Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit 201: Ngineering: Working in E
Uploaded by
Abby TakarsOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Unit 201: Ngineering: Working in E
Uploaded by
Abby TakarsCopyright:
Available Formats
SmartScreen
2850 Level 2 in Engineering Unit 201 Handout 4
Unit 201: Working in Engineering
Handout 4: Personal Protective Equipment
Personal protective equipment (PPE)
The main requirement of the Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) at Work
Regulations 1992 is that personal protective equipment is to be supplied and used at
work wherever there are risks to health and safety that cannot be adequately
controlled in other ways.
The regulations also require that PPE:
• is properly assessed before use, to
ensure it is suitable
• is maintained and stored properly
• is provided with instructions on how
to use it safely
• is used correctly by employees.
An employer cannot ask an employee to
pay for their own PPE.
The PPE at Work Regulations1992 do not apply where other regulations require the
provision and use of PPE against particular hazards (e.g. COSHH).
Respiratory protection equipment (RPE)
Divided into two groups:
• respirators (or face masks) – filter and clean the air
• breathing apparatus – supplies breathable air (self-contained
breathing, fresh air hose or compressed air line).
SmartScreen
2850 Level 2 in Engineering Unit 201 Handout 4
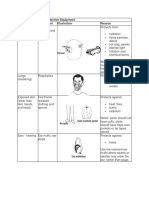
Body
part / Hazards Options
Function
Chemical or metal splash Safety spectacles
Dust Goggles
Eyes Projectiles Face shields
Gas and vapour Visors
Radiation
Impact from falling or Range of helmets
flying objects Bump caps
Risk of head bumping
Head
Hair entanglement
Dust Disposable filtering
Vapour facepiece or respirator
Gas Half- or full-face
Breathing
Oxygen-deficient respirators
atmospheres Air-fed helmets
Breathing apparatus
Temperature extremes Conventional or
Adverse weather disposable overalls
Chemical or metal splash Boiler suits
Spray from pressure Specialist protective
leaks or spray guns clothing (e.g. chain
Protecting
Impact or penetration mail aprons, high
the body
Contaminated dust visibility clothing)
Excessive wear or
entanglement of own
clothing
Abrasion Gloves
Temperature extremes Gauntlets
Cuts and punctures Mitts
Hands Impact Wrist cuffs
and arms Chemicals Armlets
Electric shock
Skin infection
Disease or contamination
Wet Safety boots and shoes
Electrostatic build-up with protective toe caps
Slipping and penetration-resistant
Feet and Cuts and punctures mid-soles
legs Falling objects Gaiters
Metal and chemical Leggings
splash Spats
Abrasion
You might also like
- Workplace Vocabulary for Esl Students: With Exercises and TestsFrom EverandWorkplace Vocabulary for Esl Students: With Exercises and TestsNo ratings yet
- 2850 L3u330 Handout 04Document5 pages2850 L3u330 Handout 04isaacolivierjeanlouisNo ratings yet
- Module-3 Mechanical Safety: Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)Document19 pagesModule-3 Mechanical Safety: Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)Buddies Da Neeghe Puro100% (1)
- What Are Ppes? What Are Ppes?: Personal Protective Personal Protective Equipment Orientation Equipment OrientationDocument16 pagesWhat Are Ppes? What Are Ppes?: Personal Protective Personal Protective Equipment Orientation Equipment OrientationKen FerrolinoNo ratings yet
