Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CLS MED 22 23 XII Phy Package 4 Level 2 Chapter 9
CLS MED 22 23 XII Phy Package 4 Level 2 Chapter 9
Uploaded by
Kunal Gupta0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views30 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views30 pagesCLS MED 22 23 XII Phy Package 4 Level 2 Chapter 9
CLS MED 22 23 XII Phy Package 4 Level 2 Chapter 9
Uploaded by
Kunal GuptaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 30
NZ) ea |
Chapter 9
Ray Optics and Optical
Instruments
SECTION -A
(Reflection of Lights from Spherical Plane/Mirrors)
4, Answer (1)
R
Res
5 =5om
8
2. Answer (3)
Axial magnification of a short object is given by
my
(vy
=(")1
la)
3. Answer (3)
sino usine
vio =vi-Vo o
J, =-weose + usin} -(ucosei+usine)) ‘
dl 10080 1
i, =-2ueoso? cose
Straight line and horizontal
4, Answer (3)
The reflected ray, refracted ray a incident ray and normal all ie on the same plane. Hence (3) is true.
5. Answer (1)
Digital movie projectors need parabolic mirrors to converge all incident rays to a point.
Corporate Office : Aakash Tower, 8, Pusa Road, New Delhi-110005. Phone : 011-47623456
64 Ray Optics and Optical Instruments Solutions of Assignment (Level-)
6. Answer (1)
Real images are images formed from actual intersection of light rays.
Positon of “Se virus object
imaoe “
In plane mior formation of ea images is shown above
7. Answer 2)
For numberof mages formed from plane miror
m= 3603605
oe
If it was at any other point the number of images (n) = m but this is not so.
Since it is placed symmetrically
n=m-1
or n=5-1
or n= 4 images
8, Answer (2)
A
tane @ My
8
tana i) 3m By,
ce
9. Answer (1)
U9 =¥, 40, =V-(-v)= 2
(Refraction)
40. Answer (1)
coin = t(1-
64)
= 2(1-z4)
Corporate Office : Aakash Tower, 8, Pusa Road, New Delhi-110005. Phone : 011-47623456
Solutions of Assignment (Level) Ray Optics and Optical Instruments 65)
41. Answer (4) 1, NRed
When refraction occurs through parallel glass stab, Nr
the emergent ray is parallel to incident ray.
3
e254 | 4
because 1 ||2 Se
> 2is
12. Answer (1)
Real depth
© Apparent depth
When an image is least raised its apparent depth is highest.
Ril. is lowest which happens to be for red light.
13. Answer (1)
Colour of a wave depends more on frequency than wavelength as it depicts the amount of energy is carries.
Since frequency and energy doesnot change it will simply remain red.
(Total Internal Reflection)
14, Answer (4)
All the statements are true.
15. Answer (3)
2
V
16. Answer (4)
hen
(Numerical aperture)
hysin
hi, = 1.68, u,
Aa
Corporate Office : Aakash Tower, 8, Pusa Road, New Delhi-110005. Phone : 011-47623456
66 Ray Optics and Optical Instruments Solutions of Assignment (Level-)
17. Answer (3)
180° =/ +90 +r
90-7 ili
y= sini a
sinr
wes tan /
18. Answer (3)
sinig = EE
om
Where 1, = Ril. of rarer medium
y= RL. of denser medium
sinjg -4
i=
3
(Refraction at Spherical Surfaces)
19. Answer (4)
beet
wets
= 2h om, ef
R=+120m 7 ea)
v= becomes parallel to the principal axis.
(On second face, wy = 1.5, pp = 1,U> =, R=— 12cm
Ba Hy Bei
24 om
Final image at 24 cm from the surface and from centre of sphere.
