Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Physical Edu Capsule Notes Athletes Fuel
Uploaded by
Greeshma Reddy0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views13 pagesPh
Original Title
physical edu capsule notes athletes fuel
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPh
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views13 pagesPhysical Edu Capsule Notes Athletes Fuel
Uploaded by
Greeshma ReddyPh
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 13
Quick Review
1, Strength-Definition, Types and Methods of
improving Strength-Isometric, Isotonic &
Isokinetic.
Strength : Strength is one of the most important
components of physical fitness. It can be defined
as the amount of force a muscle can exert.
Three types of strength.
Maximum strength, Explosive strength &
Strength endurance
Methods of Improving Strength - Isometric,
Isotonic & Isokinetic
Isometric exercises : Isometric exercises are
those exercises in which the length of muscle
remains the same during isometric workout.
These exercises develop high level of static
strength. These are effective for total muscular
strength. Examples: Arm press, squat-press,
Isotonic exercises : In isotonic exercises the
length of muscles change and external
movement is visible. It is the most famous type of
contraction used in weight lifting. It is used in
rehabilitation of weak muscles. Examples :
Squat, Bent over rowing.
Isokinetic Exercises : Isokinetic exercises are
more advanced as compared to isometric &
isotonic exercises. In these exercises the muscle
is made to contract maximally through the
whole range of joint. These exercises are
performed on specially designed equipment.
Examples : Cycling, swimming.
2, Endurance-Definition, Types and Methods to
develop endurance-Continuous training,
Interval training and Fartlek training
Enduranceis one of the components of physical
fitness. It is the ability of the body to work for a
long time without getting fatigued.
Types of endurance : Muscular endurance &
Cardiovascular endurance.
Continuous Training : It consists of long
distance running without break or recovery
pause. It is further divided into following
methods.
© Slow continuous method
© Fast continuous method
© Variable pace method
Interval Training: Internal training is widely
used for the development of speed and
endurance. It is a training which contains fast
and slow periods of exercise.
Fartlek Training : Fartlek is a swedish word
which means speed play. It was a swedish
physiologist who developed a conditioning
programme with the combination of interval
training and fartlek training. Itis mostly liked by
athletes as the route selected for fartlek is
natural and pleasing. This is an effective method
for development of endurance and speed.
Advantages
Fartlek training is more pleasing to the
athletes as it is performed on natural terrain,
© Free from polluted area.
© This can be performed without a coach. The
fartlek training can be given to masses instead
of individuals.
Speed-Definition, Types and Methods to
Develop Speed- Acceleration Runs and Pace
Runs
‘Speed : Speed is defined as the capability of the
body to perform successive movements at the
fastest rate.
Type of speed :
‘© Reaction Ability © Movement Speed
© Acceleration Ability © Locomotor Ability
Speed Endurance
Methods to Develop Speed - Acceleration
Runs and Pace Runs
e Development of Reaction Time : Reaction
time is known as the time taken to respond to
astimulus. This canbe developed by giving
practice of reacting repeatedly on a particular
signal.
© Acceleration Runs : It is the capacity of a
body to acquire maximum speed in minimum
possible time,
© Pace Runs : It means running the whole
distance at constant speed.
4.
Flexibility :
Flexibility-Definition,
Types and
Methods to Improve Flexibility
Flexibility is defined as the
maximum range of movement possible at a joint.
Types : Active flexibility, passive flexibility
Methods to improve flexibility
Dynamic Stretching : It is the flexibility
performed during motion.
Static Active Stretching : It is the flexibility
performed from a stationary position.
Examples : Halasana, Chakrasana.
Static Passive Stretching : Static passive
stretching is done with the application of an
external force to hold the stretch in position.
PNF stretching : It is one of the most
effective forms of flexibility training for
developing flexibility in the shortest possible
time.
Important Guidelines for PNF Stretching
Keep a gap of 48 hours between PNF
stretching workouts.
Perform only one exercise per session.
For each muscle group only 2-5 sets should
be done.
Each set should consist of one stretch held
for upto thirty seconds after the contracting
phase.
PNF stretching not allowed below the age of
18.
Thorough warming up should be done
before PNF stretching.
. Coordinative Abilities ~ Definition & Types
Co-ordinative Ability is the ability of the body
to perform various movements accurately &
efficiently with proper coordination e.g.
Gymnastics, Kho-Kho, Basketball.
