0% found this document useful (0 votes)
271 views2 pagesFormula Booklet
The document outlines various formulas for calculating:
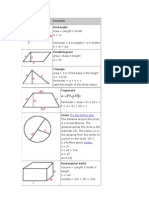
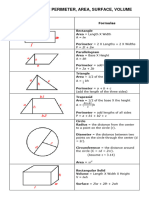
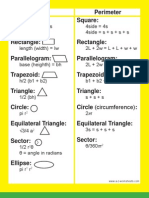
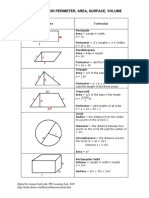
1) Area and perimeter of basic shapes like squares, rectangles, triangles, parallelograms, trapezoids, and circles.
2) Surface area and volume of cubes, cuboids, pyramids, cylinders, cones, spheres, and prisms.
3) Trigonometric ratios, area of a circle sector, and length of a circular arc based on central angle and radius.
Uploaded by
Om PatelCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
271 views2 pagesFormula Booklet
The document outlines various formulas for calculating:
1) Area and perimeter of basic shapes like squares, rectangles, triangles, parallelograms, trapezoids, and circles.
2) Surface area and volume of cubes, cuboids, pyramids, cylinders, cones, spheres, and prisms.
3) Trigonometric ratios, area of a circle sector, and length of a circular arc based on central angle and radius.
Uploaded by
Om PatelCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Perimeter: Discusses how to determine the perimeter of different shapes like squares, rectangles, and circles.
- Volume: Focuses on methods to derive the volume of various solid shapes, including cubes and prisms.
- Area: Covers the calculation of area for various geometric shapes including squares, rectangles, and trapezoids.
- Surface Area: Explores formulas for calculating the surface area of 3D shapes such as cuboids, cylinders, and spheres.
- Area of Sector: Provides the formula for finding the area of a sector within a circle.
- Length of Arc: Describes how to calculate the length of an arc in a circle using given angles and radius.
- Trigonometric Ratios: Introduces trigonometric ratios and their fundamental relationships including sine, cosine, and tangent.