Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ejmed 1383
Uploaded by
Irvin MarcelOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ejmed 1383
Uploaded by
Irvin MarcelCopyright:
Available Formats
RESEARCH ARTICLE
European Journal of Medical and Health Sciences
www.ejmed.org
Type B Progesterone Receptor Polymorphism Increases
the Risk of Pelvic Organ Prolapse in Balinese Women
I Gede Mega Putra, I Wayan Megadhana, Putu Doster Mahayasa, Made Suyasa Jaya,
I Gusti Ngurah Harry Wijaya Surya, and Ngakan Ketut Darmawa
ABSTRACT
This study aims to determine the role of type B progesterone receptor gene
polymorphisms as a risk factor for pelvic organ prolapse in Balinese women. Submitted : June 3, 2022
This paired case-control study involves 29 patients with pelvic organ Published : July 12, 2022
prolapse as the case group and 29 patients without pelvic organ prolapse as
ISSN: 2593-8339
the control group. The study was conducted at Sanglah Hospital, Denpasar
and the Integrated Biomedical Laboratory, Faculty of Medicine, Udayana DOI: 10.24018/ejmed.2022.4.4.1383
University. Three milliliters of venous blood samples were taken from each
patient and PCR examination was performed to determine the type b I. G. M. Putra
progesterone receptor gene polymorphisms. Risk assessment of the type b Department of Obstetrics and
progesterone receptor gene polymorphism for pelvic organ prolapse was Gynecology, Medical Faculty of
done by controlling for confounding variables, including age, parity, body Udayana University/Sanglah Hospital,
mass index, occupation, menopausal status, and history of hysterectomy, Indonesia.
through multiple logistic regression tests. The type b progesterone receptor I. W. Megadhana
gene polymorphism increased the risk of pelvic organ prolapse three times Department of Obstetrics and
Gynecology, Medical Faculty of
compared to non-prolapsed in Balinese women (OR 3.90, 95%CI 1.16-13.07,
Udayana University/Sanglah Hospital,
p = 0.023). After controlling for various confounding variables, type b Indonesia.
progesterone receptor gene polymorphism still increased the risk of pelvic P. D. Mahayasa
organ prolapse up to four times (AOR 4.54, 95%CI 1.16-17.68, p = 0.029). Department of Obstetrics and
The type b progesterone receptor gene polymorphism significantly Gynecology, Medical Faculty of
increases the risk of pelvic organ prolapse in Balinese women. Udayana University/Sanglah Hospital,
Indonesia.
M. S. Jaya
Keywords: Polymorphism, type B progesterone receptor, pelvic organ Department of Obstetrics and
prolapse. Gynecology, Medical Faculty of
Udayana University/Sanglah Hospital,
Indonesia.
I. G. N. H. W. Surya
Department of Obstetrics and
Gynecology, Medical Faculty of
Udayana University/Sanglah Hospital,
Indonesia.
N. K. Darmawan*
Department of Obstetrics and
Gynecology, Medical Faculty of
Udayana University/Sanglah Hospital,
Indonesia.
(e-mail:
wawandarmawan291289@ gmail.com)
*Corresponding Author
intrinsic and extrinsic factors. Age is wrong; one factor
I. INTRODUCTION intrinsic in the development of dysfunction base hip, where
incident and prevalence POP reported increase along with
Prolapse organ hip (POP) is wrong. One problem is
enhancement age. Prevalence relative POP increases about
gynecology which is defined as dropping one or more aspects
40% each additional decade life begins from 40 years. Age
of the vagina and uterus, including the anterior vaginal wall,
role in POP events is associated with various factors like
posterior vaginal wall, uterus (cervical), or apex from the
existence change physiology from the component base pelvis
vagina [1], [2]. The prevalence of POP worldwide varies,
and hormonal changes that occur during post-menopause [4],
starting from 2.9% to about 75%, depending on the diagnostic
[5].
criteria used. The prevalence of POP increases along with
Progesterone is one hormone believed sexual have a role
increased age hope life in females. Though the disease has
in pelvic organ prolapse (POP). Progesterone directly plays a
several low mortalities, POP can cause disturbance quality of
role in incident POP through enhancement expression
meaningful life [3].
enzyme GGCT, which helps metabolism glutathione,
Various factors play a role in POP events, consisting of
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.24018/ejmed.2022.4.4.1383 Vol 4 | Issue 4 | July 2022 5
RESEARCH ARTICLE
European Journal of Medical and Health Sciences
www.ejmed.org
antioxidant important which is required for preventing stress B progesterone receptor gene polymorphism as a factor risk
oxidative induce damage cell by enhancement reactive happening pelvic organ prolapse in Balinese women.
oxygen species (ROS). This is supported by research that
marker stress oxidative increase meaning in the sacrouterine
ligament on a patient with POP and found enhancement II. MATERIALS AND METHODS
fibroblast on group case consequence existence stress Study this is a study case-control in pairs involving 58
mechanic. Progesterone also increases the expression of Balinese women. A total of 29 Balinese women who were
Epithelial Cadherin (CDH1), which therefore prevents diagnosed with POP at Sanglah Hospital, Denpasar, were
transition epithelial-mesenchymal (EMT) so which hinder selected using consecutive sampling. Furthermore, 29
happening degradation component composer base pelvis and Balinese women were selected who did not experience POP
allow the start process synthesis component matrix To do matching on variable parity, index mass body and work
extracellular (ECM) [6]. Progesterone, together with with comparison Among case and control 1:1 to reduce
estrogen, also plays a role in push activity proteolytic matrix selection bias or confounding bias. Criteria inclusion in
metalloproteinase (MMP)-13. MMP-13 is collagenase which research is Balinese women aged 30-70 years, diagnosed with
plays a role in degrading fibrillar collagen and initiating POP (for group case) or patient other gynecology (for group
cascade degradation by activating other MMPs. Degradation control) who underwent check-in clinic Urogynecology
causes strength muscle composer base pelvis to weaken and Reconstruction and clinic gynecology, Obstetrics and
triggers the pelvic prolapse floor [7]. Gynecology Clinics Sanglah Hospital Denpasar, and readily
Progesterone needs to bond with the receptor to use follow as well as in study after signing informed consent.
produce an effect biologically. Receptors progesterone (PR) Criteria exclusion in research is the presence of a diagnosis
has been researched and found in the female genital structure, or comorbid in the form of malignancy and pregnant
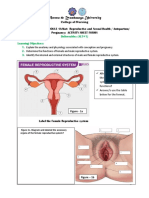
including the vagina, cervix, uterus, fallopian tubes, conditions. POP diagnostic criteria used in the study drop one
ligaments sacrouterine, muscle levator ani, and urethra, and or more pelvic organs (uterus, bladder, rectum) through the
cardinal ligaments pelvic floor [8]. Reference [9] shows that hole vagina at least 1 cm above the hymenal line. POP staging
expression PR in ligament sacrouterine is significantly lower uses the system POP-Q where POP which includes in the
on group POP than control that is not experiencing POP. study, is POP degree II or more.
