Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Document 1
Uploaded by
malik zadaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Document 1
Uploaded by
malik zadaCopyright:
Available Formats
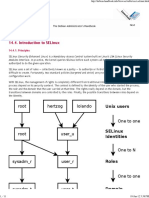
SELINUX
discretionary access control ==========>permissions are set usually by the resource owner.
its desicion base on user identity , ownership and group id .
mandatory access control ===========>permissions are set by fixed rules based on policies and cannot be overridden
by users
it use when using linux in enforcing mode
if malik wnt to access root file first discretionary access control if they allow then selinux is checked
Selinux ===========>is linux security module that built into the linux kernal . when security relavent access
is taking place such as process attempt to open a file the operation is intercepted in kernal by selinux
if selinux rule allow operation it continue otherwise operation block and process receive error
it add mandatory access control to kernal and execute the untrustworthy application safely .
in selinux files, directory , devices called objts
processes such as user runnig command and application calleld subjcts .
discretionary access control system control how subject interact with object and how subject with each other.
in this user control the permission of objects .
Selinux Context =========>The context contains additional information about a system object: the SELinux user, their
role, their type, and the security level.
SELinux uses this context information to control access by processes, Linux users, and files
Benefits .....
all processes and file labelled with type . a type define domain for processes and type for file
processes are seprataed from each other by running in their own domain . selinux define khow processes
intercat with each other as well as files
selinux administrater k through define ki ja skti , system vise pr enforce ki ja skti hy .
reduce escalation attack . if process compromised then attcker just acces to process normal funcation and
and to file the process has been configured to have access .
................
however selinux is not a .............>>
antivirus software
it is not a replacment of password , firewall , and other security
not a all in one security solution
................
selinux is deigned to enhance the existing security solution not replace them .
default acces is deny .if selinux policy rule does not exist to allow access suach as process
to opening a file access is denied .
some confined and unconfined user exist in selinux policy .
selinux limit damage if you make mistake in system configuration
///////////////////////
Access vector cache
selinux desicion such as allowing and disallowing access is cache called Access vector cache .
when cached desicion use selinux check rule need to be cehcked less .
.....................
Selinux Three modes
Enforcing =============> selinux policy is enforced , selinux denies access based on selinux policy rule
var/log/audit.log =====> store log if they allow or they deny .
Permissive =============>selinux policy is not enforced . selinux does not deny access but ye log kr ly ga un ko
jo deny ho jany thy agr enforcing mode open hota .
Disabled ==========> selinux is disabled only the Dac rule is applied .
........................
configuration file is ===========> /etc/selinux/config
setenforcing 0 ============> set selinux in permissive mode temporary
setenforcing 1 ==========> set selinux in enforcing mode temporary .
getenforcing ==============> show selinux enforcing mode .
.autorelabel ==================> reset the existing defined selinux context and default selinux context
is applied when system reboot .
3 selinux types
===>Targeted ......> it is default policy in selinux
two mode in targeted policy
====> Confined (mean access during domain).....> targeted processses started .this is for services that listen on
network
and processes run as root such as passwd utility .
======>unconfined (means access to all domain ) -----> system processes during init. and logged-in users.
====>minimum
=====>mls
sestat =====> show selinux info
chcon -t type_name dir/file_location ======> chnage selinux temporary
restorecon sservice_name/file_name/dir_name ===========> to restore the selinux context js k name bhi dy gy .
semanage boolean -l ======> show all boleans in selinux bolean is liye agr ap ik service ko do type ki selinux
context allow krna chaty ho
semanage fcontext -a -t type_name file/dir/service_name
semanage login -l =============> show local user mapping with selinux user
seinfo -u ===========> show selinux users
seinfo -r ============> show rule for user
setboolean ===> executable writeable memory chunks use for changing in selinux policy for confined users.
semanage boolean -l ========> show all boolean
confined user ko access dani ho kesi service pr tu us ki boolean value ko on kr dy gy .
