Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 1
Uploaded by
Niña Morada0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views12 pageschapter 1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentchapter 1
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views12 pagesChapter 1
Uploaded by
Niña Moradachapter 1
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 12
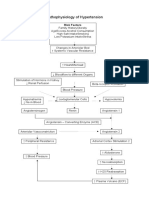
Alterations in Blood Systemic arterial
Pressure blood pressure
is the
Arterial Blood
physiologic
Pressure
result of the
produced by the
cardiac output
force of the left
and the
ventricular
resistance to the
contraction
ejection of blood
overcoming the
from the heart.
resistance of
Cardiac output
aorta to open
(CO) is the
aortic valve.
product of 2
the pressure
variables: stroke
maintained in
volume (SV) and
arterial system
heart rate (HR)
throughout the
(CO = SV × HR).
cardiac cycle.
Stroke Volume
Determinants of
is the specific
Systemic Blood
volume of blood
Pressure
leaving the heart
with each Measurement of
contraction. Blood Pressure
Preload is Systolic blood
determined by pressure is the
the amount of peak pressure in
blood returned the aorta during
to the heart ventricular
between contraction.
contractions. Diastolic blood
Systemic pressure is the
vascular minimum
resistance (SVR) pressure during
is the resistance ventricular
to ejection into diastole.
the arterial Pulse Pressure is
circulation. the difference
Major between systolic
determinant and diastolic
of diastolic BP blood pressure.
Mean Arterial
Pressure (MAP)
is the calculated
average pressure (proteinuria) is
within circulatory reflective of
system increased
throughout the glomerular
cardiac cycle. permeability
Korotkoff sounds and an early
is the sounds indicator of
produced by the hypertensive renal
turbulent flow injury.
through the Primary
partially Hypertension
occluded artery. also called
Metabolic essential
Syndrome hypertension,
Characterized by does not have a
elevated clearly identifiable
circulating insulin known etiology
and lipid levels, and is therefore
hypertension, and an idiopathic
obesity. disorder.
The presence of Secondary
microalbuminuria Hypertension
When o Family History
hypertension is o Obesity
found to have a o Sedentary
specific Lifestyle
identifiable cause. o Metabolic
the elevated Syndrome
blood pressure is o Diet
the result of o Tobacco Use
identifiable Labs
pathologic o ↑ CBG
conditions or o ↑ Total
certain drugs or Cholesterol
foods. o ↑ Triglycerides
It is less common
o ↑ LDL
in adults, but is
o ↓ HDL
the major cause
Lifestyle
of hypertension in
Modifications to
children.
Treat and Prevent
Risk Factors for
Primary
Developing Primary
Hypertension
Hypertension
o Increasing age
o Weight hemorrhagic
Reduction stroke, liver
o DASH diet failure, and acute
o Low Sodium renal failure are
Intake all potential
o Exercise outcomes of
o Moderate hypertension
Intake of during pregnancy.
alcohol When HTN is
diagnosed during
pregnancy, it is
Hypertension classified into
during Pregnancy one of 4
Hypertension categories:
arises in 5-12% of chronic
all pregnancies. hypertension
Preterm labor, (preexisting),
abruptio preeclampsia,
placentae, chronic
disseminated hypertension
intravascular with
coagulation, superimposed
preeclampsia, or a long-term
or gestational basis.
hypertension. Hypertensive crisis
Obstructive sleep (HTN-C) was the
apnea (OSA) is term
closely associated introduced to
with obesity; it is replace the initial
found in 2-4% of term malignant
adults, and hypertension.
hypertension is Hypertensive
present in 45-60% emergencies
of those diagnosed are situations
with OSA. characterized
Pheochromocytom by a sudden
a is a increase in
catecholamine- either or both
secreting tumor of systolic and
the adrenal medulla diastolic
that generates pressures
hypertension on accompanied
either a short-term by evidence of
acute end- that is ≥10 mm Hg
organ damage. within 3 minutes
Hypertensive of moving to an
urgency upright position.
describe similar Short Term
blood Regulation of
pressure Systemic Blood
elevations, but Pressure
without the is mediated by the
end-organ sympathetic
damage. branch of the
Orthostatic autonomic
Hypotension is the nervous system
drop in blood (the sympathetic
pressure with nervous system
position change. [SNS]).
