Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Balance of Payments Breakdown
Uploaded by
Kamesh RamamoorthyOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Balance of Payments Breakdown
Uploaded by
Kamesh RamamoorthyCopyright:
Available Formats
EXTERNAL SECTOR
MODULE 1
BALANCE OF PAYMENT
External sector deals with export and import of goods and services, and
financial capital between nations. The countries export goods and services
over which it has advantage over other countries and import goods and
services in which it lacks advantage over others.
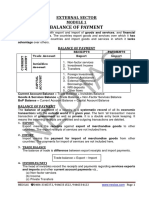
BALANCE OF PAYMENT
RECEIPTS PAYMENTS
Trade Account Export Import
CURRENT
ACCOUNT
1. Non-factor services
Invisibles
2. Investment Income
Account
3. Transfers
1. Foreign Investment
2. External Assistance
ACCOUNT
CAPITAL
3. External Commercia
Borrowings (ECBs)
4. NRI deposits
5. Other flows
Current Account Balance = Trade Balance + Invisibles Balance
Goods & Services Balance = Trade Balance + Non-Factor Services Balance
BoP Balance = Current Account Balance + Capital Account Balance
BALANCE OF PAYMENT
The balance of payment of a country is a systematic record of all its
economic transactions with the outside world in a given year. The term
‘all transaction’ means transaction of government as well as private. It is a
double entry book keeping. It means the incoming receipts are credited and
outgoing transactions are debited.
1. EXPORT
Export means the receipts against export of merchandise goods to other
countries. The export receipts of services are not included here.
NEO IAS 0484-4030104, 9446331522, 9446334122 Page 1
www.neoias.com | www.youtube.com/neoias | www.facebook.com/neoias | www.twitter.com/neoias
2. IMPORT
Import means the payment for import of merchandise goods from other
countries. The payments for import of services are not included here.
3. TRADE BALANCE
The balance of trade is difference between export receipts and import
payments.
Trade balance = Export – Import
4. INVISIBLES (NET)
The head of invisibles record the receipts and payments regarding services
exports and imports and other current account payments viz.,
(a) Non-factor services
(b) Income
(c) Private Transfers
(a) NON-FACTOR SERVICES
Non-factor services refer to all invisible receipts or payments not
attributable to conventional factor of production, i.e., labour (remittance
from overseas migrants). Thus Non-factor services mean the export and
import of services alone. The non-factor services includes Group of
Services viz., Travel, Transportation, Insurance and Miscellaneous
Services, which encompass communication services, construction
services, financial services, software services, news agency services,
royalties, management services and business services etc. The
software services comprise information technology (IT) and IT-enabled
services (ITeS).
(b) INCOME
Income includes transactions regarding income from investments in the
form of dividends, profit and interest from loans.
(c) PRIVATE TRANSFERS
Private transfers include grants, gifts, remittances, etc., which do not
have any quid pro quo. Among the private transfers, the remittances is the
major source.
NEO IAS 0484-4030104, 9446331522, 9446334122 Page 2
www.neoias.com | www.youtube.com/neoias | www.facebook.com/neoias | www.twitter.com/neoias
Remittance is directly earned by labour which is a factor of production and
incomes like dividend, profit and interest are earned by capital which is also
a factor of production. So the income from both these heads is called factor
income services.
5. GOODS AND SERVICES BALANCE
It is the sum of trade balance and non-factor services
Goods and services balance = Trade balance + Non-factor
services.
6. CURRENT ACCOUNT BALANCE
Current account balance is the sum of trade balance and net invisibles.
Current account balance = Trade balance + Net
invisibles.
If the current account balance is positive, it is said to be surplus which
means favourable current account balance. If the current account
balance is negative, it is said to be deficit which means unfavorable
current account balance.
NEO IAS 0484-4030104, 9446331522, 9446334122 Page 3
www.neoias.com | www.youtube.com/neoias | www.facebook.com/neoias | www.twitter.com/neoias
7. EXTERNAL ASSISTANCE (NET)
External assistance means the transaction of official (government)
bilateral and multilateral loans. The bilateral loans are loan transactions
between two countries. Multilateral loans are official loan transactions
between a country and multilateral bodies like World Bank, IMF and Asian
Development Bank etc.
8. COMMERCIAL BORROWINGS (NET)
Commercial borrowings mean loan transaction by commercial enterprises.
It is also called as External Commercial Borrowing (ECB).
9. NON-RESIDENT DEPOSITS
The deposit received from non-resident Indians come under this head.
