Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Dokumen Google Keep
Uploaded by
FahrudinCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Dokumen Google Keep
Uploaded by
FahrudinCopyright:
Available Formats
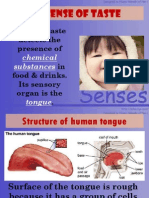
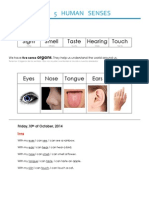
The sense of taste is one of a person's five senses.
We taste with the help of taste-buds
There are four main kinds of taste, sweet, sour, salty, and bitter. All other tastes are just
mixtures of two or more of these main types.
The surface of the tongue has more than fifteen thousand taste-buds (or cells). These are
connected to the brain by special nerves which send the so-called 'tastes messages'.
When the tongue comes into contact with food of any kind, the taste-buds will pick up the
taste. The nerves then send a message to the brain. This will make us aware of the taste. All
this happens in just a few seconds.
There are four kinds of taste-buds, each of which is sensitive to only a particular taste. These
four groups are located in different parts of the tongue.
The taste-buds for salty and sweet tastes are found around the tip of the tongue and along its
sides. Sour tastes can be picked up only at the sides of the tongue. The taste-buds for the
bitter taste are found at the innermost edge of the tongue. There are taste-buds at the centre
of the tongue.
The sense of smell and sight can affect taste. The good smell of food increases its taste.
Similarly, attractive colors can make food appear tastier and more delicious. If food doesn't
smell good or is dull-colored, it will not look tasty and may not taste good at all.
Very hot or sensations can make the taste-buds insensitive. Food that is too hot or too cold,
when placed in the mouth, will have no tastes at all.
You might also like
- The Flavour PyramidDocument5 pagesThe Flavour Pyramidboab235No ratings yet
- Flavors and FlavoringsDocument9 pagesFlavors and FlavoringsDaniela BerdugoNo ratings yet
- The Sense of TasteDocument6 pagesThe Sense of TastesuperultimateamazingNo ratings yet
- Taste and SmellDocument36 pagesTaste and SmellKarthikeyan Balakrishnan100% (2)
- Is it Hot or Is it Cold? Senses for Kids! - Baby & Toddler Sense & Sensation BooksFrom EverandIs it Hot or Is it Cold? Senses for Kids! - Baby & Toddler Sense & Sensation BooksNo ratings yet
- Jawaban (Explanation Text)Document2 pagesJawaban (Explanation Text)Ribhi GustizioNo ratings yet
- How Does Our Sense of Taste Work - National Library of Medicine - PubMed HealthDocument3 pagesHow Does Our Sense of Taste Work - National Library of Medicine - PubMed HealthBill LeeNo ratings yet
- 11 Paper Title Food Analysis and Quality Control Module-08 SensoryDocument11 pages11 Paper Title Food Analysis and Quality Control Module-08 Sensorymonera carinoNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Sense of Taste: Sense of Taste Detects The Presence of in Food & Drinks. Its Sensory Organ Is TheDocument6 pages1.4 Sense of Taste: Sense of Taste Detects The Presence of in Food & Drinks. Its Sensory Organ Is TheMissz WazeeNo ratings yet
- Sensation of TasteDocument16 pagesSensation of TasteSaikhul IslamNo ratings yet
- The Five Senses Conversation Topics Dialogs - 76877Document2 pagesThe Five Senses Conversation Topics Dialogs - 76877Brenda LimaNo ratings yet
- The Five SensesDocument14 pagesThe Five SensesBren GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Taste #1Document4 pagesTaste #1maliyhaNo ratings yet
- Physiology o F GustationDocument26 pagesPhysiology o F GustationPrakash PanthiNo ratings yet
- Running Head: CHEMICAL SENSES 1Document7 pagesRunning Head: CHEMICAL SENSES 1Carter CarsonNo ratings yet
- The Five Sense PDFDocument1 pageThe Five Sense PDFRakel Terron MugaNo ratings yet
- Notebook 4º - 2014 PDFDocument4 pagesNotebook 4º - 2014 PDFSandra PastorNo ratings yet
- Organoleptic Properties of FoodDocument2 pagesOrganoleptic Properties of FoodVeronica ZayasNo ratings yet
- 1.4 - Questions The - Five - Senses - Vallejo - VázquezDocument3 pages1.4 - Questions The - Five - Senses - Vallejo - VázquezEmilio VallejoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 TastingDocument11 pagesChapter 4 TastingHannah Mae BolalinNo ratings yet
- EFR Global FlavorsDocument2 pagesEFR Global FlavorsimjuuNo ratings yet
- The Nose Knows: Discover The Difference Between Taste and SmellDocument6 pagesThe Nose Knows: Discover The Difference Between Taste and SmellAntoniio Ernestto CoronaNo ratings yet
- AnalyticalDocument4 pagesAnalyticalfikrialdiNo ratings yet
- What Are Taste BudsDocument3 pagesWhat Are Taste BudsLoumelyn Rose B. BayatoNo ratings yet
- Taste BudsDocument7 pagesTaste BudsTURARAY FRANCES MERLENENo ratings yet
- Sensory StimuliDocument1 pageSensory StimuliJohnnie HarrisonNo ratings yet
- 1510584146organoleptic Qualities of FoodsDocument14 pages1510584146organoleptic Qualities of FoodsAnisa -No ratings yet
- C1 Cambridge Advanced Part 8 2z2Document1 pageC1 Cambridge Advanced Part 8 2z2Sandra WłodarczykNo ratings yet
- LidahDocument2 pagesLidahNur AsiahNo ratings yet
- Smell and TasteDocument26 pagesSmell and TastemayrajjdNo ratings yet
- 5 Senses Lesson 9Document3 pages5 Senses Lesson 9api-3370782780% (1)
- Class-1 Science PPT - Our Sense OrgansDocument16 pagesClass-1 Science PPT - Our Sense OrganssenthilNo ratings yet
- The Senses - Taste, Smell, TouchDocument23 pagesThe Senses - Taste, Smell, TouchAlvand HormoziNo ratings yet
- The Chemical SensesDocument1 pageThe Chemical Senseskristine maeNo ratings yet
- Universiti Kuala Lumpur Malaysian Institute of Chemical & Bioengineering TechnologyDocument6 pagesUniversiti Kuala Lumpur Malaysian Institute of Chemical & Bioengineering TechnologyNur AsiahNo ratings yet
- Sex and Senses WPS OfficeDocument3 pagesSex and Senses WPS OfficeMabeth PagatpatNo ratings yet
- Bahasa Inggris RevisiDocument7 pagesBahasa Inggris RevisiAkuntansi lanjutan6204No ratings yet
- Physical Education DemoDocument22 pagesPhysical Education DemoMaria Fe GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 0ne4Document45 pagesChapter 0ne4Umar HarizNo ratings yet
- 12 Weekly Planning For English - November 26th, 2018Document7 pages12 Weekly Planning For English - November 26th, 2018Cristina MihuNo ratings yet
- The Role of TastesDocument1 pageThe Role of TastesRičardasNo ratings yet
- Taste Sense: All You Need To KnowDocument18 pagesTaste Sense: All You Need To KnowOldemary DeschampsNo ratings yet
- Taste Receptor Cells: Left Image: Diagram of Taste Cells Right Image: Papillae of TongueDocument2 pagesTaste Receptor Cells: Left Image: Diagram of Taste Cells Right Image: Papillae of Tongueapi-333961542No ratings yet
- Sense of TasteDocument10 pagesSense of TasteGatita LindaNo ratings yet
- Taste Zones by Habiba 12DDocument2 pagesTaste Zones by Habiba 12DHabiba HelmyNo ratings yet
- Degustarea Vinului - Manual SenzorialDocument8 pagesDegustarea Vinului - Manual SenzorialvinuriNo ratings yet
- Taste and Taste Work in LanguageDocument26 pagesTaste and Taste Work in LanguageSallarNo ratings yet
- LET'S TALK ABOUT THE MATRIX: PHILOSOPHY PSYCHOLOGY SOCIOLOGYFrom EverandLET'S TALK ABOUT THE MATRIX: PHILOSOPHY PSYCHOLOGY SOCIOLOGYNo ratings yet
- Mid Term Asssignment - The Five Senses - PrimaryDocument5 pagesMid Term Asssignment - The Five Senses - PrimaryPrajna MoodabidriNo ratings yet
- The Five Senses: English ConversationDocument14 pagesThe Five Senses: English ConversationWayan NovieNo ratings yet
- The Five Senses & Their FunctionsDocument11 pagesThe Five Senses & Their FunctionsCherry Anne Castillejos100% (1)
- The Science of Taste, Smell and Flavor - LinkedInDocument10 pagesThe Science of Taste, Smell and Flavor - LinkedInJessa Beth GarcianoNo ratings yet
- Sci 2Document7 pagesSci 2Thameiyenthi LetchumananNo ratings yet
- Ready For CAE Ss P 38.the SENSES. SpeakingDocument2 pagesReady For CAE Ss P 38.the SENSES. SpeakingtomeualoyNo ratings yet
- Food Selection and EvaluationDocument14 pagesFood Selection and EvaluationRizabelle TubioNo ratings yet
- Faiza ShabeerDocument8 pagesFaiza ShabeerMuneeb U RahmanNo ratings yet
- Soal Mid Kelas XIDocument2 pagesSoal Mid Kelas XIemanuhutuNo ratings yet
- Gustatory and Olfactory Senses: of Sensory Physiology. New YorkDocument11 pagesGustatory and Olfactory Senses: of Sensory Physiology. New Yorktherisa adarethNo ratings yet
- Soal Bahasa Inggris Kelas Xi Semua Pas 2022Document8 pagesSoal Bahasa Inggris Kelas Xi Semua Pas 2022FahrudinNo ratings yet
- Materi - Let's Learn (Exposition Text)Document10 pagesMateri - Let's Learn (Exposition Text)FahrudinNo ratings yet
- Materi - Introduction (Exposition Text)Document11 pagesMateri - Introduction (Exposition Text)FahrudinNo ratings yet
- PerintahDocument1 pagePerintahFahrudinNo ratings yet
- Materi - Introduction (Exposition Text)Document11 pagesMateri - Introduction (Exposition Text)FahrudinNo ratings yet
- Materi - Let's Learn (Exposition Text)Document10 pagesMateri - Let's Learn (Exposition Text)FahrudinNo ratings yet