Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gene Technology Questions
Uploaded by
yasser farhanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Gene Technology Questions
Uploaded by
yasser farhanCopyright:
Available Formats
Gene technology questions
Explain the use for fluorescent or easily stained substances markers in
gene technology (Ms answer) 8 marks gained in this answer
- Gene markers are inserted downstream the promoter region
beside the gene of interest, so when the gene of interest is
transcribed the gene marker is transcribed along with it
- Where gene markers such as GFP OR GUC, have ability of
fluorescing a visible colour such as green, when they are
exposed to ultraviolet rays
- This is easily identifiable, facilitating identification of the
genetically modified organism
- Where they have no harmful effect on the host cell
Explain why plasmids re frequently used in gene technology
1. They have a small piece of circular DNA, so they do not
contribute much to the DNA of host cell
2. They have ability to replicate independently from the host
cell
3. Have large number of recognition sites on the DNA for
restriction enzyme
4. Where DNA can be easily cut and added using DNA ligase
5. It can be easily extracted from bacteria and easily taken in by
bacteria
6. Have ability to act as vectors transferring substances from
one organism to another
7. They possess gene markers, where they have gene for
antibiotic resistance
8. They carry a promoter to allow expression of desired gene
How bioinformatics help identify the gene as suitable form to insert in
human
1. Bioinformatics is a stores and process data on DNA and proteins
2. Where it can be compared with the human DNA
3. To make sure they are similar
Differences between gene expression in prokaryotes and eukaryotes
using eukaryotic and prokaryotic promoter
- The sequence of bases in eukaryotic promoters is different from
the sequence of bases in prokaryotic promoters
- As well as the RNA polymerase enzymes are different in
eukaryotic and prokaryotes
- So the RNA polymerase will not be able to recognize promoter
from different cell type
- Therefore transcription will not be initiated
Describe how the gene coding for human insulin can be obtained and
inserted into a plasmid vector 11 marks were gained in this answer
1. mRNA from B cells in the islets of Langerhans is extracted
2. where DNA primers are added to anneal to the mRNA as
reverse transcriptase can only work on double stranded
3. where reverse transcriptase enzyme uses the mRNA as a template
strand to form a cDNA single stranded
4. so the DNA polymerase is then used to create a complementary DNA
strand forming a double stranded DNA with sticky ends
5. where the plasmids are obtained using restriction endonuclease
enzyme
6. forming complementary sticky ends to the cDNA
7. the cDNA and the plasmid are mixed together
8. where the complementary sticky ends anneal to one another
forming hydrogen bonds
9. DNA ligase is then used to link the cDNA with the plasmid forming
phosphodiester bonds within the sugar phosphate back bone
Advantages of using theoretical models in research rather than
testing possible drugs in the laboratory
1. It is cheaper, as no drugs or materials are purchased or
produced
2. It is less time consuming as computer software modelling can
easily be stimulated and modified to suit experimental
changes
3. No need to test drugs on humans or animals
4. No need for purchase of laboratories equipment’s or
resources
Suggest how a verity of flower that has gene for survival in dark
conditions could be produced from the existing flowers WITHOUT
USING GENE TEGNOLOGY
1. By selective breeding
2. Crossing the flower with a flower that is well adapted in dry
conditions
3. And then choose the offspring that has gained the genes for
surving in dark conditions
4. Repeat this for several generations
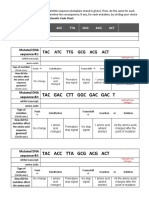
REMEMBER THAT THE RESTRICTION ENZYME HAS A
SPECIFIC RECOGNITION SITE, ya3ni it has a specific sequence of
bases at which it will cut
- What happens if a mutation (change is base sequence) occurs at
on of the sites which it recognizes
The restriction enzyme will no longer be able to
recognize it
Thus that part is not cut
So this will lead to DNA fragment cut of different
size
Explain why the production of memory cells prevents gene
therapy from working in long-term chronic conditions such as
CF, as the insertion of the virus (vector) causes an increase in the
memory cells production ?
