Professional Documents
Culture Documents
EQ Booklet C
Uploaded by
mickey mouse0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views37 pageschem
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentchem
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views37 pagesEQ Booklet C
Uploaded by
mickey mousechem
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 37
HIGHER LEVEL
Topic 10 : Organic EQ Booklet C BOOKLET Y 101
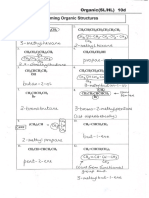
Homologous Series, Functional Groups, Naming, 1°,2°,3° (SL/HL)
|... Which statement about a homologous series is correct?
‘A. Members of the series differ by CH,.
B. Members of the series have the same physical properties,
C. Members of the series have the same empirical formula
D. Members of the series have similar chemical properties.
Z,, Which compound has the lowest boiling point? Which molecule contains an ester group?
A. CH,CH,CH,OH A. CH,CH,COOH
B. CH,CH,CH,Br B. CH,COOCH,
C.CH,CH,COOH C. CH,COCH,CH,OH
D. CH,CH,CH,CH, D. OHCCH,CHO
AL, Which of the following pairs are members of the same homologous series?
A. CH,CH,CH,OH and CH,CH,CHO
B. CH,CH(OH)CH, and CH,CH,CH(OH)CH,
C. CH,COCH, and CH,CH,COOH
D. CH,COCH,CH, and CH,CH,CHO
5) Which three compounds can be considered to be a homologous series?
A. CHNH, CH,CH.NH, CH,CH,CH.NH,
B. CH,CH,CH,NH, CH,CH(NH)CH, CH,(NH)CH,CH,
C. C(CH,), CH,CH,CH,CH,CH, (CH,),CHCH,CH,
D. CH,CH,COOH CH,COOCH, HCOOCH,CH,
6. Which of the structures below is an aldehyde?
A. CH,CH,CH,CHOH —C,_CH,CH,COOCH,
B. CH,CH,COCH, D. CH,CH,CH,CHO
7_| The drug methadone contains several different functional groups. Which functional groups are
° present in methadone?
CH,
|
ON Nc
no || | a
a a a a
So.
A. ketone, benzene ring, amine C. aldehyde, alkene, amide
B. _ ketone, benzene ring, amide D. aldehyde, alkene, amine
Whats the name of the following molecule applying IUPAC rules?
A. 1,l-dimethylbutane
B. Hexane
C. 2-methylpentane
D. 4-methylpentane
@
Whats the name of the following compound applying TUPAC rules?
CH; A. 1,1,1+trimethylpropane
HyC-—C-—CH;—CHy B. 2,2-dimethylbutane
C. 3,3-dimethylbutane
CH
D. 2-methyl-2-ethylpropane
(©. Whatis the name of (CH,),CHCOCH, applying IUPAC rules?
A. 3,3-dimethylpropan-2-one C. 2-methylbutan-3-one
B, 3-methylbutan-2-one D, 3-methylbutanal
2
Ue
IB.
(5.
Which of the following are isomers of pentane?
c
D.
(2. Which compound is not an isomer of hexane?
I. 2-methylpentane
A. CH,CH(CH,)CH,CH,CH,
TL. methylbutane
I. dimethylpropane B. CH,CHCHCH,CH,CH,
Tand II only C. (CH,),CCH,CH,
Land Ill only D. CH,CH,CH(CH,)CH,CH,
Mand [il only
1, Mand II
Which organic molecule is not a structural isomer of pentan-1-ol?
A
B.
e
D.
pentan-2-ol
2-methylpentan-2-ol
2-methylbutan-2-ol
pentan-3-ol
Which molecules are isomers of hex-1-ene?
c
D.
HL pss CHy. _ OH
Y cc c= CH,CHCHCH,CH,CH,
Hy nt W ‘CH;
L IL Mm.
Tand Il only
Tand IIT only
Mand III only
I, Wand IIL
How many non-cyclic structural isomers exist with the molecular formula C,H,,?
A.
