100% found this document useful (1 vote)
2K views10 pagesFitting Shop
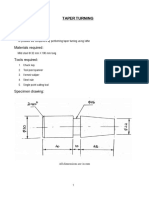
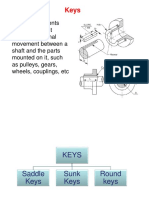
The document provides information on tools and techniques for fitting components together accurately through hand work. It describes holding tools like bench vices, V-blocks, and C-clamps. It also covers marking and measuring tools, cutting tools, files, and miscellaneous tools. The document discusses fitting operations like chipping and provides step-by-step instructions for making a T-fit between two metal plates using tools like hacksaws, files, and chisels. Safety precautions are emphasized for precise hand fitting work.
Uploaded by
Simon RileyCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
2K views10 pagesFitting Shop
The document provides information on tools and techniques for fitting components together accurately through hand work. It describes holding tools like bench vices, V-blocks, and C-clamps. It also covers marking and measuring tools, cutting tools, files, and miscellaneous tools. The document discusses fitting operations like chipping and provides step-by-step instructions for making a T-fit between two metal plates using tools like hacksaws, files, and chisels. Safety precautions are emphasized for precise hand fitting work.
Uploaded by
Simon RileyCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd