Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Major Serum Electrolytes Concentration and Functions Electrolyte Reference Range Functions Increased Decreased Hypernatremia Hyponatremia
Major Serum Electrolytes Concentration and Functions Electrolyte Reference Range Functions Increased Decreased Hypernatremia Hyponatremia
Uploaded by
Kimberly Louise Lopez0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views3 pagesOriginal Title
Electrolytes
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views3 pagesMajor Serum Electrolytes Concentration and Functions Electrolyte Reference Range Functions Increased Decreased Hypernatremia Hyponatremia
Major Serum Electrolytes Concentration and Functions Electrolyte Reference Range Functions Increased Decreased Hypernatremia Hyponatremia
Uploaded by
Kimberly Louise LopezCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
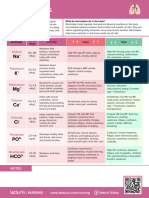
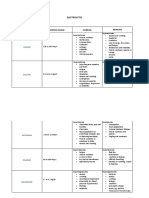
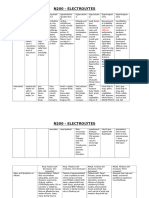
Major Serum Electrolytes Concentration and Functions
Electrolyte Reference Range Functions Increased Decreased
Sodium (Na+) 136 – 145 mEq/L Maintenance of plasma Hypernatremia Hyponatremia
and interstitial osmolarity Thirst Anorexia, nausea,
Generation and Increased temperature vomiting, abdominal
transmission of action Dry, sticky mucous cramping and
potentials membranes diarrhea
Maintenance of acid-base Restlessness Headache
balance Weakness Altered mental status
Maintenance of Altered mental status Muscle cramps,
electroneutrality Decreasing level of weakness, and
consciousness tremors
Muscle twitching Seizures
Seizures Coma
Potassium (K+) 3.5 – 5.0 mEq/L Regulation of intracellular Hyperkalemia Hypokalemia
osmolarity Tall, peaked T waves, Arrythmias
Maintenance of electrical widened QRS ECG changes
membrane excitability Arrythmias Nausea and Vomiting
Maintenance of plasma Cardiac arrest Anorexia
acid-base balance Nausea and Vomiting Decreased bowel
Abdominal cramping sounds
Diarrhea Muscle weakness
Muscle weakness Leg cramps
Paresthesia
Flaccid paralysis
Calcium (Ca2+) 9.0 – 10.5 mg/dL Co factor in blood clotting Hypercalcemia Hypocalcemia
cascade Muscle weakness, Tetany
Excitable membrane fatigue Paresthesia
stabilizer Decreased deep tendon Muscle spasm
Adds strength /density to reflexes Positive Chvostek’s
bones and teeth Personality changes sign
Essential element in Altered mental status Positive Trousseau’s
cardiac, skeletal, and Decreasing level of sign
smooth muscle consciousness Laryngospasm
contraction Abdominal pain Seizures
Constipation Anxiety, confusion,
Anorexia, nausea, psychoses
vomiting Decreased cardiac
Arrhythmias output
Hypertension Hypotension
Polyuria, thirst Arrhythmias
Abdominal cramping
Diarrhea
Chloride (Cl-) 98 – 106 mEq/L Maintenance of plasma Hyperchloremia Hypochloremia
acid-base balance Tachypnea Hyperexcitability of
Maintenance of plasma Weakness muscles,
electroneutrality Lethargy tetany,
Formation of hydrochloric Deep, rapid respiration hyperactive deep
acid Diminished cognitive tendon reflexes,
ability twitching
muscle cramps
cardiac dysrhythmias
slow shallow
respirations
Magnesium (Mg2+) 1.3 – 2.1 mEq/L Excitable membrane Hypermagnesemia Hypomagnesemia
stabilizer Muscle weakness Hyperactive reflexes,
Essential in cardiac, Depressed deep tendon tremors
skeletal, and smooth reflexes Tetany, seizures
muscle contraction Nausea and vomiting Dysphagia
Co-factor in blood clotting Hypotension Anorexia, nausea,
cascade Bradycardia vomiting, diarrhea
Co-factor in carbohydrate Cardiac arrest Tachycardia
metabolism Respiratory depression Arrhythmias
Co-factor in DNA and Coma Hypertension
Protein synthesis Mood and personality
changes
Paresthesia