Percentage expression receptors Progesterone is also seen History, examination physique general, and inspection of
higher in women who have not experienced menopause than urogynecology performed on every subject research. History
in women who have menopause. You are welcome to is conducted to get characteristics like identity, age, parity,
experience POP [9]. Decreased progesterone levels in complaints, and job history—inspection physique general for
circulation and tissue will lower the amount of receptors knowing existence disease attendant prolapse organ pelvis
progesterone in a network. Adequate protection against POP and forget index mass body. Inspect urogynecology to
will also be disturbed. Importance role of progesterone and determine the degrees of clinical prolapse organ pelvis using
PR in pathogenesis happening POP cause development study the POP-Q standard. They were next, done taking as much
about both, wrong the only one is polymorphism venous blood as 3 ml. Sample venous blood is inserted into a
progesterone receptors [8]. tube containing EDTA and carried to Laboratory biomedical
Polymorphism is a variation of sequence DNA that occurs Integrated Faculty Medical University Udayana Denpasar
in a population with a 1% or more frequency [10]. One study Bali for DNA isolation and examination DNA sequencing
by [12] in China has evaluated polymorphism PR rs484389 through PCR test to determine the existence of PR-B
(3'-untranslated region C/T) and PR rs500760 (exon 8 A/G) polymorphism.
in POP. Mutation specific to sour nucleotide amino is known
to push work bus on receptors progesterone type B (PR-B) so TABLE I: CHARACTERISTICS SUBJECT STUDY
that damage regulation genetics on PR-B and change from Risk Factor
Group Case Group Control P-
PR-B Becomes receptors progesterone type A (PRE). The (n = 29) (n = 29) value
Age (mean ± SD) 58.45±10.35 56.10 ± 9.57 0.378 a
second type of PR has a structure and mechanism work which
Parity (n, %)
different. PRE, opposite from PR- B, will hinder activator Multipara 28 (96.6) 28 (96.6)
1,000 b
transcription next and affect proliferation from working Nullipara 1 (1.7) 1 (1.7)
estrogen for activates processes that lead to protection Work weight (n, %)
Yes 15 (51.7) 15 (51.7)
occurrence of POPs [11], [12]. Results of study obtained that Not 14 (48.2) 14 (48.2)
1,000 b
PR rs484389 CT genotype associated significantly with POP, BMI (n, %)
where genotype this increase the risk of POP is 3.02 times Fat
compared to those who do not have genotype CT. Whereas (BMI > 25 kg/m 2 ) 9 (31.0) 8 (27.6)
0.773 b
Normal (BMI 20 (69.0) 21 (72.4)
for polymorphism PR rs500760 no found difference 18.5-25 kg/m )2
genotype, which was significant Among group control and Menopause Status (n, %)
case [12]. Menopause 24 (82.8) 21 (72.4)
0.345 b
Not menopausal 5 (17.2) 8 (27.6)
Studies about description polymorphism receptors
History of Hysterectomy (n, %)
progesterone in the POP patient have only been implemented Once 1 (3,4) 1 (3,4)
0.754 b
in China, and research similar has not yet been done in Not 28 (96.6) 28 (96.6)
Indonesia. This causes information about PR polymorphism *P value<0.05 is considered significant
a
in the case of POP to be very limited in Indonesia, precisely T-independent test ; b Fisher-exact test ; c Chi-square test
in Bali. because of that, the study aims to know the role type
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.24018/ejmed.2022.4.4.1383 Vol 4 | Issue 4 | July 2022 6
RESEARCH ARTICLE
European Journal of Medical and Health Sciences
www.ejmed.org
All data obtained analysed use device soft Statistical requiring hospitalization compared to nulliparous women
Product and Service Solutions (SPSS) version 21.0 for [18]. Research by [16] on 228 women showed the mean parity
Windows. All data collected conducted analysis descriptive. in the group of women with POP was 5.2 ± 2, while in the
Test normality was conducted for knowing distribution data control group it was 3.97 ± 2.3. Women with parity >5 have
parity, index time body, and profession using Shapiro-Wilk. almost three times higher risk of experiencing POP than
Test Chi-Square to know the ratio odds polymorphism gene women with parity more than 5. Despite being a primary risk
receptors progesterone with pelvic organ prolapse. Study this factor for POP, parity did not show a significant relationship
already get agreement appropriateness ethics from Research with POP risk recurrence [17]. The role of parity in increasing
Ethics Commission Faculty Medical University Udayana / the risk of POP is related to the traumatic impact of vaginal
RSUP Sanglah Denpasar dated 23 June 2020, number delivery. Vaginal delivery can cause damage to the pudendal
1290/UN.14.2.2.VII.14/LT/2020. A study with design case- nerve, which plays a role in the pathophysiology of POP. 16
control was performed on 29 samples of pelvic organ Other pelvic structures that are traumatized by childbirth are
prolapse (POP) as group cases and 29 non-POP patients as the levator ani muscle complex, pelvic nerves, pelvic fascial
group control. Table I shows no difference in average age, structures, and the anal sphincter [5] parity with labour
parity, occupation weight, BMI, menopausal status, and vaginal have risk experience complaint related POP as big as
history of meaningful hysterectomy in the second group 5.5 times compared with labour per abdominal [19].
