Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MBA MAnagerial Economic Unit 5
MBA MAnagerial Economic Unit 5
Uploaded by
Naman Maheshwari0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views22 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views22 pagesMBA MAnagerial Economic Unit 5
MBA MAnagerial Economic Unit 5
Uploaded by
Naman MaheshwariCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 22
a
n2 Gina | question Bank for Mea,
Its common measure is money. Value of all
in terms of money. Total value of all the fi
year is called national income.
Definitions: The term ‘National Income’ has been defined as under:
‘Anational income estimate measures the volume of commodities and services that are turned out
during a given period counted without duplication’ —National Income Committee of India, 1951
‘National income is the net output of commodities and services flowing during the year from the
country's productive system into the hands of the ultimate consumers or into net additions to the
country’s stock of capital goods’ Rial
“The national dividend is that part of the objective income of the community including of course,
the income derived from abroad which can be measured in money! A.C. Pigou
“The labour and capital of the country acting on its natural resources produce annually a certain
net aggregate of commodities, material and immaterial, including services of all kinds. This is the true
net annual income or revenue of the country or the national dividend’ —Allfred Marshall
‘Thus, national income means the sum total of value of all the final goods and services produced in
an economy during one year.
Q.2. How will you measure the national Income in India?
Ans. Measurement of National Income in India: For the purpose of measurement of national
income, Central Statistical Organisation (CSO) has divided whole of the economy into 14 sectorsas follows:
1. Agriculture, 2. Forestry and logging,
3. Mining and quarrying, 4, Fishing,
5. Registered manufacturing, 6. Unregistered manufacturing,
7. Electricity, gas and water, 8. Construction,
9. Transport, communication and storage, 10. Trade, hotels and restaurants,
Real estate, ownership of dwellings and business services,
i 13. Publicadministration and
the goods and services produced in an economy is
inal goods and services produced in an economy during one
‘There are three methods of measuring national income of a country:
1. Net output method, 2. Income method and 3. Expenditure method.
In India, it is not possible so far to estimate national income
by anyone of these methods because of non-availability and
‘unreliability of data.
14 (Gye: | Question Bank for Man,
‘Inflation is an expansionary trend of purchasing power that tends to be the effect of an increase
in price level’ —Paul
“Inflation isa stage when value of money and credit relative to available goods result in a substantia}
and continuing rise in the general price level! —Webster
“The stage in which there is over issue of currency is called inflation”
‘Thus we see that Hawtrey defines inflation as the ‘Issue of too much currency’ and Coulbourn has
defined fafletion as "Too much money chasing too few goods’ These definitions seek to establish cate
‘and effect relationship between supply of money and the price level. According to these definitions, the
rise in the prices is caused by an increase in the supply of money. The increase in the supply of money
is the cause, the rise in the price level is the effect.
Q.5. What are the causative factors to the inflation? (2006-07)
‘Or Write note on causes of inflation. (2009-10)
Ans. Causes of Inflation: Increase in money income and low production are the two main factors
responsible for inflation. These can be described as follows:
L Increase in Money Income
Following are the factors that help in increasing money income:
1. Credit Policy of Bank: The Central Bank's policy of rate of interest, purchase and sale of
securities in the open market affects the amountof credit. Ifthe bank lowers the rate of interest,
it will lead to increase in the demand of loan which creates inflation. Similarly, when bank
“ increases currency in the open market by purchasing securities, it again results in inflation.
| 2, Deficit Financing: When government resorts to deficit financing to meet its budget deficit, it
; creates inflationary conditions in the country.
“Government Policy: When the government tides over the crisis in the country through
‘of fresh notes, the quantity of money exceeds its requirement and inflationary
as are thereby created.
Jin Velocity: The velocity of money affects the supply sides of money which
es inflation by raising the prices of goods and services. ‘
inflation stems from natural factors, such as: famines,
16 Gye. | Question Bank for 4,
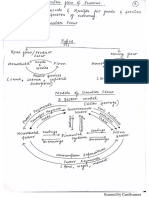
Definitions: The term ‘trade-cycle’ has been defined as under:
‘A trade-cycle is composed of periods of goods trade thatis characterised by rising prices and.low
‘unemployment percentages altering with period of bad trade characterised by falling prices and higher
unemployment’ —Keynes
‘The business-cycles in general sense may be defined as an alteration of period of prosperity ang
depression of good and bad trade’ }
‘Business-cycles are a series of fluctuations in the economic activities of organised communities:
—Mitchett
‘Cyclical fluctuations are characterised by alternative waves of expansion and contraction. They
do not have a fixed rhythm but they are cyclic in that the phases of contraction and expansion recur —
frequently and in fairly similar patterns?
On the basis of above definitions, it can be concluded that business cycles are the regular and
frequent fluctuations in the economic activities of a country. It may also be defined as a period of
prosperity followed by a period of depression. |
Q.9. What are the main causes for giving birth to trade-cycles?
Ans. Important causes giving birth to trade-cycles may be explained as follows:
1, Mal-adjustment between Demand and Investment: If there is mal-adjustment between
‘and investment, it causes trade-cycles. When there is over investment, it leads to the phase of
cy and when there is under-investment, it leads to the phase of depression.
18 | Gia | Question Bank for M.8.8
Q.12. Which is the best method that you would recommend to be used for forecasting business cycles?