a decrease in Activation of the
systolic blood SNS influences
pressure of ≥20 both heart rate
mm Hg or a and SVR.
decrease in The autonomic
diastolic pressure nervous system
maintains a basal during periods of
level of arteriolar rest.
smooth muscle Long Term
tone through the Regulation of
SNS and provides Systemic Blood
heart rate control Pressure
through a balance the role of the
of SNS and renin–
parasympathetic angiotensin–
nervous system aldosterone
(PSNS) activity. system (RAAS) has
Stimulation of the been seen as the
SNS results in the primary
increased release contributor to this
of the process.
neurotransmitters Prorenin, the
epinephrine and inactive form of
norepinephrine. renin, is
PSNS is synthesized and
responsible for stored by
maintaining a specialized smooth
slower heart rate muscle cells
located in the resulting in the
afferent arterioles release of
of the kidney. angiotensin I, a
Juxtaglomerular peptide possessing
cells are stimulated minimal
by a decrease in vasoconstrictive
arterial pressure to capacity.
enzymatically Angiotensin I
cleave the continue to be
precursor and created by renin
release the for about 30-60
activated renin mins, until renin is
enzyme into the removed from the
vascular bed of the body. While the
kidney. blood carrying
Most of the renin angiotensin I
travels into the circulates through
general circulation, the pulmonary
where it acts on a vessels, an enzyme
circulating plasma produced by the
protein called vascular
angiotensinogen, endothelium
(angiotensin- increased, raising
converting enzyme BP.
[ACE]) comes in Angiotensin II also
contact with is an intermediary
angiotensin I, and 2 for an additional
amino acids are means of raising
fragmented from blood pressure—
angiotensin I to increasing
produce circulating volume
angiotensin II. to significantly
Angiotensin II increase venous
Angiotensin II is an return to the heart
extremely potent and therefore
vasoconstrictor, stroke volume.
primarily of the In the general
arterial bed, but circulation reaches
also slightly the cortex of the
affecting the adrenal glands,
venous system. stimulating the
The SVR is release of the
therefore hormone
aldosterone.
Aldosterone movement, and
circulates to the release of renin.
kidneys, where it Suprachiasmatic
binds to receptors nuclei—the body’s
in the renal internal clock.
tubules, causing For those
the kidneys to individuals age 18
reabsorb more years and older,
sodium. normal blood
Endothelin-1 (ET- pressure is defined
1) is a peptide as <120 mm Hg
produced in the systolic and <80
renal medulla. It mm Hg diastolic;
binds to receptors stage 1
within the kidney, hypertension
initiating an begins at a systolic
autocrine-induced pressure of 140 mm
vasodilatory Hg or a diastolic
response affecting pressure of 90 mm
renal perfusion, Hg.
water & electrolyte
You might also like
- Hypotension: Sandeep Sharma Priyanka T. BhattacharyaDocument10 pagesHypotension: Sandeep Sharma Priyanka T. Bhattacharyaمحمود محمدNo ratings yet
- Antihypertensive Drug LongDocument21 pagesAntihypertensive Drug Longa.muhsinNo ratings yet
- 6 HypertensionDocument95 pages6 HypertensionZeleke temechewNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument11 pagesHypertensionJyoti singhNo ratings yet
- Cardio Vascular SystemDocument26 pagesCardio Vascular SystemmayankNo ratings yet
- Baroreceptors and Therefore The Sympathetic SystemDocument5 pagesBaroreceptors and Therefore The Sympathetic SystemS GNo ratings yet
- 12-Blood Vessels PathologyDocument37 pages12-Blood Vessels PathologyRodriguez Vivanco Kevin DanielNo ratings yet
- Hypertensive Emergency PDFDocument14 pagesHypertensive Emergency PDFOsiithaa CañaszNo ratings yet