Corporate Office : Aakash Tower, 8, Pusa Road, New Delhi-110005. Phone : 011-47623456
Solutions of Assignment (Level) Ray Optics and Optical Instruments 67
20. Answer (4)
24
= 16,u,=1,u= 120m, R= —6om
116 1-18
vo 12-6
v= — 30 om. (Virtual image)
(Refraction by Lenses)
22. Answer (3)
Hs _ aby
bs Fy
23. Answer (3)
For parallel incidence image is at f, distance from O,. For final emergence to be parallel object for Il is at
distance f, from O,. The distance between | and II would be f, + f,
24, Answer (4)
In displacement method
mm, = 1
n= Jinn
h=V24x6
h= 120m
Corporate Office : Aakash Tower, 8, Pusa Road, New Delhi-110005. Phone : 011-47623456
68 Ray Optics and Optical Instruments ‘Solutions of Assignment (Level)
25.
26.
a.
28.
29,
30.
31
Answer (3)
f+
Tra, Tru,
u, = 40 om, u, = -30 em
#0
“f= 40) = f= 30
+40 =f-30
f= #35 om
‘Answer (1)
Power of concave lens =
‘Adding combination = -4 D
Answer (1)
25D=-15D
‘Total power of combination will be more than power of given lens and focal length will be less.
Answer (3)
D
reo
a
60
(
V= +80 om
1 1
4 ae 7
; =a (Object)
20 <— 80cm —>
Corporate Office : Aakash Tower, 8, Pusa Road, New Delhi-110005. Phone : 011-47623456
Solutions of Assignment (Level) Ray Optics and Optical Instruments 69
32. Answer (3)
Maximum magnification is when final image is at near point D.
33. Answer (3)
34, Answer (1)
mym, = 1 which is a fact.
Here the lens is moved between the object and the screen.
vand wu interchange values between the two positions a clear image is formed on the screen,
v uw
~ and m, = =
u v
itm,
mm, = 1
35. Answer (2)
By principle of reversibility where must be symmetry in the two position
qd vou
dta
Hence, “se
2,2 1
Putting in lens equation 7+ =F
aa °
4d 7
In, -m,]
36. Answer (4)
Net power of combination
P=2P,+P,,
where P, is power of lens
P,, is power of mirrors
Corporate Office : Aakash Tower, 8, Pusa Road, New Delhi-110005. Phone : 011-47623456
70 Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
P=100
Focal length of combination (f)
4 mor 10. cm
a
10
alt
v 60
14
v0 7
120m
37. Answer (4)
38.
Initially it is simply a concave mirror with
1
Power of miror(P,,) = 5
Focal length of lens =
Power of lens =
os
100
50
Equivalent power
2P, +P,
50,
P 6
Net focal length
Answer (3)
Final image coincides with the object when rays fall normal
to the mirror or parallel to principal axis. For this virtual
object must be at the focus of concave lens.
Distance of virtual object from concave lens = 50 - 10
Focal length of concave lens = 40 cm,
Solutions of Assignment (Level-)
Corporate Office : Aakash Tower, 8, Pusa Road, New Delhi-110005. Phone : 011-47623456
Solutions of Assignment (Level)
(Refraction through a Prism)
39. Answer (3)
For light to retrace its path it must reflect normally
in the mirror.
When it does so, by geometry r= 30°
he
40, Answer (2)
ite=Ats
Ray Optics and Optical Instruments 741
>
7
38° and 58° can be / or e in the equation as 8 will be same for both values of incidence ray.
38° + 58° = A+ 50°
A= 46
41, Answer (4)
From triangle interior angles
A= 180° — 60° - 30°
= 90°
iteaAts
45° + 60° = 90 +5
8s 18°
42, Answer (4)
By geometry r= 45° (Atemate angi
sinsor 5
~ snase 72
B
" 2
(Dispersion by a Prism)
43, Answer (3)
5,
Dispersive power =
Corporate Office : Aakash Tower, 8, Pusa Road, New Delhi-110005. Phone : 011-47623456
72 Ray Optics and Optical Instruments Solutions of Assignment (Level)
44, Answer (2)
For dispersion without deviation
Axis = 1) + Ag, = 1) = 0
6(0.5) + A,(0.75) = 0
A= 4
45. Answer (2)
ale
vr
48, Answer (3)
(iy = DA, = (iy Ay
47. Answer (2)
8 = (ly ~Hhg)A = (1.659—1.641)5°
48, Answer (1)
Greve
49. Answer (3)
(iy “Hei _ (1.66 ~1.62)10
= 0.625 em
a Tey 708250
50. Answer (1)
(Optical Instruments)
51. Answer (3)
7 50
P=42D
52, Answer (1)
For normal adjustment m =
27 = Bf +f,
f= 30m
1,= 240m
Corporate Office : Aakash Tower, 8, Pusa Road, New Delhi-110005. Phone : 011-47623456
Solutions of Assignment (Level) Ray Optics and Optical Instruments 73
SECTION - B
4. Answer (4)
With larger aperture of objective lens, the light gathering power in telescope is high.