Phosphorus 3.0-4.5 mg/dL Activation of B-complex Hyperphosphatemia Hypophosphatemia
vitamins Circumoral and Paresthesia
Formation of adenosine peripheral paresthesia Muscle weakness
triphosphate Muscle spasm Muscle pain and
Co-factor in carbohydrate, Tetany tenderness
protein, and lipid Soft tissue calcification Confusion, decreasing
metabolism level of consciousness
Seizures
Bone pain,
osteomalacia
Anorexia
Dysphagia
Decreased bowel
sound
Possible acute
respiratory failure
You might also like
- NGN Ati RN Mental Health Proctored A, B, C, ExamDocument5 pagesNGN Ati RN Mental Health Proctored A, B, C, Exammarcuskenyatta2750% (2)
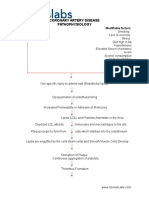
- Coronary Artery Disease PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesCoronary Artery Disease Pathophysiologynursing concept maps50% (4)
- Mms-Diseases and ProtocolDocument8 pagesMms-Diseases and ProtocolWeb Any100% (1)
- For More Information, and To Download Other MaterialsDocument3 pagesFor More Information, and To Download Other MaterialsMatthew NathanielNo ratings yet
- Beck Anxiety Inventory Name: Gender: AgeDocument1 pageBeck Anxiety Inventory Name: Gender: AgeAnton FernandoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology HypokalemiaDocument1 pagePathophysiology HypokalemiaRnspeakcomNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing 1Document43 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing 1Tifanny Shaine Tomas100% (2)
- MedSurg and Pharm BonusDocument13 pagesMedSurg and Pharm BonusThe Treasure ChestNo ratings yet
- NurseBoss Store Nursing FreebieDocument15 pagesNurseBoss Store Nursing FreebieNaveen ShrivasNo ratings yet
- PotassiumDocument2 pagesPotassiumtuffie85No ratings yet
- Sodium: Na+: Hyponatremia: Below 135Document7 pagesSodium: Na+: Hyponatremia: Below 135Martha Marty BalintNo ratings yet
- Adrenal DisordersDocument1 pageAdrenal DisordersjoethemangoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnoses Data BaseDocument34 pagesNursing Diagnoses Data BaseEnyew TaddieNo ratings yet
- Concept Map Hypercalcemia Part 2Document2 pagesConcept Map Hypercalcemia Part 2Queenie Rose ArsenalNo ratings yet
- Potassium (K) 3.5 - 5.0 Meq/L (3.5 - 5.0 Mmol/L) : Hypokalemia HyperkalemiaDocument5 pagesPotassium (K) 3.5 - 5.0 Meq/L (3.5 - 5.0 Mmol/L) : Hypokalemia HyperkalemiaHenric CasimiroNo ratings yet
- Felixcharlie Electrolyte Homeostasis Part 3Document3 pagesFelixcharlie Electrolyte Homeostasis Part 3Nur Fatima SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Imbalances Assignment PDFDocument1 pageImbalances Assignment PDFVirgs SilvanoNo ratings yet
- Name of Drugs Kaligen 8Document2 pagesName of Drugs Kaligen 8mellany100% (1)
- Viii. Pathophysiology A. Overview of The Disease HypokalemiaDocument4 pagesViii. Pathophysiology A. Overview of The Disease HypokalemiaCleo Joyce C. CristalNo ratings yet
- Fluids and ElectrolytesDocument23 pagesFluids and ElectrolytesJonah MaasinNo ratings yet
- Understanding ElectrolytesDocument2 pagesUnderstanding Electrolytessurviving nursing schoolNo ratings yet
- OTM 101 Nursing MnemonicsDocument2 pagesOTM 101 Nursing MnemonicsMarlena Nicole100% (6)
- PathophysiologyDocument7 pagesPathophysiologyJerica Mae VenoyaNo ratings yet
- Nursing CS Electrolytes 03Document1 pageNursing CS Electrolytes 03Lia neNo ratings yet
- Acid Base BalanceDocument4 pagesAcid Base BalanceHenric CasimiroNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of CVADocument7 pagesPathophysiology of CVAsarzlasco0967% (3)
- Antidotes - and - Poisoning (Clinical Chemistry)Document2 pagesAntidotes - and - Poisoning (Clinical Chemistry)Mae AnnNo ratings yet
- Hemolysis, Increase Serum K+: Ventricular Dysrrhytmias or Cardiac Arrest May OccurDocument2 pagesHemolysis, Increase Serum K+: Ventricular Dysrrhytmias or Cardiac Arrest May OccurArian BelogotNo ratings yet