Types
Coupling Ability : Coupling ability of the
body is considered as capacity of an
individual to perform better coordination of
different parts of the body. For example
while dribbling a basketball, the
coordination of both the limbs is required,
Reaction Ability : Reaction ability is a ski.
to react quickly to a stimulus. For example
chaser in Kho-Kho runs quickly after Kho is
given.
Balance Ability : Balance ability is known
as capability of an individual to maintain
balance while the body is in motion. Even
during disturbed balance regaining the lost
balance is known as balance ability.
Orientation Ability : The orientation ability
is a skill to determine and change the
position in complex situations. For example
defending an opponent in football, the
position is changed according to the
movement of opponent.
Adaptation Ability : Adaptation ability is
the capability of a person to change the
movement on the basis of predicted
changes. This ability is achieved after
mastering the skills.
Rhythm Ability : Rhythm ability is to make
out motor actions on a well defined rhythm.
Mainly this ability plays a vital role in the
events like synchronized swimming, floor
exercises in gymnastics and rhythmic
gymnastics. ~ foes <<
PSYCHOLOGY & SPORTS
aes
Quick Review
1. Personality; its definition & types-traits &
types (Sheldon and Jung classification) & Big
five theory.
Meaning of personality :
‘The term personality is derived from the latin
word personameaning a mask. These masks
were used by Roman actors. That time
personality was just look of the person as seen by
others. However, personality consist of habits,
traits, attitudes and ideas of an individual.
Generally, personality is the sum of those
characteristics that make a person unique.
Personality consists of a person's characteristics
like physique, appearance, intellect, knowledge,
psyche, conduct, expression or performance.
Dimensions of Personality
Extraversion : Extroverts are sociable and active
people who enjoy meeting people. They are fond of
social gatherings, having leadership qualities,
they assert in groups, possess positive outlook,
friendly, energetic & adaptable.
Neuroticism : These people are sensitive in
nature, having trait of anxiety and negative
emotionality.
Psychoticism : They are tough minded people,
always ready to take risks, sometimes engage in
antisocial behaviour, aggressive
Personality types according to(Carl G. Jung)
1, Extroverted & Hyper introverted ‘They
represent the source and course of
individuals energy expression.
2, Sensing intuition : Signifies the technique by
which an individual perceives information.
Sensing is a way in which an individual
believes and understands the information he
or she obtains directly from outside sources.
Intuition represents the information an
individual perceives from the ingenious or
imaginative world.
3. Thinking - feeling : Thinking is taking a step
in which an individual makes a decision
chiefly through judgement or logic. Feeling is
making a decision based on feeling and
emotion.
4, Judging-perceiving : It portrays an
individuals information in implementation
way. Perceiving means that the individual is
Prone to improve and identify alternative
choices.
Big Five Theory
Modern view of dimensions of personality are
eee Tere eee
low:
1. Extraversion : The first dimension of
personality is considered as extraversion.
They display excitability, sociability,
assertiveness and high amount of emotional
expressiveness.
2. Agreeableness : This includes attributes
such as trust, kindness, affection and other
prosocial behaviours. They always show
amicability.
3. Conscientiousness : Having high levels of
thoughtfulness, good impulse control and goal
directed behaviours.
4, Neuroticism :Individuals possessing high
neuroticism display emotional instability
anxiety, moodiness, irritability, and sadness.
5. Openness : This trait refers to imagination
and insight. This type of individual has broad
range ofinterests.
Types of personality on the basis of
temperament
~ Choleric - Melancholy
~ Phlegmatic ~ Sanguine
‘Types of personality according to the built of
the person.
—Aesthetic —Athletic_ ~Pyknic
Sheldon classification types
Sheldon types on the basis of physique &
temperament
(i) Endomorphic
(ii) Ectomorphic
() Endomorphic : Their body is solid & soft.
‘They store fat. They have wider and higher
waist. Their built up is shorter with thick
limbs. They are very fond of comfort and are
sociable.
(i) Mesomorphic
Gi) Mesomorphic : A person with
mesomorphic body has large bones and
muscles. They easily gain or lose weight. They
love adventure. They are assertive and energetic.
(iii) Ectomorphic : An ectomorphic physique 1s
a typical skiny person. They have a light build
with small joints and lean muscles
Temperament of ectomorphs is marked by
inhibition and restraint.