Aiso, the resolving power or the ability to observe two objects distinctly also depends on the diameter of the
objective, Thus objective of large diameter is preferred.
Also, with large diameters fainter objects can be observed. Hence it also contributes to the better quality and
visibility of images.
Hence, all options are correct.
2. Answer (3)
Parallel beam of light after refraction from convex lens converge at the focus of convex lens. In question itis.
given light after refraction pass through concave lens becomes parallel. Therefore light refracted from convex
lens virtually meet at focus of concave lens.
According to above ray diagram d = f,
3. Answer (2)
From the ray diagram shown in the figure.
‘At point P, from Snell's law
Sind __Haie
SIN prem
sin30°_ 1
= ne “S (4r= Ze emergent angle)
1
= sine= 3-5
= 2e=60"
4. Answer (1)
Using lens formula for frst refraction from convex lens
60 em, f= 30 cm
114
ara 800em <— sem 0m
1, hore is first image by lens
‘The plane mirror will produce an image at distance 20 cm to left of it.
For second refraction from convex lens,
w= 20m, v=, f= 30 cm
Corporate Office : Aakash Tower, 8, Pusa Road, New Delhi-110005. Phone : 011-47623456
7A Ray Optics and Optical Instruments Solutions of Assignment (Level-)
tatty 4a lt
vu fv" 20 30
= 1-4 4 y--60em
v 30 20
Thus the final image is virtual and at a distance, 60 ~ 40 = 20 cm from plane mirror.
5. Answer (2)
Light ray emerges normally from another surface, hence, e(angle of emergence) = 0
= nea
Applying Snell's law on first surface
{sini = usinr,
= sini = usinA
For small angles (sin6 = 8)
hhence i= WA
6. Answer (2)
By mitror formula
1
v
1
1
v
= 3F
7. Answer (3)
1
sinc = >
u
1
sin4s° = —
n
wave
Velocity of light in medium
©
vee
iu
3xto®
v2
Corporate Office : Aakash Tower, 8, Pusa Road, New Delhi-110005. Phone : 011-47623456
mis
Solutions of Assignment (Level) Ray Optics and Optical Instruments 75)
8 Answer (1)
9, Answer (1)
Principal axis
If lens is cut in two half as shown in the figure, then power of one part will be same. i.e. P, as focal length
remains same,
10. Answer (4)
Focal length of lens is
1 S-Me toe
1 3
A os
wa)
11. Answer (2)
PP
Gass (18) ass (18
\r
ps
Glass (1.5) Glass (1.5)
alycerin’ (1.5)
Corporate Office : Aakash Tower, 8, Pusa Road, New Delhi-110005. Phone : 011-47623456
76 Ray Optics and Optical Instruments Solutions of Assignment (Level-)
142
F
1
Equivalent focal length in air = 7-47 =
1
When glycerin is filled inside, glycerin lens behaves lke a diverging lens of focal length (-f)
12. Answer (3)
Rainbow can't be observed when observer faces towards sun.
13, Answer (4)
Ati=/j,, refracted ray grazes with the surface
‘So angle of refraction is 90°,
14. Answer (2)
f= 15m
Q 40cm
1404
Pa
+44
—18 v2 20
+244
v2 20 15
Vp = -60 em
So, image shifts away from mirror by = 60 ~ 24 = 36 cm.
15, Answer (1)
When mirror is rotated by @ angle reflected ray will be rotated by 26.
