Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Module 2 (1-3 Pages)
Uploaded by
Stephanie QuirolOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Module 2 (1-3 Pages)
Uploaded by
Stephanie QuirolCopyright:
Available Formats
Module 2:
21st CENTURY SKILL CATEGORIES
LEARNING OUTCOMES:
1. Identify the categories of 21st century skills
2. Apply the 21st century skills in preparing, planning and developing a lesson
3. Cite ways on how to enhance the 21st century skills of learners
4. Explain how 21st century skills be integrated in the teaching-learning process
5. Cite implications of 21st century skills to educators and to pre-service teacher
preparation
6. Draw relevant life lessons and significant values from the personal experience in
attaining 21st century skills
7. Analyze research abstract on 21st century skills and its implications on the
teaching-learning process
8. Craft a curriculum plan matrix imbued with 21 st century learning outcomes
INTERACTIVE PRESENTATION
Group Mapping Activity: this is a strategy where members of the class present their
prior knowledge on the topic 21st century skill categories through group
drawing/illustration.
Procedure:
1. Group the students into 4 or 5 depending on the class size.
2. Provide each group a topic on 21st century skill category to brainstorm about.
3. The group will synthesize their consolidated ideas and present in a form of
illustration or drawing in a cartolina or Manila paper using any medium of their
choice.
4. Each group will be given a chance to present the synthesis in class.
5. The class will find time for a brief reflection of the activity.
Topics to be assigned to the groups:
1. Life and Career skills
2. Information, Media and Technology skills
3. Learning and Innovation skills
4. Social and Cross-cultural skills
5. Leadership and Productivity skills
CONCEPT EXPLORATION
21st Century Skills refer to a broad set of knowledge, skills, work habits, and character
traits that are deemed necessary in coping with today’s world and future careers and
workplaces. Thus, it can be applied in all academic subject areas and educational
settings throughout a student’s life.
The 21st Century Skills
The 21st Century skills may include the following:
1.) Critical thinking, problem-solving, reasoning, analysis, interpretation, synthesizing
information;
2.) Research skills and practices, interrogative questioning;
3.) Creativity, artistry, curiosity, imagination, innovation, personal expression;
4.) Perseverance, self-direction, planning, self-discipline, adaptability, initiative;
5.) Oral and written communication, public speaking and presenting, listening;
6.) Leadership, teamwork, collaboration, cooperation, facility in using virtual
workplaces;
7.) Information and communication technology (ICT) literacy, media and internet
literacy, data interpretation and analysis, computer programming;
8.) Civic, ethical, and social justice literacy;
9.) Economic and financial literacy, entrepreneurialism;
10.) Global awareness, multicultural literacy, humanitarianism;
11.) Scientific literacy and reasoning, the scientific method;
12.) Environmental and conservation literacy, ecosystem understanding; and
13.) Health and wellness literacy, including nutrition, diet, exercise, and public
health and safety,
Framework for 21st Century
According to the Partnership for 21st
Century Skills, this concept encompasses
a wide array of a body of knowledge and
skills that have to be categorized.
Moreover, this concept has been
interconnected with applied skills, cross-
curricular skills, cross-disciplinary skills,
interdisciplinary skills, transferable skills,
transversal skills, noncognitive skills and
soft skills.
The 21st century skills concept is grounded on the belief that students must be educated
in a more relevant, useful, in-demand and universally applicable manner. The idea
simply lies in the fact that students needs to be taught different skills and reflect on the
specific demand that will be placed upon them in a complex, competitive, knowledge-
based, information-age and technology-driven society. Therefore, 21 st Century
education addresses the whole child or the whole person (AACTE, 2010).
Hence, the curriculum should be designed to be interdisciplinary, integrated and project-
based. Tony Wagner (2010), in his book “The Global Achievement Gap”, advocated the
seven survival skills, namely: (1) critical thinking and problem-solving; (2) collaboration
across networks and leading by influence; (3) agility and adaptability; (4) initiative and
entrepreneurialism; (5) effective oral and written communication; (6) accessing and
analyzing information; and (7) curiosity and imagination.
