Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cholecyctitis Nursing Concept Map Doc
Uploaded by
SteffiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cholecyctitis Nursing Concept Map Doc
Uploaded by
SteffiCopyright:
Available Formats
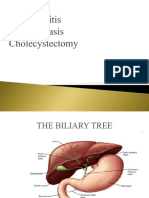
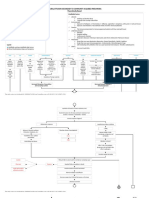
Nursing Concept Map
Cholecystitis - Week 8
(Harding, 2020)
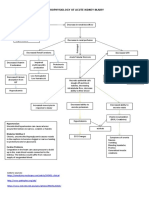
Pathophysiology = RT Risks for Developing Nursing Diagnosis
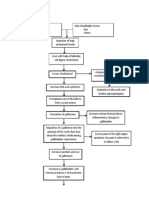
The cause of gallstones is unknown. Gangrenous cholecystitis, subphrenic * Acute Pain related to obstruction
They develop when the balance that abscess, pancreatitis, cholangitis of the ducts by stones as evidenced
keeps cholesterol, bile salts, and (inflammation of biliary ducts), biliary
calcium in solution is changed so that cirrhosis, fistulas, and rupture of the by reporting pain at the abdomen
these substances precipitate. In gallbladder, which can cause bile * Deficient Knowledge related to
patients with gallstones, the bile peritonitis
secreted by the liver is supersaturated Unfamiliarity with information
with cholesterol (lithogenic bile). The resources as evidenced by request
bile in the gallbladder then becomes
supersaturated with cholesterol and for information and questions on
Disease Process
precipitation of cholesterol occurs in the disease process.
the gallbladder. Other components of Diagnostics Medications
bile that precipitate into stones are Alkaline phosphatase, • IV fluid; Antiemetics
bile salts, bilirubin, calcium, and ALT, and AST • Analgesics;Anticholinergics
protein. (Harding, 2020, p. 999) Direct and indirect • Antibiotics (for secondary Nursing Interventions
bilirubin levels, and infection)
Urinary bilirubin • Fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, * Administer pain meds as ordered
levels E, and K) * Administer meds for relieving
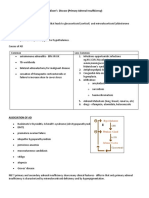
Signs & Symptoms = AEB nausea and vomiting,
* Maintain fluid & electrolyte
Initial symptoms of cholecystitis: balance, nutrition
* acute pain and tenderness in the Education * Oral hygiene, care of nares,
right upper quadrant, pain may be accurate I & O monitor
accompanied by nausea and 1. Remove the bandages on the puncture sites the day after * Observe for signs of obstruction
surgery and you can shower. of the ducts by stones include
vomiting, restlessness, and
2. Notify your HCP if any of the following s/s occurs: Redness, jaundice; clay-colored stools; dark,
diaphoresis; Abd distended swelling, bile-colored drainage or pus from any incision; Severe foamy urine; steatorrhea; fever;
* Fever, chills, and jaundice abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, fever, chills and increased WBC count.
* Inflammation results in 3. You can gradually resume normal activities. * Assessment for infections: vital
leukocytosis and fever; 4. Return to work within 1 wk of surgery. signs, fever with chills jaundice may
*Jaundice, icteric sclera 5. You can resume your usual diet, but a low-fat diet is usually indicate choledocholithiasis
better tolerated for several weeks after surgery.
