Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3 - HIPERTONIC SALINE VS MANITOL - Diah M
Uploaded by
lawrensiusr0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views25 pagesThis document discusses different options for managing increased intracranial pressure (ICP), including mannitol, furosemide, and hypertonic saline. Mannitol works by increasing the gradient across the blood-brain barrier to rapidly reduce ICP over 6 hours, while hypertonic saline's primary mechanism is also increasing this gradient for immediate ICP reduction over 4 hours. Both have hemodynamic and potential adverse effects that require monitoring. The document concludes that while controversial, hypertonic saline 3% may be superior to mannitol 20% for treating elevated ICP.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses different options for managing increased intracranial pressure (ICP), including mannitol, furosemide, and hypertonic saline. Mannitol works by increasing the gradient across the blood-brain barrier to rapidly reduce ICP over 6 hours, while hypertonic saline's primary mechanism is also increasing this gradient for immediate ICP reduction over 4 hours. Both have hemodynamic and potential adverse effects that require monitoring. The document concludes that while controversial, hypertonic saline 3% may be superior to mannitol 20% for treating elevated ICP.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views25 pages3 - HIPERTONIC SALINE VS MANITOL - Diah M
Uploaded by
lawrensiusrThis document discusses different options for managing increased intracranial pressure (ICP), including mannitol, furosemide, and hypertonic saline. Mannitol works by increasing the gradient across the blood-brain barrier to rapidly reduce ICP over 6 hours, while hypertonic saline's primary mechanism is also increasing this gradient for immediate ICP reduction over 4 hours. Both have hemodynamic and potential adverse effects that require monitoring. The document concludes that while controversial, hypertonic saline 3% may be superior to mannitol 20% for treating elevated ICP.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 25
Mannitol ,Furosemide or
Hypertonic Saline in Management
of Increased Intracranial Pressure
Splachnic Brain
Diah Mustika HW dr,SpN,KIC
JCCA, 20 Maret 2022
Intracranial Component
AUTOREGULATION
• Maintain the cerebral perfusion pressure (CPP)
• Effective at MAP 60-150 mmHg
• CBF = CPP (MAP-ICP)
CVR
5
MANAGEMENT
• Elevation of head 30o
• Analgesia and sedation
• Hyperventilation
• Maintain : blood pressure, volume status,
body temperature, CPP
• Monitoring : haemoglobin, blood glucose,
sodium
• Hyperosmolar therapy
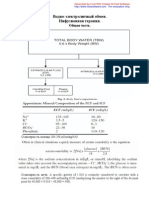
OSMOLALITY
2(Na+K) + GD/18 + BUN/2,8
OR
2(Na+K) + GD/18 + Ur/6,4
Keep Osmolality between 310-320 mOsm/L
COMPARATION OF HYPEROSMOLAR
THERAPY
MANNITOL 20%
• Dose : 0,25 – 1gr/kgBB every 3-6
hours over 15-30 minutes
• Infuse via peripheral line, central line
• Monitoring :
– ICP (goal <20 mmHg)
– Hypovolemia
– Serum osmolality (<325 mOsm)
• Contraindication : Renal failure, CHF
HYPERTONIC SALINE 3% BOLUS
• Dose : 250 ml IV every 3-6 hours over
20-30 minutes
• Infuse via central line
• In a emergency, HTS 3% may
administered via infuse via peripheral line
• Monitoring :
– ICP (goal <20 mmHg)
– Serum sodium (<155 mEq/L)
HYPERTONIC SALINE 3% INFUSION
• Dose : 50 - 150 ml/hours
• Infuse via central line
• Monitoring :
– ICP (goal <20 mmHg),
– Serum sodium (<155 mEq/L)
– Serum osmolality (<325 mOsm)
HYPERTONIC SALINE 23,4%
• Dose: 30ml every 3-6 hours over 15 – 30
minutes
• Infusion via central line
• Monitoring :
– ICP (goal <20 mmHg)
– Serum sodium (goal <155 mE q/L)
– Central pontine myelinolysis
FUROSEMIDE
• Dose : 1mg/kgBB every 8 hours
• Better administration if combine with
mannitol
• Contraindication : Hypotension
MANNITOL VS HTS 3% (1)
Mannitol HTS 3%
Primary - Increases gradient across - Increases gradient across
mechanism BBB BBB