Types of Personality
‘Type A Personality : They are competitive and
high achievers. They have high sense of time and
always try to finish their job in time. They can be
easily aroused to anger.
Type B Personality : They are extroverts in
nature. They are very entertaining and not easily
stressed. They can be achievers but do not want
to be competitive. They can delay the work and
try to doitat the last moment.
‘Type C Personality : They try to spend a lot of
time on finding how the things work. They are
very cautious and reserved in nature. They are
not assertive & always suppress their own
desires and emotions. They are very susceptible
todepression.
Type D Personality : Thy have a negative
outlook towards life and are pessimistic. They
are characterized as those people who resist any
form of change and prefer the monotony of
routine. They are not adventurous and always
resist responsibility. They withdraw as a fear of
rejection. The main cause of depression is
suppressing their emotions for long periods of
time.
Role of Sports in Personality Development
‘The regular sporting activities not only develop
physique but also enhance personality of the
person. Participation in sports also helps in
Maintaining mental well-being. Following
points play a major role in the development of
the personality:
s Development of physique
© Development of social skills
Relieves stress
Develops discipline and assertiveness
Develops leadership qualities
Develops mental toughness
Improves confidence
Improves self-esteem
2. Motivation, its types & Techniques
Motivation : Motivation has been derived from
the Latin word ‘Movere’ which means to 'moye
Motivation is a process in which the learner jg
made eager towards attainment of the goal
‘Types & techniques of motivation
(Internal motivation
(u) External motivation
3. Meaning, concept & types of aggression in
sports
Meaning & Concept
‘Aggression in sports is an attribute that can
have many negative as well as positive effects on
performance. It is a malicious, vicious, nasty,
or harmful behaviour. It can be visible in
physical actions, such as physical violence
towards others, or in a more emotional way,
such as cruel words or unkind behaviour.
‘Assertive behaviour becomes aggression and
the player plays within the rules of the sport ata
very high intensity, but has no objective to harm
an opponent. Aggression is very important to
excel in the field of sports.
Types of aggression are: Hostile aggression &
instrumental aggression.
1. Physiological factors determining
‘components of physical fitnes:
Components of physical fitne:
speed, endurance & flexibility
«Physiological factors determining strength
‘The muscle strength is defined as the greatest
amount of force that muscles can produce in a
single or maximal effort. This depends upon the
following factors :
Muscle cross-sectional area, types of muscle
fibres, muscle length, age, gender, point of
tendon insertion, energy level & nerve impulse.
«Physiological factors determining speed
Speed is defined as the maximal speed that can
be reached by a part or all of the body. In few
sports the body as a whole does not move fast, but
a part of the body does. The following factors
determine the speed :
Composition of muscle fibres. nervous system &
its mobility, flexibility, phosphogen stores,
explosive strength.
© Physiological factors determining endurance
Endurance is the ability of the body to work for a
long time without getting fatigued. This depends
upon following factors :
Maximal oxygen uptake, pulmonary diffusion,
cardiac output, blood volume, lactate threshold,
hydration, slow-twitch muscle fibers.
«Physiological factors determining flexibility
Flexibility is defined as the maximum range of
movement possible at a joint. The following
Jactors determine the flexibility :
Structure of the joint, elasticity of ligaments,
muscular strength, stretchability of muscles,
age, gender, connective tissue.
2. Effect of exercise on cardiorespiratory system
Whenever we perform strenuous exercise the
demand of oxygen increases. Therefore during
exercise the supply of oxygen to the muscles 15
the urgent need as oxygen cannot be stored in.
Muscles. Hence heart rate functions faster to
increase the systemic circulation as well as the
Pulmonary circulation.
are : Strength,
2
De
Effect of exercise on cardiovascular system
Immediate effects ofexercise
© Increase in stroke volume
© Respiratory rate increases
© Increase in vital capacity
© Increase in B.P.
Long Term Effects
© Decrease inB.P.
Increase in heart size
e Increase in stroke volume
© Increase in tidal volume
e Avoids second wind
Effect of exercise on respiratory system
The demand of oxygen increases due to
participation in physical activity. During
exercise the level of carbon dioxide increases in
blood. Carbon dioxide is acidic in medium and
this stimulates respiratory center in the medulla
oblongata. Like this the breathing frequency
increases.
Immediate effects of exercise
© increase in respiratory rate
© stroke volume increases
© heart rate increases
increase in B.P.