- Healing Hypertension: A Focus On Alternative Systems of MedicineDocument10 pagesHealing Hypertension: A Focus On Alternative Systems of Medicinedeepa rNo ratings yet
- Chapter 33 HypertensionDocument5 pagesChapter 33 HypertensiongytmbiuiNo ratings yet
- Krisis Hypertensi: Sigit Widyatmoko Fakultas KedokteranDocument85 pagesKrisis Hypertensi: Sigit Widyatmoko Fakultas KedokteranSeptian WidiantoNo ratings yet
- BAB 2 OkDocument19 pagesBAB 2 OkHelny TariganNo ratings yet
- Hypertension: Hypertension Is One of The Most Common Worldwide Diseases Afflicting Humans. BecauseDocument8 pagesHypertension: Hypertension Is One of The Most Common Worldwide Diseases Afflicting Humans. BecauseKramojNo ratings yet
- Drugs For Cardiovascular DiseasesDocument74 pagesDrugs For Cardiovascular Diseasesmjd13mjd4No ratings yet
- Hypertensive CrisisDocument23 pagesHypertensive CrisisJayarani Ashok100% (1)
- Anatomy & Physiologyc: Y CC CC CC C C CCC CCCCC C CDocument4 pagesAnatomy & Physiologyc: Y CC CC CC C C CCC CCCCC C CroothanngNo ratings yet
- Calixtro, Narrative HypertensionDocument2 pagesCalixtro, Narrative HypertensionKim SunooNo ratings yet
- HipotensiDocument12 pagesHipotensiAfdhalia Khairunnisa SyammarhanNo ratings yet
- Hypertensive Emergencies: Lakshmi Beeravolu, MDDocument32 pagesHypertensive Emergencies: Lakshmi Beeravolu, MDmecdarlingNo ratings yet
- داتا حيداشر محاضرة فسيولوجىDocument6 pagesداتا حيداشر محاضرة فسيولوجىMohaned MokhtarNo ratings yet
- HCVDDocument99 pagesHCVDMiguel CuevasNo ratings yet
- Heart Rate Blood PressureDocument128 pagesHeart Rate Blood PressureShubhra ShettyNo ratings yet
- Assessment of The Cardiovascular SystemDocument48 pagesAssessment of The Cardiovascular Systemkimberlyrwarren8817No ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument15 pagesHypertensiondeaNo ratings yet
- Approach To Patient With Syncope: Iman Sulaiman Al-HatmiDocument49 pagesApproach To Patient With Syncope: Iman Sulaiman Al-HatmiAlexandru CozmaNo ratings yet
- Hipertensi Berasal Dari Bahasa Latin Yaitu Hiper: Bab Ii Tinjauan TeoriDocument14 pagesHipertensi Berasal Dari Bahasa Latin Yaitu Hiper: Bab Ii Tinjauan Teorirangga barcokNo ratings yet
- Hypertension Group 9Document19 pagesHypertension Group 9Putri AuliaNo ratings yet
- K19 - Kuliah HipertensiDocument49 pagesK19 - Kuliah HipertensiRahma Dhita FitrianiNo ratings yet
- Hormone and Cardiovascular SystemDocument46 pagesHormone and Cardiovascular SystemTiyaTyraSidoraNo ratings yet
- Pathology 1016-Test 2-Path 3Document3 pagesPathology 1016-Test 2-Path 3Nicholas ObasiNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument65 pagesHypertensionImtiyazNo ratings yet
- Chapter 31 HypertensionDocument3 pagesChapter 31 HypertensionVen SemillaNo ratings yet
- Hypertension: Nursing Care PlansDocument7 pagesHypertension: Nursing Care PlansSamah AdnanNo ratings yet
- CVS Lect 6 Blood Pressure, PathophysiologyDocument13 pagesCVS Lect 6 Blood Pressure, PathophysiologySherwan R Shal100% (5)
- Cardiac PharmocologyDocument17 pagesCardiac Pharmocologysuhas.kandeNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho Physiology of HypertensionDocument2 pagesPa Tho Physiology of HypertensionBenedict SyNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure Lily ModifiedDocument57 pagesHeart Failure Lily ModifiedSabila FatimahNo ratings yet
- Mitchell 2005Document8 pagesMitchell 2005DianNo ratings yet
- Goal of The Cardiovascular System: Deliver Blood To All Parts of The BodyDocument20 pagesGoal of The Cardiovascular System: Deliver Blood To All Parts of The BodyNestor BalboaNo ratings yet
- Antihypertensive Drugs: Pharmacology For Cardiovascular SystemDocument74 pagesAntihypertensive Drugs: Pharmacology For Cardiovascular SystemGeraldineMoletaGabutinNo ratings yet