- Rapid reduction of ICP - Immediate reduction of ICP
- Duration : 6 hours - Duration : 4 hours
Secondary - Cerebral vasoconstriction - Mixed immunomodulatory and
Mechanism - Decreases blood viscosity antiinflamatory effects
- Increases cerebral blood
flow
Hemodynamic - Transient expansion of - Expand intravascular volume
effects intravascular volume - Increases MAP
- Brisk osmotic diuresis
MANNITOL VS HTS 3% (2)
Mannitol HTS 3%
Adverse event - Acute Kidney Injury - Osmotic demyelination
- Dehydration syndrome
- Hypotension - Fluid overload
- Electrolite Imbalances - Hyperchloremic metabolic
- Rebound ICP acidosis
- Hyperoncotic hemolysis
Monitoring - Through osmolar gap (<20 - Serum sodium every 4-6
mOsm/kg) hours
- Renal function - Hypernatremia goal (<155
- Electrolytes mEq/L)
CONCLUSION
• Elevation of ICP can be treated with
hyperosmolar therapy such as Mannitol
20% or HTS 3%
• Even it still controversial, administration of
HTS 3% is superior than mannitol 20%
• Furosemide can administered as
concomitant therapy to reduce ICP
25
You might also like
- Malignant Hyperthermia AlgorithmDocument1 pageMalignant Hyperthermia AlgorithmCesar David CaceresNo ratings yet
- HyponatremiaDocument39 pagesHyponatremiakrataiwanNo ratings yet
- Cardio Lab MedsDocument11 pagesCardio Lab MedsDianne Erika MeguinesNo ratings yet
- Stupor and Coma in AdultsDocument23 pagesStupor and Coma in AdultsFdo RMNo ratings yet
- (-1) PE ASTA O CITESTI PRIMA José Biller-Practical Neurology-LWW (2017) PDFDocument1,470 pages(-1) PE ASTA O CITESTI PRIMA José Biller-Practical Neurology-LWW (2017) PDFDutaCristianNo ratings yet
- Central Nervous System: Zalak Patel, MBBSDocument25 pagesCentral Nervous System: Zalak Patel, MBBSMinaz PatelNo ratings yet
- Adrenocortical HyperfunctionDocument132 pagesAdrenocortical Hyperfunctionshobharamkrishna100% (2)
- Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Disorders Robert B Schonberger 2018Document18 pagesFluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Disorders Robert B Schonberger 2018Akhmad Fadhiel Noor100% (1)
- Tatalaksana Krisis HipertensiDocument38 pagesTatalaksana Krisis HipertensiDr Edi HidayatNo ratings yet
- Fluid & Electrolite Management in Surgical WardsDocument97 pagesFluid & Electrolite Management in Surgical WardsBishwanath PrasadNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Anesthesia PDFDocument55 pagesCardiac Anesthesia PDFvincent.chauvette100% (3)
- HyponatremiaDocument40 pagesHyponatremiaarchana p sNo ratings yet
- 17 - Toronto Notes 2011 - NephrologyDocument92 pages17 - Toronto Notes 2011 - NephrologyKhairulsani Yusof100% (2)
- Sepsis: Pathophysiology and Management in The ICUDocument38 pagesSepsis: Pathophysiology and Management in The ICUprashsubbuNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Emergencies CompiledDocument102 pagesEndocrine Emergencies CompiledSubhkanish RavindraNo ratings yet
- Cerebral EdemaDocument40 pagesCerebral EdemaMithun GorreNo ratings yet
- Nephrology Board Review May 2008-McfaddenDocument77 pagesNephrology Board Review May 2008-McfaddenarmymdNo ratings yet
- Robert W. Schrier - Atlas of Diseases of The Kidney Volume 01 PDFDocument316 pagesRobert W. Schrier - Atlas of Diseases of The Kidney Volume 01 PDFAtu Oana100% (3)
- Neurology Case 6Document3 pagesNeurology Case 6muhammadridhwanNo ratings yet
- Electrolyte ImbalanceDocument44 pagesElectrolyte ImbalanceDevi Christina Damanik (Papua medical School)No ratings yet
- Strokes Student HandoutDocument4 pagesStrokes Student HandoutMiss LindiweNo ratings yet
- MannitolDocument9 pagesMannitolNadiah Nasuha ZolkafleeNo ratings yet
- Traumatic Brain InjuryDocument14 pagesTraumatic Brain InjurySamuel Hananiel RoryNo ratings yet
- Mannitol: It'S Place in Current Clinical PracticeDocument11 pagesMannitol: It'S Place in Current Clinical PracticecardiacanesthesiaNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For The Management of Pediatric Severe Traumatic Brain InjuryDocument36 pagesGuidelines For The Management of Pediatric Severe Traumatic Brain InjuryRachelle Celina AlmonteNo ratings yet
