Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Async and Await
Uploaded by
mohammed0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views8 pagesAsync functions return a Future and execute asynchronously. Await expressions suspend execution of an async function until a Future is complete. Dart is single-threaded so Futures represent asynchronous operations that produce a result.
Original Description:
Flutter
Original Title
Async and await
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAsync functions return a Future and execute asynchronously. Await expressions suspend execution of an async function until a Future is complete. Dart is single-threaded so Futures represent asynchronous operations that produce a result.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views8 pagesAsync and Await
Uploaded by
mohammedAsync functions return a Future and execute asynchronously. Await expressions suspend execution of an async function until a Future is complete. Dart is single-threaded so Futures represent asynchronous operations that produce a result.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 8
Async and await
The async and await approaches in Dart are very similar to
other languages, which makes it a comfortable topic to grasp
for those who have used this pattern before. However, even if
you don’t have experience with asynchronous programming
using async/await, you should find it easy to follow along here
:Async functions
Functions form the base of asynchronous programming. These
async functions have async modifiers in their body. Here is an
example of a general async function below:
When an async function is called, a Future is immediately
returned and the body of the function is executed later. As the
body of the async function is executed, the Future returned by
the function call will be completed along with its result. In the
above example, calling demo() results in the Future.
Any functions you want to run asynchronously need to have
the async modifier added to it. This modifier comes right
after the function signature, like this:
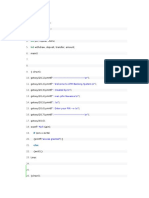
void hello () async {
print (“………………..”)
}
Typically, the function you want to run asynchronously would have
some expensive operation in it like file I/O (an API call to a RESTful
service).
:Await expressions
Await expressions makes you write the asynchronous code almost
as if it were synchronous. In general, an await expression has the
form as given below:
void main() async {
await hello();
print('all done');
}
Typically, it is an asynchronous computation and is expected to evaluate to a
Future. The await expressions evaluate the main function, and then suspends
the currently running function until the result is ready–that is, until the Future
has completed. The result of the await expression is the completion of the
Future.
:Await expressions
•There are two important things to grasp concerning the block of code
above. First off, we use the async modifier on the main method because
we are going to run the hello() function asynchronously.
•Secondly, we place the await modifier directly in front of our
asynchronous function. Hence, this is frequently referred to as the
async/await pattern.
•Just remember, if you are going to use await, make sure that both the
caller function and any functions you call within that function all use
the async modifier.
:Futures
Dart is a single-threaded programming language. Future<T>
object represents the result of an asynchronous operation
which produces a result of type T. If the result is not usable
value, then the future’s type is Future<void>. A Future
represents a single value either a data or an error
asynchronously
There are 2 ways to handle Futures:
•Using the Future API
•Using the async and await operation.
:Example
String createOrderMessage() {
var order = fetchUserOrder();
return 'Your order is: $order';
}
Future<String> fetchUserOrder() =>
// Imagine that this function is more complex and slow.
Future.delayed(
const Duration(seconds: 2),
() => 'Large Latte',
);
You might also like
- OrcafAPI ManualDocument39 pagesOrcafAPI ManualgenmikNo ratings yet
- Allen Bradley Low Voltage Switchgear and ControlgearDocument176 pagesAllen Bradley Low Voltage Switchgear and Controlgearbsunanda01No ratings yet
- Tamás Sallai - Asynchronous Programming Patterns in Javascript - How To Use Async - Await and Promises To Solve Programming Problems-Leanpub (2021)Document135 pagesTamás Sallai - Asynchronous Programming Patterns in Javascript - How To Use Async - Await and Promises To Solve Programming Problems-Leanpub (2021)jial171979No ratings yet
- Best Practices in Asynchronous Programming PDFDocument7 pagesBest Practices in Asynchronous Programming PDFnikolatesla2009No ratings yet