The term “21st Century skills” refers to certain core competencies, such as collaboration,
digital literacy, critical thinking, and problem-solving that schools need to teach the
students for them to thrive in today’s world.
Learning and Innovation skills
These are the primary skills orchestrated in the 21 st century. They are attributes that
differentiate students who are prepared for a complex life and work environment from
those who are not. Therefore, there is a need to stress on creativity, critical thinking,
communication and collaboration in preparing learners for the future.
A.Critical Thinking and Problem Solving. These may include effectively analyzing
and evaluating evidence, arguments, claims and beliefs; and solving different kinds of
non-familiar problems in both conventional and innovative ways.
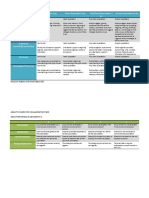
Skill Sub-skills
1. Work together effectively in them Establish clear definitions and agreements
on the roles of partners in the collaborative
process
Keep communication open within teams to
carry out tasks
Carefully identify obstacles and address
problems cooperatively
Skill Sub-skills
2. Reason effectively Use various types of reasoning (inductive,
deductive, etc.) as appropriate to the
situation
Use systems thinking
Analyze how parts of a whole interact with
each other to produce overall outcomes in
complex systems
You might also like
- Elearning Theories & Designs: Between Theory & Practice. a Guide for Novice Instructional DesignersFrom EverandElearning Theories & Designs: Between Theory & Practice. a Guide for Novice Instructional DesignersNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document16 pagesModule 2ROSE ANN MAULANA100% (1)
- Emerging Technologies for the Classroom: A Learning Sciences PerspectiveFrom EverandEmerging Technologies for the Classroom: A Learning Sciences PerspectiveNo ratings yet
- BAENLAC Module 2 - 21st Century Skill CategoriesDocument20 pagesBAENLAC Module 2 - 21st Century Skill CategoriesBaby Blue SwiftNo ratings yet
- BUILDING AND ENHANCING NEW LITERACIES ACROSS THE CURRICULUM Module 2Document11 pagesBUILDING AND ENHANCING NEW LITERACIES ACROSS THE CURRICULUM Module 2Mette Louisse DeLa CruzNo ratings yet
- Learning Material No. 2 Lesson 1-3Document7 pagesLearning Material No. 2 Lesson 1-3Ace EchavezNo ratings yet
- Module 2 21st Century SkillsDocument14 pagesModule 2 21st Century SkillsZyra Ann Dema-alaNo ratings yet
- Be Presentor 1 Module 2Document52 pagesBe Presentor 1 Module 2Den RaysNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document52 pagesModule 2jennifferpabuayaNo ratings yet
- Canillas, Khoebe Kyle S. Unit 3-21st Century Skills CategoriesDocument10 pagesCanillas, Khoebe Kyle S. Unit 3-21st Century Skills CategoriesKyle CanillasNo ratings yet
- Module 2 SilvanoDocument19 pagesModule 2 SilvanoEfigenia Macadaan Fontillas100% (1)
- Module 2Document10 pagesModule 2Lovelin DeveraNo ratings yet
- 21st CenturyDocument20 pages21st CenturyReign ReyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: The 21 Century Skill Categories: Rechelyn G. Salem-Magbanua, Maed-MathDocument50 pagesChapter 2: The 21 Century Skill Categories: Rechelyn G. Salem-Magbanua, Maed-MathBainaot Abdul SumaelNo ratings yet
