Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Git Interview Question Answer Set
Uploaded by
Akash NinavCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Git Interview Question Answer Set
Uploaded by
Akash NinavCopyright:
Available Formats
GIT Interview Questions & Answers
1. What is GIT?
GIT is a distributed version control system and source code management (SCM) system
with an emphasis to handle small and large projects with speed and efficiency.
2. What is Distributed Control System?
We work in our local machine and later we transfer the code to Centralized repository
(GitHub). We don’t need to connect to centralized repository to work.
3. What is GIT version control?
• GIT version control allows you to track the history of a collection of files (code files).
• It supports creating different versions of file collection. Each version captures a
snapshot of the files at a certain point of time and You can revert the collection of
files using the snapshot. (You can develop the code in different versions of java. and
you can merge in Git)
• VCS allows you to switch between these versions. These versions are stored in a
specific place, typically called as repository. (You can switch between different
versions of java in between development process)
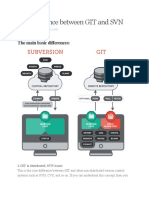
4. What is difference between SVN and Git?
SVN GIT
SVN is centralized repository, that means Git is distributed repository, first we are
directly we involved in the centralized working in our laptop after that we are
repository. transferring the code from our laptop to
centralized repository. Git have three
phases the phases are work space,
staging/index, local repo.
We working on SVN means if we are facing In git we are doing in local systems only so
any networking issue we can’t work on SVN no need to internet connection, when
because of we are directly involve into the pushing the code from our system to
centralized repository. centralized repository at that time we need
network connection. Without network also,
we can do some work.
Developed directly interact with the Developers not directly interact with the
centralized repository. Centralized repository.
5. What is a repository in GIT?
A Git repository contains the history of a files.
6. How can you create a local repository in Git?
By using # git init command create a local repository.
7. What is ‘bare repository’ in GIT?
A bare repository in Git just contains the version control information and no working
files (no tree) and it doesn’t contain the special .git sub-directory.
8. How to configure GitHub repository locally?
# git config --global user.name "user_name"
# git config --global user.email "user_email"
9. How to Create Alias to git commands
# git config --global alias.lo "log --oneline" -----> To create an Alias to Command
# git config --global --unset alias.lo -----> To Remove an Alias
# git config --global --unset user.name -----> to remove username
10. What is the git clone?
To download an existing repository from Centralized (Github) to local system.
# git clone <url>
11. What is ‘git add’?
To add files from work area to Index/staging/cache area.
# git add <file_name1> <file_name2>
12. What is Staging Area?
staging area means “holding area”. Before the commits, it can be formatted and reviewed in
an intermediate area known as staging or Index Area.
13. What is the use of ‘git log’?
To see the commits. Also, we can find specific commits in your project history- by author,
date, content or history.
# git log -----> To show the Git Commits
# git log -5 -----> To show Recent 5 Commits
# git log --oneline -----> To Display the each commit in one line
# git log --since=2018-01-21
# git log --until=2018-03-18
# git log --author="user_name"
# git log --grep="Index"
# git log --oneline --author="user_name"
14. How can we add modified/updated/edited files to the staging area and commit then
at the same time?
# git commit -a -m "Do Something once more"
15. How to edit an incorrect commit message in Git? Or How can you fix a broken
commit?
# git commit --amend -m "This is your new Git Message"
16. How to get back a commit to staging area?
# git reset --soft <previous_commit id>
17. How to get back a file from staging area to working area?
# git reset head <file_name>
18. How to get back a commit to work area?
# git reset --mixed <previous commit id>
19. What is git reset?
Reset the current HEAD state to specific state.
20. What is ‘head’ in git and how many heads can be created in a repository?
A ‘head’ is simply a reference to a commit object. In every repository, there is a default
head referred as “Master”. A repository can contain any number of heads.
21. What is .gitignore file?
Keep the files names in .gitignore then that files not add and commit, just skip that files
while adding and committing.
22. How to see the difference between 2 commits?
# git diff <commit_id1>..<commit_id2>
23. when file have staging area or file have committed if file is deleted in local repository
unfortunately how to get back that file to staging area?