Corporate Office : Aakash Tower, 8, Pusa Road, New Delhi-110005. Phone : 011-47623456
Solutions of Assignment (Level) Ray Optics and Optical Instruments 77
20
x
o>
7
L=r05 0-4
x 2x
46. Answer (2)
(1-1 A+(u'-1A"=0
[u-dal=|wr- 94]
(1.42—1)x10° = (1.7-)4"
42= 07K > A
17. Answer (4)
2 3)
Hg VR lte gp RaE
18. Answer (3)
d= (d, * d,) w= 1.5(5 + 3) = 12 em
19. Answer (2)
Maximum distance of distinct vision = 400 cm. So image of object at infinity is to be formed at
400 cm.
Use lens formula,
1
400 =
P=-025D
Corporate Office : Aakash Tower, 8, Pusa Road, New Delhi-110005. Phone : 011-47623456
7B Ray Optics and Optical Instruments Solutions of Assignment (Level-)
20, Answer (2)
Ab and ¢; 8 +b and ¢; Cb and d; D > a and d
21, Answer (1)
Objective
50 omy
200 om
For normal adjustment = L = v + f, = 54 om
22. Answer (3)
Ray pass symmetrically through prism
Bpig = (i + €) — A= 30°
(A+bpy)
sin( Pe
wee
sind
(23. Answer (1)
‘At normal adjustment M = 2 0 eajecive
eyepiece
fet L !
Ail) |
Using lens equation
1
v
1
a
(iy
Corporate Office : Aakash Tower, 8, Pusa Road, New Delhi-110005. Phone : 011-47623456
Solutions of Assignment (Level)
24, Answer (1)
Ray Optics and Optical Instruments 79)
Refractive index of light rays that can just pass through the prism at grazing emergence at 2nd surface is.
we ae ote
Light having refractive index < 1.414 takes refraction but light having j. > 1.414 suffers total internal reflections.
Only red colour light will come out of prism.
25. Answer (3)
sin( 445, )
pan) AL
cna 2
2
A (A
ot afin
cnt on
z 8%
=> By =(180-2A)
26. Answer (4)
Alt ayt
rhe
(A
co( Asa)
Corporate Office : Aakash Tower, 8, Pusa Road, New Delhi-110005. Phone : 011-47623456
80 Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Solutions of Assignment (Level-)
27. Answer (4)
uP ot mioszope = Et
MP ot taescope =f
28. Answer (2)
2A r=A
sini
sinr
sin2A
sina
28. Answer (2)
30. Answer (2)
31. Answer (1)
f, +f =20
= u=2c0sA
f,
beg
fo
Solving (i) and (ii), f,
32. Answer (3)
rtmsA
For ray to pass normally r,
aA
Bom, f, = 2em
‘sind,
sind = sini
If both A and / are small
AL
33. Answer (1)
d= 2h +h
2h,
34, Answer (3)
Power of lens is eugal to zero.
tte 44)
r bn Ne, Ra}
> Hs
2
Ai)
il)
Corporate Office : Aakash Tower, 8, Pusa Road, New Delhi-110005. Phone : 011-47623456
Solutions of Assignment (Level)
Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
36.
36.
37.
38.
Answer (2)
ite-A
Bain =A
2A
A
Now,
sin +8,
sina sin sin A
A
= 20s 4
e 2
(ash
UW = 20s 45° = 2 cos 0°
As Rl. lies between 2 and V2
Answer (4)
©, is at C, image of O, will form at same position
For image of O,
30 em
40 cm
15 cm
Length of image
Ip = [Ply ~ Phil = 115 ~ 20] = 5 em
Answer (8)
Real & apparent depth are explained on the basis of rftaction ony. TIR not involved here
‘Answer (4)
1 (414
7218-9) 3535) = f= 20 om
a
Tea
__20
20-30
m 2 (Real and inversed)
Corporate Office : Aakash Tower, 8, Pusa Road, New Delhi-110005. Phone : 011-47623456
81
82 Ray Optics and Optical Instruments Solutions of Assignment (Level-)
hy=—4em
39. Answer (1)
For virtual object u = +10 cm, v = +15 om
‘The ray diagram is as shown.
