Professional Documents
Culture Documents
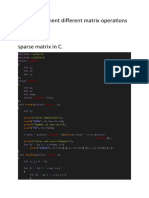
STL
STL
Uploaded by
Ninja DogeOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
STL
STL
Uploaded by
Ninja DogeCopyright:
Available Formats
### vector (#include<vector>)
- vector<int> v
- vector<int> v(n)
- vector<int> v(n, 0)
- vector<int> v = {10, 20, 30};
- v.push_back()
- v.pop_back()
- v.size()
- v[i] (or) v.at(i)
- v.insert(pos, val) // inserts val at that pos
- v.insert(pos, {1, 2, 3..}) // insert multiple val at that pos
- v.erase()
- v.clear()
- for(auto it = v.begin(); it!=end(); it++) cout << *it;
- for(auto elem : v) cout << elem
- vector<vector<int>> v(n, vector<int> m, 0) // 2d vector
- vector<vector<int>> v(n) // fixed row, variable column size
- v[i][j]
- fill(v.begin(), v.end(), num)
- v2 = v1 (assign v1 to v2)
- vector<int> v2(v1) // another way of copying vector
- reverse(v.begin(), v.end())
- vec.erase(std::remove(vec.begin(), vec.end(), 8), vec.end()) // erase by value
### array
- int a[100];
- memset(a, 0, sizeof(a)) // fill all values with 0 or -1 only.
- fill(arr, arr + n, num)
### sort (#include<algorithm>)
- sort(arr, arr + n)
- sort(vector.begin(), vector.end())
- sort(vector.begin(), vector.end(), greater<int>()) // descending
- sort(vector.begin(), vector.end(), compare)
> bool compare(vector<int> a, vector<int> b){
return a < b; // ascending
}
### string (#include<string>)
- string str
- str.push_back('s')
- str.pop_back()
- str1.insert(index/iterator, string1, string1 index, no of character of string
1)
- str.erase(str.begin() + 0, str.end() - 6) // erase from to
- str.erase(1, 4) // delete 4 characters from index 1
- str1.find(str2) // returns index or npos (end)
- string::npos // end of string - no position, this constant is defined with a
value of -1
### stack (#include<stack>)
- stack<int> s
- s.push()
- s.pop()
- s.top()
- s.size()
- s.empty()
- s.insert(index, string)
### queue (#include<queue>)
- queue<int> q
- q.push()
- q.front() // note front not top
- q.pop()
- q.size()
- q.empty()
### priority queue (#include<queue>)
- priority_queue<int> pq // max-heap
- pq.push()
- pq.pop()
- pq.top()
- pq.size()
- pq.empty()
- priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> pq // min-heap
### pairs (#inlcude<utility>)
- pair<int, char> p
- pair p; //default
- pair p(1, 'a'); //initialized, different data type
- pair p(1, 10); //initialized, same data type
- pair p(g3); //copy of g3
- pair <int, int> p = make_pair(1, 10)
- pair <int, int> p = {1, 10} // prefer
- p.first, p.second;
- pair<int, pair<int, char> > p1 = { 3, { 4, 'a' } };
### tuple (#include<tuple>)
- tuple<char, int, float> t;
- t = make_tuple('a', 1, 1.1);
- get<0> t, get<1> t, get<2> t
- auto [a, b, c] = t // structured binding (c++17 !caution)
### set (#inlcude<set>)
- set<int> s
- set<int> s = {1, 2, 3}
- s.insert() // add elem
- set<int> s2(s) // copy set to another set
- s.size()
- s.empty()
- s.clear()
- s.count(val) // returns 0/1 tell if an element exists or not in a set
- s.find(val) // return the pos of the num or s.end() if not exists
- s.lower_bound(val)
- s.upper_bound(val)
### map (#include<map>)
- map <int, int> m
- m[key] = val
- m.insert({1, 4}) // another way of inserting
- m.erase()
- m.clear()
- m.size()
- m.upper_bound(val)
- m.lower_bound(val)
- for(auto it : map) cout << "key" << it.first << "value" << it.second
- m.find(key) // returns iterator of that element or m.end() if not present
- m.empty()
