Professional Documents
Culture Documents
7.1 DNA Structure
Uploaded by
Kamilion FnOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
7.1 DNA Structure
Uploaded by
Kamilion FnCopyright:
Available Formats
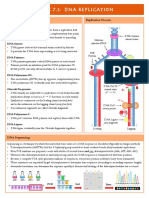
Topic 7.
1: DnA STRuCTuRE
Genetic Material
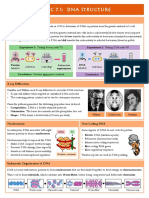
Hershey and Chase conducted experiments in 1952 to determine if DNA or proteins were the genetic material of a cell
It was previously known that viruses insert their genetic material into cells and so radioactively labeled viruses were prepared
• Viruses grown in 35S had radioactive proteins but did not transfer this radioactivity to bacterium (remained in supernatant)
• Viruses grown in 32P had radioactive DNA and did transfer this radioactivity to infected bacterium (found in pellet)
Experiment 1: Testing Protein with 35S Experiment 2: Testing DNA with 32P
300 300
Protein Radioactive DNA Radioactive
Infection Centrifuge labelled Infection Centrifuge pellet
labelled supernatant
Conclusion: Proteins not genetic material Conclusion: DNA is the genetic material
X-ray Diffraction
Franklin and Wilkins used X-ray diffraction to elucidate DNA structure
• X-rays will diffract when targeted at crystallised DNA molecules
• The scattering pattern created can be used to determine structure
From the patterns generated, the following properties were deduced: Wilkins
• Composition: DNA is a double-stranded molecule
• Orientation: The bases face inwards and the phosphates face out
• Shape: DNA forms a double helix (10 bases per twist) Wilkins Diffraction Franklin
Nucleosomes Non-Coding DNA
In eukaryotes, DNA associates with eight Some regions of DNA do not code for protein
DNA H1
histone proteins to form a nucleosome
• Satellite DNA (tandem repeats)
• Telomeres (chromosome ends)
Nucleosomes help to supercoil the DNA
• Introns (non-coding sequences)
• Makes DNA compact (better storage)
• Prevents DNA damage (less exposed) • Non-coding RNA genes
• Gene regulatory sequences
• Assists in cell division (more mobility)
• Involved in transcriptional regulation Histones (octamer) Tandem repeats are used in DNA profiling
Eukaryotic Organisation of DNA
DNA is bound with histone proteins to form nucleosomes that are then linked together to form strings of chromatosomes
These coil to form solenoids, which condense into 30 nm fibres, before being compressed and folded into chromatin
DNA Nucleosome Chromatosome Solenoid 30 nm fibre Chromatin Chromosome
You might also like
- Topic 7.1: Dna Structure: Genetic MaterialDocument1 pageTopic 7.1: Dna Structure: Genetic Materialikha nilaNo ratings yet
- Bio Ninja Unit 7 MergedDocument4 pagesBio Ninja Unit 7 Mergedshwooby shawoobyNo ratings yet
- Chromosome, DNA, RNADocument5 pagesChromosome, DNA, RNAShahrat Farsim ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Dna The Code of Life Notes 2019Document12 pagesDna The Code of Life Notes 2019mthokozisiandile09No ratings yet
- DNA PackagingDocument25 pagesDNA PackagingChamara ChathurangaNo ratings yet
- Genetics Lecture 2 - DNA and Chromosome Structure PDFDocument58 pagesGenetics Lecture 2 - DNA and Chromosome Structure PDFMarlee SandersonNo ratings yet
- Molecular GeneticsDocument15 pagesMolecular GeneticsBiruk SamuelNo ratings yet
- Nucliec AcidDocument5 pagesNucliec AcidJoyce Fraulein T. LejosNo ratings yet
- Molecular Basis of InheritanceDocument23 pagesMolecular Basis of InheritanceParthNo ratings yet
- Summary OCPEG and Cancer 2018Document18 pagesSummary OCPEG and Cancer 2018Jonathan Wee Cheng YangNo ratings yet
- DNA Isolation From Onion, Ultraviolet Measurement of Isolated DNA and Chemical Characterization of DNADocument6 pagesDNA Isolation From Onion, Ultraviolet Measurement of Isolated DNA and Chemical Characterization of DNAmarilujaneNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Molecular Biology Lecture 1 27-10-2020Document50 pagesIntroduction To Molecular Biology Lecture 1 27-10-2020Tanveer KhanNo ratings yet
- Genome OrganizationDocument19 pagesGenome OrganizationChristin Natalia KalembangNo ratings yet
- Genome Sequencing: Jutta Marzillier, PH.DDocument56 pagesGenome Sequencing: Jutta Marzillier, PH.DNada MaizaNo ratings yet