10. FOREIGN INVESTMENTS
There are two types of foreign investments. One is foreign direct
investment and another is portfolio investment. Portfolio investment is
also called as rentier investment.
(a) FOREIGN DIRECT INVESTMENT (FDI)
Foreign Direct Investment refers to direct bulk investment in a domestic
company by a foreign individual or company. The foreign direct investors
have control over company’s management and day to day affairs of
company which is possible by enough voting rights in his hand due to bulk
investment.
(b) PORTFOLIO (OR) RENTIER INVESTMENT
Portfolio investment refers to investment minimally in various financial
instruments like shares, debentures of a company. The portfolio investor
cannot have any control over company management.
11. OTHER FLOWS
Other flows include, delayed export receipts, leads and lags in export
receipts (the difference between the customs data and the banking channel
data), funds held abroad, and other capital transactions not included
elsewhere such as flows arising from cross-border financial derivative
and commodity hedging transactions, and sale of intangible assets such
as patents, copyrights, trademarks etc., and errors and omissions.
NEO IAS 0484-4030104, 9446331522, 9446334122 Page 4
www.neoias.com | www.youtube.com/neoias | www.facebook.com/neoias | www.twitter.com/neoias
The difference between the customs data and the banking channel data
arises because banking channels data relies on foreign exchange release/
receipt returns which are actual cash outgo and cover all flow and customs
data are based on bills of entries (import document field with the customs),
which might remain somewhat incomplete for a number of reasons in the
short run.
12. CAPITAL ACCOUNT TOTAL
Capital Account total (net) = External Assistance (net) + Commercial
Borrowings (net) + Non-resident deposits (net) + Foreign investments (net)
+ Other flows (net).
If the capital account balance is positive, it is said to be surplus. Surplus
capital account balance means favorable capital account balance. If the
capital account balance is negative, its said to be deficit. Deficit capital
account balance means unfavorable capital account balance.
13. RESERVES
Reserve means foreign exchange reserve. The sum of current and capital
account balance is the balance of payment.
Balance of payment = current account balance + capital account balance
NEO IAS 0484-4030104, 9446331522, 9446334122 Page 5
www.neoias.com | www.youtube.com/neoias | www.facebook.com/neoias | www.twitter.com/neoias
The balance is added to foreign exchange reserve if the balance of
payment is in surplus. The balance is deducted if the balance of payment
is in deficit. It means payment is made out of old balance (foreign
exchange reserve.)
IMPORT COVER
Import cover of reserves is a traditional trade-based indicator of
reserve adequacy. It is defined in terms of the number of months of
import equivalent to reserves.
After declining from seven months of imports as of March-end 2013 to
6.6 months of imports as of September-end 2013, the import cover of the
country’s reserves steadily climbed in each of the half-year periods
since then. The import cover of India’s foreign exchange reserves has
increased to 12 months as on September-end 2016 from 10.9 months
as on March-end 2016.
PREVIOUS YEARS’ QUESTIONS (PRELIMS)
1. Which one of the following best describes the term ‘import cover’,
sometimes seen in the news? (2016)
(a) It is the ratio of value of imports to the Gross Domestic Product of a
country
(b) It is the total value of imports of a country in a year.
(c) It is the ratio between the value of exports and that of imports
between two countries.
(d) It is the number of months of imports that could be paid for by a
country’s international reserves.
2. With reference to Balance of payments, which of the following
constitutes / constitute the Current Account? (2014)
1. Balance of trade
2. Foreign assets
3. Balance of invisibles
4. Special Drawing Rights
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 only (b) 2 and 3 (c) 1 and 3 (d) 1, 2 and 4
NEO IAS 0484-4030104, 9446331522, 9446334122 Page 6
www.neoias.com | www.youtube.com/neoias | www.facebook.com/neoias | www.twitter.com/neoias
3. Which of the following constitute Capital Account? (2013)
1. Foreign Loans
2. Foreign Direct Investment
3. Private Remittances
4. Portfolio Investment
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only (b) 1, 2 and 4 only
(c) 2, 3 and 4 only (d) 1, 3 and 4
4. The balance of payments of a country is a systematic records of (2013)
(a) all import and export transactions of a country during a given period
of time, normally a year
(b) goods exported from a country during a year
(c) economic transaction between the government of one country to
another
(d) capital movements from one country to another
5. In terms of economy, the visit by foreign nationals to witness the XIX
Common Wealth Games in India amounted to (2011)
(a) Export (b) Import (c) Production (d) Consumption
6. Assertion (A): ‘Balance of Payments’ represents a better picture of a
country’s economic transactions with the rest of the world than the
‘Balance of Trade’.
