0% found this document useful (0 votes)
472 views17 pagesLesson 4 Multimedia Formats
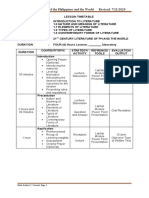
This document discusses multimedia formats for interpreting literary texts. It introduces blogs, mind mapping, mobile phone text tula, slideshow presentations, tag clouds, and videos as different multimedia formats. It then provides examples and definitions of each format. The last section discusses applying information and communication technology skills in interpreting literary works.
Uploaded by
Sarah naomi BelarminosantosCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
472 views17 pagesLesson 4 Multimedia Formats
This document discusses multimedia formats for interpreting literary texts. It introduces blogs, mind mapping, mobile phone text tula, slideshow presentations, tag clouds, and videos as different multimedia formats. It then provides examples and definitions of each format. The last section discusses applying information and communication technology skills in interpreting literary works.
Uploaded by
Sarah naomi BelarminosantosCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Multimedia Formats in Interpreting Literary Text
- Applying ICT Skills in Interpreting Literary Texts