# git checkout --<file_name>
24. How to create a branch?
# git branch <branch_name>
25. How to checkout to branch?
# git checkout <branch_name>
26. How to create branch while checkout?
# git checkout -b <branch_name>
27. How do you rename the local branch?
# git branch -m <old_branch_name> <new_branch_name>
28. How to see the branch list?
# git branch
29. How to see the remote branch list?
# git branch -r
Or
# git remote show origin
30. How to see the local and remote branch list?
# git branch -a
31. How to delete a branch?
# git branch -d <branch_name>
Or
# git branch -D <branch_name>
32. How to delete a Remote Branch?
# git push origin -d <branch_name>
33. How to see the difference between 2 branches
# git diff <branch1>..<branch2 >
34. What is git push?
git push is to push commits from your local repository to a remote repository.
35. How do you push the files to master branch in remote repo?
#git push (you must be in master branch)
36. How do you push files from local to particular branch in remote repo?
#git push origin <branch_name>
(or)
#git push --set-upstream <branch_name>
37. How to push new branch and its data to remote repository?
#git push <github_repository_path> <branch_name>
(or)
#git push --set-upstream <branch_name>
38. What is git pull?
Git pull downloads and merges a ‘branch data’ from remote repository to local repository.
It may also lead to ‘merge conflicts’ if your local changes are not yet committed. Use ‘git
stash’ command to Hide your local changes before git pull.
# git pull (git fetch + git merge.)
39. How do you pull a file from particular remote branch?
# git pull origin <branch_name>
40. How do you download a remote branch to local without merge?
# git fetch origin <branch_name>
# git checkout <downloaded_branchname>
41. What is git Fetch?
git fetch is only downloads new data from a remote repository, but it doesn’t integrate
any of the downloaded data into your working files. All it does is provide a view of this
data.
# git fetch <branch_name>
# git fetch origin <branch_name>
42. What is difference between git clone & git pull?
• If you want to download whole existing repository than use Git Clone.
• If you have already repository but you want to take new updates of existing
repository than use git pull command.
43. What is git merge?
Git merge is used to combine two branches.
# git merge <branch_name>
Note: you should be in target branch. Then run the command
44. What is git conflict? What is the scenario you will get git conflict error?
For example, if you and another person both edited the same file on the same lines in
different branches of the same Git repository, you'll get a merge conflict error when you
try to merge these branches. You must resolve this merge conflict with a new commit
before you can merge these branches.
45. How do you resolve merge conflict?
Will inform the developers regarding this merge conflict. They will change the code and
inform us. edit the files to fix the conflicting changes and then add & commit.
46. How do you skip from merge conflict?
#git merge --abort
47. What is the function of ‘git rm’?
To remove the file from the work area/staging area and also from your disk ‘git rm’ is
used. You can revert a deleted file.
if it is deleted using ‘git rm’. If you deleted a file ‘rm’ command then you can’t get it.
48. How will you know in GIT if a branch has been already merged into master?
git branch -merged It lists the branches that have been merged into the current branch.
git branch -no-merged It lists the branches that have not been merged.
49. What is branching? What is the purpose of branching in GIT?
Git supports branching which means that you can work on different versions of your
collection of files. A branch allows the user to switch between these versions so that he
can work on different changes independently from each other.
50. What is the criteria u merge two branches?
We have developed one module in one branch and another module in another branch.
After the development, based on the requirement we do merge these two branches.
Or One branch is development branch, another branch is test branch.
51. Describe branching strategy you have used?
Feature branching
A feature branch model keeps all of the changes for a particular feature inside of a branch.
When the feature is fully tested and validated by automated tests, the branch is then
merged into master.
Task branching
In this model each task is implemented on its own branch with the task key included in the
branch name. It is easy to see which code implements which task, just look for the task key
in the branch name.
Release branching
Once the develop branch has acquired enough features for a release, you can clone that
branch to form a Release branch. Creating this branch starts the next release cycle, so no
new features can be added after this point, only bug fixes, documentation generation, and
other release-oriented tasks should go in this branch. Once it is ready to ship, the release
gets merged into master and tagged with a version number. In addition, it should be merged
back into develop branch, which may have progressed since the release was initiated.
52. What is git stash?
Stashing takes the Temporary stored state of your working directory.
# git stash save "<message>" ------> to store the data into stash
# git stash list ------> to see the stash list
# git stash apply <stash#> ------> to copy the data into branches
# git stash pop <stash#> ------> to move the data into branches
# git stash drop <stash#> ------> to delete the particular stash
# git stash clear ------> delete the entire stash list
53. When we use git Stash?
• If you are checking out from one branch to another branch but you have
uncommitted file that you don't want to move then keep that file in stash area.
• When you are merging two branches and you don't want some files to merge, then
we move that files to stash area.