Long term effects of exercise
© vital capacity increases
© tidal volume increases
© residual volume increases
Effect of exercise on Muscular system.
Due to participation in long term training
programmes, the development of muscular
system takes place. The training develops the
capacity of an individual. These effects depend
upon the types of training given to an individual.
Following are the effects of exercise on muscular
‘system.
‘Strength of muscles increase
Muscular endurance increases
Anaerobic capacity increases
Delays fatigue
Improves efficiency
Increase in blood supply
@
4. Sports Injuries : Classification (Soft Tissue
Injuries: Abrasion, Contusion, Laceration,
Incision, Spi
Injuries: (Dislocation, Fractures: Stress
Fracture, Green Stick, Comminuted,
Transverse Oblique & Impacted) Causes,
Prevention & treatment
Classification of sports injuries
Sports injuries are very common in this
competitive world. Mainly in contact sports the
occurrence of sports injuries are more.
Classification of sports injuries is mainly based
on cause and type of tissue. Sports injuries are
mainly classified into two categories.
A. Classification due to cause
1. Direct injury : Direct injuries are caused due
to impact of external forces. e.g. collision of two
players in football.
2. Indirect injury : Indirect injuries typically
involve the athlete himself by damaging the soft
tissues. Sprain & strain are common examples.
8. Overuse injury : This type of injury is caused
due to overuse of the body parts e.g. tennis elbow
in javelin throw.
B. Classification due to type of tissues
Types:
G@) Soft tissue injuries : These injuries are like
sprain, strain, abrasion etc. which is caused on
soft tissue of skin, muscles, tendons, fat, blood
vessels, nerves and ligaments. Soft tissue injuries
occur more than hard tissue injuries.
(i) Hard tissue injuries : Hard tissue injuries
‘occur in bones and cartilages. e.g. fractures.
‘Common causes of sports injuries
In this competitive world the athletes want to
achieve their best and this is the reason that
sports injuries are prevalent. The following are
the causes of sports injuries:
Improper warming up, overuse, age, sudden
stopping or twisting, improper sports equipment,
fatigue, poor training, improper development of
muscles, falls, weight, incorrect technique, lack
of safety equipment.
Common Prevention of Sports Injuries
Sports injuries are commonly caused due to
overuse, over twisting, over stretching, collision,
etc. Sports injuries can be prevented to a great
extent.
The following methods should be used to prevent
sports injuries:
Proper warming up. proper Conditioning, use of
protective sports gear, use of proper footwear
hdequate rest, balanced dict, use of right
technique, appropriate nutrition, playfield with
fety equipment, playing under rules g
regulation.
Soft Tissue Injuries
‘Abrasion : Abrasion Is an injury to the surface of
skin. This injury {s commonly caused by sliding
or friction. Most common site of abrasion ig
knees, palms and elbows.
Contusion: It fs superficial injury in which the
skin is not broken but often produces bruise,
‘There may be pain, swelling and discolouration
of the skin. Generally contusion is caused due to
hitting of blunt abject.
Laceration/Incision
It is tear in any tissue in the body. It may be
external or internal. When a ball hits the skin
which is over a sharp bone may create laceration
wound.
Management of Abrasion, Contusion and
Laceration/Incision
These injuries can be prevented by using
protective equipment. Wash the wound
immediately with soap and water. A cotton gauze
rinsed with antiseptic lotion can be used.
Bandage the area which is still bleeding. In case
ofcontusion ice can be applied on injured part.
‘Sprain : Itis an injury toa joint in which some of,
the ligaments are stretched or torn.
Strain : Itis an injury of muscle generally known
as ‘muscle pull’. This injury causes tearing or
overstretching of muscle fibres.
‘Management of Strain and Sprain
Strain and sprain can be prevented by warming
upand conditioning. Conditioningle ads to
increased strength and capacity of muscles and
ligaments which can prevent strains and
sprains. Taping, knee caps, crape bandage can
be helpful in preventing strain and sprain.
Bone & Joint Injuries
Dislocation is an injury of joint. Due to
overtwisting the ends of bones are forced away
from their normal position. This injury
temporarily deforms and immobilizes the joint.
Dislocation is most common in the shoulders.
fingers, elbows, knees and hips.
