Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Labour
Uploaded by
Thuy LaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Labour
Uploaded by
Thuy LaCopyright:
Available Formats
LABOUR CASE STUDY
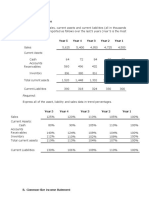
You have information for the year N concerning Labour, a firm which main activity is to
exploit luxury hotels:
Market value of equity $1,070,000,000
Number of shares 11,000,000
Net debts $321,000,000
Working capital 10 days of sales
Daily price of a room $300
Occupancy rate of rooms 60%
Number of rooms 9,000
EBITDA 24% of sales
Depreciations $70,000,000
Capital expenditures $80,000,000
Suppose that for the N+1/N+5 period:
The occupancy rate of rooms increases each year by 200 basis points (means that the
occupancy rate of rooms will be 60% in the year N, 62% in the year N+1 and so forth)
The price of a room increases each year by 4 %,
The EBITDA to sales ratio increases each year by 100 basis points (means 24% in N, 25% in
N+1 and so forth)
The net debts of N can be considered as being close to their long-run level,
The capital expenditures and the depreciation are each year $80,000,000 and $70,000,000
respectively.
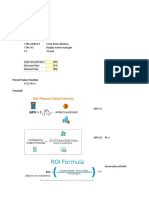
The interest rate of the net debt is 4.2%, the risk free rate is 3.2%, the historical return of the
market is 8.8%, the tax rate is 34% and the β of the firm is 0,94.
From the year N+6 the free cash flows of Labour are a growing perpetuity with a growth rate
of 2 %.
According to the DCF model, what is the price of a Labour stock?
You might also like
- Bilal Hyder I170743 20-SEPDocument10 pagesBilal Hyder I170743 20-SEPUbaid0% (1)
- Core Chapter 09 Excel Master 4th Edition StudentDocument77 pagesCore Chapter 09 Excel Master 4th Edition StudentShaunak ChitnisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Current LiabilitiesDocument6 pagesChapter 1 - Current LiabilitiesXiena100% (1)
- Exam Revision QuestionsDocument5 pagesExam Revision Questionsfreddy kwakwalaNo ratings yet
- A. Trend Percentages: RequiredDocument5 pagesA. Trend Percentages: RequiredAngel NuevoNo ratings yet
- 20211016231949-A4362 - 201093M 2Document4 pages20211016231949-A4362 - 201093M 2bucin yaNo ratings yet
- Rethink Property Investing: Become Financially Free with Commercial Property InvestingFrom EverandRethink Property Investing: Become Financially Free with Commercial Property InvestingNo ratings yet
- The Intelligent Advertiser: Advertising Handbook: More Customers, More Profit, More ImpactFrom EverandThe Intelligent Advertiser: Advertising Handbook: More Customers, More Profit, More ImpactNo ratings yet
- Cash+flow+estimation (14-1759)Document9 pagesCash+flow+estimation (14-1759)M shahjamal QureshiNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Question 3. Blindfold Technologies Inc. (BTI) Is Considering Whether To Introduce A NewDocument2 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Question 3. Blindfold Technologies Inc. (BTI) Is Considering Whether To Introduce A NewFaradibaNo ratings yet
- B.B.A., Sem.-III CC-202 Fundamentals of Financial Management-2017Document4 pagesB.B.A., Sem.-III CC-202 Fundamentals of Financial Management-2017Harshit MistryNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Presentation - Virtual Classroom - MDocument50 pagesChapter 8 - Presentation - Virtual Classroom - Mrebeccahf7No ratings yet
- Chap12 Pbms MBF12eDocument10 pagesChap12 Pbms MBF12eBeatrice BallabioNo ratings yet
- FM11 CH 11 Mini CaseDocument16 pagesFM11 CH 11 Mini CaseDora VidevaNo ratings yet
- CVP ProblemsDocument6 pagesCVP ProblemsKronisa ChowdharyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Mini Case: Cash Flow EstimationDocument60 pagesChapter 11 Mini Case: Cash Flow EstimationafiNo ratings yet
- SMU MBA104 FINANCIAL AND MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING Free Solved AssignmentDocument10 pagesSMU MBA104 FINANCIAL AND MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING Free Solved Assignmentrahulverma251233% (3)
- Marginal Costing SumsDocument3 pagesMarginal Costing SumsMedhaNo ratings yet
- Scenario AnalysisDocument2 pagesScenario AnalysisDickson WongNo ratings yet
- S16 - Scenario Manager - NPVDocument9 pagesS16 - Scenario Manager - NPVSRISHTI ARORANo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word Document-1Document2 pagesNew Microsoft Word Document-1Praveen.RNo ratings yet
- Activity Ratios - Practice QuestionsDocument15 pagesActivity Ratios - Practice QuestionsOsama SaleemNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 - Risk Analysis and Project Evaluating: Financial Management TaskDocument11 pagesChapter 13 - Risk Analysis and Project Evaluating: Financial Management TaskFaradibaNo ratings yet
- Assignment Drive SPRING 2017 Program MBA Semester I Ssubject Code & Name MBA104 Financial and Management Accounting BK Id B1624 Credit 4 Marks 60Document3 pagesAssignment Drive SPRING 2017 Program MBA Semester I Ssubject Code & Name MBA104 Financial and Management Accounting BK Id B1624 Credit 4 Marks 60rakeshNo ratings yet