• When you are pulling (fetch + merge) a branch/file and you don't want some files to
merge, then we move that files to stash area.
54. What is another option for merging in git?
# git rebasing command is an alternative to merging in git.
55. What is difference between git merge and git rebase?
• git merge applies all unique commits from branch A into branch B in one commit with
final result.
• git rebase gets all unique commits from both branches and applies them one by one.
• git merge doesn’t rewrite commit history, just adds one new commit
• git rebase rewrites commit history but doesn’t create extra commit for merging
56. How do you undo the last commit?
# git revert <commit_id>
57. How to Change the URL for a remote Git repository?
# git remote set-url origin git://this.is.new.url
58. What is pull request?
Take some changes from a particular branch and bring them into another branch.
59. Why GIT better than Subversion (SVN)?
Git is an opensource version control system; it will allow you to run ‘version' of a project.
Multiple developers can check out, and upload changes and each change can then be
attributed to a specific developer.
60. How to Lock a branch? why we need to lock a branch?
• On GitHub, navigate to the main page of the repository.
• Under your repository name, click Settings.
• In the left menu, click Branches.
• Select the branch you want to mark protected using the drop-down menu.
• Select Protect this branch.
61. How to delete Repository in GitHub?
• On GitHub, navigate to the main page of the repository.
• Under your repository name, click Settings.
• Scroll to the bottom of the page and you will find Delete this repository button
• When you click on that button, another pop up will appear, here you need to type in
the name of your repository name and click on the button bellow which says: I
understand the consequences, delete the repository.
62. how to give an access to a specific person to repository?
You can invite users to become collaborators to your personal repository.
• Under your repository name, click Settings.
• In the left sidebar, click Collaborators.
• Under "Collaborators", start typing the collaborator's username.
• Select the collaborator's username from the drop-down menu.
• Click Add collaborator.
• The user will receive an email inviting them to the repository. Once they accept your
invitation, they will have collaborator access to your repository.
You might also like
- GIT Interview Questions & AnswersDocument8 pagesGIT Interview Questions & AnswersRanjithNo ratings yet
- Top GIT Interview QuestionDocument10 pagesTop GIT Interview QuestionmagillaniNo ratings yet
- Name: Dhanraj B. Ranvirkar Topic: Basics of GitDocument7 pagesName: Dhanraj B. Ranvirkar Topic: Basics of GitRitik bhadoriaNo ratings yet
- Git vs SVN, basic Git commands and resolving conflictsDocument20 pagesGit vs SVN, basic Git commands and resolving conflictsPRABHU SORTURNo ratings yet
- DevOps Interview QuestionsDocument45 pagesDevOps Interview QuestionsManupal SinghNo ratings yet
- DevOps Interview Questions & AnswersDocument23 pagesDevOps Interview Questions & AnswersmaazNo ratings yet
- Ans: GIT SVNDocument6 pagesAns: GIT SVNAkhil AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Git 31 FefDocument15 pagesGit 31 FefDeepak DNo ratings yet
- All Commands You Need To Know About GitDocument11 pagesAll Commands You Need To Know About Gitopensoft khawlaniNo ratings yet
- 1) What Is GIT?Document7 pages1) What Is GIT?Madhu KumarNo ratings yet
- Git and GitHubDocument4 pagesGit and GitHubsubodh kumarNo ratings yet
- Git Interview QuestionsDocument21 pagesGit Interview QuestionsPradeepReddyNo ratings yet
- Top 100 Git Questions and AnswersDocument30 pagesTop 100 Git Questions and Answersopensoft khawlaniNo ratings yet
- 1000 Java Interview Questions-5Document112 pages1000 Java Interview Questions-5Yannick TCHATONo ratings yet