Reason (R): ‘Balance of Payments’ takes into account the exchange of
both visible and invisible items whereas ‘Balance of Trade’ does not.
(2006)
NEO IAS 0484-4030104, 9446331522, 9446334122 Page 7
www.neoias.com | www.youtube.com/neoias | www.facebook.com/neoias | www.twitter.com/neoias
You might also like
- Balance of Trade and Balance of PaymentDocument21 pagesBalance of Trade and Balance of Paymentfazilshareef1885No ratings yet
- B. Bop - FinalDocument42 pagesB. Bop - Finalsamy7541No ratings yet
- (Rethinking Southeast Asia) Peter Warr - Thailand Beyond The Crisis-Routledge (2004)Document368 pages(Rethinking Southeast Asia) Peter Warr - Thailand Beyond The Crisis-Routledge (2004)nur rachmawatiNo ratings yet
- Balance of Payment: External SectorDocument6 pagesBalance of Payment: External SectorVishnuvardhan RavichandranNo ratings yet
- Balance of PaymentDocument4 pagesBalance of PaymentTabish MirzaNo ratings yet
- Ifm BopDocument18 pagesIfm Bopsunil8255No ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Bop-Fe 2021Document20 pagesChapter 8 Bop-Fe 2021Sireen IqbalNo ratings yet
- Balance of Payments (IMT)Document6 pagesBalance of Payments (IMT)vinaykn53No ratings yet
- Unit 3Document19 pagesUnit 3karthik.bNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2 - BoPDocument36 pagesQuiz 2 - BoPGuneesh ChawlaNo ratings yet
- CH 7Document4 pagesCH 7Aryan RawatNo ratings yet
- Components of Balance of PaymentsDocument8 pagesComponents of Balance of PaymentsAnonymous dZpgL93UNo ratings yet
- Balance of Payments: Systematic Records OF All Economic TransactionsDocument50 pagesBalance of Payments: Systematic Records OF All Economic TransactionsnishantkastureNo ratings yet
- Balance of Payments: Dr. Raj AgrawalDocument22 pagesBalance of Payments: Dr. Raj AgrawalAmit JainNo ratings yet
- Components of Balance of PaymentsDocument2 pagesComponents of Balance of PaymentsNeeta Singh100% (3)
- Class 12 Notes - Balance of PaymentsDocument5 pagesClass 12 Notes - Balance of PaymentsAryan ph vlogsNo ratings yet
- B. A .Programme Economics VI Semester Paper: Economic Development and Policy India-IIDocument8 pagesB. A .Programme Economics VI Semester Paper: Economic Development and Policy India-IIShubham SinghNo ratings yet
- Alance OF Ayments: Presented By: Vikas Roll No.: 31Document54 pagesAlance OF Ayments: Presented By: Vikas Roll No.: 31saratkarvivekNo ratings yet
- BOP-India's international transactions in 2020-21Document6 pagesBOP-India's international transactions in 2020-21Phalguni MuthaNo ratings yet
- Balance of Payment of IndiaDocument4 pagesBalance of Payment of IndiaNirmal PanditNo ratings yet
- 61bdddd0673e5 - Economy PEP Sample HandoutDocument6 pages61bdddd0673e5 - Economy PEP Sample Handoutamanraj tomarNo ratings yet
- Composition of Balance of PaymentsDocument8 pagesComposition of Balance of PaymentsYashonidhi ShuklaNo ratings yet
- BoP and ForexDocument33 pagesBoP and ForexNeha RathoreNo ratings yet
- International Economy PDFDocument73 pagesInternational Economy PDFAnurag BhartiNo ratings yet
- Importance of Balance of Payment and Balance of Trade Concepts in International TradeDocument34 pagesImportance of Balance of Payment and Balance of Trade Concepts in International TradeMeghana OakNo ratings yet
- IFM - Lecture 2.3Document19 pagesIFM - Lecture 2.3Kancherla Bhaskara RaoNo ratings yet
- Balance of Payments Causes of Disequilibrium Approaches To Bop Policy Traditional Absorption and Monetary Approach1678901130918Document42 pagesBalance of Payments Causes of Disequilibrium Approaches To Bop Policy Traditional Absorption and Monetary Approach1678901130918UPSC 2022100% (1)
- Epathshala BOPDocument9 pagesEpathshala BOPSiddhant AthawaleNo ratings yet
- BOP GUIDEDocument9 pagesBOP GUIDESujataNo ratings yet