B,
2
3
-14- ‘MI12/4/CHEMU/SPM/ENG/TZ2/XX.
tb. Diamorphine (heroin) contains several different functional groups. Which of the following two
functional groups are present in diamorphine?
A. ester, benzene ring
B. _ ketone, benzene ring
aldehyde, alkene
D. ketone, alkene
2212-6116
177, Atkenes are important starting materials for a variety of products.
(a) State and explain the trend of the boiling points of the first five members of the alkene
homologous series. BI
(& (i) _ Outline three features of a homologous series. GB)
[Q.| @ Describe what is meant by the term structural isomers. fy
(b) Both hex-2-ene and hex-1-ene can be converted to hexane by a reaction with hydrogen in
the presence of a nickel catalyst.
()__Deduce the names of three isomers of hexane. B]
Gi)
Identify the compound with the molecular formula C,H,, which has the highest
boiling point and explain your choice. By
4.
a
Gi)
Identify the names of two functional groups present in cortisone. 2]
Draw a circle around each of these two functional groups in the structure above and
label them 1 and 2 as identified in (a) (i). re]
6
QO. @) Deduce the structural formulas of 2-bromobutane and 1-bromo-2-methylpropane,
and identify each molecule as primary, secondary or tertiary. ion
(& Draw the structure of a primary amine, a secondary amine and a tertiary amine of
molecular formula C,H.N. 3)
Primary Secondary Tertiary |
(© State and explain whether the following molecules are primary, secondary or tertiary
halogenoalkanes. M4]
Lui
H
|
|
H
hdd
al- @
‘An organic compound, X, with a molar mass of approximately 88 g mol contains
54.5 % carbon, 36.3 % oxygen and 9.2 % hydrogen by mass.
(Distinguish between the terms empirical formula and molecular formula, 2
Empirical formula:
Molecular formula:
(ii) Determine the empirical formula of X. 2)
(iii) Determine the molecular formula of X. fy
ay
(¥) Draw the structural formula of an isomer of X which is an ester. uy
Topic 10 : Organic EQ Booklet C 10.2a
Alkanes, Free radical Mechanism, Alkenes (SL/HL)
{_. which equation represents a propagation step in the mechanism for the reaction between ethane,
C,H, and chlorine, Cl,, in the presence of sunlight/UV?
A. CH, +Ch>C,H,++HCl
B. C,H, + Ck C,H, Cl+H-
c cl, 2ck
D. C,Hy++Cl+ > C,H,Cl
Q_ Which equation represents the initiation reaction when methane reacts with chlorine in the presence
of ultraviolet light?
AL CH, > CH, + He
B. Cl, >2Ck
© c,>clt+cr
D. CHy++Cl, + CH,Cl+Cle
3. Which of the following statements about alkenes is not correct?
A. They have reactive double bonds. C. They react mainly by substitution.
B. They can form addition polymers. D. They can react with water to form alcohols.
Which reaction of but-2-ene produces 2-chlorobutane?
A. Addition reaction with chlorine
B. Substitution reaction with hydrogen chloride
C. — Substitution reaction with chlorine
D. Addition reaction with hydrogen chloride
557 Which compound is produced in the reaction between but-2-ene and steam?
A. CH,CHOHCHOHCH,
B. CH,OHCH,CH,CH,OH
C. CH,CH,CHOHCH,
D. CH,CH,CH,CH,OH
6. From which monomers this polymer made?
“7, @ (i) Hexane reacts with chlorine to form different products. The reactions can be
represented by the following equation, where R is an alkyl chain,
R-H+Cl, > R-CI+HCI
Describe the stepwise mechanism by giving one equation for each step and state the
essential condition in the initiation step. 4]
Initiation:
Essential condition:
‘Termination:
ii) Deduce the number of straight-chain structural isomers produced with the molecular
formula C,H,,Cl. uy
10.
8. @ Explain, using equations, the following steps in the free-radical mechanism of the reaction
of methane with chlorine.
+ Initiation
+ Propagation
+ Termination
on
(Describe a chemical test that could be used to distinguish between pent-I-ene and pentane. [2]
4... The alkenes are an example of a homologous series.