- Appendix A Survey AnalysisDocument2 pagesAppendix A Survey Analysisahmed naveed100% (1)
- Smaw Common 3 PpeDocument60 pagesSmaw Common 3 PpeReymart LunarioNo ratings yet
- Personal Protective EquipmentDocument48 pagesPersonal Protective Equipmentjenesis dimayugaNo ratings yet
- PPE Training ModuleDocument56 pagesPPE Training Modulehadeed shaikh100% (2)
- LP34 Personal Protective EquipmentDocument2 pagesLP34 Personal Protective Equipmentglenn salandananNo ratings yet
- TYPES OF PPE YOU CAN USE TranslatorDocument3 pagesTYPES OF PPE YOU CAN USE TranslatorDiego Aarón AvendañoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4Document4 pagesLesson 4mdiwuuNo ratings yet
- Ppe American STDSDocument30 pagesPpe American STDSChetana HamsagarNo ratings yet
- Personal Protective EquipmentDocument9 pagesPersonal Protective EquipmentM Ali JadoonNo ratings yet
- Personal Protective EquipmentDocument65 pagesPersonal Protective EquipmentDevashish SharmaNo ratings yet
- Safety: By: Rajesh KumarDocument18 pagesSafety: By: Rajesh KumarNitish SharmaNo ratings yet
- Information Sheet About Safety in Welding MachineDocument7 pagesInformation Sheet About Safety in Welding MachineMaryjoy VillajosNo ratings yet
- Construction Safety - Part 3 (Ppe)Document27 pagesConstruction Safety - Part 3 (Ppe)Henry TuraldeNo ratings yet
- 09 Personal Protective Equipment (CST)Document27 pages09 Personal Protective Equipment (CST)LEMUEL CANADANo ratings yet
- Electrical Safety: Electrical Safety Is A System of Organizational MeasuresDocument19 pagesElectrical Safety: Electrical Safety Is A System of Organizational MeasuresVijaya KumarNo ratings yet
- Ppe Hazard Assessment FormDocument10 pagesPpe Hazard Assessment FormRoba KintoNo ratings yet
- Ersonal Rotective Quipment : P P E PPEDocument28 pagesErsonal Rotective Quipment : P P E PPEChandni SinghNo ratings yet
- Saf102-Lecture 3: Basic Safety in ConstructionDocument8 pagesSaf102-Lecture 3: Basic Safety in ConstructionLin VictoriaNo ratings yet
- Power Plant Enginnering Lab Sheet. 2 PDFDocument2 pagesPower Plant Enginnering Lab Sheet. 2 PDFMd. Mehadi Hasan Shamim 171-33-422No ratings yet
- Module 3. Mech Safety.Document45 pagesModule 3. Mech Safety.Akhila RNo ratings yet
- Personal Protective EquipmentDocument26 pagesPersonal Protective EquipmentJericho DagamiNo ratings yet
- EPAS 8 Quarter 1 - Week 5-6Document12 pagesEPAS 8 Quarter 1 - Week 5-6manolito mulatNo ratings yet
- CES NC II LMG9 p110-137Document28 pagesCES NC II LMG9 p110-137Rojen SabileNo ratings yet
- SoladaduraDocument7 pagesSoladaduraAntónio PereiraNo ratings yet
- Welding - Personal Protective Equipment Body Part Equipment Illustration ReasonDocument3 pagesWelding - Personal Protective Equipment Body Part Equipment Illustration ReasonClark MercadoNo ratings yet
- L2 - Personal Protective EquipmentDocument19 pagesL2 - Personal Protective EquipmentPrincewillNo ratings yet
- Disaster Management Safety OrientDocument55 pagesDisaster Management Safety OrientVishalNo ratings yet
- Consumer Electronics Servicing NC II Lmg9 p110-137Document29 pagesConsumer Electronics Servicing NC II Lmg9 p110-137ShanikMendoza100% (1)
- Ppe-Guide - EnglishDocument12 pagesPpe-Guide - EnglishUsman AhmadNo ratings yet
- Health, Safety & Environment: Department of Mechanical Engineering Ned University of Engineering & TechnologyDocument41 pagesHealth, Safety & Environment: Department of Mechanical Engineering Ned University of Engineering & TechnologyhyNo ratings yet