### unordered_map (#include unordered_map)
- same as elements are stored unorderedly
### unordered_set (#include <unordered_set>)
- same as set but stored in randomized way
### multiset (#include <set>)
- same as set but allow multiple elements to be inserted
### unordered_multiset (#include <unordered_multiset>)
- same as set but allow multiple elements stored in randomised way
### useful functions
## accumulate (#inlcude <numeric>)
int sum = 0
accumulate(arr, arr + n, sum) // sum of elements
accumulate(arr, arr + n, sum, myfun) // perform custom operation on adjacent elem
int myfun(int x, int y) return x * y; // sum of product of adjacent elem
## BinarySearch (#inlcude <algorithm>)
binary_search(v.begin(), v.end(), val) // on a sorted datastructure
## lower_bound, upper_bound (#inlcude <algorithm>)
lower_bound(v.begin(), v.end, val);
upper_bound(v.begin(), v.end, val);
## remove (#include <algorithm>)
remove(vec1.begin(), vec1.end(), 20)
## lambda expression
sort(v.begin(), v.end(), [](const int& a, const int& b) -> bool
{
return a > b;
});
You might also like
- C++ STLDocument4 pagesC++ STLHemachandra M mm21b029No ratings yet
- 4 PersistentSegmentTreeCodeDocument3 pages4 PersistentSegmentTreeCodeAshuNo ratings yet
- Interval MapDocument2 pagesInterval Mapperez0z0No ratings yet
- Name - Aryan Gupta REG. NO. 199301088 Section - BDocument18 pagesName - Aryan Gupta REG. NO. 199301088 Section - BbruhNo ratings yet
- C++ GuidesDocument6 pagesC++ GuidesrajeshdawadiNo ratings yet
- New Text DocumentDocument4 pagesNew Text Documenttudybogdan2No ratings yet
- DA Suhil - 1 PDFDocument11 pagesDA Suhil - 1 PDFSuhil IrshadNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Range Minimum QueriesDocument4 pagesDynamic Range Minimum Queriesshripadabhinav.01No ratings yet
- Practical Fil1 (Ankush Shukla 206320040)Document32 pagesPractical Fil1 (Ankush Shukla 206320040)sathwikNo ratings yet
- Problem Statement:-: Prim's Algorithm For Minimum Spanning TreeDocument6 pagesProblem Statement:-: Prim's Algorithm For Minimum Spanning TreeSouradeep GhoshNo ratings yet
- DS CodeDocument20 pagesDS CodeutshasharesNo ratings yet
- LabDocument13 pagesLabDileep VaraprasadNo ratings yet
- PracticeDocument22 pagesPracticesunsam098No ratings yet
- Ai ML ProgramsDocument34 pagesAi ML ProgramsYasar BilalNo ratings yet
- DSA Practical Codes - 122436Document16 pagesDSA Practical Codes - 122436Har JadNo ratings yet
- Re Pandas PD Glob Scipy - Cluster.hierarchy Matplotlib Shutil Os PathlibDocument2 pagesRe Pandas PD Glob Scipy - Cluster.hierarchy Matplotlib Shutil Os PathlibMarco LongobardiNo ratings yet
- DSFILEDocument35 pagesDSFILEimgoyal2005No ratings yet
- PedDocument9 pagesPedHenryMorgan1No ratings yet
- A-Star AlgorithmDocument4 pagesA-Star AlgorithmVIVEK WANINo ratings yet
- Python Short NotesDocument2 pagesPython Short Notesnirbhaygandhi2000No ratings yet
- Max - SizeDocument7 pagesMax - Sizesoura manNo ratings yet
- Func 3Document2 pagesFunc 3piyushjindal98No ratings yet
- Week 8Document13 pagesWeek 8saikrishan1929No ratings yet
- JavascriptDocument3 pagesJavascriptAkshata AhireNo ratings yet
- Aiml Lab PGMDocument15 pagesAiml Lab PGMShubham KumarNo ratings yet
- DDocument3 pagesDعمر نبيلNo ratings yet
- QueueDocument5 pagesQueueyvanishree123No ratings yet
- ADS Lab Week 9Document12 pagesADS Lab Week 9KesavaNo ratings yet
- Data Structures and Algorithms Algorithms in C++: Jordi Petit Salvador Roura Albert AtseriasDocument69 pagesData Structures and Algorithms Algorithms in C++: Jordi Petit Salvador Roura Albert AtseriasMohamed YassineNo ratings yet