setsebool -P bolean_name on ========> change the boolean value permanent
You might also like
- 20 Linux Server Hardening Security TipsDocument25 pages20 Linux Server Hardening Security TipsIla IlanNo ratings yet
- Rhcsa ExamDocument9 pagesRhcsa ExamДенис МишенькинNo ratings yet
- Overview of Some Windows and Linux Intrusion Detection ToolsFrom EverandOverview of Some Windows and Linux Intrusion Detection ToolsNo ratings yet
- 40 Linux Server Hardening Security TipsDocument18 pages40 Linux Server Hardening Security TipsMazanaNo ratings yet
- Rhel 7Document17 pagesRhel 7info info100% (2)
- Linux Security and Server Hardening Part-1Document5 pagesLinux Security and Server Hardening Part-1eduardo.araujo4555No ratings yet
- Exam For Rhcsa Rh134 7Document17 pagesExam For Rhcsa Rh134 7Azri Omar0% (2)
- SEcurity Enhanced Linux OverviewDocument25 pagesSEcurity Enhanced Linux OverviewHelenNo ratings yet
- MySQL Security Best PracticesDocument6 pagesMySQL Security Best PracticesAdrian MjNo ratings yet
- VOS3000 - Manual 2.1.4.0Document217 pagesVOS3000 - Manual 2.1.4.0Ahmad Hassan ZiaNo ratings yet
- Solaris CommandsDocument14 pagesSolaris CommandsImraneANo ratings yet
- Gateway Vs AppleDocument2 pagesGateway Vs Applesummiyailtaf100% (1)
- Pmbok Sixth Edition PDF Cartesiansbiz PDFDocument5 pagesPmbok Sixth Edition PDF Cartesiansbiz PDFsaqlain0% (1)
- SELinuxDocument2 pagesSELinux20bca1355No ratings yet
- Introduction To SELinuxDocument11 pagesIntroduction To SELinuxAlan FoxNo ratings yet
- SELinux For DummiesDocument38 pagesSELinux For DummiesdbahanyNo ratings yet
- Aim/Overview of The Practical:: Linux Worksheet - 3.1Document6 pagesAim/Overview of The Practical:: Linux Worksheet - 3.1Shubhangi 21MCC2006No ratings yet
- 49.2. Introduction To SelinuxDocument31 pages49.2. Introduction To SelinuxVidhya DharanNo ratings yet
- Security-Enhanced Linux (Selinux) Is That Provides A Mechanism For Supporting Access Control Security Policies. (/Etc/Selinux/Config)Document2 pagesSecurity-Enhanced Linux (Selinux) Is That Provides A Mechanism For Supporting Access Control Security Policies. (/Etc/Selinux/Config)datta ikheNo ratings yet
- Selinux: Security Enhanced LinuxDocument28 pagesSelinux: Security Enhanced LinuxAjeet Singh RainaNo ratings yet
- SELINUXDocument9 pagesSELINUXPN RobbieNo ratings yet
- SELinux Explained With Examples in Easy LanguageDocument18 pagesSELinux Explained With Examples in Easy Languagegurdev singhNo ratings yet
- Selinux Four ThingsDocument10 pagesSelinux Four Thingsscribd.com.ieNo ratings yet
- SELinux InstallationDocument5 pagesSELinux Installationmahesa agniNo ratings yet
- Tech Skills - Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 - 3.0 Securing ServicesDocument2 pagesTech Skills - Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 - 3.0 Securing ServicesDDDDNo ratings yet
- Steps To Install LAMP in A Offline Centos MachineDocument16 pagesSteps To Install LAMP in A Offline Centos MachineRed IeNo ratings yet
- Linux Security On HP Servers: Security Enhanced Linux: Technical IntroductionDocument13 pagesLinux Security On HP Servers: Security Enhanced Linux: Technical IntroductionsuryaNo ratings yet
- Chapter7 Managing SELinux SecurityDocument2 pagesChapter7 Managing SELinux SecurityBrent Michel Farmer100% (1)
- Hardware-Assisted Security Enhanced Linux in Embedded Systems: A ProposalDocument7 pagesHardware-Assisted Security Enhanced Linux in Embedded Systems: A ProposalMichail ArampatzisNo ratings yet
- 07 - SELinuxDocument46 pages07 - SELinuxridaNo ratings yet