- Apply Safety PracticesDocument59 pagesApply Safety PracticesEugenio Jr. MatesNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Protective TextilesDocument34 pagesNuclear Protective TextilesVikas SinghNo ratings yet
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)Document52 pagesPersonal Protective Equipment (PPE)Yeyeri SantosNo ratings yet
- TME 121 LR Lecture 4 Four Lecture LR1SPDocument26 pagesTME 121 LR Lecture 4 Four Lecture LR1SPBishopNo ratings yet
- Personal Protective Equipment: Office of Environmental, Health, & SafetyDocument70 pagesPersonal Protective Equipment: Office of Environmental, Health, & SafetyPedro SousaNo ratings yet
- Personal Protective EquipmentDocument9 pagesPersonal Protective EquipmentMuhammad Abdul RaufNo ratings yet
- 05 OPF Safety Program Manual - Personal Protective EquipmentDocument6 pages05 OPF Safety Program Manual - Personal Protective EquipmentKarla CatherineNo ratings yet
- Study On Personal Protective DeviceDocument9 pagesStudy On Personal Protective DeviceNaimul HasanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 08 Basic Occupational Safety and HealthDocument75 pagesLesson 08 Basic Occupational Safety and HealthJohn MaloneNo ratings yet
- Welding Safety Lectures: Know Your Worksite and SafetyDocument8 pagesWelding Safety Lectures: Know Your Worksite and SafetyNick PieperNo ratings yet
- Bosh PpeDocument86 pagesBosh PpekathleenbayotNo ratings yet
- Plumbing Safety 2Document264 pagesPlumbing Safety 2Glenn Fortades SalandananNo ratings yet
- BoshiDocument11 pagesBoshiNathaniel BaguioNo ratings yet
- Use of Personal Protective EquipmentDocument18 pagesUse of Personal Protective EquipmentApril John ArbutanteNo ratings yet
- Protective What'S It All About?: Personal EquipmentDocument28 pagesProtective What'S It All About?: Personal EquipmentTri SubaktiNo ratings yet
- 2 EpiDocument16 pages2 EpisaadNo ratings yet
- Agri 7 Lesson 2.2 Personal Protective EquipmentDocument20 pagesAgri 7 Lesson 2.2 Personal Protective EquipmentArianne Joy EsquivelNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document25 pagesLecture 2Fakhir RehanNo ratings yet
- Ppe For SafetyDocument12 pagesPpe For SafetyAnonymous wxL9DSuYkNo ratings yet
- Personal Protective Equipment: Health Safety and Environment Training CourseDocument97 pagesPersonal Protective Equipment: Health Safety and Environment Training CourseBecha MouradNo ratings yet
- M2-Lesson 3Document5 pagesM2-Lesson 3zyx xyzNo ratings yet
- National Safety Council-Seminar: Presentation On Ppe P EDocument92 pagesNational Safety Council-Seminar: Presentation On Ppe P EvarunstuffNo ratings yet
- Safety TengDocument22 pagesSafety TengrisqisanipNo ratings yet
- 7.PPE For Sanitation WorkersDocument24 pages7.PPE For Sanitation Workersvivek.sadevraNo ratings yet
- Protective TextilesDocument36 pagesProtective TextilesDewan Ajuad Hossain Rifat100% (1)
- Hubungan Beban Kerja, Faktor Demografi, Locus of Control Dan Harga Diri Terhadap Burnout Syndrome Pada Perawat P..Document11 pagesHubungan Beban Kerja, Faktor Demografi, Locus of Control Dan Harga Diri Terhadap Burnout Syndrome Pada Perawat P..widyaNo ratings yet
- How To Prepare A Chemical RegisterDocument29 pagesHow To Prepare A Chemical RegisterRAZMAN BIN MOHD MAULOTNo ratings yet