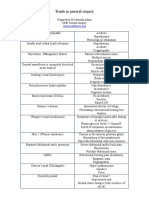
- Triads in General Surgery: Prepared by DR Narendra Allam DNB General SurgeryDocument3 pagesTriads in General Surgery: Prepared by DR Narendra Allam DNB General Surgerysk50% (2)
- Hypercalcemia HPWDocument1 pageHypercalcemia HPWfredericktingsyNo ratings yet
- Fluids & Electrolytes 5Document14 pagesFluids & Electrolytes 5Justin Angelo SildoraNo ratings yet
- Hypercalcemia Concept MapDocument3 pagesHypercalcemia Concept MapAlvin Dagumbal100% (1)
- Imbalance Values Causes Assessment InterventionDocument4 pagesImbalance Values Causes Assessment InterventionKat Sobremente DuranNo ratings yet
- Handout Ms Prof. Ej FlaminianoDocument50 pagesHandout Ms Prof. Ej FlaminianoJustine Jacob BarengNo ratings yet
- Hyperkalemia VS HypokalemiaDocument1 pageHyperkalemia VS HypokalemiaAnmari OnespinNo ratings yet
- Blok 24 Skenario 1 - Analisa Gas Darah Akibat Ketidakseimbangan ElektrolitDocument15 pagesBlok 24 Skenario 1 - Analisa Gas Darah Akibat Ketidakseimbangan ElektrolitGogmaFirmansyahSiraitNo ratings yet
- Wk8 - Electrolyte Imbalances & Acid-Base ImbalancesDocument65 pagesWk8 - Electrolyte Imbalances & Acid-Base ImbalancesPotato PceeNo ratings yet
- Meds - KaplanDocument3 pagesMeds - KaplanJodi BairNo ratings yet
- Mark Billy L. Perpetua, Man RN: Fluids, Electrolytes andDocument96 pagesMark Billy L. Perpetua, Man RN: Fluids, Electrolytes andMaica LectanaNo ratings yet
- Assignment#1Document13 pagesAssignment#1Mark Jefferson LunaNo ratings yet
- 3A - BOLDIOS Electrolytes Tabular ComparisonDocument20 pages3A - BOLDIOS Electrolytes Tabular ComparisonPsyche Valerie BoldiosNo ratings yet
- Fluids and Electrolytes (Concentration and Composition Changes)Document6 pagesFluids and Electrolytes (Concentration and Composition Changes)Kristin SaberonNo ratings yet
- ElectrolytesDocument4 pagesElectrolytesGhadeer AbedNo ratings yet
- Pathway Vertigo NewDocument1 pagePathway Vertigo Neweko67% (3)
- Fluid & ElectrolyteDocument69 pagesFluid & ElectrolytePaul Ebenezer100% (1)
- Signs and Symptoms:: NeurologicDocument1 pageSigns and Symptoms:: NeurologicJheanAlphonsineT.MeansNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Assess AnginaDocument3 pagesDrug Study: Assess Anginadeo_gratias14No ratings yet
- Med-Surg 1Document42 pagesMed-Surg 1Stephen Gabriel Tito100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease: Chest Pain Muscle Weakness Shortness of BreathDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease: Chest Pain Muscle Weakness Shortness of BreathCyril Jane Caanyagan AcutNo ratings yet
- Primary Defect: Proteinuria Tertiary Spiral: Compensatory Salt RetentionDocument4 pagesPrimary Defect: Proteinuria Tertiary Spiral: Compensatory Salt RetentionCici Novelia ManurungNo ratings yet
- Fluids and Renal DisorderDocument139 pagesFluids and Renal DisorderLhara MañoNo ratings yet
- Electrolyte Imbalances Causes: Signs & Symptoms:: Physical Exam: Lab FindingsDocument4 pagesElectrolyte Imbalances Causes: Signs & Symptoms:: Physical Exam: Lab Findingsworleyb83No ratings yet
- Electrolytes TableDocument4 pagesElectrolytes TableMeg NoriegaNo ratings yet
- Feedback Mechanisms Stimulus Receptor Control Center Effector ResponseDocument1 pageFeedback Mechanisms Stimulus Receptor Control Center Effector ResponsekimNo ratings yet
- F&E Normal RangesDocument4 pagesF&E Normal RangesTikTok TrendzNo ratings yet
- CKD Discharge Plan FINALDocument4 pagesCKD Discharge Plan FINALSienaNo ratings yet
- Common Plants Poisonous To LivestockDocument88 pagesCommon Plants Poisonous To LivestockSunilNo ratings yet
- Electrolyte ChartDocument3 pagesElectrolyte Chartsurviving nursing schoolNo ratings yet