This study source was downloaded by 100000857940251 from CourseHero.com on 12-13-2022 14:20:35 GMT -06:00
Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org)
You might also like
- A Simple Guide to Parathyroid Adenoma, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Parathyroid Adenoma, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Chinwon Rim Department of Chemistry Southern Methodist UniversityDocument18 pagesIrritable Bowel Syndrome: Chinwon Rim Department of Chemistry Southern Methodist UniversityAviation MedicineNo ratings yet
- Unit-Iii Gordon's Functional Health PatternsDocument3 pagesUnit-Iii Gordon's Functional Health Patternsalphabennydelta4468No ratings yet
- Cholecystitis Litiasis EctomyDocument23 pagesCholecystitis Litiasis EctomyTimothy WilliamsNo ratings yet
- DB31 - Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus and HypoglycemiaDocument5 pagesDB31 - Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus and HypoglycemiaNeil Alcazaren かわいいNo ratings yet
- Addison'sDocument4 pagesAddison'sKoRnflakesNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nsg. Diagnosis Sci. Explanation Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument6 pagesAssessment Nsg. Diagnosis Sci. Explanation Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationRoMarie AbainzaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Diagram of Kawasaki Disease: Precipitating Factors: Predisposing FactorsDocument2 pagesPathophysiology Diagram of Kawasaki Disease: Precipitating Factors: Predisposing FactorsAb Staholic Boii100% (1)
- Hepatocellula R CarcinomaDocument45 pagesHepatocellula R Carcinomamhean azneitaNo ratings yet
- Addison's Disease. FinalDocument10 pagesAddison's Disease. FinalAnn KelseaNo ratings yet
- Chelsea Amman Pku Case StudyDocument37 pagesChelsea Amman Pku Case Studyapi-365955738No ratings yet
- Hypertension Pathophysiology and Treatment PDFDocument6 pagesHypertension Pathophysiology and Treatment PDFBella TogasNo ratings yet
- REVALIDADocument53 pagesREVALIDAMercy Anne EcatNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Hypertension, Diabetes, Ubm, BPHDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Hypertension, Diabetes, Ubm, BPHCarly Beth Caparida LangerasNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was Shared Via: HypoparathyroidismDocument1 pageThis Study Resource Was Shared Via: HypoparathyroidismDeo FactuarNo ratings yet
- 6 Med Ward (WK - 1) PathophysiologyDocument3 pages6 Med Ward (WK - 1) PathophysiologyZaijean Kate Dianne LigutomNo ratings yet
- Mycobacterium Tuberculosis: Precipitating Factors: Predisposing FactorsDocument1 pageMycobacterium Tuberculosis: Precipitating Factors: Predisposing FactorsYoko Mae Yano100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of DiarrheaDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of DiarrheaFathur RahmatNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology FinalDocument2 pagesPathophysiology FinallarissedeleonNo ratings yet
- DM Case StudyDocument21 pagesDM Case StudyBern TolentinoNo ratings yet
- GastritisDocument17 pagesGastritisSri Wahyuni HarliNo ratings yet
- Addison Disease, Penyakit AddisonDocument11 pagesAddison Disease, Penyakit AddisonKertiasihwayanNo ratings yet
- Case 052: Biliary ColicDocument4 pagesCase 052: Biliary ColicZauzaNo ratings yet
- First Level AssessmentDocument9 pagesFirst Level AssessmentGelo IcoNo ratings yet
- Schematic Diagram of Alcoholic Cirrhosis: Liver Steatosis/ Fatty LiverDocument2 pagesSchematic Diagram of Alcoholic Cirrhosis: Liver Steatosis/ Fatty LiverCarmelli Mariae CalugayNo ratings yet
- Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument4 pagesDiabetic KetoacidosisHasan A. AsFourNo ratings yet
- Lupus Case ReportDocument1 pageLupus Case ReportMendy HararyNo ratings yet
- Addison's Disease (Primary Adrenal Insufficiency)Document5 pagesAddison's Disease (Primary Adrenal Insufficiency)sunnnydayNo ratings yet
- CKD + HPN Concept Map DRAFTDocument1 pageCKD + HPN Concept Map DRAFTInah Floresta BesasNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Type II Diabetes MellitusDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Type II Diabetes MellitusMarion Mendez100% (1)
- Covid 19 (Case 1)Document53 pagesCovid 19 (Case 1)cendy andestriaNo ratings yet
- HPN Patopisyo!Document1 pageHPN Patopisyo!Raprap TristanNo ratings yet
- Hypothyroidism PathophysiologyDocument1 pageHypothyroidism PathophysiologyCleo Joyce C. CristalNo ratings yet
- Rheumatic Heart DiseaseDocument13 pagesRheumatic Heart Diseasedy15No ratings yet
- Kawasaki DiseaseDocument7 pagesKawasaki DiseaseRitamariaNo ratings yet
- AssesmentDocument9 pagesAssesmentmizrypNo ratings yet
- ConceptMap AMLDocument1 pageConceptMap AMLnursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- Pernicious AnemiaDocument7 pagesPernicious AnemiaTracy PearlNo ratings yet
- NCP GeDocument14 pagesNCP GeSuluhTriUtomoNo ratings yet
- PATHOPHYSIO (Megaloblastic Anemia)Document3 pagesPATHOPHYSIO (Megaloblastic Anemia)Giselle EstoquiaNo ratings yet
- CVD HypertensionDocument15 pagesCVD HypertensionAbigail BascoNo ratings yet
- 4th Yr. Med Cardio Module Question - Copy-1Document11 pages4th Yr. Med Cardio Module Question - Copy-1Sheda BondNo ratings yet
- Pahtophysiology of EsrdDocument5 pagesPahtophysiology of EsrdCarl JardelezaNo ratings yet
- AFPMC V. Luna General Hospital: Case StudyDocument27 pagesAFPMC V. Luna General Hospital: Case StudyLemuel GuevarraNo ratings yet
- Schematic Diag DMDocument1 pageSchematic Diag DMReynaKatNo ratings yet
- St. Paul University Philippines: School of Nursing and Allied Health Sciences College of NursingDocument5 pagesSt. Paul University Philippines: School of Nursing and Allied Health Sciences College of NursingChristian UmosoNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho Physiology of ParkinsonDocument2 pagesPa Tho Physiology of Parkinsoncuriosity_killsNo ratings yet
- Hypertensive Renal DiseaseDocument2 pagesHypertensive Renal DiseaseHenry KaweesaNo ratings yet
- AGE With Pa Tho PhysiologyDocument3 pagesAGE With Pa Tho PhysiologyChichi Licuben OresacamNo ratings yet
- Addison's DiseaseDocument14 pagesAddison's Diseasedivya4nirmalaNo ratings yet
- Diabetes PathoDocument2 pagesDiabetes Pathodrewcel100% (1)
- Anorexia NervosaDocument11 pagesAnorexia NervosaSashMalikNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation (Final)Document35 pagesCase Presentation (Final)Denie BoyonasNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageNursing Care PlanDaisy PacoNo ratings yet
- NRG 302 13a G2 Copar ModuleDocument14 pagesNRG 302 13a G2 Copar ModuleRhea CruzNo ratings yet
- Amoebiasis Case StudyDocument12 pagesAmoebiasis Case StudyGrace NazarenoNo ratings yet
- Case Study in KidneyDocument3 pagesCase Study in KidneyVenice VelascoNo ratings yet
- PATHODocument9 pagesPATHOj_averilla2012No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of CholelithiasisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of CholelithiasisSherilNo ratings yet
- CalcCarbonFootprint StudentHODocument4 pagesCalcCarbonFootprint StudentHOSteffiNo ratings yet
- FDAR FormatDocument1 pageFDAR FormatSteffiNo ratings yet
- CHN 2-Borderfree++Module 5Document20 pagesCHN 2-Borderfree++Module 5SteffiNo ratings yet