- CH 11 - CF Estimation Mini Case Sols Excel 14edDocument36 pagesCH 11 - CF Estimation Mini Case Sols Excel 14edأثير مخوNo ratings yet
- Ma 2Document3 pagesMa 2123 123No ratings yet
- Multiple Choices: Assignment 1Document4 pagesMultiple Choices: Assignment 1Rogger SeptryaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 CVP AnalysisDocument2 pagesLesson 1 CVP AnalysisLorille LeonesNo ratings yet
- Practice Sheet Session 11Document11 pagesPractice Sheet Session 11Savana AndiraNo ratings yet
- Solution: - A) Gross Profit Net Sales-Cost of Sales 3,000,000-2,000,000Document4 pagesSolution: - A) Gross Profit Net Sales-Cost of Sales 3,000,000-2,000,000Eyasu DestaNo ratings yet
- BUS Tutorial 4 - Financial Statement 19Document4 pagesBUS Tutorial 4 - Financial Statement 19Setsuna TeruNo ratings yet
- Capital Budgeting-ClassDocument91 pagesCapital Budgeting-ClassAditi AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Question4 Solved With GraphDocument8 pagesQuestion4 Solved With GraphShafiqUr RehmanNo ratings yet
- Problems On Marginal CostingDocument7 pagesProblems On Marginal Costingrathanreddy2002No ratings yet
- Coporate FinanceDocument12 pagesCoporate Financeđức nguyên anhNo ratings yet
- Coporate FinanceDocument12 pagesCoporate Financeđức nguyên anhNo ratings yet
- FM Lab Week 8Document2 pagesFM Lab Week 8M shahjamal QureshiNo ratings yet
- Accounting For ManagementDocument4 pagesAccounting For ManagementShabana ShabzzNo ratings yet
- MARGINAL COSTIN1 Auto SavedDocument6 pagesMARGINAL COSTIN1 Auto SavedVedant RaneNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6-Problems (Scanned Copy)Document5 pagesChapter 6-Problems (Scanned Copy)codebreaker911No ratings yet
- 1stpreboard Oct 2013-2014Document19 pages1stpreboard Oct 2013-2014Michael BongalontaNo ratings yet
- Case Study - Discounted Cash FlowDocument14 pagesCase Study - Discounted Cash FlowSalman AhmadNo ratings yet
- Answer ALL The Questions (10 2 20) Answer ALL The Questions (10 2 20) Answer ALL The Questions (10 2 20)Document4 pagesAnswer ALL The Questions (10 2 20) Answer ALL The Questions (10 2 20) Answer ALL The Questions (10 2 20)Harish KapoorNo ratings yet
- General Data: Lessee:: Input Data: Key OutputDocument10 pagesGeneral Data: Lessee:: Input Data: Key OutputShafiqUr RehmanNo ratings yet
- Investment Appraisal Camb AL New (1) RIKZY EESADocument14 pagesInvestment Appraisal Camb AL New (1) RIKZY EESAAyesha ZainabNo ratings yet
- Midterm 1 - With Answers PDFDocument7 pagesMidterm 1 - With Answers PDFSamuel BrodriqueNo ratings yet
- MICROECONOMICSDocument11 pagesMICROECONOMICSMichael GuanzingNo ratings yet
- Ex08 Capital Budgeting XXDocument16 pagesEx08 Capital Budgeting XXbrmo.amatorio.uiNo ratings yet
- CVP Finance AssignmentDocument12 pagesCVP Finance AssignmentVivek VashisthaNo ratings yet
- Capital Investment/Net Present Value: Interest Rate DataDocument9 pagesCapital Investment/Net Present Value: Interest Rate DataWILLAM FABIAN PASTUÑA CAISAGUANONo ratings yet
- PropertyDocument8 pagesPropertyRameeshaAmanNo ratings yet
- Week 8 - Tugas IndividuDocument1 pageWeek 8 - Tugas IndividuRangga Dhia MajduddinNo ratings yet
- Ex 02a NOIDocument15 pagesEx 02a NOIgiannimizrahi5No ratings yet
- Mma's Business PlanDocument8 pagesMma's Business PlanIgbani VictoryNo ratings yet
- May 4519201 May 2019Document4 pagesMay 4519201 May 2019PILLO PATELNo ratings yet
- Buy Now: The Ultimate Guide to Owning and Investing in PropertyFrom EverandBuy Now: The Ultimate Guide to Owning and Investing in PropertyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Start Your Own Airbnb Business: How to Make Money With Short-Term RentalsFrom EverandStart Your Own Airbnb Business: How to Make Money With Short-Term RentalsNo ratings yet
- KahootDocument8 pagesKahootThuy LaNo ratings yet
- Huicholes Del TabacoDocument1 pageHuicholes Del TabacoThuy LaNo ratings yet
- Top 15 Financial Functions in ExcelDocument23 pagesTop 15 Financial Functions in ExcelThuy LaNo ratings yet
- Final Exam CorrectionDocument31 pagesFinal Exam CorrectionThuy LaNo ratings yet
- Digital Heath in VietnamDocument2 pagesDigital Heath in VietnamThuy LaNo ratings yet
- Examen Terminal CFVG 2020-2021Document14 pagesExamen Terminal CFVG 2020-2021Thuy LaNo ratings yet
- Hong 2016Document8 pagesHong 2016Thuy LaNo ratings yet
- AUSTRIA TEAM - Final ReportDocument17 pagesAUSTRIA TEAM - Final ReportThuy LaNo ratings yet
- OB ThesisDocument1 pageOB ThesisThuy LaNo ratings yet
- EI QuestionaireDocument7 pagesEI QuestionaireThuy LaNo ratings yet
- Asd Closure: Do Nguyen Tin MDDocument64 pagesAsd Closure: Do Nguyen Tin MDThuy LaNo ratings yet
- 1. Bài giảng Chẩn đoán và điều trị bệnh lý động mạch ngoại biênDocument112 pages1. Bài giảng Chẩn đoán và điều trị bệnh lý động mạch ngoại biênThuy LaNo ratings yet