- Disturbances of Fluid and Electrolyte BalanceDocument3 pagesDisturbances of Fluid and Electrolyte BalanceJezel B. AnadonNo ratings yet
- Clinical Signs in Humans and Animals Associated with Minerals, Trace Elements and Rare Earth ElementsFrom EverandClinical Signs in Humans and Animals Associated with Minerals, Trace Elements and Rare Earth ElementsNo ratings yet
- Leg Cramps, A Simple Guide to The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandLeg Cramps, A Simple Guide to The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- MalpresentationDocument16 pagesMalpresentationAnghel CruzNo ratings yet
- MCN - Midterm Quiz 1&2Document4 pagesMCN - Midterm Quiz 1&2Anabelle RicoNo ratings yet
- Conversion DisorderDocument27 pagesConversion DisorderKhalil Ullah100% (1)
- Paediatric Orthopaedic Diagnosis Asking The Right Questions by Benjamin Joseph, James Robb, Randall T Loder, Ian Torode (Auth.)Document441 pagesPaediatric Orthopaedic Diagnosis Asking The Right Questions by Benjamin Joseph, James Robb, Randall T Loder, Ian Torode (Auth.)Gabriela Iuliana CAZACNo ratings yet
- Heat StressDocument2 pagesHeat StressKceey CruzNo ratings yet
- Genu VarumDocument8 pagesGenu VarumnavenNo ratings yet
- NHL 2k09 GuideDocument7 pagesNHL 2k09 GuideARTURO CARRETERONo ratings yet
- DR Vibhor PardasaniDocument19 pagesDR Vibhor PardasaniPushpanjali Crosslay HospitalNo ratings yet
- Benefits of Rhythmic Movement For ADHDDocument1 pageBenefits of Rhythmic Movement For ADHDBrainFitnessStrategiesNo ratings yet
- Research PaperDocument14 pagesResearch Paperapi-534460012No ratings yet
- KUL 8 EpilepsyDocument41 pagesKUL 8 EpilepsyErina NopiyantiNo ratings yet
- Mental Health ProjectDocument12 pagesMental Health ProjectGabriel ParksNo ratings yet
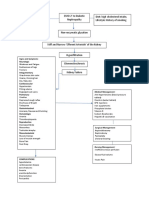
- Acute Kidney InjuryDocument4 pagesAcute Kidney InjuryMinerva BertumenNo ratings yet
- Depression and Anxiety Concept MapDocument4 pagesDepression and Anxiety Concept Mapsammillepointer86No ratings yet
- Changan Auto - Basic First Aid TrainingDocument54 pagesChangan Auto - Basic First Aid TrainingZubair SoomroNo ratings yet
- Autism/Autism Spectrum Disorders: Autistic Disorder (Also Called "Classic" Autism)Document10 pagesAutism/Autism Spectrum Disorders: Autistic Disorder (Also Called "Classic" Autism)priya swathiNo ratings yet
- DNB General Surgery Paper4Document2 pagesDNB General Surgery Paper4Malavika RaoNo ratings yet
- The Role of Mutations On Genes NSD1 and NFIX, in Sotos SyndromeDocument4 pagesThe Role of Mutations On Genes NSD1 and NFIX, in Sotos SyndromeasclepiuspdfsNo ratings yet
- Psychology Schizophrenia NotesDocument11 pagesPsychology Schizophrenia NotesClaudia Martin HernandezNo ratings yet
- Circulationaha 110 970939Document21 pagesCirculationaha 110 970939Michelle TedjaNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis of Diabetes MellitusDocument4 pagesCase Analysis of Diabetes MellitusJeanne CastroNo ratings yet
- Telepractica y Fonoaudiologia - Referencias (Retamal-Walter) PDFDocument2 pagesTelepractica y Fonoaudiologia - Referencias (Retamal-Walter) PDFAlejandro QuezadaNo ratings yet
- Term Paper PTSDDocument7 pagesTerm Paper PTSDafmzmxkayjyoso100% (1)
- TABLE 132 - Recreational Substances - Intoxication WithdrawalDocument3 pagesTABLE 132 - Recreational Substances - Intoxication WithdrawalDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- 5 FAST Facts About Stroke Infographic Ucm500739Document1 page5 FAST Facts About Stroke Infographic Ucm500739roseNo ratings yet
- Principles of Lesion Localization in Neurology - University of MiamiDocument35 pagesPrinciples of Lesion Localization in Neurology - University of MiamiErick AlbanNo ratings yet