- Eunice Foote and GHG HWDocument8 pagesEunice Foote and GHG HWSteffiNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Vital Sign Normal RangesDocument1 pagePediatric Vital Sign Normal RangesSteffiNo ratings yet
- ANESTHESIADocument53 pagesANESTHESIASteffiNo ratings yet
- 6 - Computer SystemDocument18 pages6 - Computer SystemSteffiNo ratings yet
- Oxygen Therapy and Administration V2Document32 pagesOxygen Therapy and Administration V2SteffiNo ratings yet
- 4 - Historical Perspective in Nursing and ComputerDocument13 pages4 - Historical Perspective in Nursing and ComputerSteffiNo ratings yet
- Urinary CatheterizationDocument41 pagesUrinary CatheterizationSteffiNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Misoprostol PDFDocument5 pagesDrug Study Misoprostol PDFSteffiNo ratings yet
- 11 Core Elements of Evidence - Based Gerontological Nursing PracticeDocument29 pages11 Core Elements of Evidence - Based Gerontological Nursing PracticeSteffiNo ratings yet
- InstrumentsDocument55 pagesInstrumentsSteffiNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - Community Health AssessmentDocument8 pagesModule 4 - Community Health AssessmentSteffiNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - E-Health and Community DevelopmentDocument28 pagesModule 5 - E-Health and Community DevelopmentSteffi100% (2)
- 7 Summary Understanding Chronic IllnessDocument4 pages7 Summary Understanding Chronic IllnessSteffiNo ratings yet
- A Nursing Case Study On EctopicPregnancy PDFDocument60 pagesA Nursing Case Study On EctopicPregnancy PDFSteffiNo ratings yet
- Fluid and ElectrolyteDocument26 pagesFluid and ElectrolyteSteffiNo ratings yet
- Postpartum Hemorrhage: Prevention and Treatment: Table 1Document10 pagesPostpartum Hemorrhage: Prevention and Treatment: Table 1erikafebriyanarNo ratings yet
- Nanotechnology 1Document4 pagesNanotechnology 1SteffiNo ratings yet
- Pleural Effusion Secondary To Community Acquired Pneumonia PathophysiologyDocument5 pagesPleural Effusion Secondary To Community Acquired Pneumonia PathophysiologySteffiNo ratings yet
- 9 Summary Health Education in Chronic IllnessDocument5 pages9 Summary Health Education in Chronic IllnessSteffiNo ratings yet
- Cs With BTLDocument16 pagesCs With BTLSteffiNo ratings yet
- 8 Summary Major Chronic Illness of Older Adult Understanding The Pathophysiology and Nursing InterventionDocument21 pages8 Summary Major Chronic Illness of Older Adult Understanding The Pathophysiology and Nursing InterventionSteffiNo ratings yet
- Vital Signs BP: CR: RR: Temp: HT WT: O2 Saturation: Biophysical Psychosocial and Functional AssessmentDocument2 pagesVital Signs BP: CR: RR: Temp: HT WT: O2 Saturation: Biophysical Psychosocial and Functional AssessmentSteffiNo ratings yet
- Applications That Support Nursing ResearchDocument23 pagesApplications That Support Nursing ResearchSteffiNo ratings yet
- NCP Tissue Perfusion For Pre-EclampsiaDocument2 pagesNCP Tissue Perfusion For Pre-Eclampsiaanreilegarde83% (23)
- NCP Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument4 pagesNCP Ineffective Tissue PerfusionSteffiNo ratings yet
- Template For Case PresDocument13 pagesTemplate For Case PresSteffiNo ratings yet
- Veterinary Internal Medicne - 2008 - Bruchim - Heat Stroke in Dogs A Retrospective Study of 54 Cases 1999 2004 andDocument9 pagesVeterinary Internal Medicne - 2008 - Bruchim - Heat Stroke in Dogs A Retrospective Study of 54 Cases 1999 2004 andGuillermo MuzasNo ratings yet
- Microbial SafariDocument5 pagesMicrobial SafariClauu VargasNo ratings yet