- Program of Matrix Multiplication: Lab Practical No. - 1Document45 pagesProgram of Matrix Multiplication: Lab Practical No. - 1ashu345No ratings yet
- VP (Maps) + OB + S&R + GGSHOT + HHDocument60 pagesVP (Maps) + OB + S&R + GGSHOT + HHHimanshu HimanshuNo ratings yet
- Queue & StackDocument12 pagesQueue & Stackarmanmund27No ratings yet
- Bai Tap 3-21Document17 pagesBai Tap 3-21060 nemesisNo ratings yet
- LuatutorialDocument9 pagesLuatutorialAlanNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 8 Data Mining and WarehousingDocument9 pagesAssignment - 8 Data Mining and WarehousingTim WooNo ratings yet
- Com LabDocument11 pagesCom LabRakshitha PNo ratings yet
- Assignment No-3Document8 pagesAssignment No-3akshaypbagul12002No ratings yet
- Collection Dependency-Setter and Constructor Injection:: Package Import Import Import ImportDocument4 pagesCollection Dependency-Setter and Constructor Injection:: Package Import Import Import ImportPrabhakar PrabhuNo ratings yet
- 2-3 TreesDocument38 pages2-3 TreesD R IthihaasNo ratings yet
- Submitted By:-Aditya KumarDocument24 pagesSubmitted By:-Aditya KumarSatnam AzrotNo ratings yet
- R Basics PDFDocument10 pagesR Basics PDFSAILY JADHAVNo ratings yet
- B TreeDocument7 pagesB Treewickykumar05No ratings yet
- Plot RSIDocument11 pagesPlot RSIBipinNo ratings yet
- DAA MaualDocument24 pagesDAA MaualManoj MNo ratings yet
- Assembly Line Scheduling and Optimal PathDocument57 pagesAssembly Line Scheduling and Optimal PathAditya ThakreNo ratings yet
- Assignment#3 (Naive Bayes)Document5 pagesAssignment#3 (Naive Bayes)Faran KhalidNo ratings yet
- 7ADocument4 pages7ASeif ElnaggarNo ratings yet
- LRU&LFU&WinDocument7 pagesLRU&LFU&WinPooja BhagatNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet For BLPC 2016Document13 pagesCheat Sheet For BLPC 2016Michael BoentoroNo ratings yet
- New Text DocumentDocument3 pagesNew Text DocumentofficalnahmareNo ratings yet
- Theory Paper: Arid Agriculture University, RawalpindiDocument14 pagesTheory Paper: Arid Agriculture University, RawalpindiUmair KhanNo ratings yet
- Poor DogsDocument24 pagesPoor DogsDavid GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Gaurav KumarDocument12 pagesGaurav KumarShakeeb ParwezNo ratings yet
- Document 1Document106 pagesDocument 1Arpit SinghNo ratings yet
- Greedy XMDocument11 pagesGreedy XMHugu JujuNo ratings yet
- C++ STL (Quickest Way To Learn, Even For Absolute Beginners)Document19 pagesC++ STL (Quickest Way To Learn, Even For Absolute Beginners)aerNo ratings yet
- Programmi Svolti PythonDocument84 pagesProgrammi Svolti PythonGrezooNo ratings yet
- PolylineEncoder Class PHPDocument6 pagesPolylineEncoder Class PHPmreall100% (6)
- All IgationDocument8 pagesAll IgationNinja DogeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Calendar ProblemsDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Calendar ProblemsNinja DogeNo ratings yet
- Reversal of Linked List: SolutionDocument11 pagesReversal of Linked List: SolutionNinja DogeNo ratings yet
- MGT1023 - Syllabus For Fundamentals of Human Resource ManagementDocument2 pagesMGT1023 - Syllabus For Fundamentals of Human Resource ManagementNinja Doge100% (1)
- SQL Injection Authentication Bypass Method:: Chinni DiwakarDocument21 pagesSQL Injection Authentication Bypass Method:: Chinni DiwakarhurryNo ratings yet
- КТП 8 кл 2022-2023 Рогова В.В.Document13 pagesКТП 8 кл 2022-2023 Рогова В.В.aiymNo ratings yet