(@) State the name of the alkene shown. tid
G Hydrogen atom|
(ii) Draw the structural formula and state the name of the product formed. 7 2
i
JO, @ Below is a schematic diagram representing some reactions of ethene. The letters A-D
” represent the organic compounds formed from the reactants and catalysts shown.
H,0/ 1,80, H,/Ni
H,C=CH,
HCI cl,
Deduce the structural formulas of compounds A, B, C, and D and state the IUPAC name
of compound C. (5)
Cz TUPAC name:
[[. 2 @q State the structural formula of the organic products, Q and R formed in the
following reactions. PJ
(0 cee
a
CH,CH-CHCH,—pyi,om
CH,CH=CHCH, + H,(g) —“> R
In.
\ Q.. GN Bromoethane can be produced either from ethene or from ethane. State an equation
. for each reaction. py
(b) Propane can be formed by the hydrogenation of propene.
CH,CH=CH, (g) + H,(g) + CH,CH,CH,(g)
(State the conditions necessary for the hydrogenation reaction to occur. Py
| 3 @) Under certain conditions propene can polymerize to form poly(propene). State the
“ type of polymerization taking place and draw a section of the polymer to represent
the repeating unit PI
(Other than polymerization, state one reaction of alkenes which is of economic
importance. ay
(@) The conversion of carbon-carbon double bonds to carbon-carbon single bonds
is an important stage in the synthesis of a commercial product, Identify this
commercial product. [i]
(3,
(@) But-2-ene is a straight-chain alkene with formula C,H, The molecule contains both
cand x bonds.
7
b) Identify the structural formula of an isomer of but-2-ene which does not decolourize
bromine water, Br,(aq).
(© The polymerization of the alkenes is one of the most significant reactions of the
‘twentieth century
(i Outline two reasons why the polymers of the alkenes are of economic importance. [2]
(ii) State the type of polymerization reaction shown by the alkene in part (a). ty
Gili) Deduce the structure of the resulting polymer showing three repeating units. uy
(iv) Explain why monomers are often gases or volatile liquids, but polymers are solids. 2]
(State one use of the plastic PVC. +++ 0-+00r2+ me ey
14,
Topic 10 : Organic EQ Booklet C 10.2b
Alkenes : Electrophilic Addition Mechanism (AL)
[. Deduce the structural formulas of the major product: formed in the following reactions.
@ a, Js
c=. + HBr +c
4 S
HC ‘CHCH,CHy
(& CH,CH,CH=CH, + HBr > A
@ HCCH=CH, + ICL >
(@) Identify each of the types of reaction in (a) (6) < Cc)
(@ Describe the mechanism of the conversion, which occurs when bromine is added to
but-1-ene forming 1,2-dibromobutane, using curly arrows to show the movement of electron pairs.
[3]
Topic 10 : Organic EQ Booklet C 10.3
Benzene (SL/AL)
\ | Benzene, C,H,, is found naturally in crude oil.
A.
(a) Describe the chemical structure of benzene. By
(b) State one piece of chemical evidence that supports this description. i)
The structure of benzene originally described by August Kekulé is shown below.
Explain, giving two different pieces of evidence, why thisis not a valid structure for the bonding
in benzene. Ry
Ie
r “7
YZ. Benene, C,H,, is a planar compound which differs from the non-planar structure of
cyclohexane, C,H... The structures of benzene and the most stable form of cyclohexane
are represented below.
©
Benzene Cyclohexane
(a) With reference to the compounds benzene, cyclohexane and 1,3-cyclohexadiene,
state which compound would contain the shortest carbon-carbon bond length. ty
(6) Explain why it is more common for benzene to undergo substitution reactions than
addition react
uy
3744
ts
‘Turn over
I I
Topic 10 : Organic EQ Booklet C 10.4a
Alcohols — Oxidation and Esters (SL/HL)
© What are possible products of the incomplete combustion of propan-2-0l?
A. _ carbon monoxide, hydrogen and carbon
B. _ carbon dioxide, carbon and hydrogen
C. carbon, carbon monoxide and water
D. carbon dioxide and water only
Z- Which statement about the oxidation of alcohols is correct?
