Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DENGUE HEMORRHAGIC FEVER NURSING CARE
Uploaded by
Michaela ArellanoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
DENGUE HEMORRHAGIC FEVER NURSING CARE
Uploaded by
Michaela ArellanoCopyright:
Available Formats
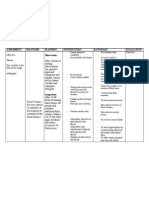
ASSESMENT
11 Year old male pedia patient with Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever rushed in the E.R
SUBJECTIVE :
Nahihilo po ako, Nauuhaw at nanlalata as verbalized by the client. [ Means, I AM DIZZY, THIRSY AND I FEEL SO WEAK" ]
OBJECTIVE :
+ Sunken, Dry eyes + Pale palpebral conjunctiva + Dry lips and mouth +Prolonged Capillary refill time [ 7 seconds ] + Poor skin turgor + Rapid, Thready Pulse
Heart rate 110 Bpm RR 21 Bpm BP 90/60 Temp 39.2 C
DIAGNOSIS Fluid Volume Deficit R/T Intravascular to Extravascular Plasma Leakage Secondary to Increase in Vascular Permeability.
OBJECTIVES
SHORT TERM: After an hour of spontaneous fluid replacement, Patient will gradually abate signs and symptoms of fluid volume deficiency as evidenced by increasing blood pressure, decreasing heart rate, improving capillary refill time preferably below 5s and an improving skin turgor.
{ LONG TERM : After 2 days of nursing intervention, Patient will maintain fluid volume at an amount optimum for normal functioning as evidenced by a normal urine output with normal specific gravity, stable vital signs, moist mucus membrane, good capillary refill time and resolution of third spacing.}
INTERVENTION 1. Anticipate fluid replacement by preparing peripheral route for IV transfusion.
2. Obtain doctors order for IV therapy As soon as possible to replace fluid volume loss IMMEDIATELY.
3. Encourage fluid intake by placing a glass of juice or water within the patients reach.
4. Monitor total fluid intake and output every 2 hours.
5. Watch trends in output for 3 days; include all routes of intake and output and note color and specific gravity of urine.
6. Monitor vital signs of clients with deficient fluid volume every hour. Observe for decreased pulse pressure first, then hypotension, tachycardia, decreased pulse volume, and increased or decreased body temperature
RATIONALE
1. IV transfusion is a dependent nursing function. Anticipate doctors order by providing route for IV fluid replacement to save time and decrease risk for complications.
2. IV is considered as MEDICATION. Before initiating IV Replacement therapy, make sure that there is a current standing or verbal order from the doctor.
3. placing a glass of water or juice at patients bedside is the best way to encourage fluid intake. DHF patient are always thirsty prior to the defervescence stage.
4. A urine output of .5 ml per kg/hr is insufficient for normal renal function and indicates onset of renal damage
5. Monitoring for trends for 2 to 3 days gives a more valid picture of the client's hydration status than monitoring for a shorter period. Dark-colored urine with increasing specific gravity reflects increased urine concentration.
6. To monitor and assess clients response and progress in the fluid replacement therapy.
EVALUATION
SHORT TERM : After an hour of intervention, Patients BP increased to 100/70, Tachycardia resolved as evidenced by a normal HR of 80bpm. CRT decreased from 7s down to 4s and there is a noticeable improvement in the clients skin turgor.