- Converting Recurring Decimals To FractionsDocument11 pagesConverting Recurring Decimals To FractionsNafiath AbdullaNo ratings yet
- EasyGate SPT-G Technical SpecificationDocument2 pagesEasyGate SPT-G Technical SpecificationJose FernandesNo ratings yet
- OSA542211 5 1CLIReferenceGuideDocument884 pagesOSA542211 5 1CLIReferenceGuidelaidoudihlmNo ratings yet
- BillDocument5 pagesBillPrince PaulNo ratings yet
- Service Manual: EP1080/DX1080/OP1990/VE810/DP7290/ PV8530/P350/TX1080Document90 pagesService Manual: EP1080/DX1080/OP1990/VE810/DP7290/ PV8530/P350/TX1080Alejandro LeviNo ratings yet
- ABB PLCs PDFDocument140 pagesABB PLCs PDFdiego ortizNo ratings yet
- Network Administration Laboratory ManualDocument322 pagesNetwork Administration Laboratory ManualedrisNo ratings yet
- Input and Output ManipulationsDocument29 pagesInput and Output ManipulationsJoselito ApolinarioNo ratings yet
- Prime Time Practice Answers: Investigation 1 Additional Practice Skill: Factors, Multiples, and PrimesDocument4 pagesPrime Time Practice Answers: Investigation 1 Additional Practice Skill: Factors, Multiples, and PrimesGuller AyvazovaNo ratings yet
- An Operating System (OS) Is That Manages, Resources, and Provides Common ForDocument19 pagesAn Operating System (OS) Is That Manages, Resources, and Provides Common ForBDlive. LandNo ratings yet
- Archmodels Vol 128Document48 pagesArchmodels Vol 128gombestralalaNo ratings yet
- Esque Mati CosDocument2 pagesEsque Mati Cosromantisely gonzalezNo ratings yet
- SpaceClaim ShortcutsDocument2 pagesSpaceClaim ShortcutsMariusz MilewskiNo ratings yet
- Institutional Competency Assessment Tools: (ICAT)Document13 pagesInstitutional Competency Assessment Tools: (ICAT)Novi EmberNo ratings yet
- Signals and Systems: Laboratory ManualDocument4 pagesSignals and Systems: Laboratory ManualFakhar AbbasppNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1: Lofting Between Surfaces: Loft, Which Was Covered inDocument10 pagesExercise 1: Lofting Between Surfaces: Loft, Which Was Covered inmohamedNo ratings yet
- Panasonic Industry Robot and Welding Training Courses 2020 EnglishDocument28 pagesPanasonic Industry Robot and Welding Training Courses 2020 Englishpatel swetangNo ratings yet
- Joinery HandbookDocument120 pagesJoinery HandbookjoshikaNo ratings yet
- CISCO - Secure Endpoint User GuideDocument258 pagesCISCO - Secure Endpoint User GuidePAUL VINCENT FAJARDONo ratings yet
- mpc96 62a PDFDocument102 pagesmpc96 62a PDFatifamanNo ratings yet
- INP MOD2 JavaScriptDocument15 pagesINP MOD2 JavaScriptMs. Noah NaomiNo ratings yet
- Analogue Duo: User GuideDocument11 pagesAnalogue Duo: User GuideLucas PaeseNo ratings yet
- 2018 USACE. Hydrologic Engineering Requirements For ReservoirsDocument244 pages2018 USACE. Hydrologic Engineering Requirements For ReservoirsMateus DutraNo ratings yet
- Ifoa Examination Handbook April 2023Document39 pagesIfoa Examination Handbook April 2023108-B JATIN CHAUDHARYNo ratings yet
- A Quick Guide Tol Tex: What Is L Tex? Text Decorations ListsDocument2 pagesA Quick Guide Tol Tex: What Is L Tex? Text Decorations ListsSteve Jurado PinillaNo ratings yet
- IMS Registration Flow Analysis ISSUE 1 0Document81 pagesIMS Registration Flow Analysis ISSUE 1 0Ranjeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Iapfree-Compatibility-List Last Update 28 June 2012Document77 pagesIapfree-Compatibility-List Last Update 28 June 2012alexholi6No ratings yet
- Resume Website Template FreeDocument9 pagesResume Website Template Freevyp0bog1w1m3100% (2)