\Z
=
Zi\
“15a
40. Answer (4)
Angle = 15°
bya 45
hy = 1.75
15(h4, — 1) + Alt - 1) = 0
75 +0.75A=0
O75 A=-75
78
“O75
A= 10
41. Answer (4)
c< 4s
sin © < sin 45°
1
<< sin 45°
u
ne v2
Only possible with y= 1.5
42, Answer (3)
Focal length will not change as long as curvature of lens does not change
led
d= Diameter of aperture
1 Intensity of image
= Aperture is covered by black paper
2
ret
:
i
r=! costed by por
Corporate Office : Aakash Tower, 8, Pusa Road, New Delhi-110005. Phone : 011-47623456
Solutions of Assignment (Level)
43,
44,
48.
46.
47.
Answer (3)
irc
sini > sin © sin i>
sing > sini> 3
y a
“4 (3)
sini > Zt i> sin (3)
Answer (2)
{At minimum deviation
r
According to geometry of prism
A
a= A
r= 30°
‘Answer (1)
1a
mh
+h
Pe
fh
Answer (2)
10 om
1.5 * 10" m
Image diameter
Magnification = 7; = “Sun's diameter
o4 Image
18x10" 1.39% 10°
1
x1,39x10° = Image diameter
18x10
1.39.
10° = Image diameter
or 9.2 10 = Image diameter
Image diameter = 9.2 « 104 m
‘Answer (4)
= 2 (Meo)
f(a
Corporate Office : Aakash Tower, 8, Pusa Road, New Delhi-110005. Phone : 011-47623456
Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
84 Ray Optics and Optical Instruments Solutions of Assignment (Level-)
ce
Bin
_ 3xt0®
2x10
48, Answer (2)
6000x107" = 3
34
0s excl angle sino = 2 =
le sind =F =
5
weg 3m
vin air (C)
Vin medium Any ‘5m
Hy
3 4
vin medium = = * 3 x 10
© xc 408
5 10
1.8 * 108
49, Answer (1)
Shift
So the microscope must be moved by 1 cm upwards
__ Real depth
‘Apparent depth
2
Apparent depth = Reel depth 2.3.0m = 2 cm
Shift
So the microscope must be moved 1 cm upwards.
50. Answer (4)
Each lens of same power but different is sign.
When added P= P, +P,
P=P,-P,
P=0
51. Answer (2)
Height - 6 ft
To see any object ina plane mirror complete, a mirror must be half the height of object.
tom
So minimum height of mirror
Corporate Office : Aakash Tower, 8, Pusa Road, New Delhi-110005. Phone : 011-47623456
Solutions of Assignment (Level)
52. Answer (3)
53. Answer (3)
‘360
@
45°
54. Answer (1)
55. Answer (2)
t
V (Speed in glass)
Time =
£
v
e
vee
u
Time = 4
¢
56, Answer (1)
i
r+ r= 90"
i+ r= 90°
= 90°
1
sine=
WRT of denser wrt rarer)
sin ¢ =u (RIL of rarer wert denser)
sin 7
sinr
sini
sine = ‘Sin(90?-7)
sin ¢ = tan 1 (
© = sin“ (lan 1)
57. Answer (4)
1.83 = (Speed of ight in water)
Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Corporate Office : Aakash Tower, 8, Pusa Road, New Delhi-110005. Phone : 011-47623456
85
86
58.
59.
60,
61
62,
63,
Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Solutions of Assignment (Level-)
Answer (4)
By definition of refractive index
Velocity of light becomes ~
ty of lig u
a
2 becomes
u
But frequency is constant.
‘Answer (2)
i208
sin jg =
Hy
3
sin ig= =
C5
3 3
ton i= oe GF
4 tan i,
r=3m
‘Answer (2)
‘When ray enters water
R v
‘becomes 5° and velocity becomes [>
Intensity also changes
Only frequency n remains same so answer is (2).
