Shelton100% (9)
- Dev Psych - Midterm Exam Sean SheltonDocument3 pagesDev Psych - Midterm Exam Sean SheltonSean SheltonNo ratings yet
- Psychosexual and Moral DevelopmentDocument37 pagesPsychosexual and Moral DevelopmentSean SheltonNo ratings yet
- Differences Between Men and Women in Indian CultureDocument2 pagesDifferences Between Men and Women in Indian CultureSean SheltonNo ratings yet
- +1 Chap All em PvmhssDocument113 pages+1 Chap All em PvmhssSean SheltonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Cognitive TheoryDocument32 pagesLesson 5 Cognitive TheorySean SheltonNo ratings yet
- Self ConceptDocument1 pageSelf ConceptSean SheltonNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration & Heat PumpDocument36 pagesRefrigeration & Heat PumpMd. Ahsanur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Thermal Degassing Fundamentals R4i1 enDocument6 pagesThermal Degassing Fundamentals R4i1 enAnonymous v5uipHNo ratings yet
- PLN Berita SatuDocument25 pagesPLN Berita SatuAndre SNo ratings yet
- Physical & Chemical Parameter of Effluent Treatment Plant For Thermal Power PlantDocument11 pagesPhysical & Chemical Parameter of Effluent Treatment Plant For Thermal Power PlantPatan Abdul Mehmood KhanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Introduction To Ecology PDFDocument40 pagesLecture 1 - Introduction To Ecology PDFSangga Buana Komara100% (1)
- Heat Transfer: Mechanical EngineeringDocument10 pagesHeat Transfer: Mechanical EngineeringVenkatasairamreddy KandulaNo ratings yet
- FM Question PaperDocument50 pagesFM Question PapervijaykhannaNo ratings yet
- Soil & Tillage Research: Alicja Kici Nska, Justyna WikarDocument11 pagesSoil & Tillage Research: Alicja Kici Nska, Justyna WikarYoselin GomezNo ratings yet
- Rgeo 171211 A FinalDocument28 pagesRgeo 171211 A FinalChandramouleeswar Sundara IyerNo ratings yet
- Pemodelan Oksigen Terlarut (Dissolved Oxygen/DO) Di Perairan Teluk BenoaDocument11 pagesPemodelan Oksigen Terlarut (Dissolved Oxygen/DO) Di Perairan Teluk BenoaIbnu Khusnuz ZainNo ratings yet
- Types of Exhaust Gas Boiler (EGB) Fires and Ways To Prevent ThemDocument4 pagesTypes of Exhaust Gas Boiler (EGB) Fires and Ways To Prevent ThemGiorgi KandelakiNo ratings yet
- Power Generation Using Fast Pyrolysis Liquids From BiomassDocument31 pagesPower Generation Using Fast Pyrolysis Liquids From BiomassPrakash SothivadivelNo ratings yet
- THEME 4 Writing HandoutDocument11 pagesTHEME 4 Writing HandoutMai Anh PhanNo ratings yet
- Chul Park The Limits of Two-Temperature ModelDocument13 pagesChul Park The Limits of Two-Temperature ModellazharNo ratings yet
- Midterm Solar ThermalDocument1 pageMidterm Solar ThermalAshavi ShahNo ratings yet
- Electrons in Atoms: Light and Quantized EnergyDocument9 pagesElectrons in Atoms: Light and Quantized EnergyRicki HanNo ratings yet
- Linton-2014-Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews - WaterDocument10 pagesLinton-2014-Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews - WaterJad JariNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 1 - 2013 PDFDocument6 pagesChemistry 1 - 2013 PDFAlexNo ratings yet
- E2 General Notes and SpecificationDocument1 pageE2 General Notes and Specificationrafael velardeNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Due 1-16-2014Document4 pagesAssignment 1 Due 1-16-2014Evan Baxter0% (1)
- 1 - Management of Electrical SafetyDocument38 pages1 - Management of Electrical SafetyMock ProjectNo ratings yet
- Types of InsulatorsDocument10 pagesTypes of InsulatorsFidel FernandezNo ratings yet
- Memo - Ice SkatingDocument3 pagesMemo - Ice SkatingRafay AsharNo ratings yet
- ĐỀ BD HSG ANH NGÀY 15-7-2021 SỐ 1Document5 pagesĐỀ BD HSG ANH NGÀY 15-7-2021 SỐ 1Nguyen Minh NgocNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Chemistry Notes - Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure - AglaSem SchoolsDocument14 pagesCBSE Class 11 Chemistry Notes - Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure - AglaSem SchoolsAswar ShaileshNo ratings yet
- Aquatic Ecology: Limnology-Study of Freshwater Ecosystems Lentic - Standing Water Lotic - Moving WaterDocument31 pagesAquatic Ecology: Limnology-Study of Freshwater Ecosystems Lentic - Standing Water Lotic - Moving WaterSarthak Khatri100% (1)
- Petrobras SDA Paper PDFDocument5 pagesPetrobras SDA Paper PDFProcess EngineerNo ratings yet
- Rocks CrosswordDocument1 pageRocks CrosswordKarylle GodesNo ratings yet
- Quantum PhysicsDocument21 pagesQuantum PhysicsMartin DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Disaster Awareness, Preparedness & M, AnagementDocument16 pagesDisaster Awareness, Preparedness & M, Anagementrmm0415No ratings yet