- Antihypertensive DrugsDocument78 pagesAntihypertensive DrugsOsannah Irish InsongNo ratings yet
- General Internal Medicine Hour: HypertensionDocument33 pagesGeneral Internal Medicine Hour: HypertensionRadley Jed C. PelagioNo ratings yet
- Hypertension: Yogi PR, MD, FihaDocument39 pagesHypertension: Yogi PR, MD, FihaPebryan RizkyNo ratings yet
- .SHOCK, Alice - 1704638750000Document12 pages.SHOCK, Alice - 1704638750000Nakintu AliceNo ratings yet
- Classification of HT Goal of Therapy Lifestyle Modifications Pharmacological Therapy Management HT ConclusionDocument82 pagesClassification of HT Goal of Therapy Lifestyle Modifications Pharmacological Therapy Management HT ConclusionBima Ewando KabanNo ratings yet
- LAS 4 Drugs For HypertensionDocument28 pagesLAS 4 Drugs For HypertensionMuhammad Haroon RazaNo ratings yet
- Hypertension: Jumarang, Kim Enrico M. BSN401 STI - Global CityDocument6 pagesHypertension: Jumarang, Kim Enrico M. BSN401 STI - Global CityKim Enrico JumarangNo ratings yet
- Inotropes and Vasoconstictor PackageDocument25 pagesInotropes and Vasoconstictor PackageYoussef MokdadNo ratings yet
- Blood PressureDocument58 pagesBlood PressureAyurveda PgNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Hipertensi IiDocument34 pagesTutorial Hipertensi Iikemuning nasutionNo ratings yet
- Patofisiologi HipertensiDocument18 pagesPatofisiologi HipertensiZebyyNo ratings yet
- Cardiac OutputDocument18 pagesCardiac OutputGauravSinghNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting in CVSDocument63 pagesDrugs Acting in CVSMeghan Norico Cristuta100% (1)
- Disorders of Blood Pressure Regulation - 10Document31 pagesDisorders of Blood Pressure Regulation - 10Cres Padua QuinzonNo ratings yet
- Hypertension ReviewerDocument9 pagesHypertension Reviewermecleo93No ratings yet
- Hypertension: Prepared By: Eden Marie D. Francisco Lorraine Nicolne B. CortejoDocument27 pagesHypertension: Prepared By: Eden Marie D. Francisco Lorraine Nicolne B. CortejoAlecNo ratings yet
- Cvs PharmacologyDocument75 pagesCvs PharmacologyTamratKelelegn100% (1)
- Porth2014 Apa 2018 Disorder of Blood Pressure RegulationDocument27 pagesPorth2014 Apa 2018 Disorder of Blood Pressure RegulationMumtaz MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Hypertension: S F Vascular SystemDocument12 pagesHypertension: S F Vascular SystemSNo ratings yet
- Alterations in Oxygen Transport: Hemoglobin Is TheDocument43 pagesAlterations in Oxygen Transport: Hemoglobin Is TheNiña MoradaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document16 pagesChapter 3Niña MoradaNo ratings yet
- Benefits Summaries-Health Dental VisionDocument6 pagesBenefits Summaries-Health Dental VisionNiña MoradaNo ratings yet
- Caregiver Benefits BrochureDocument8 pagesCaregiver Benefits BrochureNiña MoradaNo ratings yet
- Imogene King'S Goal Attainment Theory 1 Semester 2021-2022Document14 pagesImogene King'S Goal Attainment Theory 1 Semester 2021-2022Niña MoradaNo ratings yet
- Memorandum of Agreement For StudentsDocument2 pagesMemorandum of Agreement For StudentsNiña MoradaNo ratings yet
- Brent Berlin-Covert Categories and Folk TaxonomyDocument10 pagesBrent Berlin-Covert Categories and Folk TaxonomyKawita ChuachengNo ratings yet
- Uttar Pradesh Universities Act 1973Document73 pagesUttar Pradesh Universities Act 1973ifjosofNo ratings yet
- Noorul Islam Centre For Higher Education Noorul Islam University, Kumaracoil M.E. Biomedical Instrumentation Curriculum & Syllabus Semester IDocument26 pagesNoorul Islam Centre For Higher Education Noorul Islam University, Kumaracoil M.E. Biomedical Instrumentation Curriculum & Syllabus Semester Iisaac RNo ratings yet