- Git DocksDocument4 pagesGit DocksRISHI SURYAWANSHINo ratings yet
- Top 40 Interview Questions On GitDocument8 pagesTop 40 Interview Questions On GitsainathhpNo ratings yet
- Software Version Control: Setting UpDocument7 pagesSoftware Version Control: Setting Upkhalled meneoualiNo ratings yet
- GIT INTERVIEW QUESTIONS GUIDEDocument10 pagesGIT INTERVIEW QUESTIONS GUIDEKashyapkumarNo ratings yet
- Basic Git Interview QuestionsDocument6 pagesBasic Git Interview QuestionsAriful Islam ArifNo ratings yet
- Git Branching StrategyDocument12 pagesGit Branching Strategykotojuvenu06No ratings yet
- Day 9 Task: Deep Dive in Git & Github For Devops EngineersDocument8 pagesDay 9 Task: Deep Dive in Git & Github For Devops Engineerssheak ImranNo ratings yet
- Git and GitHub Notes by TrainWithShubhamDocument13 pagesGit and GitHub Notes by TrainWithShubhamSarvepalli Uday KiranNo ratings yet
- Sqa 2Document24 pagesSqa 2Khadija AfzalNo ratings yet
- Git Quick GuideDocument41 pagesGit Quick GuideLakshmi Sravanthi Chowdam100% (1)
- Linus Torvalds For Linux Kernel DevelopmentDocument8 pagesLinus Torvalds For Linux Kernel DevelopmentSrikanth SharmaNo ratings yet
- The Difference Between GIT and SVNDocument6 pagesThe Difference Between GIT and SVNsongacoNo ratings yet
- Git From Scratch: A Concise IntroductionDocument61 pagesGit From Scratch: A Concise IntroductionKuldeep Singh100% (4)
- DevOps Cours Partie2Document51 pagesDevOps Cours Partie2chaima sakkaNo ratings yet
- Git Cheat SheetDocument28 pagesGit Cheat SheetBharath Kumar100% (2)
- Git MockDocument4 pagesGit MockTEJAS KHARTODENo ratings yet
- Git Tutorial - Learn Git Branching in Less Than 6 MinutesDocument6 pagesGit Tutorial - Learn Git Branching in Less Than 6 MinutesSegunOdewoleNo ratings yet
- How To Use Git Branches - DigitalOceanDocument12 pagesHow To Use Git Branches - DigitalOceandioporcoNo ratings yet
- 1 - Git TerminologyDocument5 pages1 - Git TerminologyKashif KamalNo ratings yet
- Basic GIT Commands: Understanding The GIT WorkflowDocument6 pagesBasic GIT Commands: Understanding The GIT WorkflowRaphael AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- Git and GitHubDocument17 pagesGit and GitHubcreate world100% (1)
- PDF Git Interview QuestionsDocument21 pagesPDF Git Interview QuestionsRajNo ratings yet
- 03 - Git HandoutDocument20 pages03 - Git Handoutdhoni2234No ratings yet
- Programming Foundations Version Control With GitDocument4 pagesProgramming Foundations Version Control With GitSolution GuruNo ratings yet
- Git Basics in Under 10 MinutesDocument22 pagesGit Basics in Under 10 MinutesMohd AshfaqNo ratings yet
- Git Is A Version Control System of Distributed Nature That Is Used To Track Changes in Source Code DuringDocument1 pageGit Is A Version Control System of Distributed Nature That Is Used To Track Changes in Source Code Duringapotamkin123No ratings yet
- Main GitDocument8 pagesMain Gitilyas2sapNo ratings yet
- Hints For Using GitDocument5 pagesHints For Using GitphpoopwayNo ratings yet
- Git and Github DatasheetDocument14 pagesGit and Github DatasheetXander Rodriguez100% (1)
- Git-IqaDocument11 pagesGit-IqaMurali TungaNo ratings yet
- Git_Cheat_SheetDocument18 pagesGit_Cheat_SheetpanatishivakumarNo ratings yet
- Version Control System QuestionsDocument3 pagesVersion Control System QuestionsdeepuNo ratings yet
- Git Workflow: Git Init Git Status Git Add Git Diff Git CommitDocument4 pagesGit Workflow: Git Init Git Status Git Add Git Diff Git CommitAchmad RofiqNo ratings yet
- Git - GithubDocument29 pagesGit - GithubHAHANo ratings yet
- Git-GitHub Hands-on Session GuideDocument14 pagesGit-GitHub Hands-on Session GuideLavNo ratings yet
- Git For ScribdDocument43 pagesGit For ScribdRonTheHumanNo ratings yet
- GitDocument2 pagesGitrajehshsjNo ratings yet
- Revision Control: INF5750/9750 - Lecture 1 (Part III)Document47 pagesRevision Control: INF5750/9750 - Lecture 1 (Part III)darwinvargas2011No ratings yet