- Hyponatremia Topic DiscussionDocument4 pagesHyponatremia Topic Discussionapi-647904873No ratings yet
- Somchodok Chakreeyarat, MD. Endocrine Unit, Department of Medicine Bhumibol Adulyadej HospitalDocument53 pagesSomchodok Chakreeyarat, MD. Endocrine Unit, Department of Medicine Bhumibol Adulyadej HospitalLing TaerahkunNo ratings yet
- Farma StrokeDocument37 pagesFarma StrokeDAHLIANo ratings yet
- Acute Management of StrokeDocument19 pagesAcute Management of StrokeBKGUBIONo ratings yet
- Traumatic Brain Injury and Other Neurocritical ConditionsDocument8 pagesTraumatic Brain Injury and Other Neurocritical Conditionslim sjNo ratings yet
- Hypovolemic ShockDocument27 pagesHypovolemic Shock'govamaniacs' Insave IVNo ratings yet
- 01-Guidelines For Use of Hypertonic SalineDocument13 pages01-Guidelines For Use of Hypertonic SalineSatish VeerlaNo ratings yet
- Surgical Updates - ICPDocument16 pagesSurgical Updates - ICPIffan Indra SalamaNo ratings yet
- Management of Anesthesia: Diabetes MellitusDocument29 pagesManagement of Anesthesia: Diabetes MellitusHari PrasadNo ratings yet
- Fluids & ElectsDocument61 pagesFluids & ElectsYousif Ahmed DANo ratings yet
- Head Injury Management: Ahimbisibwe Alaphael Lecturer DR - JulietDocument33 pagesHead Injury Management: Ahimbisibwe Alaphael Lecturer DR - JulietNinaNo ratings yet
- Sepsis: Pathophysiology and Management in The ICU: Moderator: DR Kavita Rani Sharma Presenter: Dr. PrashanthDocument38 pagesSepsis: Pathophysiology and Management in The ICU: Moderator: DR Kavita Rani Sharma Presenter: Dr. Prashanthprashsubbu100% (1)
- Intra-Cranial PressureDocument36 pagesIntra-Cranial PressureKapil LakhwaraNo ratings yet
- 12a. Kuliah Aki 2017Document36 pages12a. Kuliah Aki 2017yussikafernandaNo ratings yet
- Final PresentationDocument28 pagesFinal PresentationMudabbir QuamarNo ratings yet
- HONK by AijazDocument40 pagesHONK by AijazMuhammad Imran AlamNo ratings yet
- Водно-электролитный балланс.Document12 pagesВодно-электролитный балланс.misha202008No ratings yet
- Lab DataDocument63 pagesLab Datab202104023 TMUNo ratings yet
- Approach To ShockDocument40 pagesApproach To ShockDivesh NaiduNo ratings yet
- Epinephrine (Adrenaline)Document9 pagesEpinephrine (Adrenaline)Tushar GhuleNo ratings yet
- Acute Complications of DM ESS 2016Document41 pagesAcute Complications of DM ESS 2016teodordragnev1No ratings yet
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) - Presentation Slide EditedDocument22 pagesDiabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) - Presentation Slide EditedTerence Chin0% (1)
- Hyper Calc Emi ADocument26 pagesHyper Calc Emi AAman Tayal0% (1)
- Surat-2019 Septic Shock Clinical PolicyDocument49 pagesSurat-2019 Septic Shock Clinical PolicyBaronKornNo ratings yet
- Med-Lgis-Diabetes Mellitus Complications-Dr. Saima Ambreen Mu1 HFHDocument47 pagesMed-Lgis-Diabetes Mellitus Complications-Dr. Saima Ambreen Mu1 HFHHassan Latif SheikhNo ratings yet
- Hipotalamus-Pituitari-Sumbu Adrenal (Axis) Regulasi Sirkadian Korteks Adrenal CRH ACTHDocument9 pagesHipotalamus-Pituitari-Sumbu Adrenal (Axis) Regulasi Sirkadian Korteks Adrenal CRH ACTHAnastasia PinkyNo ratings yet
- Surgery YbDocument67 pagesSurgery YbTamirat geletaNo ratings yet
- Hyperkalemia Approach AND Management: Dr. Renuka RayanaDocument38 pagesHyperkalemia Approach AND Management: Dr. Renuka RayanaSap Modules100% (1)
- Topic Gyne ERASDocument60 pagesTopic Gyne ERASCrown SakulprakopkitNo ratings yet
- 3 SalineDocument3 pages3 Salineeko aNo ratings yet
- Management of Acute Kidney InjuryDocument31 pagesManagement of Acute Kidney InjurysumitNo ratings yet
- PATIENT WITH ENDOCRINE DYSFUNCTION - PPTX Diabetes EmergenciecyDocument45 pagesPATIENT WITH ENDOCRINE DYSFUNCTION - PPTX Diabetes Emergenciecysembakarani thevagumaranNo ratings yet