(p>0.05) The heavy profession is a main factor in a study classified
becomes where is the complex work activity mainly can
cause an increase in pressure intra-abdominal, like a farmer,
III. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION a trader in market or laborer builder, and there is no heavy
Pathogenesis happening POP is influenced by various profession that can make no increase intra-abdominal
factor risk (multifactorial), both modifiable and not. Risk pressure, such as office workers or housewife. Research by
factors that cannot be modified are age. In contrast, what can [16] showed that the history of strenuous physical activity in
be modified are parity factors, heavy work, obesity as the group of women with POP was significantly different
indicated by the index body mass (BMI), menopausal status, from that of women without POP. A history of strenuous
and history of hysterectomy. Age distribution increased physical activity contributes to an increased risk of
significantly in women who experienced symptoms of POP multiparity (>5) women experiencing POP two times higher
(POP symptomatic). A study by [13] shows that almost 50% than without a history of strenuous physical activity. Another
of women with POP are aged 80 years, while 31% of them study involved women in Tanzania and Nepal who worked as
are aged 50-59 years, and the remaining 6% are aged 20-29 sand and stone carriers. The results showed that women
years. There is a positive relationship between increasing age carrying heavyweights in Tanzania (median 20 kg) and Nepal
of women and the number of patients seeking POP treatment. (median 57.5 kg) had higher mean lower abdominal symptom
The number of women aged 30-39 years with POP who visit scores related to POP than those who lifted light weights. A
health services is as much as 1.7/1,000. This number self-administered questionnaire measured the assessment of
increases in women aged 60-69 years to 13.2/1,000. The lower abdominal symptoms [20]. However, different results
highest number of groups seeking consultation medical for were obtained from [19] research. Physically inactive or
POP reported for age 70-79 as significant as 18.6/1,000 [14]. physically active women who lift weights of 15 kg experience
Older age is a primary risk factor for POP. A woman who more POP-related complaints than women who lift heavier
experiences POP at a younger age is more likely to weights. These different results may be caused by lifting
experience recurrence POP after surgery than older women weights as an exercise program of choice and not being
because of connective tissue weakness. Although however, carried out routinely. The daily life of the study population
the relationship between age as a risk factor for POP is still may be less exposed to strenuous activities than in previous
controversial. Research by [15] shows that women aged >35 studies. Women with the risk of experiencing POP are
years are associated with an increased risk of POP by six recommended to avoid heavy professions, like lifting objects
times compared to those under 35 years of age. Every heavy. This is related to increased intraabdominal pressure
increase in age by ten years, there will be an increased risk of and transmission of pressure to supporting structures pelvic
POP by 40%. Research by [16] shows the mean age group of organs when lifting weights, thereby contributing to pelvic
women with POP is 53.96 ± 10.91 years, while in the control dysfunction floor. Physiological research shows that when
group without POP, it was 49.60 ± 8.82 years. There is a women do activity physique, there is a correlation positive
significant difference between the over 50 years old Between lift burden with an enhancement of intra-abdominal
proportion of a woman with POP compared with the control. pressure [19].
A systematic review by [17] showed different results on age Index mass body (BMI) is the highest risk factor significant
as a risk factor for recurrence POP. Many studies show age in for primary POP but not significant for recurrence POP [17].
the lower 60 years to be a significant risk factor for POP On a cross-sectional study, 964 women showed a positive
recurrence; other studies have shown no significant correlation between BMI and compartment prolapse posterior
difference between ages more than 70 years or less than 70 (rectocele) based on physical examination or
years with POP. ultrasonography, but not with compartment anterior and
Parity is a modifiable primary POP risk factor. Multiparity central [21]. Different results from several studies show no
can be the most decisive predisposing factor for POP. Women relationship significant among obesity and POP [15], [19].
with one child had a four times higher risk. Women with two Study in 3,934 women by classifying BMI into less/normal
children had an 8.4 times higher chance of developing POP BMI, overweight, and obesity, no find a connection which
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.24018/ejmed.2022.4.4.1383 Vol 4 | Issue 4 | July 2022 7
RESEARCH ARTICLE
European Journal of Medical and Health Sciences
www.ejmed.org
significant among group POP and non-POP [19]. Difference TABLE II: POLYMORPHISM GENE PR - B AS FACTOR POP RISK
results could be influenced by the absence of standardized Group
PR-B.
Case Control OR CI95% P-value
POP assessments and population differences between polymorphism
n(%) n(%)
research [22]. In theory, POP is more common in obese Positive 13 (44.8) 5 (17.2) 1.163 –
patients for various reasons, including chronically elevated 3,90 0.023 a
Negative 16 (55.2) 24 (82.8) 13.078
intra-abdominal pressure, damage to the muscle hip, damaged Score p<0.05 is considered significant; a Test Chi Square
nerve, and the existence of comorbid related obesity other
TABLE III: RELATIONSHIP RECEPTOR GENE POLYMORPHISM
like Diabetic neuropathy intervertebral disc herniation [23]. PROGESTERONE TYPE B AND POP AFTER CONTROLLED WITH VARIABLE
Obesity directly affects POP symptoms. Pressure increases CONTROL
intra-abdominal chronic, damage nerve, and comorbid on Variable
Adjusted
CI 95% P-Value
woman obesity contribute to dysfunction base pelvis. OR
1.168-
Enhancement pressure intra- the abdomen causes Polymorphism PR 4,544
17,680
0.029 a
overstretching of the pelvic structures, including the nerves
Age 0.985 0.895-1.085 0.863 a
pudendal [23], [24]. However, in this study, it was not found
0.047-
that there was an influence of BMI factors on increasing Parity 1,921
78,691
0.730 a
incident POP. Load Heavy Work 1,736 0.496-6.069 0.388 a
Postmenopausal women experience more organ damage
BMI 1.251 0.345-4.531 0.733 a
buffer, which causes protrusion organ pelvis past hymen,
0.192-
compared with a woman which not yet menopause [25]. Status Menopause 1,480 0.707 a
11.407
Change hormones when menopause causes a drop in 0.055-
concentration. Systemic estrogens and hypoestrogenic History Hysterectomy 1.091 0.954 a
21,470
conditions in the pelvic organs play a role in changes in the Score p<0.05 considered significant; a Test Regression Logistics multiple
composition and strength of collagen [14]. Symptoms of POP
vaginal like enhancement sensitivity could be caused by Several confounding variables, such as age, parity, heavy
changes in hormones at menopause. There is a high work, index body mass (BMI), menopausal status, and history
percentage of postmenopausal women with inactive and of hysterectomy, which are known to play a role in incident
strenuous activity women (21.6% and, respectively) 24.3%) POP also analyzed in this study. Analysis multivariate use
who experience symptoms of POP, possibility consequence test conditional regression logistics conducted for control
awareness existence sensation bump on the vagina [19]. variable confounder and result could be seen on Table III.