- Technology For Teaching and Learning: Elementary GradesDocument13 pagesTechnology For Teaching and Learning: Elementary GradesJessie CusiNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Week 18Document4 pagesCurriculum Week 18KylaMayAndrade100% (1)
- Educ221a - M8 Lesson 1 2Document6 pagesEduc221a - M8 Lesson 1 2FUENTES ANDREANo ratings yet
- Peduc 10 Module 2Document6 pagesPeduc 10 Module 2Stefanie Rose DomingoNo ratings yet
- Ped 110x BallesterDocument64 pagesPed 110x BallesterNistan jen SolanoNo ratings yet
- BUILDING ENHANCEMENT (Module2) - KELLY PRESENTACIONDocument5 pagesBUILDING ENHANCEMENT (Module2) - KELLY PRESENTACIONKelly PresentacionNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - 21st Century Skill CategoriesDocument34 pagesModule 2 - 21st Century Skill CategoriesARLENE PILAR AVECILLA100% (3)
- Building & Enhancing New Lits 1Document10 pagesBuilding & Enhancing New Lits 1rosequartzserenity2002No ratings yet
- Group 2 BenlacDocument41 pagesGroup 2 BenlacLoveniath MieerahNo ratings yet
- BENLACDocument13 pagesBENLACAlvin John ArconadoNo ratings yet
- 21st CENTURY Skills CategoriesDocument46 pages21st CENTURY Skills CategoriesClare GardoseNo ratings yet
- AaaaaaaaDocument3 pagesAaaaaaaaJuan PatricayoNo ratings yet
- Discussion For 21st Century SkillsDocument3 pagesDiscussion For 21st Century SkillsWasshiiiNo ratings yet
- PCK106EDITEDDocument43 pagesPCK106EDITEDvillanuevamary0419No ratings yet
- 21st CENTURY SKILL CATEGORIESDocument44 pages21st CENTURY SKILL CATEGORIESFC 1997100% (2)
- 21st Century SkillsDocument2 pages21st Century SkillsLý Thanh NguyênNo ratings yet
- E Portfolio RubricDocument3 pagesE Portfolio RubricKyle Hamilton-LeckyNo ratings yet
- Nurdiana - 0203522022 - ICT - SUMMARY PPT TOPIC 1-13Document26 pagesNurdiana - 0203522022 - ICT - SUMMARY PPT TOPIC 1-13Nurdiana Kusuma AstutiNo ratings yet
- Bilbao TTL 101 (Reporting)Document27 pagesBilbao TTL 101 (Reporting)Arnny BilbaoNo ratings yet
- EDU MS06 Module 2Document11 pagesEDU MS06 Module 2Lazy ArtNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Topic 3298fDocument5 pagesUnit 1 - Topic 3298fKeneth NagumNo ratings yet
- Module 10 - 21 Century Skill Categories: Learning Activity 1Document5 pagesModule 10 - 21 Century Skill Categories: Learning Activity 1Sheila AguadoNo ratings yet
- Educ 2 Semi-Final NotesDocument5 pagesEduc 2 Semi-Final NotesChristie TirolNo ratings yet
- Ict PresentationDocument22 pagesIct PresentationairamNo ratings yet
- Activity.3 21st Century SkillsDocument6 pagesActivity.3 21st Century SkillsGARCIA EmilyNo ratings yet
- 21st Century Learning METHODDocument10 pages21st Century Learning METHODNur islamiyahNo ratings yet
- 21st Century SkillsDocument15 pages21st Century SkillsRey-ann VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document3 pagesLesson 2Wowie MarianoNo ratings yet
- Curricular Landscape in The 21 Century ClassroomsDocument17 pagesCurricular Landscape in The 21 Century ClassroomsAlyssa AlbertoNo ratings yet
- 21 StcenturyskillsDocument24 pages21 StcenturyskillsIJ TongcuaNo ratings yet
- De Jesus - 21ST Century SkillsDocument10 pagesDe Jesus - 21ST Century SkillsLeomel De Jesus100% (1)