- Balance of Payment AccountDocument16 pagesBalance of Payment AccountDhiren AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Balance of Payment: Prof Mahesh Kumar Amity Business SchoolDocument56 pagesBalance of Payment: Prof Mahesh Kumar Amity Business SchoolasifanisNo ratings yet
- FINALDocument26 pagesFINALSidharth GuptaNo ratings yet
- SEBI Grade A 2020 Economics Balance of PaymentsDocument11 pagesSEBI Grade A 2020 Economics Balance of PaymentsThabarak ShaikhNo ratings yet
- DEY's Balance of Payments PPTs As Per Revised Syllabus (Teaching Made EasierDocument325 pagesDEY's Balance of Payments PPTs As Per Revised Syllabus (Teaching Made EasierAditya P NairNo ratings yet
- Ibo-03 2020-21Document22 pagesIbo-03 2020-21arun1974No ratings yet
- Balancing BOP: Expenditure PoliciesDocument34 pagesBalancing BOP: Expenditure Policieschanchal22No ratings yet
- BopmDocument9 pagesBopmAreej AslamNo ratings yet
- 12 - Chapter 3Document30 pages12 - Chapter 3Karan KhatriNo ratings yet
- Unit-3 (BALANCE OF PAYMENTS)Document15 pagesUnit-3 (BALANCE OF PAYMENTS)Shivam SharmaNo ratings yet
- Balance of Trade and Balance of PaymentDocument16 pagesBalance of Trade and Balance of PaymentDr-Shefali Garg100% (1)
- Balance of Payments: International FinanceDocument42 pagesBalance of Payments: International FinanceSoniya Rht0% (1)
- BALANCE OF PAYMENT TITLEDocument36 pagesBALANCE OF PAYMENT TITLENadeem AhmadNo ratings yet
- Balance of PaymentsDocument43 pagesBalance of PaymentsAkhil SusarlaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Balance of PaymentDocument3 pagesChapter 12 Balance of Paymentayushsingh7173No ratings yet
- Balance of PaymentsDocument42 pagesBalance of PaymentsHarvinder SinghNo ratings yet
- International Economics IIDocument237 pagesInternational Economics IImeghasunil24No ratings yet
- Balance of Payments: Kapil Chaudhary DmhsDocument20 pagesBalance of Payments: Kapil Chaudhary DmhsKapil ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- BopDocument11 pagesBopPallak ObhanNo ratings yet
- Balance of Payment and Its Related ConceptsDocument5 pagesBalance of Payment and Its Related ConceptsTilahun ShemelisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-Flow of FundsDocument78 pagesChapter 2-Flow of Fundsธชพร พรหมสีดาNo ratings yet
- Balance of Payments (BoP)Document23 pagesBalance of Payments (BoP)sathsihNo ratings yet
- Balance of Payments and Foreign Exchange Rate Important Questions1Document10 pagesBalance of Payments and Foreign Exchange Rate Important Questions1Monica MalhotraNo ratings yet
- Chapter V The Balance of PaymentDocument25 pagesChapter V The Balance of PaymentAshantiliduNo ratings yet
- Assignment On International Financial ManagementDocument7 pagesAssignment On International Financial ManagementKiran NayakNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics Topic 7Document103 pagesManagerial Economics Topic 7Renuka Badhoria (HRM 21-23)No ratings yet
- International Flows and Monetary SystemsDocument13 pagesInternational Flows and Monetary SystemsAbhishek AbhiNo ratings yet
- Components of Balance of PaymentsDocument2 pagesComponents of Balance of PaymentsJeyaprabha JeslinNo ratings yet
- Balance of Payments - IfMDocument35 pagesBalance of Payments - IfMMuthukumar KNo ratings yet
- STRUCTURE AND DISEQUILIBRIUM IN BALANCE OF PAYMENTSDocument8 pagesSTRUCTURE AND DISEQUILIBRIUM IN BALANCE OF PAYMENTSСоня НиколаеваNo ratings yet
- Import Business: A Guide on Starting Up Your Own Import BusinessFrom EverandImport Business: A Guide on Starting Up Your Own Import BusinessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- FULL Download Ebook PDF International Financial Management 3rd Edition by Jeff Madura PDF EbookDocument41 pagesFULL Download Ebook PDF International Financial Management 3rd Edition by Jeff Madura PDF Ebooksally.marcum863100% (30)