Answer (1)
Optical fibres depend on total intemal reflection
Answer (3)
i,=90-r
1)
sin(@o~r) =|
(90-1) lig] “
sinase
Also Hy = SE ay
cosr = 20
sina5®
tanr = sin4s® =
‘sine
Answer (2)
In case of multiple medium of different R.|
Corporate Office : Aakash Tower, 8, Pusa Road, New Delhi-110005. Phone : 011-47623456
Solutions of Assignment (Level) Ray Optics and Optical Instruments 87
d=8+6
= 14cm
64, Answer (3)
sino = "8
Ha
uy sin
c
Mg = 7
Ye
Ssino-2
Ye
vg =e
‘8 Sind
65, Answer (4)
rma
sin
tano= =>
= tno=
at
ar 7
6m
66. Answer (2)
let wavelength of light in air is 2
Wavelength in medium
ye
He
x
y We
Mey
Hy x
67. Answer (3)
RL. of part IV is highest. So velocity will be lowest. Hence, maximum time is taken in part IV.
Corporate Office : Aakash Tower, 8, Pusa Road, New Delhi-110005. Phone : 011-47623456
88 Ray Optics and Optical Instruments, Solutions of Assignment (Level-Il)
68, Answer (3) =~
sind < Yn? 4 yr
n> Vein? 0+
Maximum value of 0
n>v2
69. Answer (1)
R=
70. Answer (2)
Since parallel beams of ight will regain their original direction. They will again become parallel after emergence.
71. Answer (1)
By geometry r = 90° - 60° = 30°
Sing0®
1
sini=
i= 45°
72. Answer (1)
73. Answer (3)
This is application of the displacement method for finding focal length
Here mm, = 1
Let A, be area of object
AA y
Ayo
Ay = VAIAy
74, Answer (4)
by > By
‘A converging lens with higher refractive index will converge rays more hence value of f, Hy
Acconverging lens with greater refractive index will bend rays more converging them closer,
Let 2r
a
oo
a
Answer (2)
Mea
4
Moz,
ref
a
= 2M
Answer (2)
Magnification are same
m,=-m,
30 18
30-0 15-0
= v= 200m
Answer (1)
<0 (Diverging)
Corporate Office : Aakash Tower, 8, Pusa Road, New Delhi-110005. Phone : 011-47623456
92 Ray Optics and Optical Instruments Solutions of Assignment (Level-)
91. Answer (4)
92. Answer (4)
By the construction of the telescope f, + f,
93, Answer (4)
m=10
(i)
f+ f= 440m io
Solving (i) and (i)
f, = 40 cm
94. Answer (4)
Ray optics is valid on 2 more macro scale compared to wavelength of light. On micro scale wave optics and
wave-particle duality is more prominent.
95. Answer (1)
Blue colour of the sky is due to scattering of light also called the Rayleigh scattering
96. Answer (4)
Rainbow's colours appear due to dispersion, which occurs after refraction.
qaa
Corporate Office : Aakash Tower, 8, Pusa Road, New Delhi-110005. Phone : 011-47623456
You might also like
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5813)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
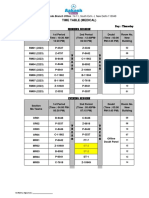
- MED-477DL - Preet Vihar Centre - Time Table - 26-30 - 09 - 2022Document3 pagesMED-477DL - Preet Vihar Centre - Time Table - 26-30 - 09 - 2022Kunal GuptaNo ratings yet
- 477DL - Preet Vihar Centre - Time Table - 12.09.2022 - MedicalDocument4 pages477DL - Preet Vihar Centre - Time Table - 12.09.2022 - MedicalKunal GuptaNo ratings yet
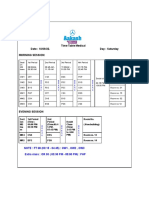
- 477DL - Preet Vihar Centre - Time Table - 17 - 11 - 2022 - Med - FINALDocument1 page477DL - Preet Vihar Centre - Time Table - 17 - 11 - 2022 - Med - FINALKunal GuptaNo ratings yet
- MED-477DL - Preet Vihar Centre - Time Table - 19.09.2022Document2 pagesMED-477DL - Preet Vihar Centre - Time Table - 19.09.2022Kunal GuptaNo ratings yet
- MEDI-477DL - Preet Vihar Centre - Time Table - 20-21-22 - 10.2022Document2 pagesMEDI-477DL - Preet Vihar Centre - Time Table - 20-21-22 - 10.2022Kunal GuptaNo ratings yet