1. The repeat of treatment, causes a more rapid immune response
2. So the target cells which express the new/healthy protein
become short lived as they will be attacked by the immune
system
3. Thus this decreases the gene expression on re administration
Describe the problems associated with an immune response using
other types of vectors
- Naked DNA
o Has to be injected into the target cell
o It could be rapidly broken down
- Viruses
o Small so only small amount of DNA can be carried
o Low probability of integration into host genome
o Could cause mutations in the host DNA ‘
- Liposomes
o Have low ability to insert DNA into host cell
You might also like
- Introduction To Genetic Analysis (12th Edition)Document819 pagesIntroduction To Genetic Analysis (12th Edition)Tatheer Zahra100% (7)
- Biotechnology: Quarter 3 - Module 3: Steps in Recombinant DNA TechnologyDocument24 pagesBiotechnology: Quarter 3 - Module 3: Steps in Recombinant DNA TechnologyPedrosa Nard75% (12)
- Recombinant DNA TechnologyDocument66 pagesRecombinant DNA TechnologySrishti SikariaNo ratings yet
- A Complete Guide To Gene Cloning From Basic To Advanced Springer PDFDocument177 pagesA Complete Guide To Gene Cloning From Basic To Advanced Springer PDFmesele tilahunNo ratings yet
- Recombinant DNA Lecture Notes - AP BioDocument10 pagesRecombinant DNA Lecture Notes - AP Bioshiva121294No ratings yet
- TranscriptionDocument100 pagesTranscriptionSreshttNo ratings yet
- Armamentarium Used For Oral SuregeryDocument20 pagesArmamentarium Used For Oral Suregeryyasser farhan100% (1)
- Genetic TechnologyDocument36 pagesGenetic TechnologyAnggraeni Kusuma WardaniNo ratings yet
- Biotech Q4 Weke 5 6Document23 pagesBiotech Q4 Weke 5 6Arins Zae BajamundiNo ratings yet
- Gene Technologies Allow The Study and Alteration of Gene Function Allowing A Better Understanding of Organism Function and The Design of New Industrial and Medical ProcessesDocument43 pagesGene Technologies Allow The Study and Alteration of Gene Function Allowing A Better Understanding of Organism Function and The Design of New Industrial and Medical ProcessesMaisarah HalimNo ratings yet
- Making Paper PlasmidsDocument5 pagesMaking Paper PlasmidsShamaica SurigaoNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2 Q3 - SLK - W1 - Recombinant DNADocument26 pagesGeneral Biology 2 Q3 - SLK - W1 - Recombinant DNANikkaa XOXNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Chapter 9 DNA-Based Technologies LectureDocument20 pagesUnit 3 Chapter 9 DNA-Based Technologies LectureNeedBooksDontSueNo ratings yet
- Bio Pat ExerciseDocument6 pagesBio Pat ExerciseElizabeth HariyantoNo ratings yet
- 2.7. Application of Reproduction and GeneticsDocument7 pages2.7. Application of Reproduction and GeneticsJenNo ratings yet
- R DNA TchnologyDocument32 pagesR DNA TchnologyReena GuptaNo ratings yet
- Handout Week 1Document8 pagesHandout Week 1Vien Lovelle Macanip Cabug-osNo ratings yet
- Genetic EngineeringDocument27 pagesGenetic EngineeringSeema QureshiNo ratings yet
- SBB 2102Document165 pagesSBB 2102Arshad Ali AnsariNo ratings yet
- Transgenic Fly FinalDocument7 pagesTransgenic Fly FinalJOHN THRONN DE JESUS100% (1)
- Gene CloningDocument18 pagesGene CloningLathikaNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1Document63 pagesGeneral Biology 1kenneth mendozaNo ratings yet
- CAIE Biology A-Level: Topic 19: Genetic TechnologyDocument7 pagesCAIE Biology A-Level: Topic 19: Genetic TechnologysanjidaNo ratings yet
- Biology Investigatory ProjectDocument14 pagesBiology Investigatory ProjectPulkit0% (1)
- Micro BiotechDocument28 pagesMicro Biotechreynaldo banaria jrNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology TechniquesDocument19 pagesMolecular Biology Techniquesmayanksangam703No ratings yet
- BiotechnologyDocument31 pagesBiotechnologyJijendarNo ratings yet
- 6 Recombinant DNA TechnologyDocument18 pages6 Recombinant DNA TechnologyJuan Sebastian100% (1)