Management of Dislocation
The management of dislocation is doné
following ways,
© Reduction
© Immobilization
WV
e Surgery ° Rehabilitation
Fractures
Fracture is a broken or
cracked bo:
accidentally by a wren,
‘ ne. Itis caused
ching force.
Types
e Stress fracture ° Green stick fracture
e Oblique fracture Impacted fracture
e Comminuted fracture
e Transverse fracture
Open Fracture : Open fracture causes
to bone and skin, so
Closed Fracture : In closed fracture the broken
OOK
7. PHYSIOLOGY & INJURIES IN SPORTS (XI)
bone does not pierce the skin but internal
injury to surrounding tissues may be caused.
First Aid-Aims & Objectives
First aid is the immediate help given to an
injured or ill person. A timely help can save a
victim's life.
Aims & Objectives
e Preserve life e Decrease pain
© Promote recovery Prevent deterioration
Principles
© Don't panic
© CPRadministration
e Immediate medical help
PHYSICAL EDUCATION & SPORTS
=
FOR CWSN (CHILDREN WITH SPECIAL NEEDS-DIVYANG)
Quick Review
1. Concept of Disability & Disorder
Disability : When the capacity to perform any
physical or mental work decreases that stage 1s
called disability.
Disorder : Itis defined as a state of confusion or a
mental or physical problem that interrupts
normal functions ofa person.
of disability, its causes and nature
(Cognitive, intellectual and physical
disability)
¢ Cognitive disability: This category includes
the people who have problems associated with
memory, thinking, remembering, learning
disorders and problems associated with
perceiving things.
« Intellectual disability : Intellectual disability
means that a child learns and develops more
slowly than other children. But having an
intellectual disability doesn’t mean a person can't,
learn.
© Physical disability : Physical disability affects
a person's mobility. They cannot perform daily
activities independently.
Causes of disability :
Heredity causes, Physical ailments or diseases,
mental factors, occupational environment,
physical factors, social factors, chemical factors,
accidents, diet factors, drug addiction, lack of
education
3. Types of disorder, its causes and nature
(ADED, SPD, ASD, ODD, OCD)
(@ ADHD : Attention deficit hyperactivity
disorder (ADHD) is a brain disorder marked
by an ongoing pattern of inattention,
hyperactivity and impulsivity. This interferes
with functioning or development.
Symptoms of ADED
Troubles in finishing assignments of school.
Problem in focusing on instructions.
Mainly forgetting things like homework.
Chances of distractions are more.
Problems in paying close attention.
Increase in careless mistakes,
Difficulty in organizing tasks and activities,
Unnecessarily interrupting others.
wc eee we
er
LOG z\
* Fidgeting with hands or feet or having
trouble sitting tll
© Restlessness increases.
© Talking a lot and having trouble in doing
things quietly.
Causes of ADHD
Brain functioning in ADHD, heredity, exposure
to toxic substances, brain injury
(i) SPD : Sensory Processing Disorder is
condition when the nervous system receives
messages from the senses and turns them
into appropriate motor and behavioural
responses. A child suffering from SPD finds
it hard to process and act upon information
received through the senses.
Symptoms of SPD
© Over or under responsive behaviour
© Children frequently throw tantrums or
have meltdowns
« Affect sensory organs
Causes of SPD
© Genetic
Environmental
© Lowbirthweight
© Drugaddtction
© Neurological disorder
© Abnormal brain activity
(ii) ASD (autism Spectrum Disorder): ASD is
a neurological & developmental condition
that affects the brain's growth and
development.
‘Symptoms of ASD
© Feels difficult with communication and
interacting with others.
© Repetitive and different behaviours, moving
their bodies in different ways.
© Unusual reactions to what they see, hear,
smell, touch or taste.
© Preference forroutines and dislike change.
* siitore can affect the way that individuals
n others and how
theworldaround them." ~Perience
Causes of ASD : Genetic, biological,
environmental,
(tv) ODD (Oppositional Defiant Disorder)
It is a behaviour disorder. Children with ODD
are uncooperative, defiant and hostile towards
Peers, teachers, parents and other authority
figures.
Symptoms of ODD
© Frequent display ofbad temperament.
© They argue excessively with adults.
© Active disobedience and refusal to comply
with adult's request.
© Intentional attempts to annoy or upset others.
® Blaming others for their mistakes or
misbehavior.
© Often being sensitive or easily annoyed by
others.
