Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Infection Prevention
Uploaded by
Gina BoligaoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Infection Prevention
Uploaded by
Gina BoligaoCopyright:
Available Formats
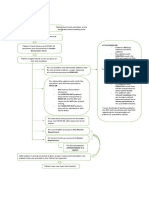
Essentials of the standard precautions to be
used in the care of all patients
A. Hand washing
• Wash hands after touching blood, secretions, excretions and contaminated
items, whether or not gloves are worn. Wash hands immediately after gloves are
removed, between patient contacts.
• Use a plain soap for routine hand washing.
• Use an antimicrobial agent for specific circumstances.
B. Gloves
• Wear gloves when touching blood, body fluids, secretions, excretions, and
contaminated items. Put on clean gloves just before touching mucous membranes and non-intact skin.
C. Mask, eye protection, face shield
• Wear a mask and eye protection or a face shield during procedures and patientcare activities that are
likely to generate splashes or sprays of blood, body
fluids, secretions, and excretions.
D. Gown
• Wear a gown during procedures and patient-care activities that are likely to
generate splashes or sprays of blood, body fluids, secretions, or excretions.
E. Patient-care equipment
• Ensure that reusable equipment is not used for the care of another patient until
it has been cleaned and reprocessed appropriately.
F. Environmental control
• Ensure that the hospital has adequate procedures for the routine care, cleaning,
and disinfection of environmental surfaces.
G. Linen
• Handle used linen, soiled with blood, body fluids, secretions, and excretions in
a manner that prevents skin and mucous membrane exposures, and that avoids
transfer of microorganisms to other patients and environments.
H. Occupational health and bloodborne pathogens
• Take care to prevent injuries when using needles, scalpels, and other sharp
instruments or devices.
• Use ventilation devices as an alternative to mouth-to-mouth resuscitation
methods.
I. Place of care of the patient
• Place a patient who contaminates the environment or who does not assist in
maintaining appropriate hygiene in an isolated (or separate) room
The 10 Standard Infection Control Precautions (SICP)
Patient assessment for infection risk.
Hand hygiene.
Respiratory and cough hygiene.
Personal protective equipment (PPE)
Safe management of equipment.
Safe management of environment.
Safe management of blood and body fluids.
Safe management of linen.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5807)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Quarantine Monitoring Sheet To Your Attending Physician For ClearanceDocument1 pageQuarantine Monitoring Sheet To Your Attending Physician For ClearanceGina BoligaoNo ratings yet
- Triage Processing MapDocument1 pageTriage Processing MapGina BoligaoNo ratings yet
- Patient Surge PlanDocument3 pagesPatient Surge PlanGina BoligaoNo ratings yet
- Tubigon Emergency Response Service and Support Unit (T.E.R.S.S.U)Document81 pagesTubigon Emergency Response Service and Support Unit (T.E.R.S.S.U)Gina BoligaoNo ratings yet
- Donning & Doffing-ShortlistDocument1 pageDonning & Doffing-ShortlistGina BoligaoNo ratings yet
- Diseases, Syndromes & Health Events Under SurveillanceDocument61 pagesDiseases, Syndromes & Health Events Under SurveillanceGina BoligaoNo ratings yet
- Monthly Cases of Dengue Fever Admitted in Tubigon Community Hospital: Tubigon ResidentsDocument2 pagesMonthly Cases of Dengue Fever Admitted in Tubigon Community Hospital: Tubigon ResidentsGina BoligaoNo ratings yet