- How To Read A Research PaperDocument16 pagesHow To Read A Research PaperHena Afridi100% (1)
- Simple Past TenseDocument6 pagesSimple Past Tenseanggun muslimahNo ratings yet
- Causing v. ComelecDocument13 pagesCausing v. ComelecChristian Edward CoronadoNo ratings yet
- 2013 03 01 Maurizio Di Noia PresentationDocument80 pages2013 03 01 Maurizio Di Noia PresentationRene KotzeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7: Identifying and Understanding ConsumersDocument3 pagesChapter 7: Identifying and Understanding ConsumersDyla RafarNo ratings yet
- 11v.jigisha Chaptear2Document53 pages11v.jigisha Chaptear2Anirban PalNo ratings yet
- Phrygian Gates and China Gates RecordingsDocument1 pagePhrygian Gates and China Gates RecordingsCloudwalkNo ratings yet
- Public ParticipationDocument17 pagesPublic ParticipationAinul Jaria MaidinNo ratings yet
- Task 1 Methods in Teaching LiteratureDocument2 pagesTask 1 Methods in Teaching LiteratureJaepiNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Latin Course Book I Vocabulary Stage 1 Stage 2Document3 pagesCambridge Latin Course Book I Vocabulary Stage 1 Stage 2Aden BanksNo ratings yet
- Literacy Block Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesLiteracy Block Lesson Planapi-286592038No ratings yet
- Gender Religion and CasteDocument41 pagesGender Religion and CasteSamir MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Mag Issue137 PDFDocument141 pagesMag Issue137 PDFShafiq Nezat100% (1)
- Kematian Di ICUDocument24 pagesKematian Di ICURahmida RahmyNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Climatic and Cultural Factors On Openings in Traditional Houses in MaharashtraDocument14 pagesThe Impact of Climatic and Cultural Factors On Openings in Traditional Houses in Maharashtracoldflame81No ratings yet
- Akhbar Al Fuqaha Narration - Non Raful Yadayn From Ibn Umar - Reply To Zubair Ali ZaiDocument15 pagesAkhbar Al Fuqaha Narration - Non Raful Yadayn From Ibn Umar - Reply To Zubair Ali ZaiAbdullah YusufNo ratings yet
- Iver Brevik, Olesya Gorbunova and Diego Saez-Gomez - Casimir Effects Near The Big Rip Singularity in Viscous CosmologyDocument7 pagesIver Brevik, Olesya Gorbunova and Diego Saez-Gomez - Casimir Effects Near The Big Rip Singularity in Viscous CosmologyDex30KMNo ratings yet
- Catalogue Raisonne, Occult Sciences, Vol 2, Astrological Books - F Leigh GardnerDocument194 pagesCatalogue Raisonne, Occult Sciences, Vol 2, Astrological Books - F Leigh GardnerWaterwind100% (4)
- 02 - Nature and Role of Science in SocietyDocument10 pages02 - Nature and Role of Science in SocietyMarcos Jose AveNo ratings yet
- IC HDL Lab ManualDocument82 pagesIC HDL Lab ManualRakshitha AngelNo ratings yet
- Operations Research Letters: Meichun Lin, Woonghee Tim Huh, Guohua WanDocument8 pagesOperations Research Letters: Meichun Lin, Woonghee Tim Huh, Guohua WanQuỳnh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Second Unit Test 2022: Radha Madhav Public School BareillyDocument4 pagesSecond Unit Test 2022: Radha Madhav Public School BareillyRaghav AgarwalNo ratings yet
- MQM100 MultipleChoice Chapter2Document9 pagesMQM100 MultipleChoice Chapter2Nakin KNo ratings yet
- TestFunda - Puzzles 1Document39 pagesTestFunda - Puzzles 1Gerald KohNo ratings yet
- Low Intermediate Korean Vocabulary and GrammarDocument10 pagesLow Intermediate Korean Vocabulary and GrammarTuong Van Nguyen100% (3)
- Abcs Booklet Kidney-Stones PDFDocument20 pagesAbcs Booklet Kidney-Stones PDFDendhy Dwi Handana SagitaNo ratings yet
- Law On Common Carriers: Laws Regulating Transportation CompaniesDocument3 pagesLaw On Common Carriers: Laws Regulating Transportation CompaniesLenoel Nayrb Urquia Cosmiano100% (1)