- FT-11 OYMR Code-A 03.11.2022 Phase-I AnswersDocument1 pageFT-11 OYMR Code-A 03.11.2022 Phase-I AnswersKunal GuptaNo ratings yet
- FT-12 OYMR Code-A 17.11.2022 Phase-I AnswersDocument1 pageFT-12 OYMR Code-A 17.11.2022 Phase-I AnswersKunal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Medical - 477DL - Preet Vihar (10-09-22-11-09-22) 1Document2 pagesMedical - 477DL - Preet Vihar (10-09-22-11-09-22) 1Kunal GuptaNo ratings yet
- 477DL - Preet Vihar Centre - Time Table - 21 - 11 - 2022 - MedDocument1 page477DL - Preet Vihar Centre - Time Table - 21 - 11 - 2022 - MedKunal GuptaNo ratings yet
- 477DL - Preet Vihar Centre - Time Table - 15 To 20-12-2022 - MedDocument5 pages477DL - Preet Vihar Centre - Time Table - 15 To 20-12-2022 - MedKunal GuptaNo ratings yet
- CLS MED 22 23 XII Che Package 4 Level 2 Chapter 11Document10 pagesCLS MED 22 23 XII Che Package 4 Level 2 Chapter 11Kunal GuptaNo ratings yet
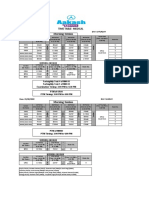
- Medical - Time Table - 13.08.2022Document1 pageMedical - Time Table - 13.08.2022Kunal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Medical - Time Table - 27.08.2022Document1 pageMedical - Time Table - 27.08.2022Kunal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Medical - Time Table - 15.08.2022Document1 pageMedical - Time Table - 15.08.2022Kunal GuptaNo ratings yet
- 477DL - Preet Vihar Centre - Time Table - 18 - 11 - 2022 - MedDocument1 page477DL - Preet Vihar Centre - Time Table - 18 - 11 - 2022 - MedKunal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Medical - Time Table - 29.08.2022Document2 pagesMedical - Time Table - 29.08.2022Kunal GuptaNo ratings yet
- CC-477 - Delhi-Preet Vihar Branch - Result of TERM-2 OW01-03, OR02 & OR03Document10 pagesCC-477 - Delhi-Preet Vihar Branch - Result of TERM-2 OW01-03, OR02 & OR03Kunal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Waves 4Document6 pagesWaves 4Kunal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Medical - 477DL - Preet Vihar Centre - Time Table - 05.09.2022Document2 pagesMedical - 477DL - Preet Vihar Centre - Time Table - 05.09.2022Kunal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Medical - Time Table - 20-08-2022 - Preet ViharDocument1 pageMedical - Time Table - 20-08-2022 - Preet ViharKunal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Medical - Time Table - 25.07.2022Document2 pagesMedical - Time Table - 25.07.2022Kunal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Medical - Time Table - 30.07.2022Document2 pagesMedical - Time Table - 30.07.2022Kunal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Atoms 2Document16 pagesAtoms 2Kunal GuptaNo ratings yet
- DocScanner 30 Apr 2022 07-27Document11 pagesDocScanner 30 Apr 2022 07-27Kunal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Waves 2Document10 pagesWaves 2Kunal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Atoms 1Document7 pagesAtoms 1Kunal GuptaNo ratings yet
- EnglishDocument11 pagesEnglishKunal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Waves 3Document7 pagesWaves 3Kunal GuptaNo ratings yet
- CLS MED 21 22 XI Phy Package 2 Level 2 Chapter 4Document16 pagesCLS MED 21 22 XI Phy Package 2 Level 2 Chapter 4Kunal GuptaNo ratings yet
- CLS MED 22 23 XII Che Package 5 Level 1 Chapter 12Document24 pagesCLS MED 22 23 XII Che Package 5 Level 1 Chapter 12Kunal GuptaNo ratings yet