Hysterectomy is associated with an increased risk of Type B PR gene polymorphism remains a risk factor for POP
recurrent POP surgery. A prospective study in Sweden shows after the variable confounder is controlled. Polymorphism
that there is an increased risk of POP is five times in gene PR Type B give risk The occurrence of POP is 4.544
individuals undergoing vaginal hysterectomy and as big as times higher than those who do not have POP polymorphism
2.5 times in individuals with a history of total hysterectomy gene PR (adjusted RO = 4.544; p=0.029; CI95% = 1,168-
abdominal compared which no once run it [26]. Results 17,680).
Similar findings were also found by [27]. The latter Previous studies have shown that the PR gene
conducted a cohort study on the woman who not yet once do polymorphism rs484389, a risk factor for POP, is the CT
operation repaired POP. The result showed that vaginal heterozygous genotype. In this study, these genotypes were
hysterectomy had three times higher risk of requiring surgical analysed and discussed as factors risk POP. Sample detected
repair of POP than total abdominal hysterectomy [27]. have to genotype heterozygous CT on gene PR categorized as
Incident POP also relate to the indication that medically having a PR polymorphism [12]. Results of statistical
performed a hysterectomy. The incidence of POP surgery was analysis in this study showed that women with PR - B gene
found to be twice as high in women undergoing hysterectomy polymorphisms had a 3.9 times risk of experiencing POP
with indications of prolapsed disease compared to other compared with which no who have polymorphism gene PR -
indications [26]. Different results were obtained by studies in B. These results are also consistent after controlling for the
America which showed that hysterectomy during POP variables confounder other.
surgery has a protective effect, namely: lower risk operation In China, one previous study by [12] assessed
POP repeated future as much 1-3%. Hysterectomy is polymorphism PR rs484389 (3'- untranslated region C/T) on
associated with a reduced risk of repeat surgery from POP POP with a case-control research design. This study found
anterior, apical, and posterior compared with those without a that the PR rs484389 CT genotype was significantly
history of hysterectomy [2]. associated with POP, whereas this genotype increased POP
As many as 13 (44.8%) POP groups experienced PRB risk by 3.02 times compared to those who did not have the
polymorphism. In contrast, only 5 (17.2%) group POP CT genotype [12]. Specific mutations in the nucleotides of
experience polymorphism PR - B. Table II shows differences these amino acids are known to suppress the action of BUS
in the proportion of polymorphisms gene PR-B between case on PR-B, thereby impairing genetic regulation of PR-B,
and control groups. Patients with PR-B polymorphism have a where there is a change from PR-B to PR-A. As it is known,
3.9 times more risk of experiencing POP tall than patients the second type of PR has a structure whole and mechanism
with no polymorphism PR (OR=3,900; 95% CI 1.163- work which different. In contrast to PR-B, PR-A will inhibit
13,078; p=0.023). transcriptional activator next, and proliferative effect of
estrogens [11]. Progesterone plays a role in the occurrence of
POP through increased expression of enzyme GGCT.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.24018/ejmed.2022.4.4.1383 Vol 4 | Issue 4 | July 2022 8
RESEARCH ARTICLE
European Journal of Medical and Health Sciences
www.ejmed.org
Enzyme GGCT follows and metabolism glutathione, which [6] Ward RM, Velez Edwards DR, Edwards T, Giri A, Jerome RN, Wu
JM. Genetic epidemiology of pelvic organ prolapse: a systematic
is expressed in the nucleus and cytoplasm from cell review. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2014; 211(4): 326-335.
epithelium in system reproduction. Glutathione is an [7] Lim VF, Khoo JK, Wong V, Moore KH. Recent studies of genetic
important antioxidant required to prevent oxidative stress- dysfunction in pelvic organ prolapse: the role of collagen defects. Aust
New Zeal J Obstet Gynaecol. 2014; 54(3): 198–205.
inducing cellular damage by increasing reactive oxygen
[8] Krissi H, Halperin R, Koren R, Peled Y. The presence and location of
species (ROS). This is supported by research that marker estrogen and progesterone receptors in the human pelvic cardinal
stress oxidative increase means in ligament sacrouterine on a ligaments. Pelviperineology. 2010; 29(1): 17–9.
patient with POP and found enhancement fibroblast on group [9] Bai SW, Yoon JM, Shin JS, Kim SK, Park KH. Roles of estrogen
receptor, progesterone receptor, p53 and p21 in pathogenesis of pelvic
case consequence existence stress mechanic. ROS is also organ prolapse. Int Urogynecol J. 2005; 16(6): 492–6.
known for directly inducing the occurrence of an EMT [6]. [10] Karki R, Pandya D, Elston RC, Ferlini C. Defining “mutation” and
Progesterone and estrogen play a role in push matrix “polymorphism” in the era of personal genomics. BMC Med Genomics.
2015; 8(1): 1–7.
metalloproteinase (MMP)-13 proteolytic activity [2], [29]. [11] Jacobsen BM, Horwitz KB. Progesterone receptors, their isoforms and
MMP-13 is a collagenase that plays a role in degrading progesterone regulated transcription. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2012;
fibrillar collagen and initiates a degradation cascade by 357(1–2): 18–29.
