Professional Documents
Culture Documents
New Syllabus Sanskrit PG
New Syllabus Sanskrit PG
Uploaded by
Tomble Bravo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views4 pagesOriginal Title
new_syllabus_Sanskrit_PG
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views4 pagesNew Syllabus Sanskrit PG
New Syllabus Sanskrit PG
Uploaded by
Tomble BravoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
SANSKRIT
.G. DEGREE STANDARD)
SUBJECT CODE: 319
Uni edas and Vedangas
Vedic and Classical periods - Vedas - classification of the Deities glorified
in the Vedas, Vedic Texts -Sarhhita, Brahmana, Aranyaka portions, the
recession of the four Vedas - Upanisads- Major and minor — Vedangas ~
The Six supplements siksa, Vyakarana, Chandas, Nirukta, Jyotisa and
Kalpa — Vedic Indices.
Unit Epics and Puranas
Epics - Ramayana — Features of the epic literature- Authorship of the
Ramayana - date - Influence of Ramayana on later Sanskrit Literature;
Mahabharata- Three Stages in the development of the Epic - Date Critical
Estimate — as a Dharma Sastra - Harivarhga~ Upakhyanas — Influence of
Mahabharata on later Sanskrit Literature - Ramayana and_Mahabharata as
the National epics of India.
Puranas- Definition — Authorship - Date - Importance — Classification —
Brief account of the Puranas — Upapuranas.
Unit-III: Pre Kalidasa Kavya Period ~ Kalidasa — Post Kalidasa Kavya
Definition of Kavya — Characteristic Features of the Mahakavya- Valmiki -
Vararuci —Pingala
Kalidasa — Date of Kalidasa - Raghuvarnga, Kumarasambhava.
Post Kalidasa Kavya
Asvaghosa — Renaissance theory - Inscriptions — Sethubandha - Janaki
Harana — Kiratarjuniyam — Sisupalavadham - Naisadiyacaritam.
Unit -IV: Lyric - Gnomic and Didactic Poetry ~ Didactic fable Anthology
= Popular tale- Prose ~ Campi Literature
Features of the lyrics — Erotic Lyrics - Meghasandega - Amarusataka -
Gitagovindaand others -Devotional Lyrics- General Features ~ works of
Sankara, Rimanuja and Vedantadesika - Narayaniyam - Karunalahari
Gnomic and Didactic - General Features - Origin and development -
works of Bhatrhari and Ksemendra - Anyapadaesa,
Anthology : Features —-Gatasaptasati - Sadukti karnamrta
Didactic fable - General Features — Paficatantra and Hitopadesa
Prose - Definition - Katha and akhyayika - Origin - Kadambari,
Vasavadatta, Dasakumaracarita, Kathasaritsagara.
Campi definition Rimayanacampii Bharatacampt.
Popular tale - General features - Brhatkatha- language - form-contents and
date - abridgements-Buddhist tales- stories of Vikramaditya and others.
Unit-V: Sanskrit Drama- Origin- Characteristics- Types, Bhasa_and
Kalidasa- Post Kalidasa Dramatists
Traditional view about the origin of Drama - early beginning - Greek
origin — Definition and Characteristic Features — Types of Rapaka and
Uparipaka.
Bhasa and Kalidasa- Trivandrum plays - their authorship -
Abhijianasakuntala
Post Kalidasa Dramatists - Sidraka - Dinnaga - Visakadatta -
Harsavardhana- Bhattanarayana - Bhavabhiti- Murari - Rajasekhara and
others - Allegorical lays of krsnamisra and Vedanta Desika.
History - Paucity of works on history discussed -Hargsacarita -
Rajatharangni- and others.
Unit- VI: Theories of Poetry and Drama
Sahitya Alankara - Theories main and subsidiary. Bharata - Dandin -
Bhamaha — Vamana -anandavardhana ~ Abhinavagupta - Rajasekhara -
Dhanafjaya - Bhoja- Ksemendra - Mammata - Ruyyaka- Appayadiksita -
Jagannatha Pandita-Jayadeva- Their works on Alarhkarasastra and theories
formulated by them.
Unit -VIl: Grammar - Texts and Concepts
Grammar - Panini -Katyayanas - Patafjali - Bhartrhari- Bhattojidtksita -
NageSaand others. Sphota theory. (Concepts: Sarhjia, Paribhasa, Sandhi,
Samasa, and Karaka) Taddhita Krdanta Stripratyaya from Siddhanta
Kaumudi,
Unit- VIII: Prosody and Lexicography ,Astronomy, Dharmasastra,
Upaveda- ayurveda- Gandharvaveda Dhanurveda Arthasastra and
Ancillary Sciences.
Prosody — Vrtta and jati. Lexicons on Homonyms and Synonyms.
Astronomy - General Features — Early Treatises - Five Siddhantas—
Indian Mathematics; Varahamihira - aryabhatta - Brahmagupta -
Bhaskaracarya.
Scope of the Upavedas - ayurveda - General Principles, Nature of
treatment - Caraka - Susruta - Vagbhata - KamaSastra -Gandharvaveda
~ Dance and music - Dhanurveda, Arthasastra-Architecture — Painting.
