0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views2 pagesStatically Indeterminate Systems
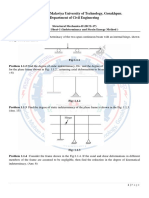
The document discusses statically indeterminate systems and provides two examples of cantilevered beams to analyze using the Maxwell-Mohr method. The first beam is simply supported and loaded at the free end to determine the deflection at that point. The second beam has a distributed load and the method is used to find the value X1.
Uploaded by
Steven G. VergheseCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views2 pagesStatically Indeterminate Systems
The document discusses statically indeterminate systems and provides two examples of cantilevered beams to analyze using the Maxwell-Mohr method. The first beam is simply supported and loaded at the free end to determine the deflection at that point. The second beam has a distributed load and the method is used to find the value X1.
Uploaded by
Steven G. VergheseCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd