Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Document For Ericsson R4 Core Network Integration - Warid
Uploaded by
Ali Sahal0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views2 pagesOriginal Title
Document for Ericsson R4 Core Network Integration -Warid
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views2 pagesDocument For Ericsson R4 Core Network Integration - Warid
Uploaded by
Ali SahalCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
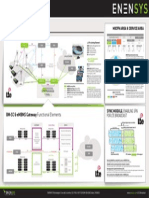
Circuit nanoBSC design
A Interface Connections - Signalling
The nanoBSC is connected to only one R99 MSC or R4 MGW
according to the technical note of nanoBSC. The interface towards
MGW is a standard A interface over TDM (E1 or T1 depending on
the configuration). The circuit BSC uses an internal Signalling Gateway
to convert the A-Interface SCCP/MTP3 message transport from
MTP2/MTP1 on E1/T1 to M2UA/SCTP and vice versa. This Signalling
Gateway, also called as Media Gateway is integral part of the BSC and
different to R4 MGW.
nanoBSC interface towards legacy MSC
nanoBSC interface towards R4 MGW
A interface connection for Speech Calls and Transcoding
The Circuit BSC Media Gateway (Signalling Gateway in the above
picture) provides the transcoding function for speech calls. The GSM FR,
EFR, or AMR speech frames are transcoded to/from 64kbit/s u-law or A-
law PCM (dependant upon configuration option). Thus no legacy Trans
Coder is required between BSC and MSC or MSS/MGW
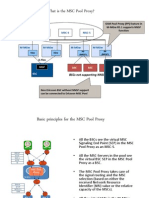
Signalling Requirement between R4 MGW and ip.access
nanoBSC
The NanoBSC is R99 compliant BSC, however it can be
connected to R4 Core Network, by using the backward
compatibility of the Core Network.
To integrate the NanoBSC into the Ericsson R4 Core, it can only
be connected to one MGW because it does not support load
sharing and quasi associated signalling. The NanoBSC supports
only Associated Signalling and from its perspective only the point
code of the MSC-S is visible, even though it is physically
connected to the MGW.
Therefore the R4 MGW needs to be set up to forward SS7
messages back and forth the between BSC and MSC-S in
transparent way for the BSC.
The NanoBSC can only be controlled by one MSC-S server
because it does not support MSC in Pool Functionality.
You might also like
- OSCDocument159 pagesOSCAdi PutraNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - OSCDocument159 pagesModule 1 - OSCRedaRebaiNo ratings yet
- 3G Core NewDocument46 pages3G Core NewPaul JosephNo ratings yet
- 01 Rn28121en20gla0 Bss OverviewDocument17 pages01 Rn28121en20gla0 Bss OverviewBuradeNo ratings yet
- Base Station SubsystemDocument65 pagesBase Station SubsystemRicardo Ngeng PitpituNo ratings yet
- OVERVIEWDocument79 pagesOVERVIEWseth_awuah100% (1)
- 3GPP Network ArchitectureDocument18 pages3GPP Network ArchitectureRmkumars100% (1)
- NSN 2G FeaturesDocument15 pagesNSN 2G Featuresmohammed0781No ratings yet
- UmgDocument37 pagesUmgBeepin JeNo ratings yet
- BSC - Base Station ControllerDocument21 pagesBSC - Base Station Controllermanthasaikarthik100% (5)
- Base Station SubsystemDocument4 pagesBase Station SubsystemDaniyal AliNo ratings yet
- From GSM to LTE-Advanced Pro and 5G: An Introduction to Mobile Networks and Mobile BroadbandFrom EverandFrom GSM to LTE-Advanced Pro and 5G: An Introduction to Mobile Networks and Mobile BroadbandNo ratings yet