{LONG TERM : 2 Days after a series of nursing care, the patient manifested a normal urine output of 30ml per hour with a specific gravity of 1.011. Stable vital signs were monitored and recorded. CRT was recorded normal. Physical assessment revealed no sign of fluid deficit.}
Subjective: (none) Objective: Decreased WBC Decreased platelet Decreased HgB Decreased capillary refill time Dysrhythmias Altered LOC Fever Chills Diaphoresis
Ineffective tissue perfusion related to decreased HgB concentration in the blood secondary to DHF 1
Short Term: After 4 hours of NI, the pt will demonstrate behaviours to improve circulation. Long Term:
Establish Rapport Monitor Vital Signs Assess patients condition
To gain pts trust To obtain baseline data To assess contributing factors For comparison with current findings To identify alterations from normal To identify / determine adequate perfusion To determine presence of thrombus formation To determine risk of anemia To promote circulation To promote comfort & decrease tissue O2 demand To decrease cardiac workload To enhance
The pt shall have demonstrated behaviours to improve circulation The pt shall have demonstrated increased perfusion as appropriate
Note customary After 4 days of baseline data NI, the pt will demonstrate Determine increased presence of perfusion as dysrhythmias appropriate Perform blanch test Check for Homans sign Note presence of bleeding Elevate HOB Encourage quiet & restful atmosphere Instruct to avoid tiring activities Encourage light ambulation Encourage use of relaxation techniques
Administer medications
venous return To decrease tension and anxiety level To treat underlying cause
You might also like
- Nursing Care Plan For Acute Gastrointestinal HemorrhageDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Acute Gastrointestinal HemorrhageCyrus De Asis92% (25)
- Eclampsia Nursing Care Plan - Altered Tissue PerfusionDocument2 pagesEclampsia Nursing Care Plan - Altered Tissue PerfusionCyrus De Asis84% (32)
- NCP Format 3 (CKD Chronic Kidney Disease DM Diabetes Mellitus Nephropathy)Document4 pagesNCP Format 3 (CKD Chronic Kidney Disease DM Diabetes Mellitus Nephropathy)John Christopher Celestino100% (10)
- NCP For DehydrationDocument3 pagesNCP For Dehydrationpeter_degamo200025% (4)
- Nursing Diagnosis of Fluid Volume ExcessDocument4 pagesNursing Diagnosis of Fluid Volume ExcessTamil Villardo100% (2)
- NCP - Fluid RetentionDocument3 pagesNCP - Fluid RetentionMichelle Teodoro100% (1)
- Hypovolemic Shock Case StudyDocument6 pagesHypovolemic Shock Case StudyJenn GallowayNo ratings yet
- SAMPLE NCP For Diabetes InsipidusDocument3 pagesSAMPLE NCP For Diabetes InsipidusClancy Anne Garcia Naval50% (2)
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument9 pagesDecreased Cardiac OutputChinita Sangbaan75% (4)
- CHF Concept MapDocument4 pagesCHF Concept MapLisaSanders99No ratings yet
- Orthopedic Inpatient Protocols: A Guide to Orthopedic Inpatient RoundingFrom EverandOrthopedic Inpatient Protocols: A Guide to Orthopedic Inpatient RoundingNo ratings yet
- Placenta Previa NCP 1Document6 pagesPlacenta Previa NCP 1Faye Nervanna Alecha Alferez83% (18)
- NCP2 - DengueDocument4 pagesNCP2 - DengueSummer SuarezNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument28 pagesNursing Care PlanChristine Karen Ang Suarez67% (3)
- NCPDocument15 pagesNCPCamille PinedaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume Excess CRFDocument3 pagesFluid Volume Excess CRFDana Fajardo RezanoNo ratings yet
- NCP-Case Presentation (CHF)Document4 pagesNCP-Case Presentation (CHF)Jessamine EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Impaired kidney function nursing careDocument21 pagesImpaired kidney function nursing careKate ManalastasNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Goal Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Goal Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationVher SisonNo ratings yet
- Manage Fluid Volume Excess in Renal FailureDocument3 pagesManage Fluid Volume Excess in Renal FailureMichael Baylon DueñasNo ratings yet
- CHRONIC HEART FAILURE CASE STUDYDocument12 pagesCHRONIC HEART FAILURE CASE STUDYMary Cris CanonNo ratings yet