A. Oxidation of propan-1-ol produces propanone.
B. Mild oxidation of butan-1-ol produces butanal
C. Strong oxidation of pentan-2-ol produces pentanoic acid.
D. Mild oxidation of butan-2-ol produces butanal.
3. What product is formed when CH,CH(OH)CH, is reacted with acidified potassium dichromate(VI)?
A. CH,COOCH,
B. CH,CH,CHO
C. CH,CH,COOH
D. CH,COCH,
AL. What isa use of the organic product formed when an alcohol and a carboxylic acid react together?
A. Pesticide CC. Flavourings in food
B. Lubricant D. Fertilizer
5, @ (State and explain which of propan-1-ol, CH,CH,CH,OH, and methoxyethane,
CH,OCH,CH,, is more volatile. BI
18
(i) Propan-1-ol, CH,CH,CH,OH, and hexan-I-ol, CH,(CH,),CH,OH, are both alcohols.
State and explain which compound is more soluble in water. PI
6 | © Consider the following reactions.
cH,coown*
(CH,),CHCH,CH,CH,OH —*="""—4 CH,COOCH,CH,CH,CH(CH,),
D G
(CH,),CHCH,CH,CHO (CH,),CHCH,CH,COOH,
E F
(i State the IUPAC names of each of the compounds, D, E, F and G. 22)
D:
E
14
@) _Propan-1-ol and propan-2-ol are two structural isomers of C,H,O.
T.
(State the equation for the complete combustion of C,H,O. Py
(i) Both propan-l-ol and propan-2-ol can be oxidized in aqueous solution by
potassium dichromate(VI). State any necessary conditions for the oxidation to
occur and describe the colour change during the oxidation process. BI
(iii) State the name(s) and structure(s) of the organic product(s) that can be formed when
each of the alcohols is oxidized and suggest why one of the alcohols gives two
BI
‘organic products and the other only gives one organic product.
@
(@) Apply IUPAC rules to state the name of this molecule. ti)
20.
(b) Deduce the structural formula of two isomers of the molecule above with the same
functional group. Py
(© _ Describe, using an equation, the oxidation by acidified potassium dichromate(VI) of the
substance shown in the diagram. Use the symbol [0] to represent the oxidizing agent. [1]
(eh) Apply IUPAC rules to state the name of this product, ]
q ‘Compound X (shown below) is produced by bacteria living in human armpits and is thought to
be partly responsible for unpleasant body smells.
@ Bromine water can be used to test for the presence of one of the functional groups in X.
x
@ The other functional group changes when X is refluxed with acidified excess potassium
dichromate(VI) to produce a compound Y.
(i) Identify the functional group present in Y but not in X. a
(ii) State the type of reaction that X undergoes to form Y. iy
2
A different compound is produced if excess X is heated with acidified potassium
dichromate(VI) and the product Z is distilled off as it forms.
(i) Identify the functional group present in Z but not in X. ay
(i) Predict the order of increasing boiling point of the compounds X, Y and Z and
explain your answer. GI
{CE © Deduce an equation for the reaction between propanoie acid and methanol. Identify the
. catalyst and state the name of the organic compound, X, formed. 4]
((. @ The product C,H,,OH formed from the reaction with I-bromopentane is warmed
with ethanoic acid in the presence of a few drops of concentrated sulfuric acid
State the name of the type of reaction taking place and the structural formula of the
organic product. 22]
Esters and amides can be produced by condensation reactions.
B) State the names of two organic compounds required to produce ethyl methanoate
and state suitable reaction conditions. 2]
{{.) @ Other than its use in food flavouring, state one use of esters. 1]
12, (@) Esters are often used in perfumes. Analysis of a compound containing the ester functional
group only, gives a percentage composition by mass of C: 62.0% and H: 10.4%.
(Draw the ester functional group. “
(i) Determine the empirical formula of the ester, showing your working. ol
(iii) The molar mass of the ester is 116.18 g mol. Determine its molecular formula. [1]
23.