[12] Chen H-Y, Chung Y-W, Lin W-Y, Chen W-C, Tsai F-J, Tsai C-H.
activating MMP other [7], [29]. Collagen is initially degraded Progesterone receptor polymorphism is associated with pelvic organ
to fragments by MMP-13 and MMP-1 and -8 before being prolapse risk. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2009; 88(7): 835–8.
dissolved by MMP-2 and -9. Enhancement expression MMP [13] Wu JM, Vaughan CP, Goode PS, Redden DT, Burgio KL, Richter HE,
et al. Prevalence and trends of symptomatic pelvic floor disorders in
indicates accelerated remodeling and collagen degradation. US women. Obstet Gynecol. 2014; 123(1): 141.
MMP is inhibited by TIMP and decreased TIMP expression [14] Weintraub AY, Glinter H, Marcus-Braun N. Narrative review of the
was associated with increased MMP expression [7] This epidemiology, diagnosis and pathophysiology of pelvic organ prolapse.
Int Braz J Urol. 2019; 46: 5–14.
degradation causes the strength of the muscles that make up
[15] Horst W, Do Valle JB, Silva JC, Gascho CLL. Pelvic organ prolapse:
the pelvic floor to become weak and lead to pelvic floor prevalence and risk factors in a Brazilian population. Int Urogynecol J.
prolapse [7], [29]. 2017; 28(8): 1165–70.
This study indicates that the PR-B gene polymorphism is a [16] Fatima Q, Razzaqe H, Kashif M, Aslam F. Association of parity and
pelvic organ prolapse. JRMC. 2016.
factor risk happening POP in Balinese women, with the hope [17] Vergeldt TFM, Weemhoff M, IntHout J, Kluivers KB. Risk factors for
existence developments in genetic screening in the future so pelvic organ prolapse and its recurrence: a systematic review. Int
that it can be known for women who have the risk of POP. Urogynecol J. 2015; 26(11): 1559–73.
[18] Patel DA, Xu X, Thomason AD, Ransom SB, Ivy JS, DeLancey JO.
Women with polymorphism POP could is recommended to Childbirth and pelvic floor dysfunction: an epidemiologic approach to
avoid or minimize the risk factors for POP that can be the assessment of prevention opportunities at delivery. Am J Obstet
modified, such as multiparity, vaginal delivery, obesity, Gynecol. 2006; 195(1): 23-28.
[19] Forner LB, Beckman EM, Smith MD. Symptoms of pelvic organ
heavy-load work or disease-causing chronically elevated prolapse in women who lift heavy weights for exercise: a cross-
intra-abdominal pressure, and hysterectomy surgery. This sectional survey. Int Urogynecol J. 2020; 31(8): 1551–8.
will help reduce the chances of this happening POP on a [20] Koyuncu A, Kadota JL, Mnyippembe A, Njau PF, Sijali TR, McCoy
SI, et al. Heavy Load Carrying and Symptoms of Pelvic Organ Prolapse
woman with polymorphism PR -B. Screening genetics is among Women in Tanzania and Nepal: An Exploratory Study. Int J
already many conducted in-country Up; however, in Environ Res Public Health. 2021; 18(3): 1279.
Indonesia and other developed countries, an inspection of [21] Young N, Atan IK, Rojas RG, Dietz HP. Obesity: how much does it
matter for female pelvic organ prolapse? Int Urogynecol J. 2018; 29(8):
genetics for knowing polymorphism gene PR -B is still hard
1129–34.
to reach and expensive. [22] Orejuela FJ, Shek KL, Dietz HP. The time factor in the assessment of
prolapse and levator ballooning. Int Urogynecol J. 2012; 23(2): 175–8.
[23] Ramalingam K, Monga A. Obesity and pelvic floor dysfunction. Best
Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2015; 29(4): 541–7.
IV. CONCLUSION [24] de Sam Lazaro S, Nardos R, Caughey AB. Obesity and pelvic floor
Polymorphism PR-B gene is a factor risk significant dysfunction: battling the bulge. Obstet Gynecol Surv. 2016; 71(2): 114–
25.
happening POP on Balinese woman. Inspection screening [25] Sze EHM, Hobbs G. A prospective cohort study of pelvic support
existence polymorphism gene PR -B on Balinese women changes among nulliparous, multiparous, and pre-and post-menopausal
could be possible in the future uses for detection existence women. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2012; 160(2): 232–5.
[26] Forsgren C, Lundholm C, Johansson ALV, Cnattingius S, Zetterström
POP risk. Study role PR-B gene polymorphism against POP J, Altman D. Vaginal hysterectomy and risk of pelvic organ prolapse
needed events that bigger scale on other women ethnic groups and stress urinary incontinence surgery. Int Urogynecol J. 2012; 23(1):
others in Indonesia will be needed in the future. 43–8.
[27] Lykke R, Løwenstein E, Blaakær J, Gimbel H. Hysterectomy technique
and risk of pelvic organ prolapse repair: a Danish nationwide cohort
study. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2017; 296(3): 527–31.
REFERENCES [28] Dallas K, Elliott CS, Syan R, Sohlberg E, Enemchukwu E, Rogo-Gupta
L. Association between concomitant hysterectomy and repeat surgery
[1] Dietz HP. Pelvic organ prolapse – a review. Australian Journal for for pelvic organ prolapse repair in a cohort of nearly 100,000 women.
General Practitioners. 2015; 44: 446-452. Obstet Gynecol. 2018; 132(6): 1328–36.
[2] Milart P, Woźniakowska E, Czuczwar P, Woźniak S. Pelvic organ [29] Zong W, Meyn LA, Moalli PA. The amount and activity of active
prolapse in women: how is it diagnosed and treated currently? Prz matrix metalloproteinase 13 is suppressed by estradiol and
menopauzalny= Menopause Rev. 2015; 14(3): 155. progesterone in human pelvic floor fibroblasts. Biol Reprod. 2009;
[3] Wilkins MF, Wu JM. Epidemiology of pelvic organ prolapse. Curr 80(2): 367–74.
Obstet Gynecol Rep. 2016; 5(2): 119–23.
[4] Kim CM, Jeon MJ, Chung DJ, Kim SK, Kim JW, Bai SW. Risk factors
for pelvic organ prolapse. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2007; 98(3): 248-251.