- System Administration: Core Concepts: in This ChapterDocument14 pagesSystem Administration: Core Concepts: in This ChapterTrancyNo ratings yet
- 25 Hardening Security Tips For Linux ServersDocument9 pages25 Hardening Security Tips For Linux Serverschinku85No ratings yet
- 8 Best Ways To Secure Linux Server (Linux Hardening Guide 2021) - SecuredYouDocument8 pages8 Best Ways To Secure Linux Server (Linux Hardening Guide 2021) - SecuredYoutester checkerNo ratings yet
- LinuxCBT SELinux NotesDocument4 pagesLinuxCBT SELinux NotesrajasekarkalaNo ratings yet
- Hardening Linux OSDocument20 pagesHardening Linux OSbashamibNo ratings yet
- 25 Hardening Security Tips For Linux ServersDocument8 pages25 Hardening Security Tips For Linux ServersMie NgeNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Linux Privilege EscalationDocument21 pagesA Guide To Linux Privilege EscalationAneudy Hernandez PeñaNo ratings yet
- Auditd Configuration On Linux To Track Activity of UsersDocument3 pagesAuditd Configuration On Linux To Track Activity of UsersBabatunde AdebayoNo ratings yet
- Week 4aDocument22 pagesWeek 4aThasleem ReyasNo ratings yet
- Firewall Off and SELinux Off FedoraDocument1 pageFirewall Off and SELinux Off FedoraMihaiSiAna-MariaConstantin-CiuntuNo ratings yet
- Netware HackingDocument43 pagesNetware HackingBhupendra Singh TanwarNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet SelinuxDocument2 pagesCheat Sheet Selinuxlol3No ratings yet
- Group 3Document10 pagesGroup 3arnold mirundiNo ratings yet
- Breaking The Ice With Selinux: Eli BillauerDocument66 pagesBreaking The Ice With Selinux: Eli BillauerPrinceTSMNo ratings yet
- System Admin Unit1 & Unit2Document112 pagesSystem Admin Unit1 & Unit2Shivansh JoshiNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Study of Security Mechanisms Inside Linux KernelDocument6 pagesAnalysis and Study of Security Mechanisms Inside Linux KernelbobNo ratings yet
- Linux Commands To Manage Local AccountsDocument25 pagesLinux Commands To Manage Local AccountsgshreyaNo ratings yet
- Fedora 8 SELinux - FAQ en USDocument26 pagesFedora 8 SELinux - FAQ en USShubhangi 21MCC2006No ratings yet
- Audit QuickstartDocument6 pagesAudit QuickstarthugorduartejNo ratings yet
- CH 15-Securing Windows ObjectsDocument27 pagesCH 15-Securing Windows ObjectsHenraNo ratings yet
- Basic System Administration: Your Daily Commands As RootDocument37 pagesBasic System Administration: Your Daily Commands As RootUmesh GowdaNo ratings yet
- Comparison - NCache, MemCache & RedisDocument6 pagesComparison - NCache, MemCache & RedisRajeev RanjanNo ratings yet
- Linux Baseline Document SantoshDocument27 pagesLinux Baseline Document SantoshutpalbasakNo ratings yet
- Systemd User Level PersistenceDocument2 pagesSystemd User Level PersistenceFF RRRNo ratings yet
- Linux System Admin EssencialDocument10 pagesLinux System Admin Essencialpasc colcheteNo ratings yet
- Schema ManagementDocument9 pagesSchema ManagementSraVanKuMarThadakamallaNo ratings yet
- Rel Notes 2000Document10 pagesRel Notes 2000Anonymous e2GKJupNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Some Intrusion Detection and Vulnerability Assessment ToolsFrom EverandEvaluation of Some Intrusion Detection and Vulnerability Assessment ToolsNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Some Windows and Linux Intrusion Detection ToolsFrom EverandEvaluation of Some Windows and Linux Intrusion Detection ToolsNo ratings yet
- Hamza IlyasDocument41 pagesHamza Ilyasmalik zadaNo ratings yet
