Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Law 6
Law 6
Uploaded by
Chilin Yurem Manzano de la Cruz0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesOriginal Title
law 6
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesLaw 6
Law 6
Uploaded by
Chilin Yurem Manzano de la CruzCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
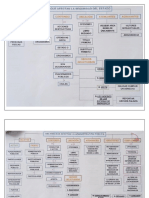
WEED Civil Procedure Rules
Civil procedure
‘Alisdair Hannah, a barrister, i talking to a visiting,
‘group of young European lawyers.
“All cases concerning goods, property, debt
repayment, breach of contract (with some
exceptions such as insolvency proceedings and
non-contentious litigation), are subject to Civil
Procedure Rules, The Rules, which came into
force in 1999 in England and Wales, made radical
changes to civil process in the County Court and
the High Court. P
‘The judge performs the role of case manager. The court sets a timetable for litigation,
with the parties being under an obligation to the court to adhere to timescales which
control the progress of the case. Procedure rules are supplemented by detailed instructions
made by the judge which support the rules, known as practice directions.”
é
Proceeding with a claim
‘Most claims are initiated by the use of a claim form, which functions as a summons.
“The claim form can be used for different types of claim, for example for specified or
unspecified monetary sums, or for the claimant to ask the court co make an order. Once
a claim has been issued, a copy is served on, that is, delivered to, the defendant with a
response pack inviting them to either admit the claim, using a form of admission, or to
defend it, using a form of defence. The response pack also contains an acknowledgement
‘of service form to confirm receipt of the claim, and a counterclaim form for the defendant
10 use if they wish to claim against the claimant. A defendant must respond within
14 days of service of the particulars of the claim. Ifthe defendant does not respond,
judgment may be given in favour of the claimant, ‘The defendant may be able to get a
‘time extension for filing a reply on defence by using the part of the acknowledgement of
service form which states an intention to defend the claim,
Cases are allocated to a regime or track by a procedural judge according to their
‘monetary value. Claims of £5,000 or less are allocated to a small claims track while
claims of up to £15,000 are allocated to a fast track. More complex claims with a greater
value are allocated to a multi track regime. Fast track directions might include disclosure,
where the claimant tells the defence of any relevant documents in their possession.
‘This is followed by inspection, initiated by a written request by the claimant to look at
relevant documents held by the defence, and an exchange of witness statements. The
multi track regime is intended to be flexible and does not have a standard procedure. In
all regimes, parties are encouraged to settle their differences and for this purpose a stay
in proceedings, that is, a temporary halt, may be agreed. Case management conferences
are often conducted by telephone and give parties the opportunity to review the process
and make decisions. fa defendant is ordered to pay by a judge and fails to do so, the
claimant can enforce the judgment in the Magistrates’ Cou
Note: The reforms to the Civil Procedure Rules led by Woolf in 1988 included the following
changes in legal language:
claim form, formerly known asa wrt of summons
specified, formerly known as a liquidated claim (afbeed monetary sum)
claimant, formerly known asa plaintiff
Professional English in Use Low
6.1
6.2
Complete the definitions. Look at A and B opposite to help you.
io ~ the process by which a claimant may look at written evidence held by the
defence
2 ssn the document in which the defendant makes a claim against the claimant
3 a snomnnnse the document in which the defendant agrees to
the claim made by the claimant
4 ~ the document starting a claim proceedings
5 _---nsnsns~ the process by which the claimant is required to inform the defendant of
documents they hold relevant to the claim
Ca = the document giving evidence by someone who saw or heard
something critical to the case
7 vesunnaenuna~ the instructions given by a judge on how procedures should be
‘carried out in a case
Make word combinations from A and B opposite using a word from each box, Then use
appropriate word combinations and information in B opposite to answer the questions
below.
admit a timetable
agree to a stay
allocate to aclaim
‘enforce the process
file ‘the judgment
issue aclaim
review aclaim on
serve a regime
set differences
settle a reply
1 How does a claim proceeding start?
2 What must a defendant do when he or she has been served
with a claim?
43 If both parties want time to try to sete the dispute out of
court, what should they ask the court to d
4 What is the purpose of a case management conference?
5 Ia defendant is ordered to pay a claimant's costs but does,
not what action ean the claimant take?
Asolicitor discusses @ claim.
Over to you
ieee ea fom a ifferent
See ee ea ee
For more information on civil procedure in England and Wales, go to:
et ea era ae Re ciara ROHR Roce
Professional English in Use Law 9
You might also like
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Contrato de Sociedad CivilDocument10 pagesContrato de Sociedad CivilChilin Yurem Manzano de la Cruz100% (3)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5807)
- Contrato de Mutuo SimpleDocument2 pagesContrato de Mutuo SimpleChilin Yurem Manzano de la CruzNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- Contrato de SuministroDocument2 pagesContrato de SuministroChilin Yurem Manzano de la CruzNo ratings yet
- Derecho Agrario - EycDocument16 pagesDerecho Agrario - EycChilin Yurem Manzano de la CruzNo ratings yet
- Delitos Que Afectan Al ESTADODocument3 pagesDelitos Que Afectan Al ESTADOChilin Yurem Manzano de la CruzNo ratings yet
- Demanda de Reconocimiento Como Legal SucesorDocument4 pagesDemanda de Reconocimiento Como Legal SucesorChilin Yurem Manzano de la CruzNo ratings yet
- Investigación Derecho Agrario. Alberto Manzano de La CruzDocument7 pagesInvestigación Derecho Agrario. Alberto Manzano de La CruzChilin Yurem Manzano de la CruzNo ratings yet
- Apunte B - DTDocument3 pagesApunte B - DTChilin Yurem Manzano de la CruzNo ratings yet
- Guia de Agrario Primer ParcialDocument4 pagesGuia de Agrario Primer ParcialChilin Yurem Manzano de la CruzNo ratings yet
- Centenario de La CPEUM 29feb2016-1Document16 pagesCentenario de La CPEUM 29feb2016-1Chilin Yurem Manzano de la CruzNo ratings yet
- CONTRATO DE DepositoDocument2 pagesCONTRATO DE DepositoChilin Yurem Manzano de la CruzNo ratings yet
- Contrato de Prestación de Servicios ProfesionalesDocument4 pagesContrato de Prestación de Servicios ProfesionalesChilin Yurem Manzano de la CruzNo ratings yet
- Delitos Contra La Fe PublicaDocument57 pagesDelitos Contra La Fe PublicaChilin Yurem Manzano de la CruzNo ratings yet
- Regularización de Licencia de Uso de TierraDocument3 pagesRegularización de Licencia de Uso de TierraChilin Yurem Manzano de la CruzNo ratings yet
- Concepto de Desarrollo Económico y SocialDocument5 pagesConcepto de Desarrollo Económico y SocialChilin Yurem Manzano de la CruzNo ratings yet
- Tratados Económicos de México en Materia Económica. Alberto ManzanoDocument1 pageTratados Económicos de México en Materia Económica. Alberto ManzanoChilin Yurem Manzano de la CruzNo ratings yet
- Resumen. DelitosDocument7 pagesResumen. DelitosChilin Yurem Manzano de la CruzNo ratings yet