[5] Razzak L. Pathophysiology of Pelvic Organ Prolapse. In: Pelvic Floor
Disorders. IntechOpen. 2018.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.24018/ejmed.2022.4.4.1383 Vol 4 | Issue 4 | July 2022 9
You might also like
- The No B.S. Guide To Anterior Pelvic Tilt: In-Depth Assessment and 6-Week ProgramDocument39 pagesThe No B.S. Guide To Anterior Pelvic Tilt: In-Depth Assessment and 6-Week ProgramKosar83% (6)
- PROLOG Reproductive Endocrinology and Infertility, 7e (2015) - (1934984442) - (ACOG)Document223 pagesPROLOG Reproductive Endocrinology and Infertility, 7e (2015) - (1934984442) - (ACOG)AE100% (5)
- RAC Exams QuestionsDocument14 pagesRAC Exams QuestionsExamsure975% (4)
- Ramsay Sedation Scale and How To Use ItDocument10 pagesRamsay Sedation Scale and How To Use ItAdinda Putra PradhanaNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy With Prolapse Utery PDFDocument2 pagesPregnancy With Prolapse Utery PDFAnwar Mahnan QomariNo ratings yet
- Oral Contraceptive As A Risk Factor of Breast Cancer in Female Patients at Dr. Cipto Mangunkusumo National Public Hospital, Jakarta, IndoneDocument5 pagesOral Contraceptive As A Risk Factor of Breast Cancer in Female Patients at Dr. Cipto Mangunkusumo National Public Hospital, Jakarta, IndoneInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Duan 2010Document3 pagesDuan 2010ShirleyNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Anemia On The Incidence of Premature Rupture of Membrane (Prom) in Kertha Usada Hospital, Singaraja, BaliDocument7 pagesThe Effect of Anemia On The Incidence of Premature Rupture of Membrane (Prom) in Kertha Usada Hospital, Singaraja, BaliFirman AmalNo ratings yet
- ProgesteronaDocument5 pagesProgesteronaDulce Ivonne Olverá LopezNo ratings yet
- Hormonal Contraceptive Use Related To Breast Cancer Among Women in Indonesia: A Nationwide StudyDocument6 pagesHormonal Contraceptive Use Related To Breast Cancer Among Women in Indonesia: A Nationwide StudyIJPHSNo ratings yet
- Does Magnesium Sulfate Delay The Active Phase of LDocument4 pagesDoes Magnesium Sulfate Delay The Active Phase of LTengku Chairannisa PutriNo ratings yet
- Gynecology & ObstetricsDocument5 pagesGynecology & ObstetricsAlfadea Irbah APNo ratings yet
- Predictors of Mortality in Newborns With EsophageaDocument5 pagesPredictors of Mortality in Newborns With EsophageaElvira PratiwiNo ratings yet
- 215 636 2 PBDocument8 pages215 636 2 PBayu permata dewiNo ratings yet
- KPD 1Document12 pagesKPD 1Muh AqwilNo ratings yet
- 1572-Article Text-4319-3-10-20220901Document6 pages1572-Article Text-4319-3-10-20220901Senna mocaNo ratings yet
- Welcome: Obstetrics and Gynaecological Nursing DepartmentDocument57 pagesWelcome: Obstetrics and Gynaecological Nursing DepartmentPriya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Journal Homepage: - : Manuscript HistoryDocument8 pagesJournal Homepage: - : Manuscript HistoryIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- 5663 PDFDocument7 pages5663 PDFwaelNo ratings yet
- Oral Allylestrenol A Pregnancy-Supporting ProgestogenDocument7 pagesOral Allylestrenol A Pregnancy-Supporting Progestogenjefri efendiNo ratings yet
- 5663 PDFDocument7 pages5663 PDFwaelNo ratings yet
- Dsjuog 2015 09 230Document4 pagesDsjuog 2015 09 230kalyanasundarNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of The Cerebroplacental Ratio in EarlyDocument2 pagesEvaluation of The Cerebroplacental Ratio in EarlyDanielle VNo ratings yet
- Articulo EndometriosisDocument7 pagesArticulo EndometriosisMaIt VeFloNo ratings yet
- Resume - Mania KavehDocument4 pagesResume - Mania Kavehmohammadrezahajian12191No ratings yet
- The Effect of Anemia On The Incidence of PrematureDocument8 pagesThe Effect of Anemia On The Incidence of PrematureDwi Puspita SariNo ratings yet
- HBI - Journa v21n5p60 enDocument10 pagesHBI - Journa v21n5p60 enEdith Carla LagosNo ratings yet
- Anc Penyakit MenularDocument7 pagesAnc Penyakit Menularhanif syabilNo ratings yet
- 05 N021 22471Document16 pages05 N021 22471Santos Morales100% (1)
- Jurnal Ibu Hamil KEKDocument7 pagesJurnal Ibu Hamil KEKSiti FathonahNo ratings yet
- Epidemiological and Clinicopathological Characteristics of Breast Cancer in Eastern IndonesiaDocument7 pagesEpidemiological and Clinicopathological Characteristics of Breast Cancer in Eastern IndonesiaBuy CuyNo ratings yet
- Jamapediatrics Sung 2020 Oi 200026Document9 pagesJamapediatrics Sung 2020 Oi 200026Chong ArthinantNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Periodontal Pathogens in Amniotic Uid and The Role of Periodontal Disease in Pre-Term Birth and Low Birth WeightDocument7 pagesEvaluation of Periodontal Pathogens in Amniotic Uid and The Role of Periodontal Disease in Pre-Term Birth and Low Birth WeightfadelNo ratings yet
- 33219-Article Text-97197-1-10-20201204Document6 pages33219-Article Text-97197-1-10-20201204ZisuhNo ratings yet
- Anomalía Uterinas Congénitas y Resultados Adversos en El EmbarazoDocument5 pagesAnomalía Uterinas Congénitas y Resultados Adversos en El EmbarazoAlexiis CabascangoNo ratings yet
- Misoprostol For Termination of Second Trimester PregnancyDocument4 pagesMisoprostol For Termination of Second Trimester PregnancybayutrihatmajaNo ratings yet