- CDMA BSC Hardware Description ZTE MakeDocument27 pagesCDMA BSC Hardware Description ZTE MakePravien Shukla100% (1)
- Mai Thanh Tin - Report Week - 2 - NGN - ContDocument38 pagesMai Thanh Tin - Report Week - 2 - NGN - ContTin Mai ThanhNo ratings yet
- Message Buffer MB (B) Message Buffer MB (B) Message Buffer MB (B) Message Buffer MB (B)Document36 pagesMessage Buffer MB (B) Message Buffer MB (B) Message Buffer MB (B) Message Buffer MB (B)odizesNo ratings yet
- Switching Network (SN (B) ) Switching Network (SN (B) ) Switching Network (SN (B) ) Switching Network (SN (B) )Document38 pagesSwitching Network (SN (B) ) Switching Network (SN (B) ) Switching Network (SN (B) ) Switching Network (SN (B) )odizesNo ratings yet
- TC & BSC OverviewDocument36 pagesTC & BSC OverviewVarun VarmaNo ratings yet
- WC Unit-3Document8 pagesWC Unit-3dr.omprakash.itNo ratings yet
- Wp-cdm625 Acm White PaperDocument14 pagesWp-cdm625 Acm White PaperarzeszutNo ratings yet
- Transcoder FunctionsDocument1 pageTranscoder Functionsbuban8888No ratings yet
- Improving The Mf-Tdma Spectral Efficiency Through Symbol Synchronous OperationDocument8 pagesImproving The Mf-Tdma Spectral Efficiency Through Symbol Synchronous OperationVinod GowdaNo ratings yet
- GO - FC3004 - E01 - 1 GPRS&EDGE Feature Package - 27Document27 pagesGO - FC3004 - E01 - 1 GPRS&EDGE Feature Package - 27noumizredhaNo ratings yet
- BSS InterfacesDocument2 pagesBSS InterfacesSherif KamalNo ratings yet
- Cisco AMR CodecDocument12 pagesCisco AMR CodecThomas CrosNo ratings yet
- On The Design Details of SS PBCH Signal Generation and PRACH in 5G-NRDocument21 pagesOn The Design Details of SS PBCH Signal Generation and PRACH in 5G-NRvikram_908116002No ratings yet
- Newtec MCX7000 Multi Carrier Satellite Gateway r2.4 DatasheetDocument4 pagesNewtec MCX7000 Multi Carrier Satellite Gateway r2.4 DatasheetarzeszutNo ratings yet
- GO - FC3004 - E01 - 1 GPRS&EDGE Feature Package - 59 (With EMS)Document59 pagesGO - FC3004 - E01 - 1 GPRS&EDGE Feature Package - 59 (With EMS)noumizredhaNo ratings yet
- LTE E-MBMS Capacity and Intersite Gains: Américo Correia, Rui Dinis, Nuno Souto, and João SilvaDocument23 pagesLTE E-MBMS Capacity and Intersite Gains: Américo Correia, Rui Dinis, Nuno Souto, and João SilvaIgor MalianovNo ratings yet
- Newtec MCX7000 Multi Carrier Satellite Gateway ModemDocument4 pagesNewtec MCX7000 Multi Carrier Satellite Gateway ModemarzeszutNo ratings yet
- Exp. No.10 Simulation of Bask, BFSK and BPSK Aim:: Amplitude Shift KeyingDocument6 pagesExp. No.10 Simulation of Bask, BFSK and BPSK Aim:: Amplitude Shift KeyingShathis KumarNo ratings yet
- 03cn34015en40gla3 MGW For Mssdoc PDFDocument68 pages03cn34015en40gla3 MGW For Mssdoc PDFDiogenes moises luzNo ratings yet
- Changes To Stage 2 Descriptions: RLC/MAC PDU Formats: Source: EricssonDocument4 pagesChanges To Stage 2 Descriptions: RLC/MAC PDU Formats: Source: EricssonAnonymous uUFj1s48nNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips - Modbus Rtu Configuration 2015 09 06modbus Rtu Configuration Standalone ArchitectureDocument21 pagesDokumen - Tips - Modbus Rtu Configuration 2015 09 06modbus Rtu Configuration Standalone Architectureelahmady.1409No ratings yet
- Modulation Type Description Applications: Frequency-Shift Keying)Document4 pagesModulation Type Description Applications: Frequency-Shift Keying)Renjan SolisNo ratings yet
- Gprs Qos and Parameters - AlcatelDocument316 pagesGprs Qos and Parameters - AlcatelOcira OyaroNo ratings yet