- 21st Century Skills Categories-Group2Document8 pages21st Century Skills Categories-Group2GLENDMARC BALANSAGNo ratings yet
- Modules in Building and EnhancingDocument10 pagesModules in Building and EnhancingBann AyotNo ratings yet
- Presentation NotesDocument14 pagesPresentation Notesapi-483718160No ratings yet
- 21st CenturylearningDocument6 pages21st Centurylearningapi-548634578No ratings yet
- 21st Century SkillsDocument46 pages21st Century Skillsjoseph.labador1992No ratings yet
- ASL 2-Topic 3Document3 pagesASL 2-Topic 3Princess Mae UrbanozoNo ratings yet
- Ped 9 (Tayo)Document10 pagesPed 9 (Tayo)Kriselle Jeanne TayoNo ratings yet
- 21st Century SkillDocument27 pages21st Century SkillSteben MeuerteNo ratings yet
- Educ 109 - Activity 2Document1 pageEduc 109 - Activity 2hannahmae surbicoNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips 21st Century Digital Learners and Teachers 590c6225c216fDocument28 pagesDokumen - Tips 21st Century Digital Learners and Teachers 590c6225c216fIwni GG100% (1)
- HumanitiesDocument2 pagesHumanitiesMary Grace Cabiles CagbabanuaNo ratings yet
- History of MathematicsDocument15 pagesHistory of Mathematicsshulammite broncanoNo ratings yet
- Learning 21st-Century 21st-Century: Skills Requires TeachingDocument6 pagesLearning 21st-Century 21st-Century: Skills Requires TeachingRafsan WakanoNo ratings yet
- Building and Enhancing New Literacies Across The Curriculum 1 For MergeDocument134 pagesBuilding and Enhancing New Literacies Across The Curriculum 1 For Mergenicacadavero06No ratings yet
- Human Computer InteractionDocument16 pagesHuman Computer InteractionJessaMae AlbaracinNo ratings yet
- Magna CartaDocument7 pagesMagna CartaSarah Jane LingbaoanNo ratings yet
- Code of Ethics For Professional TeachersDocument4 pagesCode of Ethics For Professional TeachersStephanie QuirolNo ratings yet
- Constructivist Theory-RrlDocument3 pagesConstructivist Theory-RrlStephanie QuirolNo ratings yet
- RUBRICDocument2 pagesRUBRICStephanie QuirolNo ratings yet
- About Sara DuterteDocument2 pagesAbout Sara DuterteStephanie QuirolNo ratings yet
- About BONGBONGDocument2 pagesAbout BONGBONGStephanie QuirolNo ratings yet
- Pic CollageDocument1 pagePic CollageStephanie QuirolNo ratings yet
- Movie Reflection Citizenship - (Quirol)Document1 pageMovie Reflection Citizenship - (Quirol)Stephanie QuirolNo ratings yet
- Midterm Test For Foundations in Special and Inclusive EducationDocument6 pagesMidterm Test For Foundations in Special and Inclusive EducationStephanie QuirolNo ratings yet
- February 26, 2015 Courier SentinelDocument36 pagesFebruary 26, 2015 Courier SentinelcwmediaNo ratings yet
- Bopp Judith L PDFDocument327 pagesBopp Judith L PDFWH WHNo ratings yet
- Tarushi Jain: Address - B-51 Wildwood Apartments, Yari Road, Versova, Mumbai - 400058 Mobile - +91 8425056445 Email IdDocument1 pageTarushi Jain: Address - B-51 Wildwood Apartments, Yari Road, Versova, Mumbai - 400058 Mobile - +91 8425056445 Email IdTarushi JainNo ratings yet
- Effects of Leadership Style On Organizational Performance in Small and Medium Scale Enterprises (SMEs) in Nigeria PDFDocument22 pagesEffects of Leadership Style On Organizational Performance in Small and Medium Scale Enterprises (SMEs) in Nigeria PDFAlexander DeckerNo ratings yet