- NCP - Deficient Fluid VolumeDocument2 pagesNCP - Deficient Fluid VolumerobbychuaNo ratings yet
- Mrs. MM Nursing Care PlanDocument34 pagesMrs. MM Nursing Care PlanIsobel Mae JacelaNo ratings yet
- NCP - Altered Tissue PerfusionDocument2 pagesNCP - Altered Tissue PerfusionLeigh Kristel Andrion0% (1)
- Fluid Volume DeficitDocument2 pagesFluid Volume DeficitRuby AnneNo ratings yet
- Impaired Tissue PerfusionDocument2 pagesImpaired Tissue PerfusionLyka Mae Imbat - PacnisNo ratings yet
- NCP For Nephrotic SyndromeDocument2 pagesNCP For Nephrotic SyndromeLee Jenny100% (5)
- Actual NCPDocument3 pagesActual NCPMabz BoholNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care for Patients with Decreased Perfusion and HyperthermiaDocument3 pagesNursing Care for Patients with Decreased Perfusion and HyperthermiaIvan Liquiran AvenadoNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume DeficitDocument12 pagesFluid Volume DeficitKersee GailNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care Planapi-315741653No ratings yet
- NCP 3 DEFICIT IN FLUID VOLUMEDocument2 pagesNCP 3 DEFICIT IN FLUID VOLUMEGenEsis CarandangNo ratings yet
- Postpartum Hemorrhage Nursing CareDocument3 pagesPostpartum Hemorrhage Nursing CareClaire Canapi BattadNo ratings yet
- Septic Shock Nursing Assessment and ManagementDocument6 pagesSeptic Shock Nursing Assessment and ManagementJenn GallowayNo ratings yet
- Reducing Hematoma Through Comfort MeasuresDocument10 pagesReducing Hematoma Through Comfort MeasuresKier Jucar de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Goal Intervention Rationale Expected Outcome SubjectiveDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Goal Intervention Rationale Expected Outcome SubjectiveKeith MirasolNo ratings yet
- Pre-surgery fluid monitoringDocument1 pagePre-surgery fluid monitoringkrizzia_anchetaNo ratings yet
- CKD Patient at Risk for Respiratory, Fluid and Skin IssuesDocument3 pagesCKD Patient at Risk for Respiratory, Fluid and Skin IssuesMichael Baylon Dueñas100% (2)
- NCP - Fluid Volume DeficitDocument2 pagesNCP - Fluid Volume DeficitPatrice LimNo ratings yet
- AssessmentDocument2 pagesAssessmentWajiha Esmula TiuNo ratings yet
- Deficient Fluid VolumeDocument1 pageDeficient Fluid VolumeSheila ErpeloNo ratings yet
- Course Task Week 7 NCMB 312Document6 pagesCourse Task Week 7 NCMB 312Angie BaylonNo ratings yet
- NCP AnemiaDocument1 pageNCP Anemiamashup100% (3)
- Group 5 - Hemodialysis - Chronic Kidney FailureDocument31 pagesGroup 5 - Hemodialysis - Chronic Kidney FailureKimberly Abella CabreraNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume Deficit Secondary To Post Partum HemorrhageDocument3 pagesFluid Volume Deficit Secondary To Post Partum HemorrhagePatricia Franco100% (1)
- Lung Edema Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageLung Edema Nursing Care PlanTere GuillermoNo ratings yet
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument4 pagesDecreased Cardiac OutputAdnan Khan100% (1)
- NCPINTRA1Document3 pagesNCPINTRA1Maria Rhodora PetajenNo ratings yet
- DengueDocument14 pagesDengueKarenn Joy Concepcion OctubreNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume DeficitDocument3 pagesFluid Volume DeficitDan Gerald Alcido SalungaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Mnemonics: The Ultimate Tips and Notes For NursesFrom EverandNursing Mnemonics: The Ultimate Tips and Notes For NursesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- A Simple Guide to Hypovolemia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Hypovolemia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolytes for Nursing StudentsFrom EverandFluid and Electrolytes for Nursing StudentsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (12)
- Renal Diet Cookbook: The Complete Low Sodium, Low Potassium, Healthy Kidney Cookbook to Improve your Kidney Function and Avoid DialysisFrom EverandRenal Diet Cookbook: The Complete Low Sodium, Low Potassium, Healthy Kidney Cookbook to Improve your Kidney Function and Avoid DialysisNo ratings yet
- Soak It In: Hydrotherapy Treatments In 20 Minutes or Less for Health and BeautyFrom EverandSoak It In: Hydrotherapy Treatments In 20 Minutes or Less for Health and BeautyNo ratings yet