- Basics of CDocument47 pagesBasics of CVishwajit SonawaneNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: The Basics of C++:: Code::Blocks With Mingw G++ Xcode Compatibility IssuesDocument39 pagesLesson 1: The Basics of C++:: Code::Blocks With Mingw G++ Xcode Compatibility IssuesTanveer us zaman100% (1)
- Nemio MX Product Data PDFDocument12 pagesNemio MX Product Data PDFWellington TrajanoNo ratings yet
- Async - DartDocument3 pagesAsync - DartShahid AliNo ratings yet
- W3 - P1 - Asynchronous ProgrammingDocument28 pagesW3 - P1 - Asynchronous ProgrammingMuhammad Umer FarooqNo ratings yet
- Day5-3-Asynchronous Programming - 2 Hours - 080220Document5 pagesDay5-3-Asynchronous Programming - 2 Hours - 080220noorfatima.okitNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - WebDocument16 pagesChapter 5 - WebMuzammil AhmadNo ratings yet
- Introduction To C: Getting Set Up - Finding A C CompilerDocument4 pagesIntroduction To C: Getting Set Up - Finding A C CompilerVishalSahNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: The Basics of C++Document27 pagesLesson 1: The Basics of C++Shashi Shekar KnNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Basic of C++ Lesson 1 enDocument7 pagesTutorial Basic of C++ Lesson 1 enqrembiezsNo ratings yet
- 1 Introduction To CDocument5 pages1 Introduction To CPraveen PandeyNo ratings yet
- Swift Tutorials: Shubham SinghDocument10 pagesSwift Tutorials: Shubham SinghUmut SeverNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Python Programming-2Document8 pagesAn Introduction To Python Programming-2j.poldermanNo ratings yet
- Getting Set Up - C++ Compilers: Advanced Compiler DetailsDocument6 pagesGetting Set Up - C++ Compilers: Advanced Compiler Detailskarlooz1No ratings yet
- Lesson 1: The Basics of C++Document54 pagesLesson 1: The Basics of C++Leandro SumidaNo ratings yet
- Turbo C/C++ For Windows 7/8/8.1 and 10 32/64 Bit : CodeplexDocument4 pagesTurbo C/C++ For Windows 7/8/8.1 and 10 32/64 Bit : Codeplexrahul100% (1)
- Advanced Asynchronous Techniques With FastAPI AsyncDocument10 pagesAdvanced Asynchronous Techniques With FastAPI AsyncLeonNo ratings yet
- Introduction To C Getting Set Up - Finding A C Compiler: Code::Blocks With Mingw GCC XcodeDocument12 pagesIntroduction To C Getting Set Up - Finding A C Compiler: Code::Blocks With Mingw GCC Xcodeagbo_36No ratings yet
- Lesson 1: The Basics of C++: Getting Set Up - C++ CompilersDocument5 pagesLesson 1: The Basics of C++: Getting Set Up - C++ CompilersSagar VermaNo ratings yet
- AsyncDocument91 pagesAsyncJesé AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- CH 4Document41 pagesCH 4ERMIAS AmanuelNo ratings yet
- Intro To CDocument6 pagesIntro To CAnonymous aIGVjfbeMNo ratings yet
- C ClassDocument5 pagesC Classb.eswarNo ratings yet
- CC2 ReviewerDocument10 pagesCC2 ReviewerApril Abata Aloya ElcaNo ratings yet
- The Best Way To Learn The C Programming Language Is by EXAMPLE!Document7 pagesThe Best Way To Learn The C Programming Language Is by EXAMPLE!designermsNo ratings yet
- Asynchrony in C#5.0Document24 pagesAsynchrony in C#5.0sudu22No ratings yet
- Lecture Note 1-10Document30 pagesLecture Note 1-10Shayan AbagnaleNo ratings yet
- C TutorialDocument83 pagesC Tutorialsumit7153100% (1)
- Imperia Embedded1Document143 pagesImperia Embedded1Vaibhav SinghNo ratings yet
- PG Python Units I, II, IIIDocument81 pagesPG Python Units I, II, IIIkasaganikumar20No ratings yet
- NewtonDocument73 pagesNewtonNewton NyathiNo ratings yet
- Pass StatementDocument8 pagesPass Statementcbs123abcNo ratings yet
- Welcome To The World of C: #Include Int Main (Printf ("I Am Alive! Beware./n") Getchar Return 0 )Document32 pagesWelcome To The World of C: #Include Int Main (Printf ("I Am Alive! Beware./n") Getchar Return 0 )Amar DsNo ratings yet
- C & C++ LanguageDocument12 pagesC & C++ Languageالزهور لخدمات الانترنيتNo ratings yet
- 1Document5 pages1Dhrushal PatelNo ratings yet
- Que Sont Les Widgets Flutter ?Document6 pagesQue Sont Les Widgets Flutter ?Oussama SghaierNo ratings yet
- Intro To C++Document4 pagesIntro To C++Dwayne ThorneyNo ratings yet
- C++ For Hackers - Hack InsightDocument204 pagesC++ For Hackers - Hack InsightRedemta TanuiNo ratings yet
- Module-2 Lexical AnalyzerDocument36 pagesModule-2 Lexical AnalyzerSpiderNo ratings yet
- Algorithm & Computing: Lab # 1 DE-32 DCEDocument18 pagesAlgorithm & Computing: Lab # 1 DE-32 DCEUmais BhuttaNo ratings yet
- Assignment in C++ Programming Questions 1. What Is C++: Bjarne Stroustrup (Born 30 December 1950) Is A DanishDocument5 pagesAssignment in C++ Programming Questions 1. What Is C++: Bjarne Stroustrup (Born 30 December 1950) Is A DanishKenshin HimuraNo ratings yet
- GFHHDocument11 pagesGFHHmebibegNo ratings yet
- C++ Tutorial. For BeginnersDocument26 pagesC++ Tutorial. For BeginnersLokesh BabuNo ratings yet
- Parts of C++ ProgramDocument9 pagesParts of C++ Programapi-3758479100% (7)
- Input Operator:: Cascading of I/O OperatorsDocument21 pagesInput Operator:: Cascading of I/O OperatorsVishal GuptaNo ratings yet
- 1 FuntionsDocument52 pages1 FuntionskrishthefishNo ratings yet
- C Bit BankDocument13 pagesC Bit BankIrfan NanasanaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To C/C++ Programming: DR Zulkefli Bin Mansor 28 Sept 2015Document33 pagesIntroduction To C/C++ Programming: DR Zulkefli Bin Mansor 28 Sept 2015Mohamad ZulfikrieNo ratings yet
- Async and Await PDFDocument5 pagesAsync and Await PDFnikolatesla2009No ratings yet
- The Boo Programming Language: When and WhyDocument8 pagesThe Boo Programming Language: When and WhyAbraham Chacón LandoisNo ratings yet
- C LanguageDocument96 pagesC LanguageSreenath NaniNo ratings yet
- CS6456Document164 pagesCS6456ramyajesiNo ratings yet
- C++ Chapter FourDocument11 pagesC++ Chapter FourAynalemNo ratings yet
- C Plus PlusDocument6 pagesC Plus PlusMohd EisaNo ratings yet
- Lesson4 - Language Fundamentals3Document14 pagesLesson4 - Language Fundamentals3Pavan VutukuruNo ratings yet
- EG Basics MCQ - 1Document8 pagesEG Basics MCQ - 1WAJID AJMALNo ratings yet
- Manual ArchicadDocument67 pagesManual ArchicadkhajaimadNo ratings yet
- NT00378-11-En PowerLogic T300 User ManualDocument460 pagesNT00378-11-En PowerLogic T300 User ManualmsiantexNo ratings yet
- How To Install and Configure VNC On Debian 10 - DigitalOceanDocument16 pagesHow To Install and Configure VNC On Debian 10 - DigitalOceanASNo ratings yet
- VISSIM 520 eDocument576 pagesVISSIM 520 eSuriel UrielNo ratings yet
- Application Manual Integrated Dispensing Function Package (IDFP) 3HDAK00000A0252-001Document700 pagesApplication Manual Integrated Dispensing Function Package (IDFP) 3HDAK00000A0252-001JAIR RODRIGUEZ100% (1)
- Cara Mengaktifkan IPV6 Di SwitchDocument19 pagesCara Mengaktifkan IPV6 Di SwitchNeng Mimin RohmawatiiNo ratings yet
- Strategic Analysis of Lynda ComDocument21 pagesStrategic Analysis of Lynda ComMohamed KadriNo ratings yet
- Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) : Concept and System-ModelingDocument31 pagesOrthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) : Concept and System-ModelingAsif_Iqbal_8466No ratings yet
- CGTMD Coalitional GamesDocument17 pagesCGTMD Coalitional Gamesrajan20202000No ratings yet
- ClusteringDocument7 pagesClusteringRupesh GaurNo ratings yet
- CCTV Surveillance Policy Document (IPS, 2013)Document23 pagesCCTV Surveillance Policy Document (IPS, 2013)Razi MahriNo ratings yet
- Kardiomed 521 Comfort Cycle User Manual - V1.0Document18 pagesKardiomed 521 Comfort Cycle User Manual - V1.0Mohamed TalaatNo ratings yet
- BSCE Graduation Project Proposal FormatDocument5 pagesBSCE Graduation Project Proposal FormatAhmed MohammedNo ratings yet
- Oracle How To Prepare Mass Additions - Populate FA Data in Oracle v2Document8 pagesOracle How To Prepare Mass Additions - Populate FA Data in Oracle v2JoyNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Test ICF 7Document3 pagesDiagnostic Test ICF 7Sonia AgustinNo ratings yet
- Catalog Advantys AS-I IP20-IP67 - 803510 - DIA3ED2040909EN - 200408Document30 pagesCatalog Advantys AS-I IP20-IP67 - 803510 - DIA3ED2040909EN - 200408Jean MarzanNo ratings yet
- Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Faculty of Engineering and Technology, SRM UniversityDocument6 pagesDepartment of Electronics and Communication Engineering Faculty of Engineering and Technology, SRM UniversityShubham Kumar GuptaNo ratings yet
- YOKOGAWA EXA DC402 (Ing)Document78 pagesYOKOGAWA EXA DC402 (Ing)biotech666No ratings yet
- Arch I QuantDocument93 pagesArch I QuantVictor Alonso GarciaNo ratings yet
- Bandwidth ChartDocument2 pagesBandwidth ChartVijay SinghNo ratings yet
- Eee Kit. ProjectsDocument6 pagesEee Kit. ProjectsseethiniratnakarNo ratings yet
- Lab Manaul Final Data Analytics With Excel Bcs358aDocument23 pagesLab Manaul Final Data Analytics With Excel Bcs358asushmitha748313No ratings yet
- Data Leakage DetectionDocument18 pagesData Leakage DetectionJoe1606No ratings yet
- Engl393 - Instructions Final SubmissionDocument24 pagesEngl393 - Instructions Final Submissionapi-622526151No ratings yet
- Week 2 NotesDocument19 pagesWeek 2 Notesvaibhavnaik483No ratings yet
- SRP Updated SystemDocument68 pagesSRP Updated SystemTin Zar ThweNo ratings yet
- Xerox Wireless Print Solutions Adapter: Your Modern Workflow ConnectorDocument2 pagesXerox Wireless Print Solutions Adapter: Your Modern Workflow ConnectorBestari AnwarNo ratings yet