- Bafl Q1 23Document86 pagesBafl Q1 23Hassaan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Dornbusch, R. Essays 1998-2001Document207 pagesDornbusch, R. Essays 1998-2001IoproprioioNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument8 pagesCambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationUzma TahirNo ratings yet
- Courses ECON0102 Files Afterschool-GiveawayDocument44 pagesCourses ECON0102 Files Afterschool-Giveaways20191048No ratings yet
- International Business Competing in The Global Marketplace 12th Edition Hill Test BankDocument38 pagesInternational Business Competing in The Global Marketplace 12th Edition Hill Test Bankcrastzfeiej100% (11)
- Foreign Direct Investment and Cross Border Acquisitions Eun8e CH 016 PPT MXQJDocument37 pagesForeign Direct Investment and Cross Border Acquisitions Eun8e CH 016 PPT MXQJXuan LyNo ratings yet
- 10 Years Class-12 Economics - Chapter-1Document20 pages10 Years Class-12 Economics - Chapter-1rangersuhaibNo ratings yet
- IBF ch5Document35 pagesIBF ch5meka mehdeNo ratings yet
- Grant Thornton - Budget Booklet - 2023-24Document44 pagesGrant Thornton - Budget Booklet - 2023-24sourabhshrivastava80No ratings yet
- Turkish Currency and Debt CrisisDocument5 pagesTurkish Currency and Debt CrisisKirti SinghNo ratings yet
- PMG Unit 1 Extra Qs 1Document19 pagesPMG Unit 1 Extra Qs 1Loveesh SinglaNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Economics GlossaryDocument8 pagesIGCSE Economics GlossaryJr HuangNo ratings yet
- UCCC & SPBCBA & SDHG College of BCA & IT, Surat M.C.Q. Question Bank of Macro Economics (English Medium)Document11 pagesUCCC & SPBCBA & SDHG College of BCA & IT, Surat M.C.Q. Question Bank of Macro Economics (English Medium)Parth RanaNo ratings yet
- Bangladesh macroeconomic indicators remain mixed in NovemberDocument9 pagesBangladesh macroeconomic indicators remain mixed in NovemberZeehenul IshfaqNo ratings yet
- ECON6008 - Assignment 1Document3 pagesECON6008 - Assignment 1Malley O'Mwaka AmisiNo ratings yet
- Ib Economics GlossaryDocument10 pagesIb Economics GlossaryValeriia IvanovaNo ratings yet
- Paper-2 The Government and The Economy (Macroeconomics) Book Chapter (25 To 34) Macroeconomics ObjectiveDocument39 pagesPaper-2 The Government and The Economy (Macroeconomics) Book Chapter (25 To 34) Macroeconomics ObjectiveSharif HossainNo ratings yet
- Current Macroeconomic and Financial Situation of NepalDocument9 pagesCurrent Macroeconomic and Financial Situation of NepalMonkey.D. LuffyNo ratings yet
- Australia-Switzerland Analysis: Submitted To-Submitted byDocument14 pagesAustralia-Switzerland Analysis: Submitted To-Submitted byAman GuptaNo ratings yet
- 12 Economics Eng SM 2024 PDFDocument256 pages12 Economics Eng SM 2024 PDFShivansh JaiswalNo ratings yet
- University of Zurich, Dept. of Economics Prof. Dr. Mathias Hoffmann Exam For Spring 2015 LectureDocument4 pagesUniversity of Zurich, Dept. of Economics Prof. Dr. Mathias Hoffmann Exam For Spring 2015 LectureMatthias LeuthardNo ratings yet
- Sample Import Bill For CollectionDocument6 pagesSample Import Bill For CollectionjgaeqNo ratings yet
- Pakistan, Growth, Dependency & Crisis: Matthew MccartneyDocument18 pagesPakistan, Growth, Dependency & Crisis: Matthew MccartneyMehrunnisa ShahryarNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Economics Question Paper 2019 PDFDocument21 pagesCBSE Class 12 Economics Question Paper 2019 PDFVaishali AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Final Economics RevisionDocument11 pagesFinal Economics Revisionahmed mohamedNo ratings yet
- International Business Environment InsightsDocument54 pagesInternational Business Environment Insightsaktakhil1107No ratings yet
- International Financial Management 10 Edition: by Jeff MaduraDocument18 pagesInternational Financial Management 10 Edition: by Jeff MaduraTamoor BaigNo ratings yet
- International Trade & Economic GrowthDocument64 pagesInternational Trade & Economic Growthhira123100% (1)