- Icp NewDocument50 pagesIcp Newanon_411736789No ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting Coagulation and AnticoagulantsDocument19 pagesDrugs Affecting Coagulation and Anticoagulantsuzzal ahmed0% (1)
- Intracranial HemorrhageDocument41 pagesIntracranial Hemorrhagedoctormussieaberra100% (1)
- The Principles of ManagementDocument4 pagesThe Principles of ManagementRoadtogot 2023No ratings yet
- Neuro CaseDocument25 pagesNeuro CaseHainey GayleNo ratings yet
- Osmotherapy For Treatment of Intracranial HypertensionDocument4 pagesOsmotherapy For Treatment of Intracranial HypertensionTessa CruzNo ratings yet
- DR Omar Kamal Ansari Dept of AnaesthesiologyDocument46 pagesDR Omar Kamal Ansari Dept of Anaesthesiologyvvb_frndNo ratings yet
- Neuropharmacology of Anesthetic Agents: Robert H. Sirait. DR Span Dept. Anesthesiology FK UkiDocument20 pagesNeuropharmacology of Anesthetic Agents: Robert H. Sirait. DR Span Dept. Anesthesiology FK UkiChintya Anugrah SuhendraNo ratings yet
- Dysnatremia in The ICU: Milap Pokaharel and Clay A. BlockDocument13 pagesDysnatremia in The ICU: Milap Pokaharel and Clay A. BlockJonathan Gustavo MenaNo ratings yet
- Stroke Differential Diagnosis and Mimics Part 1Document11 pagesStroke Differential Diagnosis and Mimics Part 1AnthoNo ratings yet
- Treatment Guidelines For Hyponatremia Stay The.180Document22 pagesTreatment Guidelines For Hyponatremia Stay The.180Carolyn CamposNo ratings yet
- White Matter DiseaseDocument55 pagesWhite Matter DiseasePeacemongerNo ratings yet
- 28 - White Matter DiseasesDocument92 pages28 - White Matter DiseasesDARWING PADILLANo ratings yet
- Neurologic Manifestations of Major Electrolyte AbnormalitiesDocument9 pagesNeurologic Manifestations of Major Electrolyte AbnormalitiesMartha OktaviaNo ratings yet
- Vasopressin AntagonistsDocument10 pagesVasopressin AntagonistsedsonNo ratings yet
- Filippa To S 2016Document8 pagesFilippa To S 2016Pablo IgnacioNo ratings yet
- HyponatremiaDocument16 pagesHyponatremiaRohit Mathew100% (1)
- Hyponatremia in Cirrhosis: An Update: Joseph J. Alukal, MD, Savio John, MD and Paul J. Thuluvath, MD, FRCPDocument11 pagesHyponatremia in Cirrhosis: An Update: Joseph J. Alukal, MD, Savio John, MD and Paul J. Thuluvath, MD, FRCPMuzaffar MehdiNo ratings yet
- Anatomyy PDFDocument196 pagesAnatomyy PDFDesyana KasimNo ratings yet
- Overview of The Treatment of Hyponatremia in AdultsDocument23 pagesOverview of The Treatment of Hyponatremia in AdultsAlexander ImbacuánNo ratings yet
- Overview of The Treatment of Hyponatremia in Adults - UpToDateDocument52 pagesOverview of The Treatment of Hyponatremia in Adults - UpToDateGerman Barrientos CabreraNo ratings yet
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 8Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 8JUSASBNo ratings yet
- Disorders of SodiumDocument13 pagesDisorders of SodiumteranrobleswaltergabrielNo ratings yet
- Nausea and Vomiting of Pregnancy - Treatment and Outcome - UpToDateDocument17 pagesNausea and Vomiting of Pregnancy - Treatment and Outcome - UpToDateFranz Huber QueiroloNo ratings yet
- Acute Hemodialysis PrescriptionDocument18 pagesAcute Hemodialysis PrescriptionOlga BabiiNo ratings yet
- 05 Degenerative - Demyelinating DiseasesDocument26 pages05 Degenerative - Demyelinating DiseasesMalinda KarunaratneNo ratings yet
- Body Fluid, Electrolyte FcpsDocument73 pagesBody Fluid, Electrolyte FcpsInzamamul Haque ShihabNo ratings yet
- Hyponatraemia: Dr. Peter Allan Dr. Saibal GangulyDocument8 pagesHyponatraemia: Dr. Peter Allan Dr. Saibal Gangulynur khadijahNo ratings yet
- Acute Hemodialysis PrescriptionDocument22 pagesAcute Hemodialysis PrescriptionDai Elanadil DNo ratings yet
- Disorders of Plasma Sodium - Causes, Consequences, and CorrectionDocument11 pagesDisorders of Plasma Sodium - Causes, Consequences, and CorrectionDaniel Torres Cutiva100% (1)
- Osmotic Demyelination Syndrome.Document5 pagesOsmotic Demyelination Syndrome.Nontaphon PiyawattanamethaNo ratings yet
- SiadhDocument16 pagesSiadhGokul Rajan100% (1)