- Dr. V. P. Wankhade: Vidyabharti College of Pharmacy, AmravatiDocument31 pagesDr. V. P. Wankhade: Vidyabharti College of Pharmacy, AmravatiNikita SharmaNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Molecular Cell Biology Eighth EditionDocument5 pagesSolution Manual For Molecular Cell Biology Eighth EditionChristianColemannsja100% (38)
- 18-08 Molecular Biology - Tools For Molecular BiologyDocument61 pages18-08 Molecular Biology - Tools For Molecular BiologyMichael John AguilarNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3.1 Learning Task WorksheetDocument4 pagesLesson 3.1 Learning Task WorksheetRayan abdallaNo ratings yet
- Gene Therapy - Gene Therapy Is An Experimental Technique That Uses Genes To Treat or Prevent Disease. What's NewDocument2 pagesGene Therapy - Gene Therapy Is An Experimental Technique That Uses Genes To Treat or Prevent Disease. What's Newbatutoy triaNo ratings yet
- Rdna TechnologyDocument22 pagesRdna TechnologySuresh MgNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5: Transgenesis and Genetically Modified Organisms Learning GoalsDocument8 pagesLecture 5: Transgenesis and Genetically Modified Organisms Learning GoalsAngelica SmithNo ratings yet
- Dna Recombinant Technology BiotechnologyDocument172 pagesDna Recombinant Technology BiotechnologytasniyanNo ratings yet
- NEW Genetic Probes and FingerprintingDocument4 pagesNEW Genetic Probes and FingerprintingCiwan SahinNo ratings yet
- Genetic EngineeringDocument13 pagesGenetic EngineeringbloomNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 SummerizedDocument6 pagesChapter 5 Summerizedمحمدحامد - Mohamed HamedNo ratings yet
- Cloning and Expression of Foreign Genes in E.ColiDocument12 pagesCloning and Expression of Foreign Genes in E.ColiADITYAROOP PATHAKNo ratings yet
- Recombinant DNA AssignmentDocument70 pagesRecombinant DNA AssignmentADITYAROOP PATHAKNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6: Recombinant DNA Technology: BiotechnologyDocument16 pagesLesson 6: Recombinant DNA Technology: BiotechnologybielaNo ratings yet
- BiotechDocument3 pagesBiotechminnahandrienneNo ratings yet
- Practice Exam AnswersDocument21 pagesPractice Exam AnswersGeraldine LeeNo ratings yet
- Summary NotesDocument6 pagesSummary NotesHannah IqbalNo ratings yet
- Recombinant DNA Technology in Todays Medicine-BIO PROJECTDocument8 pagesRecombinant DNA Technology in Todays Medicine-BIO PROJECTavik sadhuNo ratings yet
- C. Genetic Modification ObjectivesDocument9 pagesC. Genetic Modification ObjectivesFengyiNo ratings yet
- Recombinant DNA TechnologyDocument5 pagesRecombinant DNA TechnologyMonika KanojiaNo ratings yet
- King Joshua P. Adriano VIII-MendelDocument9 pagesKing Joshua P. Adriano VIII-MendelKing joshua adrianoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Genetic EngineeringDocument7 pagesLesson 2 Genetic EngineeringWynnie TorrecampoNo ratings yet
- Antisense TechnologyDocument3 pagesAntisense TechnologyNisha SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Genetics and BiotechnologyDocument43 pagesChapter 13 Genetics and BiotechnologyMUHAMMAD SAALIM100% (2)
- The GenomeDocument7 pagesThe GenomeCristian AlbaniNo ratings yet
- PSB 313 BIOINFORMATICS - DNA CLONING - Final - 2022Document25 pagesPSB 313 BIOINFORMATICS - DNA CLONING - Final - 2022Timson MantimNo ratings yet
- Recombinant DNA Technology - Definition, Steps, ApplicationsDocument7 pagesRecombinant DNA Technology - Definition, Steps, ApplicationsVikas PatreyNo ratings yet
- GRP 2 GeneticsDocument28 pagesGRP 2 GeneticsPaolo NaguitNo ratings yet
- 1 HBDocument8 pages1 HBMonkey LoverNo ratings yet
- Recombinant DNA Technology in Todays Medicine-BIO PROJECTDocument8 pagesRecombinant DNA Technology in Todays Medicine-BIO PROJECTavik sadhuNo ratings yet
- Evelyn Gabriela Gonzalez SimbañaDocument6 pagesEvelyn Gabriela Gonzalez SimbañaMOnzerratheManzzanitaSixxNo ratings yet