Unit - IX: Bharatiya Darganas (Indian Philosophy), Religion ~ General
Principles
Explanation and Scope of Philosophy ~ Nastika and Astika systems -
Nastika - Carvaka, Buddhism, Jainism ; Astika- Nyaya- Vaisesika,
Sarhkhya, Yoga, Mimarhsa - Parva and Uttaramimarsa on later Sanskrit
Literature a- siitra texts and Commentaries — Independent treatises of these
systems.
Uni Epigraphy ~ Manuscriptology
Inscriptions, Scripts used in Ancient Texts — Grantha, Tamil, Devanagari,
Nandinagari, Brahmi and sarada Scripts — Editing of Sanskrit Texts from
manuscripts — Preservation of manuscripts ~ materials used, Deciphering
of scripts - Textual Errors : Omissions , Deletions, additions. Use of
modern Technology to edit texts
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5810)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Aero Seminar AgendaDocument1 pageAero Seminar AgendaTomble BravoNo ratings yet
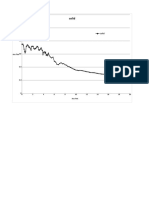
- 05 Oct 13 Exp Data Mach 1.0 Perf 1.5 MM NPR 3Document15 pages05 Oct 13 Exp Data Mach 1.0 Perf 1.5 MM NPR 3Tomble BravoNo ratings yet
- Sivasakthi ScoreCardDocument1 pageSivasakthi ScoreCardTomble BravoNo ratings yet
- 18 Aug 13 Exp Data Axial Mach 0.8 Perf 1.5 MM DiaDocument14 pages18 Aug 13 Exp Data Axial Mach 0.8 Perf 1.5 MM DiaTomble BravoNo ratings yet
- Notification For PA-SPA-PS 05.01.2024Document3 pagesNotification For PA-SPA-PS 05.01.2024Tomble BravoNo ratings yet
- Ip in Pharmaceutical Industry: Shenbagapandiyan B I Year, ME (Engineering Design), Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument8 pagesIp in Pharmaceutical Industry: Shenbagapandiyan B I Year, ME (Engineering Design), Department of Mechanical EngineeringTomble BravoNo ratings yet
- 2021-2022 Team CaptainsDocument4 pages2021-2022 Team CaptainsTomble BravoNo ratings yet
- 03 Oct 13 Exp Data Mach 1.0 Ellipse HM NPR 4Document15 pages03 Oct 13 Exp Data Mach 1.0 Ellipse HM NPR 4Tomble BravoNo ratings yet
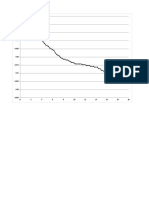
- 18 Aug 13 Exp Data Axial Mach 0.2 Perf 1.5 MM DiaDocument13 pages18 Aug 13 Exp Data Axial Mach 0.2 Perf 1.5 MM DiaTomble BravoNo ratings yet
- CFD AerodynamicsDocument14 pagesCFD AerodynamicsTomble BravoNo ratings yet
- Iare Ead Tutorial Question BankDocument9 pagesIare Ead Tutorial Question BankTomble BravoNo ratings yet
- IARE EAD Lecture NotesDocument130 pagesIARE EAD Lecture NotesTomble BravoNo ratings yet
- Psychology of Life!Document15 pagesPsychology of Life!Tomble BravoNo ratings yet
- AE17605 - CAT - 1 Result Analysis ReportDocument5 pagesAE17605 - CAT - 1 Result Analysis ReportTomble BravoNo ratings yet
- Ae17702 2Document2 pagesAe17702 2Tomble BravoNo ratings yet
- Eif Lesson Plan OutlineDocument10 pagesEif Lesson Plan OutlineTomble BravoNo ratings yet
- Visitor Hostel FormDocument2 pagesVisitor Hostel FormTomble BravoNo ratings yet
- Aerodynamics of Spinning and Non-Spinning Tennis Balls: Article in PressDocument24 pagesAerodynamics of Spinning and Non-Spinning Tennis Balls: Article in PressTomble BravoNo ratings yet
- MR - Boris Otter IntroductionDocument2 pagesMR - Boris Otter IntroductionTomble BravoNo ratings yet
- Ae6601 - FemDocument2 pagesAe6601 - FemTomble BravoNo ratings yet
- Sample Question Paper For Qualifying Examination (Fluid Dynamics)Document4 pagesSample Question Paper For Qualifying Examination (Fluid Dynamics)Tomble BravoNo ratings yet
- We Learn This Course As Gas Dynamics For PropulsionDocument9 pagesWe Learn This Course As Gas Dynamics For PropulsionTomble BravoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 - Axial Flow Turbines: - Discussion On Design Task 1 - Elementary Axial Turbine TheoryDocument22 pagesLecture 7 - Axial Flow Turbines: - Discussion On Design Task 1 - Elementary Axial Turbine TheoryTomble BravoNo ratings yet
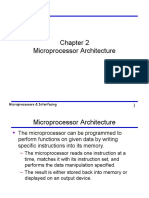
- Microprocessor Architecture: Microprocessors & InterfacingDocument46 pagesMicroprocessor Architecture: Microprocessors & InterfacingTomble BravoNo ratings yet
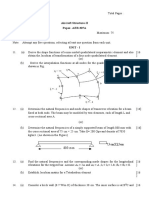
- Aircraft Structure - II (Question Bank) Unit 1: Part ADocument9 pagesAircraft Structure - II (Question Bank) Unit 1: Part ATomble BravoNo ratings yet