© Always display repeated anger and
resentment
Causes of ODD : Genetic, environmental.
(v) OCD (Obsessive Compulsive Disorder)
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder is a common,
chronic and long-lasting disorder in which a
person has uncontrollable, reoccurring
thoughts which are characterized as
obsessions. The behaviors are characterized as
compulsions that the person urges to repeat
over and over.
Symptoms of OCD
Obsessions related systems
© Fear of germs or contamination.
© Unwanted forbidden or prohibited thoughts.
© Aggressive thoughts towards others or self.
© Possessive of having things symmetrical or in
a perfect order.
© Superstitions; excessive attention to
something considered lucky or unlucky.
Compulsions related symptoms
° Excessive cleaning particularly hand
washing.
Ordering and arranging things ina particular
and precise way.
© Repeatedly checking on things, such as
repeatedly checking to see if the door is
Jocked or that the ovenis off.
© Compulsive counting.
e Accumulating “junk” such as old newspapers
or empty food containers.
© Spendinga lot of time on washing or cleaning
or bathing.
Causes of OCD : Genetic factors, biological
factors, environmental factors.
. Disability Etiquettes
Special children need special attention for whieh
some rules and guidelines have been made.
@ Always consider that he/she is a person, not
adisable.
© Language to be used must be very nice ang
humble
‘e Always offer for shake hand even if they have
artificial arm. Simply this gesture will help
them feel accepted and create a warmer
environment for communt-cation,
@ Never assume that children with special
needs as mentally retarded or mentally il. Be
patient in finding out which communication
method works best for them.
« Always give complete attention when
conversing with an individual who has
difficulty in speaking.
© Incase of crowded environment. take them to
a quieter location to talk.
© Keep in mind that individual who use
wheelchairs may require special assistance,
Always do not automatically assist the
individual without permission. It is okay
to offer assistance. However, if the offer is not,
accepted, respect his/her request!
© Always think if you are speaking with an
individual in a wheelchair for more than a
couple of minutes, find a place where you can
sit down to give the individual a more
comfortable viewing angle.
Strategies to make Physical Activities
assessible for children with special needs
Plan the activity to aim at long range goals.
Physical education teachers must give
training so that with exercises child's
physical condition can improve.
Teaching strategies should be simple so that
child can follow easily.
© Plan daily exercises for concentration and
coordination.
Encourage community based programmes.
© Involve people with disabilittes in decision
making.
© Provide a conducive environment for speci
children.
© Provide training & employment
opportunities.
© Use of special equipment.
Modify rules as per needs of children.
© Development of volunteer services.
a
ay
wumerG
Quick Review
Meaning of Yoga
‘The word yoga has been derived from the
Sanskrit word ‘yug’ which means to join
individual soul with the soul of Divine. It is a
comprehensive system linking body, breath,
mind, intelligence, wisdom and spirit. Yoga helps
in creating balance and harmony in body. Yoga
creates symmetry throughout the body, making
one strong and flexible and balanced. Yoga also
teaches to balance the mental urge to push,
control, and be assertive with the impulse to
yield, submit and be passive. Thus Yoga helps in.
attaining a balanced attitudinal equilibrium,
Importance of Yoga
Reduces stress and tension
.
© Cures various diseases
© Relaxes the body
Controls sense organs
© Improves concentration
© Increases flexibility
© Cleans respiratory organs
‘© Keeps correct posture
Asanas as Preventive Measures
Asanas are various postures of yoga. By
practicing asana one can develop agility, balance
and endurance. Asanas keep the body fit and free
from disease. These asanas train and discipline
the mind. Asanas are of different types.
‘© Meditative Asana : Padmasana, Vajrasana,
Gomukhasana.
Relaxative Asana : Shavasana.
Corrective Asana : Bujangasana,
Paschimotanasana.
Benefits of Asanas
Improves circulatory system.
Digestive system works efficiently.
Prevents mental illness.
Neuromuscular system improves.
Improves immunity.
Improves flexibility.
Develops strength & endurance
AST
YOGA & Ll FESTYLE
Ney abe
4. Obesity
Obesity is defined as excess accumulation of fat
resulting in increased body weight.
Causes
Poor lifestyle
© Genetics
Psychological factors
Lack ofphysical activity
@ Intake of more calories
Risk factors of obesity: Heart ailments,
diabetes, osteoarthritis ete.