- Genetics Midterm Exam ReviewerDocument4 pagesGenetics Midterm Exam ReviewerChristianAvelinoNo ratings yet
- 1.2 ReviewDocument3 pages1.2 ReviewAaryan ThavaranNo ratings yet
- BIOTECHNOLOGY-principles and ProcessesDocument53 pagesBIOTECHNOLOGY-principles and ProcessesColour Copy100% (1)
- BTN222-L2-DNA and Genome STR-2019Document43 pagesBTN222-L2-DNA and Genome STR-2019rafiya IsmailNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyDocument33 pagesLesson 5 - Central Dogma of Molecular BiologySherwin YenogacioNo ratings yet
- Prokaryoticneukaryoticgenome 160514180458 PDFDocument7 pagesProkaryoticneukaryoticgenome 160514180458 PDFrahul ssgiNo ratings yet
- Molecular GeneticsDocument7 pagesMolecular GeneticsSiti Hajar RevillaNo ratings yet
- Dna - NotesDocument3 pagesDna - NotesJB - 10BR 740323 Harold M Brathwaite SSNo ratings yet
- Les On ScienceDocument44 pagesLes On ScienceDanNo ratings yet
- Discussion On NucleotidesDocument2 pagesDiscussion On NucleotidesEyob TeferaNo ratings yet
- Dna StructureDocument32 pagesDna StructureHONLETH ROMBLONNo ratings yet
- DNA, RNA, and The Flow of InformationDocument31 pagesDNA, RNA, and The Flow of InformationSasa AbassNo ratings yet
- Organisation of Genomes - Eukaryotes: Non-Dividing Cells Dividing CellsDocument17 pagesOrganisation of Genomes - Eukaryotes: Non-Dividing Cells Dividing CellsTimothy HandokoNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology Principle and Processes-NotesDocument4 pagesBiotechnology Principle and Processes-NotesRohan MohantyNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Pre FinalsDocument31 pagesBiochemistry Pre FinalsArah Lyn ApiagNo ratings yet
- What You'll Learn: You Will Distinguish Among Different Types of MutationsDocument35 pagesWhat You'll Learn: You Will Distinguish Among Different Types of MutationsSeemaNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules - NADocument45 pagesBiomolecules - NAFake WalaNo ratings yet
- Notes Chap 06Document21 pagesNotes Chap 06umamahfarooq75No ratings yet
- Unit8 DnareplicationandtranscriptionDocument27 pagesUnit8 Dnareplicationandtranscriptionkramesh55107No ratings yet
- 07 - What Are GenesDocument11 pages07 - What Are GenesMarcelline WijayaNo ratings yet
- Week 1 DNADocument28 pagesWeek 1 DNAHonleth Jheney MamarilNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 3rd QuarterDocument6 pagesGen Bio 3rd QuarterzafmustaphaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Evolution and DNA ReplicationDocument2 pagesLecture 1 - Evolution and DNA ReplicationStacy Ann VergaraNo ratings yet
- Molecular GeneticsDocument14 pagesMolecular GeneticsYitbarek TesfayeNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids NOTESDocument8 pagesNucleic Acids NOTESelaineNo ratings yet
- 4 Bioc1600-DnaDocument68 pages4 Bioc1600-DnaKellyNo ratings yet
- Quiz Microbial Genetics TortoraDocument17 pagesQuiz Microbial Genetics TortorapascabioNo ratings yet
- Dnareplication 151218084840Document145 pagesDnareplication 151218084840RIYA MUNJALNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7: Nucleic Acids: 7.1: DNA Structure and ReplicationDocument5 pagesChapter 7: Nucleic Acids: 7.1: DNA Structure and ReplicationMariamNo ratings yet
- BIOL1003 - Cell StructureDocument10 pagesBIOL1003 - Cell StructuresilentscreamsofloveNo ratings yet
- DNA Structure and ReplicationDocument12 pagesDNA Structure and ReplicationJhune Dominique GalangNo ratings yet
- Bio 2 Exam 2Document23 pagesBio 2 Exam 2Msp Glam4evasNo ratings yet
- 01 04 Molecular Biotechnology Sitte (NXP) PDFDocument17 pages01 04 Molecular Biotechnology Sitte (NXP) PDFEduardo EmeriqueNo ratings yet
- The Dna: Learning Objectives (L.O.)Document13 pagesThe Dna: Learning Objectives (L.O.)masa bedaNo ratings yet
- Molecular Basis of InheritanceDocument21 pagesMolecular Basis of InheritancevidushivbpsNo ratings yet
- RDNA and Genomics 2Document159 pagesRDNA and Genomics 2Ru ConduitNo ratings yet
- Biok - 7.1 - DNA - Structure - and Replication - AHLDocument37 pagesBiok - 7.1 - DNA - Structure - and Replication - AHLZoya PadaniyaNo ratings yet
- DNA Synthesis and SequenceDocument6 pagesDNA Synthesis and SequenceInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology100% (1)