- The Electrooculogram EOGDocument40 pagesThe Electrooculogram EOGRajagopalan SadagopanNo ratings yet
- Clinical Schedule For Australian Dental Council Part 2 Exam CoachingDocument6 pagesClinical Schedule For Australian Dental Council Part 2 Exam CoachingdrrushikNo ratings yet
- Icru Report 62Document62 pagesIcru Report 62Luis Ramirez100% (1)
- Welcome To All: Nursing StaffDocument67 pagesWelcome To All: Nursing StaffMukesh Choudhary JatNo ratings yet
- AminoglycosidesDocument20 pagesAminoglycosidesHassan.shehri100% (5)
- Arcega ErlindaDocument7 pagesArcega ErlindaIvonne TernidaNo ratings yet
- English: Quarter 4 - Module 7 Making GeneralizationsDocument16 pagesEnglish: Quarter 4 - Module 7 Making Generalizationslenra esoj lasorNo ratings yet
- Assisting IV BTDocument89 pagesAssisting IV BTmhelshy villanuevaNo ratings yet
- IELTS Recent Actual Test With Answers Practice Test 30Document14 pagesIELTS Recent Actual Test With Answers Practice Test 30Ferris Wheel GuyNo ratings yet
- Perkutan Kateter Vena Sentral Dibandingkan Perifer Kanula Untuk Pengiriman Nutrisi Parenteral Ada NeonatusDocument3 pagesPerkutan Kateter Vena Sentral Dibandingkan Perifer Kanula Untuk Pengiriman Nutrisi Parenteral Ada NeonatusmuslihudinNo ratings yet
- Postherpetic Neuralgia NerissaDocument18 pagesPostherpetic Neuralgia Nerissanerissa rahadianthiNo ratings yet
- Perioperative Fasting and Feeding in Adults, Obstetric, Paediatric and Bariatric Population-Practice Guidelines From The Indian Society of AnaesthesiologistsDocument29 pagesPerioperative Fasting and Feeding in Adults, Obstetric, Paediatric and Bariatric Population-Practice Guidelines From The Indian Society of Anaesthesiologistsambitiousamit1No ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document12 pagesPresentation 1Rizka FarahinNo ratings yet
- Animal Genetic Engineering 110816 (1) Unit 4Document29 pagesAnimal Genetic Engineering 110816 (1) Unit 4Rupal ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- MCHHDocument2 pagesMCHHEDENNo ratings yet
- Factory Farming in The Developing WorldDocument10 pagesFactory Farming in The Developing WorldDaisyNo ratings yet
- FNCP (Open Drainage) For Soft BoundDocument3 pagesFNCP (Open Drainage) For Soft BoundSean Maghinay BanicoNo ratings yet
- Compare & Contrast Graphic OrganizerDocument3 pagesCompare & Contrast Graphic OrganizerMochi-chanNo ratings yet
- Semey State Medical University: Department of Psychiatry Topic Schizophrenia Raja Ali HassanDocument45 pagesSemey State Medical University: Department of Psychiatry Topic Schizophrenia Raja Ali HassanRaja HassanNo ratings yet
- Foot and Ankle Injuries Kylee Phillips - 0Document74 pagesFoot and Ankle Injuries Kylee Phillips - 0rizwan.mughal1997No ratings yet
- Over PopulationDocument60 pagesOver PopulationSpencer VenableNo ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Kirandul: Investigatory Project of BiologyDocument10 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Kirandul: Investigatory Project of BiologyAachal GayreNo ratings yet
- CFOP - Clinical Obeservations 8-1-11Document16 pagesCFOP - Clinical Obeservations 8-1-11sterlingcorryNo ratings yet
- Low Platelet CountDocument9 pagesLow Platelet Countfatimah_zkhanNo ratings yet
- CALGB Schema FinalDocument1 pageCALGB Schema FinalMohamed MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Assessing The Ear and HearingDocument32 pagesAssessing The Ear and HearingArlyn Mendenilla0% (1)
- A Epithelial - Tissue1 16 12 14Document32 pagesA Epithelial - Tissue1 16 12 14Abdulaziz AbdullahiNo ratings yet
- Curs 1 Introducere EndodontieDocument24 pagesCurs 1 Introducere EndodontieVlahul VladNo ratings yet