Topic 10 : Organic EQ Booklet C 10.5a
Halogenoalkanes (SL/RL)
1. Whatare the correct names of the reaction types shown?
cH,CH,CH, — cicH,CH,CH, 4 HOCH, CH,CH,
I bi
‘A. | nucleophilic substitution | oxidation
B. free-radical substitution oxidation
cc. | nucleophilic substitution nucleophile substitution
D. | free-radical substitution nucleophilic substitution
Z.,. @ _1-bromopropane undergoes a substitution reaction with NaOH.
CH,CH,
(i) Explain why the substitution occurs on the carbon atom that is marked as *C. uy
3. @ Abromoatkane, CJH,Br, reacts with a warm aqueous sodium hydroxide solution, NaOH.
(i State the equation for the reaction of C,H,Br with NaOH. uy
A, (®) Outline one way in which 2-bromo-2-methylbutane could be converted into
2-methylbutan-2-ol. W
24.
2.
Topic 10 : Organic EQ Booklet C 10.5b
Halogenoalkanes - Mechanisms (HL)
Which halogenoalkane will react most quickly with sodium hydroxide?
A. CH,CH,CH,CH,CL Cc. (CH),CCL
B. CH,CH,CH,CH,Br D. (CH),CBr
What is the correct order of inereasing rate of reaction between the following halogenoalkanes and a
‘warm aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide?
A. CHF D
A c
(a) (i) A reacts with HBr to form a major and a minor product. Draw the structural
formulas of these two isomers. fy
Gi) Explain the mechanism of the reaction of A with HBr to form the major product, B,
using curly arrows to represent the movement of electron pairs. i
(iii) Explain why B is the major product formed in the reaction of A with HBr. 22]
(©) Compound D, molecular formula C,H,O, is formed when C is heated with acidified
potassium dichromate(V/).
(i) Deduce the structural formula of D. fi)
3I
lo,
| G@ I-chlorobutane can be converted to methylbutanoate via a three stage process.
4 Deduce equations for each step of this conversion including any catalyst required
and name the organic product produced at each stage. 7
|
Consider the following sequence of reactions. CANS on FILE PAPER)
RCH, —eaetion 1_, ROH, Br —Peaction 2_, RCH, OH —Peaetlon 3_, RCOOH
RCH, is an unknown alkane in which R represents an alkyl group.
(a) Thealkane contains 81.7 % by mass of carbon, Determine its empirical formula, showing
your working. 1B]
(b) Equal volumes of carbon dioxide and the unknown alkane are found to have the
‘same mass, measured to an accuracy of two significant figures, at the same temperature
and pressure. Deduce the molecular formula of the alkane. ty
(©) @ State the reagent and conditions needed for reaction 1. Py
(ii) State the reagent(s) and conditions needed for reaction 3. 2]
(Reaction 1 involves a free-radical mechanism. Describe the stepwise mechanism,
by giving equations to represent the initiation, propagation and termination steps. ry
(©) The mechanism in reaction 2 is described as $,2.
(State the meaning of each of the symbols in 8,2 uy
i) Explain the mechanism of this reaction using curly arrows to show the movement
of electron pairs, and draw the structure of the transition state. By)
B25
Topic 10 : Organic EQ Booklet C 10.7
Stereoisomers (AL)
|. wich wo molecules ar cis-rans isomers of each other?
Ww HC, H x COOH
Vee KY
fro iN
HOOC’ ‘CHy HC ‘CHs
z Z
A. XandZ c Wandy
B. XandY D. WandZ
Z.. Which structure is a Q¢-frans: isomer of cis-1,2-dichlorocyclobutane?
al
acy
“ely
A. 12-dichloroethane has two geometrical isomers. (<4S- trans)
‘3. Which statement about stereoisomers is correct?
B. _ 1,2-dichloroethane has two optical isomers.
C. 1,2-dichloroethene has two geometrical isomers. (Ci S-tvans )
D. _ 1,2-dichloroethene has two optical isomers.
33,
A. E-4-methythex-2-ene
B. E-4-ethylpent-2-ene
C. Z--4-methylhex-2-ene
D. Z~-4-ethylpent-2-ene
A. B. &
fo far
& © .