- L2 Genome OrganizationDocument18 pagesL2 Genome OrganizationGaayithri RNo ratings yet
- Hsslive XII Botany CH 11 Minhad NewDocument4 pagesHsslive XII Botany CH 11 Minhad NewAKUULLLNo ratings yet
- DNA Structure and FunctionDocument42 pagesDNA Structure and FunctionBenjamin Fernandez Jr.No ratings yet
- Genomics-Lectures 1 To 8 - 2023 PDFDocument110 pagesGenomics-Lectures 1 To 8 - 2023 PDFAhire Ganesh Ravindra bs20b004No ratings yet
- Tools of Recombinant Dna TechnologyDocument3 pagesTools of Recombinant Dna Technologyamora eliNo ratings yet
- The DNA Detective: Unraveling the Mysteries of Our Genetic CodeFrom EverandThe DNA Detective: Unraveling the Mysteries of Our Genetic CodeNo ratings yet
- (Amaranthus Tricolor L.) TERHADAP INDEKS LEE DAN MASSA LEMAKDocument9 pages(Amaranthus Tricolor L.) TERHADAP INDEKS LEE DAN MASSA LEMAKFery JuliawanNo ratings yet
- Mystery of The Crooked Cell:: Investigate Sickle Cell Anemia Using Gel ElectrophoresisDocument29 pagesMystery of The Crooked Cell:: Investigate Sickle Cell Anemia Using Gel Electrophoresisschumon25No ratings yet
- Sessional 2 QP 2018 Even SemDocument2 pagesSessional 2 QP 2018 Even SemPrajwal KunderNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Metabolism in PlantsDocument40 pagesCarbohydrate Metabolism in Plantsguswinda alvaniNo ratings yet
- Biological Oxidation ETCDocument37 pagesBiological Oxidation ETCsanofazal786No ratings yet
- Perhitungan IodimetriDocument3 pagesPerhitungan IodimetriMariahNo ratings yet
- ATP ADP CycleDocument20 pagesATP ADP CycleButz AnthonyNo ratings yet
- LipidsDocument13 pagesLipidsalianaNo ratings yet
- Bioinformatics LAb ReportDocument7 pagesBioinformatics LAb ReportBriana Halbert100% (3)
- Multiple Choice Questions: 1. GlycolysisDocument4 pagesMultiple Choice Questions: 1. GlycolysisNguyễn TânNo ratings yet
- PCR (Title Aim Intro)Document4 pagesPCR (Title Aim Intro)Abby YongNo ratings yet
- Electron Transport ChainDocument9 pagesElectron Transport Chainalokesh1982100% (1)
- Hsslive-11-B - Biotech - Principles, Previous Yr HSE N Model QuestionsDocument3 pagesHsslive-11-B - Biotech - Principles, Previous Yr HSE N Model Questionsadithya4rajNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid: Group 2 ReportDocument20 pagesNucleic Acid: Group 2 ReportDiePalAPieNo ratings yet
- Enzymes: Anushree ChaturvediDocument39 pagesEnzymes: Anushree ChaturvediDeepal ShahNo ratings yet
- CARBOHYDRATES of Biochemistry Lec # 3-6Document34 pagesCARBOHYDRATES of Biochemistry Lec # 3-6RashidNo ratings yet
- 1415 BioMolecules Study GuideDocument2 pages1415 BioMolecules Study GuideJoy Mazo FaderagaoNo ratings yet
- Protiens and Amino AcidsDocument9 pagesProtiens and Amino AcidsMUHAMMAD SHOAIB MUNAWARNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of AntimicrobialsDocument15 pagesMechanism of AntimicrobialsHassan.shehri100% (6)
- Amoxan 500 MG Intermoxil 500 MG Lapimox 500 MG Opimox 500 MGDocument16 pagesAmoxan 500 MG Intermoxil 500 MG Lapimox 500 MG Opimox 500 MG20.022 Ni Putu Ayu MelcianaNo ratings yet
- KARYA ILMIAH KERIPIK MAWAR SalinanDocument13 pagesKARYA ILMIAH KERIPIK MAWAR SalinanNanda BasNo ratings yet
- Oxidative Stress and AntioxidantsDocument34 pagesOxidative Stress and AntioxidantsTauseefNo ratings yet
- Notes About BiologyDocument81 pagesNotes About BiologyRichard Coffey100% (1)
- 7 Krebs Cycle # ,!, - $ Tricarboxylic CycleDocument15 pages7 Krebs Cycle # ,!, - $ Tricarboxylic CycleHasn HsanNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics of Oligonucleotide Duplex MeltingDocument7 pagesThermodynamics of Oligonucleotide Duplex MeltingMauricio AyalaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 17 The Metabolism An OverviewDocument10 pagesCHAPTER 17 The Metabolism An Overview楊畯凱No ratings yet
- Protein Denaturation Notes - July 2021Document4 pagesProtein Denaturation Notes - July 2021BOR KIPLANGAT ISAACNo ratings yet
- BIOA01 Lab 5 PCR GMO-F2022Document1 pageBIOA01 Lab 5 PCR GMO-F2022Naiyara AranaNo ratings yet
- S.y.bsc. Biotechnology (BT 211 & 212) Question BankDocument24 pagesS.y.bsc. Biotechnology (BT 211 & 212) Question BankShahab SaqibNo ratings yet
- Biosynthesis of Purine & PyrimidinesDocument28 pagesBiosynthesis of Purine & PyrimidinesEmm NomanNo ratings yet