- Gender and Age DetectionDocument1 pageGender and Age Detectionmalik zadaNo ratings yet
- 8 Week PlanDocument1 page8 Week Planmalik zadaNo ratings yet
- Civil Hospital Management SystemDocument9 pagesCivil Hospital Management Systemmalik zadaNo ratings yet
- Civil Hospital Management SystemDocument16 pagesCivil Hospital Management Systemmalik zadaNo ratings yet
- Overview Top Rankings Family Photography in LondonDocument9 pagesOverview Top Rankings Family Photography in LondonSasa KasapicNo ratings yet
- Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) : Concept and System-ModelingDocument31 pagesOrthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) : Concept and System-ModelingAsif_Iqbal_8466No ratings yet
- HiDocument4 pagesHiTHULASINo ratings yet
- AoaDocument16 pagesAoaWesleyNo ratings yet
- Counter KPI UMTSDocument2 pagesCounter KPI UMTSZamroniMohammadNo ratings yet
- EDU 528 Project 3Document9 pagesEDU 528 Project 3wach6882No ratings yet
- White Paper WiFi 6 Accelerates A Path To A Hyper-Connected WorldDocument10 pagesWhite Paper WiFi 6 Accelerates A Path To A Hyper-Connected WorldTheophilus AikaNo ratings yet
- Hts LogDocument7 pagesHts LogRamesh KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Cloud, Virtualization and NetworkingDocument12 pagesCloud, Virtualization and NetworkingVanshikaNo ratings yet
- Analytics Workshop Redshift NotebookDocument6 pagesAnalytics Workshop Redshift NotebookAswinNo ratings yet
- Dlp-For-Life Shashi Mae BonifacioDocument20 pagesDlp-For-Life Shashi Mae BonifacioShashi Mae BonifacioNo ratings yet
- DS Lecture-1Document93 pagesDS Lecture-1Muzamal1656No ratings yet
- Neural NetworksDocument38 pagesNeural Networkstt_aljobory3911No ratings yet
- Simatic PCS 7 Process Control System CFC Readme V8.2 SP1 Upd5 (Online)Document24 pagesSimatic PCS 7 Process Control System CFC Readme V8.2 SP1 Upd5 (Online)Automation WorksNo ratings yet
- Final Assignment MAT1005Document4 pagesFinal Assignment MAT1005Như HảoNo ratings yet
- AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner (CLF-C01) Exam GuideDocument3 pagesAWS Certified Cloud Practitioner (CLF-C01) Exam GuideAriel Andres Garcia GonzalezNo ratings yet
- 10 Web CachingDocument24 pages10 Web CachingKabir J AbubakarNo ratings yet
- UnionBank Transfer GuideDocument21 pagesUnionBank Transfer GuideHoneyGrace Alfeche BalignotNo ratings yet
- Amcat - 12 - CDocument5 pagesAmcat - 12 - CShobanaNo ratings yet
- Net Banking Mini ProjectDocument65 pagesNet Banking Mini ProjectTrupti SuryawanshiNo ratings yet
- Developer Training:: Vinyl Introduction Training ManualDocument53 pagesDeveloper Training:: Vinyl Introduction Training ManualVignesh GovindarajanNo ratings yet
- Mod 1Document29 pagesMod 1Abin KurianNo ratings yet
- Anime Face Generation Using DC-GANsDocument6 pagesAnime Face Generation Using DC-GANsHSSSHSNo ratings yet
- Ebook Database Systems A Practical Approach To Design Implementation and Management 6Th Edition Connolly Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument45 pagesEbook Database Systems A Practical Approach To Design Implementation and Management 6Th Edition Connolly Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFdubitateswanmarkm4nvo100% (11)
- Introduction About BimDocument30 pagesIntroduction About Bimshanga75No ratings yet
- Oracle How To Prepare Mass Additions - Populate FA Data in Oracle v2Document8 pagesOracle How To Prepare Mass Additions - Populate FA Data in Oracle v2JoyNo ratings yet
- Reebok and Adidas Case StudyDocument14 pagesReebok and Adidas Case Studysnowgul100% (1)