- 19-03 Tools For Molecular Biology and Medical Genetics - UnlockedDocument50 pages19-03 Tools For Molecular Biology and Medical Genetics - UnlockedMichael John AguilarNo ratings yet
- Gmo Lab Assignment Biol 1500Document3 pagesGmo Lab Assignment Biol 1500ahiNo ratings yet
- Primary and Stem Cells: Gene Transfer Technologies and ApplicationsFrom EverandPrimary and Stem Cells: Gene Transfer Technologies and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- 5 1 GerdDocument9 pages5 1 Gerdyasser farhanNo ratings yet
- Oral Surgery Mix QuestionsDocument1 pageOral Surgery Mix Questionsyasser farhanNo ratings yet
- Modified 2021 FALL WITH ANSWERDocument8 pagesModified 2021 FALL WITH ANSWERyasser farhanNo ratings yet
- Modified 2021 FALL WITH ANSWERDocument8 pagesModified 2021 FALL WITH ANSWERyasser farhanNo ratings yet
- 2018 FallDocument7 pages2018 Fallyasser farhanNo ratings yet
- A202001006 - PUTRI WAHYUNI - Primer3 Output (Primer3 - Results - Cgi Release 4.1.0)Document2 pagesA202001006 - PUTRI WAHYUNI - Primer3 Output (Primer3 - Results - Cgi Release 4.1.0)sasyaNo ratings yet
- Genetic Algorithm in Artificial IntelligenceDocument5 pagesGenetic Algorithm in Artificial IntelligenceAmit TiwariNo ratings yet
- Genetic Information and Protein SynthesisDocument22 pagesGenetic Information and Protein Synthesisjason balmasNo ratings yet
- A General Biology Ii 12 Q1M1.2Document4 pagesA General Biology Ii 12 Q1M1.2Adrian MontenegroNo ratings yet
- Biology (Midterm, Hki 2021-2022) 1Document4 pagesBiology (Midterm, Hki 2021-2022) 1Nhi TrầnNo ratings yet
- Bio-Worksheet-MutationsDocument3 pagesBio-Worksheet-MutationsEbrahimNo ratings yet
- Khan Et Al 2016 rbm20 Regulates Circular Rna Production From The Titin GeneDocument8 pagesKhan Et Al 2016 rbm20 Regulates Circular Rna Production From The Titin GeneAnkurNo ratings yet
- Feschotte 2007Document38 pagesFeschotte 2007Axel GómezNo ratings yet
- Microbiology 1.7 Bacterial Genetics Dr. EuropaDocument9 pagesMicrobiology 1.7 Bacterial Genetics Dr. EuropaRyn ShadowNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument4 pagesCell DivisionMhariane MabborangNo ratings yet
- Genetic Mutations Practice WorksheetDocument3 pagesGenetic Mutations Practice WorksheetNoah HolznerNo ratings yet
- Fruit Fly Exercise 5 Ver10Document3 pagesFruit Fly Exercise 5 Ver10Kieu MuNo ratings yet
- Introduction To XenobotsDocument7 pagesIntroduction To XenobotsRONAK LASHKARINo ratings yet
- Sources-and-Variation-of-Trees 2Document10 pagesSources-and-Variation-of-Trees 2Clariss MortejoNo ratings yet
- Mitosis vs. MeiosisDocument59 pagesMitosis vs. MeiosisJohn Paul NarvasNo ratings yet
- Upload 5Document1 pageUpload 5MaxNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis WorksheetDocument5 pagesProtein Synthesis WorksheetVanessa JuatcoNo ratings yet
- G S RajuDocument1 pageG S RajuAir DropNo ratings yet
- Sts Module 8 - BacuetesDocument5 pagesSts Module 8 - BacuetesbacuetesjustinNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 12 March 30 Biology Chapter 11 Biotechnology Principles and ProcessesDocument8 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 12 March 30 Biology Chapter 11 Biotechnology Principles and ProcessesRahul ThakurNo ratings yet
- AP Bio Genetics TestDocument2 pagesAP Bio Genetics TestHunterNo ratings yet
- Ploytene and Lampbrush ChromosomeDocument5 pagesPloytene and Lampbrush ChromosomeHimanshuNo ratings yet
- A Century of Hardy-Weinberg EquilibriumDocument9 pagesA Century of Hardy-Weinberg EquilibriumPriawanIndraNo ratings yet
- Lentiviral Vector AppDocument6 pagesLentiviral Vector AppShreeya BhatNo ratings yet
- Signature Assignment 6 PedigreeDocument4 pagesSignature Assignment 6 Pedigreeapi-709276885No ratings yet
- 4 MeiosisDocument14 pages4 MeiosisMary Joy ReyesNo ratings yet
- Widespread Somatic L1 Retrotransposition in Normal Colorectal EpitheliumDocument27 pagesWidespread Somatic L1 Retrotransposition in Normal Colorectal Epithelium6ypywxdqmkNo ratings yet