- Materiale BullyDocument180 pagesMateriale Bullycora4eva5699No ratings yet
- Alumaxx PlusDocument13 pagesAlumaxx PlusRichard StanleyNo ratings yet
- Kertas Penerangan - 2 Modul 6Document17 pagesKertas Penerangan - 2 Modul 6Siti fatimahNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management: Safety, Health, and Risk ManagementDocument28 pagesHuman Resource Management: Safety, Health, and Risk ManagementA.s.qudah QudahNo ratings yet
- JSA Foundation Generator RevDocument6 pagesJSA Foundation Generator RevBeriandi HasanNo ratings yet
- Nebosh Element - 1 AnswersDocument4 pagesNebosh Element - 1 AnswersSatish KumarNo ratings yet
- Nanjing TiO2 SDS-EU V1.0Document8 pagesNanjing TiO2 SDS-EU V1.0dipen royNo ratings yet
- R.K Construction: Job Hazard AnalysisDocument2 pagesR.K Construction: Job Hazard AnalysisDwitikrushna RoutNo ratings yet
- Cleaning ServiceDocument94 pagesCleaning ServiceYousaf RichuNo ratings yet
- Amazon As An Employer: Section 4:-Group 6Document5 pagesAmazon As An Employer: Section 4:-Group 6Aarti VilasNo ratings yet
- Incident Investigation Template Checklist - SafetyCultureDocument4 pagesIncident Investigation Template Checklist - SafetyCultureSerges FokouNo ratings yet
- RPSG-IMS-HS-F - 01 - Hazard Observation CardDocument2 pagesRPSG-IMS-HS-F - 01 - Hazard Observation CardRocky BisNo ratings yet
- MEM603 Individual AssignmentDocument24 pagesMEM603 Individual AssignmentAmirul Faiz100% (1)
- Malaysian Industrial Relations & Employment Law: The Law On Occupational Safety & HealthDocument26 pagesMalaysian Industrial Relations & Employment Law: The Law On Occupational Safety & HealthNajla Nabila AurelliaNo ratings yet
- Lactarin® DX 2017 Carrageenan - FMC CorporationDocument8 pagesLactarin® DX 2017 Carrageenan - FMC CorporationAna RidaoNo ratings yet
- Salaries and WagesDocument37 pagesSalaries and WagesJay Ey Betchaida100% (3)
- Phenobarbital MSDSDocument5 pagesPhenobarbital MSDSrezaNo ratings yet
- Rocol Foodlube Multi Paste FISPQDocument7 pagesRocol Foodlube Multi Paste FISPQYuri SouzaNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet: Wet Chemical Dry Charge (Portable Fire Extinguisher Agent)Document6 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet: Wet Chemical Dry Charge (Portable Fire Extinguisher Agent)Julius MuhimboNo ratings yet
- Ethylan 992 MSDSDocument8 pagesEthylan 992 MSDSDarius IraniNo ratings yet
- Template Site Specific ESH Safety SSEP PlanDocument12 pagesTemplate Site Specific ESH Safety SSEP PlanNarendraNo ratings yet
- Complacency - Safety Toolbox Talks Meeting TopicsDocument2 pagesComplacency - Safety Toolbox Talks Meeting TopicsqhseNo ratings yet
- Hazard Analysis and Risk Control Record: Schlumberger-PrivateDocument6 pagesHazard Analysis and Risk Control Record: Schlumberger-Privatehans vatriolisNo ratings yet
- GENERAL PAYROLL of Employees KolambuganDocument50 pagesGENERAL PAYROLL of Employees KolambuganMercy LazaragaNo ratings yet
- JSA (Job Safety Analysis)Document3 pagesJSA (Job Safety Analysis)Meysam DoskiNo ratings yet
- 2023 PCL Chapter 5 Labour Standards - Employment StandardsDocument112 pages2023 PCL Chapter 5 Labour Standards - Employment StandardsSkyNo ratings yet
- Job Safety Analysis: Required References Jsa ReviewDocument3 pagesJob Safety Analysis: Required References Jsa ReviewWalid KhelfaNo ratings yet
- EPF PayrollDocument3 pagesEPF PayrollrachelNo ratings yet