- Git DocumentDocument14 pagesGit Documentbala nagellaNo ratings yet
- Git TextDocument5 pagesGit TextSubramanyaNo ratings yet
- Distributed Version Control System AdvantagesDocument32 pagesDistributed Version Control System Advantagescherry07 cherryNo ratings yet
- Weekly Report 42Document23 pagesWeekly Report 42Trần Cơ TâmNo ratings yet
- Learn The Basics of Git in Under 10 MinutesDocument18 pagesLearn The Basics of Git in Under 10 Minutespeboli1163No ratings yet
- Merge Conflicts: Git Mergetool - Tool MeldDocument6 pagesMerge Conflicts: Git Mergetool - Tool MeldAndrei DiaconescuNo ratings yet
- What Is Version Control?Document9 pagesWhat Is Version Control?Trinus BlackstarNo ratings yet
- Netwrix Auditor: Release NotesDocument14 pagesNetwrix Auditor: Release NotesTest UserNo ratings yet
- KM Maturity Model Service - vC0307Document1 pageKM Maturity Model Service - vC0307Yaj BusawonNo ratings yet
- Bachelor of Business Information TechnologyDocument6 pagesBachelor of Business Information Technologygosaye desalegn100% (1)
- Russia Ict MarketDocument63 pagesRussia Ict Markethui cathyNo ratings yet
- Case Study3-FitbitDocument11 pagesCase Study3-FitbitKwai Fong PANGNo ratings yet
- Ram and RomDocument13 pagesRam and RomJSD190No ratings yet
- EPM Add-In Academy - Enterprise Performance Management - SCN WikiDocument3 pagesEPM Add-In Academy - Enterprise Performance Management - SCN WikiBhalchandra RupeNo ratings yet
- Large It ListDocument864 pagesLarge It ListGp MishraNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 Socialmedia Mix and Cybersocial Tools - Vol 1Document26 pagesTopic 4 Socialmedia Mix and Cybersocial Tools - Vol 1Sathya ManoharanNo ratings yet
- Spring Interview QuestionsDocument4 pagesSpring Interview Questionsrguptamtech50% (2)
- Event PlanningDocument3 pagesEvent PlanningSudikcha KoiralaNo ratings yet
- Diploma - Thesis - 1.0 - Analysis of Online Shop SystemsDocument90 pagesDiploma - Thesis - 1.0 - Analysis of Online Shop SystemsNecroimiXNo ratings yet
- Data Flow Diagrams-Hrmo ProposedDocument8 pagesData Flow Diagrams-Hrmo ProposedRalph Simon Tagros0% (1)
- Cwoer Cisco Ios Access Lists by Jeff SedayaoDocument227 pagesCwoer Cisco Ios Access Lists by Jeff SedayaoYahiaKhoujaNo ratings yet
- Acronis Backup Cloud - DatasheetDocument4 pagesAcronis Backup Cloud - DatasheetJorgeNo ratings yet
- Proxy OverviewDocument9 pagesProxy OverviewKishore KumarNo ratings yet
- Checkpoint InterviewDocument18 pagesCheckpoint InterviewKaushal Kishor100% (1)
- Lalit KumarDocument16 pagesLalit Kumarrohit kumawatNo ratings yet
- Guidance PCI DSS Scoping and Segmentation v1Document26 pagesGuidance PCI DSS Scoping and Segmentation v1Andrew WebbNo ratings yet
- AWS-DevOps-DevOps Best PracticesDocument12 pagesAWS-DevOps-DevOps Best PracticesNarendraNo ratings yet
- Wso2 Esb PDFDocument62 pagesWso2 Esb PDFmjc45No ratings yet
- Ethical Hacking and Penetration Testing (Kali Linux) - IExplo1tDocument4 pagesEthical Hacking and Penetration Testing (Kali Linux) - IExplo1tSergio Bolaños CotoNo ratings yet
- Configure ILODocument3 pagesConfigure ILOsaifulNo ratings yet
- Project management software enables collaborationDocument4 pagesProject management software enables collaborationNoman AliNo ratings yet
- Display Java CalendarDocument9 pagesDisplay Java CalendarRoshith PinapalaNo ratings yet
- Itc 123 Computer Organization and ArchitectureDocument3 pagesItc 123 Computer Organization and Architectureemmanuelopoku5566No ratings yet
- AISDocument9 pagesAISBima AdetyaNo ratings yet
- Cyber Crime & Cyber Forensics - Advanced TopicsDocument19 pagesCyber Crime & Cyber Forensics - Advanced TopicsSekhar P100% (1)
- Fiori InstallationDocument11 pagesFiori InstallationrahulyedapallyNo ratings yet
- Full Spectrum Detections For Web ShellsDocument16 pagesFull Spectrum Detections For Web ShellsHamza SadiqNo ratings yet