- Faktor-Faktor Yang Meningkatkan Prognosis Fetal Dan Maternal Pada Kehamilan Dengan Kanker OvariumDocument11 pagesFaktor-Faktor Yang Meningkatkan Prognosis Fetal Dan Maternal Pada Kehamilan Dengan Kanker OvariumOctaria SaputraNo ratings yet
- Journal Reading: Influence of Interpregnancy Interval On Uterine RuptureDocument9 pagesJournal Reading: Influence of Interpregnancy Interval On Uterine RuptureIlham ErtandriNo ratings yet
- Proforma For Registration of Subject For Dissertation: Obstetrics and Gynecological NursingDocument22 pagesProforma For Registration of Subject For Dissertation: Obstetrics and Gynecological Nursingrevathidadam55555No ratings yet
- Fa Leaflet KehamilanDocument7 pagesFa Leaflet KehamilanoczkyNo ratings yet
- 4163-Article Text-41530-4-10-20220105Document5 pages4163-Article Text-41530-4-10-20220105Redia FalaNo ratings yet
- A Case Study On Ectopic PregnancyDocument7 pagesA Case Study On Ectopic PregnancyJaicca Faith Tandih AllasNo ratings yet
- Differences in Vaginal Progesterone Provision Among Racial and Socioeconomic GroupsDocument10 pagesDifferences in Vaginal Progesterone Provision Among Racial and Socioeconomic GroupsHerald Scholarly Open AccessNo ratings yet
- Tingkat Dismenorea. UGMDocument10 pagesTingkat Dismenorea. UGMNur Aini FahmiahNo ratings yet
- A Randomized Trial of Preinduction Cervical Ripening: Dinoprostone Vaginal Insert Versus Double-Balloon CatheterDocument7 pagesA Randomized Trial of Preinduction Cervical Ripening: Dinoprostone Vaginal Insert Versus Double-Balloon CatheterDILAO MPENZANo ratings yet
- Jurnal Internasional Nama Mahasiswa: PEBRIANI Nim: 202001027 Judul Penelitian, TahunDocument2 pagesJurnal Internasional Nama Mahasiswa: PEBRIANI Nim: 202001027 Judul Penelitian, TahunMahasiswa PEBRIANINo ratings yet
- Pengalaman Tenaga Kesehatan DalamDocument15 pagesPengalaman Tenaga Kesehatan Dalamayurosidi2No ratings yet
- C-Reactive Protein Level As A Diagnostic Tool For Assessment of Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes in Females With Periodontal Disease - A Randomized Clinical TrialDocument5 pagesC-Reactive Protein Level As A Diagnostic Tool For Assessment of Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes in Females With Periodontal Disease - A Randomized Clinical TrialInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- OB - 02 - Outcomes of Multifetal ReductionDocument6 pagesOB - 02 - Outcomes of Multifetal Reductionram4a5No ratings yet
- 2017 Julio Comunidad y SaludDocument3 pages2017 Julio Comunidad y SaludremediosisabelNo ratings yet
- Kekurangan Energi Kronik (BALI)Document5 pagesKekurangan Energi Kronik (BALI)ridhola15No ratings yet
- International Journal of Gynecology and ObstetricsDocument6 pagesInternational Journal of Gynecology and ObstetricsmerawatidyahsepitaNo ratings yet
- Artikel Jurnal Shinta Ramadhani 18621614Document8 pagesArtikel Jurnal Shinta Ramadhani 18621614Shinta RamadhaniNo ratings yet
- Effect of Progestin Compared With Combined Oral.3Document9 pagesEffect of Progestin Compared With Combined Oral.3Dedi SaputraNo ratings yet
- 2020 1406 OnlinePDFDocument8 pages2020 1406 OnlinePDFalaesa2007No ratings yet
- Mims Jpog August 2015 IdDocument70 pagesMims Jpog August 2015 IdDika MidbrainNo ratings yet
- 100-Article Text-165-1-10-20191127Document6 pages100-Article Text-165-1-10-20191127FATIMAH WANDANo ratings yet
- Marconi 2008Document6 pagesMarconi 2008Sri HariNo ratings yet
- Declining Age at Menarche in Indonesia: A Systematic Review and Meta-AnalysisDocument9 pagesDeclining Age at Menarche in Indonesia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysisdoggo doggoNo ratings yet
- Pone 0253957Document18 pagesPone 0253957Simon ReichNo ratings yet
- Pengaruh Pemberian Parasetamol Intravena Untuk Mengurangi Nyeri Persalinan Kala I Fase AktifDocument7 pagesPengaruh Pemberian Parasetamol Intravena Untuk Mengurangi Nyeri Persalinan Kala I Fase AktifPebryan RizkyNo ratings yet
- 2006 Cervical Cancer Associated With Pregnancy Results of A Multicenter Retrospective Korean StudyDocument6 pages2006 Cervical Cancer Associated With Pregnancy Results of A Multicenter Retrospective Korean StudyKarina MilaréNo ratings yet
- Impact of Polycystic Ovary, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity on Women Health: Volume 8: Frontiers in Gynecological EndocrinologyFrom EverandImpact of Polycystic Ovary, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity on Women Health: Volume 8: Frontiers in Gynecological EndocrinologyNo ratings yet
- Targeting Inflammation For The Treatment of Diabetic Kidney Disease: A Five-Compartment Mechanistic ModelDocument17 pagesTargeting Inflammation For The Treatment of Diabetic Kidney Disease: A Five-Compartment Mechanistic ModelIrvin MarcelNo ratings yet
- The Relationship of The Lipid Profile With The Severity of Stenosis in Coronary Artery Disease PatientsDocument10 pagesThe Relationship of The Lipid Profile With The Severity of Stenosis in Coronary Artery Disease PatientsIrvin MarcelNo ratings yet
- Can You Age Bruises Accurately in Children? A Systematic ReviewDocument3 pagesCan You Age Bruises Accurately in Children? A Systematic ReviewIrvin MarcelNo ratings yet