Prevention & Management
© Regularexercise _ Avoid unhealthy food
¢ Avoid fastfoods — * Avoid alcohol
© Take plenty of water
Ardhmatsyendrasana.
5. Diabetes
Diabetes is a condition when the pancreas in
the human body fails to produce insulin,
Insufficient secretion of insulin results in excess
of glucose level in the blood stream, resulting in
diabetes.
Risk factors of Diabetes
Family history, weight, age, inactivity.
Causes : Sugar builds up in our blood stream as
insulin producing cells get destroyed in
pancreas.
Prevention & Management
© Healthy lifestyle
© Proper coordination of meals & medication
© Balanced food
© Regular exercise
Asanas for diabetes:Bujangasana,
Paschimotasana, Pavanmuktasana,
Ardhmatsyendrasana.
6. Asthma
Asthma is a condition of constriction of airways.
In this condition extra mucus is produced which
leads to shortness of breath and coughing &
wheezing takes place.
Symptoms
© Shortness of breath
© Pain and stifiness in chest
© Frequent coughing and sneezing
© Increased difficulty in breathing
Gs)
2)
Causes
e Respiratory infections
® Some medications
e Air pollutants and irritants
e Strong emotions & stress
e Physical activity
e Occupational environment
prevention & Management
e Keepyour surroundings clean
e By using air conditioners
e Take your medicine as prescribed
e Minimize contact with your asthma trigger
e Doregular exercise
e Avoid obesity
e Take plenty of fruits & vegetables
e Control your acidity
e Dobreathing exercises
¢ Domeditation
Asanas for Asthma : Sukhasana, Chakrasana,
Gomukhasana, Parvatasana, Bhujangasana.
Paschimottanasana, Matsyasana.
4K
3.YOGA & LIFESTYLE (xi)
. Hypertension
When the pressure in blood vessels gets high
enough leading to risk other body system, is
called high blood pressure or hypertension
Symptoms
e Headache © Shortness of breath
© Face turning red © Disturbed sleep
© Nose bleeding © Irritating
Prevention & Management
© Exercise regularly © Eat healthy diet
© Reducestress © Avoid smoking
© Proper sleeping habits
e Reduce alcohol consumption
Causes
© Obesity © Less physical activity
e Smoking © Stress
© Hereditary factor © Ageing
© Gastric problem
Risk factors
Serious health problems, heart failure, heart
attack, other organs affected like kidneys, liver.
Asanas for Hypertension:
Tadasana, Vajrasana, Pavanmuktasana,
Ardhachakrasana, Bujangasana.-
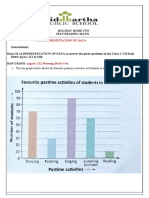
Prntetes fuel on yortveel
A
ar
TER eB STG” Di seage
I3_#PP.
FRWOH
Front,
a5l% yan Fi
Heran Br00o ae INIT eS, Vy awe Py
aye IN, ee aa
|
Besa le ago IR MD ek el
ere i
a
| y aS ees
| s ER |
es
ile ene
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5806)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Electric Field &potentialDocument49 pagesElectric Field &potentialGreeshma ReddyNo ratings yet
- Class 12 - AC Mains QuestionsDocument6 pagesClass 12 - AC Mains QuestionsGreeshma ReddyNo ratings yet
- Grade-5 MATH SELF READINGDocument4 pagesGrade-5 MATH SELF READINGGreeshma ReddyNo ratings yet
- Gr-12 English QP MDocument4 pagesGr-12 English QP MGreeshma ReddyNo ratings yet
- VOTE OF THANKS - My Class Has Got TalentDocument2 pagesVOTE OF THANKS - My Class Has Got TalentGreeshma ReddyNo ratings yet
- 5 & 6 Genetics 2021Document116 pages5 & 6 Genetics 2021Greeshma ReddyNo ratings yet
- Salt Analysis For Class XIIDocument38 pagesSalt Analysis For Class XIIGreeshma ReddyNo ratings yet
- Jugs and Mugs Day-1 NotesDocument2 pagesJugs and Mugs Day-1 NotesGreeshma ReddyNo ratings yet
- How Many Squares Grade 5Document4 pagesHow Many Squares Grade 5Greeshma ReddyNo ratings yet
- Nelson Mandela and His AchievementsDocument16 pagesNelson Mandela and His AchievementsGreeshma ReddyNo ratings yet