&
I-chlorobutane 2-chlorobutane
é D, "
¢
© ¢€
2-aminoethanoic acid 2,2-dimethylpropane
G. which motecue exhibits optical isomerism? “T. Which molecule has a chiral centre?
A. 3-chloropentane A. CH,CH=CHCHO
B. 2-chlorobutane B. (CH,),C-CHCH,OH
C. 13-dichloropropane C. CH,OCH,CH,
D. 2-chloro-2-methylpropane D. CH,CHOHCH,CH,
Sh.
8 Which compound has a chiral carbon? ._ What effect of optical isomers on
A. Propan-2-ol
A. Reflection
1-bromo-2-methylbutane
B. Emission
CC. 3bromopentane
C. Rotation
D. — Ethane-1,2-diol
D. Absorption
plane-polarized light can be measured using a polarimeter?
lo 2) @)_ State what is meant by the term stereoisomers. Wy
(b, Explain the existence of ciS—b¥an$ isomerism in but-2-ene 2)
fy
{{ ‘There are several structural isomers with the molecular formula C,H, Br.
(a) Deduce the name of one of the isomers which can exist as enantiomers and draw
three-dimensional representations of its two enantiomers.
35.
Bi
12. @%) 2-bromobutane is optically active. Draw the two enantiomers of 2-bromobutane
and compare their physical and chemical properties. PI
[3, @
‘The structures of vitamin C and the preservatives 2-BHA and BHT are shown below.
oH 7 CHy OH Cy
HOH,C—C—H io De ie
TGC ‘CHs
‘C(CHs)s .
Sen chy
2-BHA BHT
)
Determine any chiral carbon atoms in these three compounds by placing an asterisk, * ,
beside them. PRI
Amino acids can exist in +(d) and ~{I) forms. Describe how the +(d) form of alanine,
H,NCH(CH, COOK, differs in its physical properties to the ~(0) form. ul)
36,
lk. @ Menthol occurs naturally and has several isomers. State the structural feature of
menthol which is responsible for it having enantiomers. al
(bi) State the instrument used to distinguish between each of the two enantiomers,
and how they could be distinguished using this instrument. ul}
(ie) Compare the physical and chemical properties of enantiomers, 2
Physical properties:
Chemical properties:
aT.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5795)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- 11 (3) Spectroscopic ID SL HLDocument12 pages11 (3) Spectroscopic ID SL HLmickey mouseNo ratings yet
- Notes Topic 21 Spectroscopic Analysis (HL)Document6 pagesNotes Topic 21 Spectroscopic Analysis (HL)mickey mouseNo ratings yet
- Notes 10 (2) FXN Groups SL ONLY 2014Document15 pagesNotes 10 (2) FXN Groups SL ONLY 2014mickey mouseNo ratings yet
- Notes 20 (3) Stereoisomers HL ONLYDocument8 pagesNotes 20 (3) Stereoisomers HL ONLYmickey mouseNo ratings yet
- Notes 10 (2) 20 (1) 20 (2) FXN Groups, RXN Types, Syn Routes HL ONLY 2014Document27 pagesNotes 10 (2) 20 (1) 20 (2) FXN Groups, RXN Types, Syn Routes HL ONLY 2014mickey mouseNo ratings yet
- Organic 10dDocument2 pagesOrganic 10dmickey mouseNo ratings yet
- Topic 9 Redox Booklet C ANSWERS 2014 (Amended Sept 2015)Document39 pagesTopic 9 Redox Booklet C ANSWERS 2014 (Amended Sept 2015)mickey mouseNo ratings yet
- 9a Standardisation of Potassium PermanganateDocument1 page9a Standardisation of Potassium Permanganatemickey mouseNo ratings yet
- 9b Iron in An Iron Tablet IA PracticeDocument1 page9b Iron in An Iron Tablet IA Practicemickey mouseNo ratings yet