(2013-14)
‘Ans. Method for Forecasting Business Cycles: The suitable method for forecasting business
cycles is trend projection method that can be estimated by using one of these methods:
1. Least Square Method: It is based on the assumption that past rate of change is at the variable
under study and will continue in the future. It is a mathematical procedure for fitting a line to a set
of observed data points such that the sum of the squared differences between the calculated and the
observed value is minimised. This method is used to project dependant variable in the future.
2. Time Series Data: It refers to data collected over a period of time recording historical changes
in price, income and the other variables influencing demand for a commodity. The analysis is related to,
the determination of change in a variable in relation to time.
3. Moving Average Method: This method is used to compute the moving average of the sales
of the past. years. The computed average is taken as forecast for the next year or period. This is the
process of computiiig average of leaving the oldest observation and including the next one.
4, Exponential Smoothing: It is a popular technique for short-run forecasting and uses a
weighted average of past data as a basis for a forecast. The method is known to be effective when there
is randomness and no seasonal fluctuations in the data.
SectionfA
| LONG EUR QUESTIONS
ae by Gross National Product (GNP)? How is It different from Net National
(2005-06)
(2006-07)
GDP, GNP and NNP. (2014-15) —
il Income
124 Gira | question Bank for M8.
4, Non-monetised Sector: About 70% of our total population is still living in villages. In some
villages, barter system of exchange is still in use, It means that some transactions do not enter into
monetary sector and thus, these transactions are excluded from national income.
5. False Information Regarding Production and Income: Some individuals, households and
producers do not keep proper and fair accounts of their income. They destroy facts and provide false
information about their production and income. They do so to evade income tax and wealth tax, etc.
6. Problem of Double Counting: Problem of double counting isa serious problem in the: estimation
of national income in India. Many goods and services are used for more than one time in the process
of production. It is not always possible to make a clear and specific distinction between intermediate
goods and final goods. For example, wheat is a final product for a consumer but for flour mill, it is a raw
material. In such cases, it becomes difficult to estimate real contribution of each of these units to the
national income.
Il. Conceptual Problems
Important problems of this category are as follows:
—~ _ 1.Problem of New Goods and Services: National income estimates are prepared at current and
constant prices. There are some commodities that are produced now but were not produced in the
base year. Problem arises as to how to fix the base year price for such commodities.
2. Problem of the Constituents of National Income: There isa difference among ‘different countries
__ on the issue of constituents of ‘national income. Some countries include services also in national income
countries do not include services. Due to this reason, national income data of different
(2010-11)
130| Gyre. | Question Bank for Mi8.A,
Q.8. Give the measures to control the trade-cycle.
Ans. Control on Trade-Cycles
Measures to control trade-cycles can broadly be divided into two parts: I, Preventive measures,
UL, Formal measures. Details in this regard are as follows:
|. Preventive Measures :
Preventive measures are not the measures to control trade-cycles, These are the measures which
are adopted to minimise the possibility of occurrence of trade-cycles. Important preventive measures
are as follows:
All the business and industrial activities should be strictly controlled.
. Monetary and fiscal policies should be well regulated and controlled.
All the efforts should be made to maintain proper balance between demand and supply.
Wherever necessary, industries should be nationalised.
Speculative trend should be checked.
. Inequalities in the distribution of income and wealth should be reduced to minimum.
Agriculture should not depend upon rainfall. Adequate irrigation facilities should be developed
in the country,
"Il, Formal Measures
Fc Ime: es are the measures which cannothelp in removing the fundamental cause of trade-
but can minimise them. Important formal measures are as under:
Noneene
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5819)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Org EffectivenessDocument9 pagesOrg EffectivenessNaman MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Change ModelsDocument28 pagesChange ModelsNaman MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Revision Worksheet-7Document2 pagesRevision Worksheet-7Naman MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- English Haly Yearly Question PaperDocument5 pagesEnglish Haly Yearly Question PaperNaman MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Systems Model of ChangeDocument4 pagesSystems Model of ChangeNaman MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Class 6 Holiday Hmework 23-24Document19 pagesClass 6 Holiday Hmework 23-24Naman MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Leadership in OBDocument36 pagesLeadership in OBNaman MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- 1631079186-Admission-Notice MBA (Executive) 2021Document1 page1631079186-Admission-Notice MBA (Executive) 2021Naman MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- ITM PYQ - SiddhisharmaDocument3 pagesITM PYQ - SiddhisharmaNaman MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Consumer Buying BehaviourDocument17 pagesUnit 4 Consumer Buying BehaviourNaman MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Pricing and Channel DecisionsDocument61 pagesUnit 6 Pricing and Channel DecisionsNaman MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Introduction To MarketingDocument36 pagesUnit 1 Introduction To MarketingNaman MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- AgreementDocument2 pagesAgreementNaman MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Passcourse 2list 13sept21Document6 pagesPasscourse 2list 13sept21Naman MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 AttitudeDocument19 pagesUnit 3 AttitudeNaman MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- ContentDocument8 pagesContentNaman MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Target Marketing STP ApproachDocument24 pagesUnit 3 Target Marketing STP ApproachNaman MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Personality and LearningDocument25 pagesUnit 4 Personality and LearningNaman MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- ContentDocument11 pagesContentNaman MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- MBA Managerial Economic Unit 4Document28 pagesMBA Managerial Economic Unit 4Naman MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Economics MacrooDocument14 pagesEconomics MacrooNaman MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Perception and AttributionDocument15 pagesUnit 2 Perception and AttributionNaman MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- MBA Managerial Economic Unit 3Document24 pagesMBA Managerial Economic Unit 3Naman MaheshwariNo ratings yet