- Randeberg 2007Document11 pagesRandeberg 2007Irvin MarcelNo ratings yet
- Circulating Tumor Necrosis Factor ReceptorsDocument14 pagesCirculating Tumor Necrosis Factor ReceptorsIrvin MarcelNo ratings yet
- Ars 2016 6664Document28 pagesArs 2016 6664Irvin MarcelNo ratings yet
- Abstrak Kopapdi 2022 - Dr. Budi TulakaDocument1 pageAbstrak Kopapdi 2022 - Dr. Budi TulakaIrvin MarcelNo ratings yet
- Journal Reading Delirium and DementiaDocument31 pagesJournal Reading Delirium and DementiaIrvin MarcelNo ratings yet
- Results: Authors Name/s (Arial Bold 36)Document1 pageResults: Authors Name/s (Arial Bold 36)Irvin MarcelNo ratings yet
- Delirium in Older Adults in Associated With Development of New DementiaDocument11 pagesDelirium in Older Adults in Associated With Development of New DementiaIrvin MarcelNo ratings yet
- Sleep Disturbance, Sleep Disorders and Co-Morbidities in The Care of The Older PersonsDocument23 pagesSleep Disturbance, Sleep Disorders and Co-Morbidities in The Care of The Older PersonsIrvin MarcelNo ratings yet
- Visualización de Hematomas Viejos en NiñosDocument5 pagesVisualización de Hematomas Viejos en NiñosBlady GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Neutrophil To Lymphocyte Ratio and Mortality in The United States General PopulationDocument9 pagesNeutrophil To Lymphocyte Ratio and Mortality in The United States General PopulationIrvin MarcelNo ratings yet
- Bhat 2013Document5 pagesBhat 2013Irvin MarcelNo ratings yet
- Faysal Bas It,+161 54-57Document4 pagesFaysal Bas It,+161 54-57Irvin MarcelNo ratings yet
- 368 FullDocument10 pages368 FullIrvin MarcelNo ratings yet
- Fimmu 11 585880Document14 pagesFimmu 11 585880Irvin MarcelNo ratings yet
- Ye 2019Document8 pagesYe 2019Irvin MarcelNo ratings yet
- Nihms 1523522Document29 pagesNihms 1523522Irvin MarcelNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0379073819304104 MainDocument7 pages1 s2.0 S0379073819304104 MainIrvin MarcelNo ratings yet
- Olds 2016Document6 pagesOlds 2016Irvin MarcelNo ratings yet
- NBR Leaflet Krynac 4955vp Ultrahigh 150dpiwebDocument2 pagesNBR Leaflet Krynac 4955vp Ultrahigh 150dpiwebSikanderNo ratings yet
- Clinical Teaching Plan On Ncm-105 Psyhciatric NursingDocument13 pagesClinical Teaching Plan On Ncm-105 Psyhciatric NursingHazel RoseNo ratings yet
- Advantage CP File - FinalDocument254 pagesAdvantage CP File - FinalvegSpamNo ratings yet
- A Review Article On Edible Pigments Properties and Sources As Natural Biocolorants in Foodstuff and Food IndustryDocument8 pagesA Review Article On Edible Pigments Properties and Sources As Natural Biocolorants in Foodstuff and Food Industrybestread67No ratings yet
- DivorceDocument11 pagesDivorceNithesh K MogaveeraNo ratings yet
- H. Pylori IgA ELISA Package InsertDocument2 pagesH. Pylori IgA ELISA Package Inserttalha saleemNo ratings yet
- Summary of Wind Turbine Accident Data To 31 December 2016Document6 pagesSummary of Wind Turbine Accident Data To 31 December 2016أحمد دعبسNo ratings yet
- A Study On Customer Satisfaction Towards: Ankur 2018-19Document10 pagesA Study On Customer Satisfaction Towards: Ankur 2018-19Pubg GamerNo ratings yet
- Bed Making LectureDocument13 pagesBed Making LectureYnaffit Alteza Untal67% (3)
- CH 3 VocabDocument5 pagesCH 3 VocabAbdirahman Abdullahi OmarNo ratings yet
- Behaviorism in Daily LifeDocument8 pagesBehaviorism in Daily LifeMichelleTongNo ratings yet
- Leisure PoemDocument2 pagesLeisure PoemSimone NgNo ratings yet
- RA7610Document3 pagesRA7610Andrew GallardoNo ratings yet
- AAP ASD Exec SummaryDocument7 pagesAAP ASD Exec SummaryCatherine AgustinNo ratings yet
- Bakery Business PlanDocument31 pagesBakery Business PlanRohit Gupta93% (14)
- 7 DR BookletDocument13 pages7 DR BookletDebraNo ratings yet
- CDCS French Forein MinistryDocument36 pagesCDCS French Forein MinistryZakaria ABBIOUINo ratings yet
- Wu 2008Document8 pagesWu 2008SergioNo ratings yet
- Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, Excretion and Mechanisms of Action of AflatoxinsDocument3 pagesAbsorption, Distribution, Metabolism, Excretion and Mechanisms of Action of AflatoxinsMaya Innaka ArhayuNo ratings yet
- ID Faktor Faktor Yang Berhubungan Dengan Perilaku Berisiko Remaja Di Kota MakassarDocument11 pagesID Faktor Faktor Yang Berhubungan Dengan Perilaku Berisiko Remaja Di Kota MakassarEva VidiaNo ratings yet
- High PlateletsDocument9 pagesHigh PlateletsHemal VyasNo ratings yet
- Kinds of Blood. Differences Between Men and WomenDocument11 pagesKinds of Blood. Differences Between Men and WomenTiagoSantosNo ratings yet
- WONCA2013 - Book of Abstracts PDFDocument830 pagesWONCA2013 - Book of Abstracts PDFBruno ZanchettaNo ratings yet
- ASYNCHRONOUS-ACTIVITY-Module 1Document7 pagesASYNCHRONOUS-ACTIVITY-Module 1Grant Wynn ArnucoNo ratings yet
- Nina Fay Calhoun Award - Intl RelationsDocument5 pagesNina Fay Calhoun Award - Intl RelationsAltrusa International of Montrose CONo ratings yet
- 2022 HRM Systems Diagnostic ChecklistsDocument5 pages2022 HRM Systems Diagnostic ChecklistsSacred EsportsNo ratings yet
- Tonsillectomy and Adenoidectomy - Pediatric Clinics of North AmericaDocument13 pagesTonsillectomy and Adenoidectomy - Pediatric Clinics of North AmericayosefNo ratings yet