- LTE Broadcast PosterDocument1 pageLTE Broadcast PosterGürsoy PekşenNo ratings yet
- Enhanced Data Rates For Global Evolution (EDGE)Document37 pagesEnhanced Data Rates For Global Evolution (EDGE)diyor.khomitovNo ratings yet
- Wimax Mbs Power Management, Channel Receiving and Switching Delay AnalysisDocument5 pagesWimax Mbs Power Management, Channel Receiving and Switching Delay AnalysisJawed KhanNo ratings yet
- SatLink Hub Family - Rev IDocument4 pagesSatLink Hub Family - Rev IsudanoneNo ratings yet
- Technical Report On OperationsDocument16 pagesTechnical Report On OperationsSamSameleviNo ratings yet
- GSM A-Interface: Presented by Sohaib TahirDocument13 pagesGSM A-Interface: Presented by Sohaib TahirSyed Sohaib TahirNo ratings yet
- IP in MNDocument8 pagesIP in MNMashhood NasirNo ratings yet
- Cisco MWR 2941 Router OverviewDocument4 pagesCisco MWR 2941 Router OverviewDemarco Dayanghirang FormalejoNo ratings yet
- AN3312Document20 pagesAN3312Marcelo CintraNo ratings yet
- NC-FPC-N42: Multi-Protocol Serial To Ethernet GatewayDocument4 pagesNC-FPC-N42: Multi-Protocol Serial To Ethernet GatewayDon Roseller DumayaNo ratings yet
- 5G NR Cheat Sheet - 1: ST ND RD THDocument2 pages5G NR Cheat Sheet - 1: ST ND RD THأبوعمر الفاروق عبدالرحمنNo ratings yet
- BSC TRAU High CapacityDocument4 pagesBSC TRAU High CapacityNyankoye Apollinaire LouaNo ratings yet
- SIGTRAN Telecom ProtocolDocument2 pagesSIGTRAN Telecom ProtocolJitender YadavNo ratings yet
- MSC DimensioningDocument2 pagesMSC DimensioningzbekeleNo ratings yet
- MSC DimensioningDocument2 pagesMSC DimensioningzbekeleNo ratings yet
- IJETR041769Document5 pagesIJETR041769erpublicationNo ratings yet
- MSC PoolDocument5 pagesMSC Poolle_linh_53No ratings yet
- 4 3GPP System Domains and Subsystems: 4.1 Allowed Network and Terminal ConfigurationsDocument36 pages4 3GPP System Domains and Subsystems: 4.1 Allowed Network and Terminal Configurationsadityakiit007No ratings yet
- DVB S2 CalculationDocument19 pagesDVB S2 CalculationSuporteSPDNo ratings yet
- High-Performance D/A-Converters: Application to Digital TransceiversFrom EverandHigh-Performance D/A-Converters: Application to Digital TransceiversNo ratings yet
- LEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-B: A Beginners guide to next level of networkingFrom EverandLEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-B: A Beginners guide to next level of networkingNo ratings yet
- Automated Broad and Narrow Band Impedance Matching for RF and Microwave CircuitsFrom EverandAutomated Broad and Narrow Band Impedance Matching for RF and Microwave CircuitsNo ratings yet
- LEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-A: A Beginner's Guide to Next Level of NetworkingFrom EverandLEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-A: A Beginner's Guide to Next Level of NetworkingNo ratings yet
- Duplexer DatasheetDocument2 pagesDuplexer DatasheetAli SahalNo ratings yet
- NanoBTS EDGE 23dBm 1800-1900 Datasheet 22042010Document2 pagesNanoBTS EDGE 23dBm 1800-1900 Datasheet 22042010Ali SahalNo ratings yet
- nanoBTS EDGE 900-850 Datasheet 22042010Document2 pagesnanoBTS EDGE 900-850 Datasheet 22042010Ali SahalNo ratings yet
- BSC IP Setup Diagram V03Document1 pageBSC IP Setup Diagram V03Ali SahalNo ratings yet
- DBS3900 Product Description V1.0 (20121119)Document26 pagesDBS3900 Product Description V1.0 (20121119)Ali SahalNo ratings yet