- DFC BrochureDocument20 pagesDFC BrochureJaysonn KayNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae - Tiruneh Gizachew - Updated 2019 PDFDocument3 pagesCurriculum Vitae - Tiruneh Gizachew - Updated 2019 PDFTiruneh GANo ratings yet
- Transition To Post-Pandemic Education in The Philippines: Unfolding InsightsDocument7 pagesTransition To Post-Pandemic Education in The Philippines: Unfolding InsightsAshley JoyceNo ratings yet
- English Assignment Solution (Class-12) PDFDocument104 pagesEnglish Assignment Solution (Class-12) PDFAbhishek Puri60% (10)
- Mahesh S. Khairnar: FresherDocument2 pagesMahesh S. Khairnar: FresherMaheshNo ratings yet
- High-Tech Startup Management Strategies: Case Studies and Issues in JapanDocument70 pagesHigh-Tech Startup Management Strategies: Case Studies and Issues in JapanAung ThantNo ratings yet
- Minna No Nihongo Lesson 2 - All Vocabulary and Grammar With Explanation PDFDocument1 pageMinna No Nihongo Lesson 2 - All Vocabulary and Grammar With Explanation PDFmikeNo ratings yet
- List of Courses Eligible For Extended Post-Study Work Rights - With150Document98 pagesList of Courses Eligible For Extended Post-Study Work Rights - With150Hana LeeNo ratings yet
- GTPA Fact SheetDocument4 pagesGTPA Fact SheetAbu Ibrahim KhalilNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Student Partners ApplicationDocument4 pagesMicrosoft Student Partners ApplicationSerhat VarolgunesNo ratings yet
- PROJECT PROPOSAL - Egg ProductionDocument5 pagesPROJECT PROPOSAL - Egg ProductionMariella Trazo100% (1)
- CV Sofia - Kioroglanidou EngDocument4 pagesCV Sofia - Kioroglanidou EngSofia KioroglanidouNo ratings yet
- My Professional Development PlanDocument3 pagesMy Professional Development Planapi-252938448No ratings yet
- LRIZALDocument16 pagesLRIZALSHIERA MAE AGUSTINNo ratings yet
- Hobbes and Bramhall On Liberty and Necessity: Cambridge Texts in The History of PhilosophyDocument138 pagesHobbes and Bramhall On Liberty and Necessity: Cambridge Texts in The History of PhilosophyAndrés Cisneros SolariNo ratings yet
- Instant Download Ebook PDF Foundations of Nursing 8th Edition by Cooper RN MSN PDF ScribdDocument45 pagesInstant Download Ebook PDF Foundations of Nursing 8th Edition by Cooper RN MSN PDF Scribddanny.bradt610100% (43)
- 13 Esl Speaking Activities ToDocument8 pages13 Esl Speaking Activities ToOana Victoria HanchesNo ratings yet
- Solved Draw A Flow Net For The Weir Shown in Figure 8.25. Calc...Document1 pageSolved Draw A Flow Net For The Weir Shown in Figure 8.25. Calc...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- 4 F 9 e 5 D 62 F 05 Dafab 2 e 31Document70 pages4 F 9 e 5 D 62 F 05 Dafab 2 e 31zeidNo ratings yet
- Describing Vowels and Diphthongs GroupDocument15 pagesDescribing Vowels and Diphthongs GroupMisdi RaflikansyahNo ratings yet
- Arizapa D. Ldm2-Module - AsdDocument52 pagesArizapa D. Ldm2-Module - AsdCatherine RenanteNo ratings yet
- Helle NeergaardDocument301 pagesHelle NeergaardDhiru bhai0% (1)
- Assessing Presidential CharacterDocument50 pagesAssessing Presidential CharacterGonzalo SáenzNo ratings yet
- Modern MathematicsDocument34 pagesModern MathematicsCharo GironellaNo ratings yet
- Med Chapter 04Document41 pagesMed Chapter 04Ali AhmadNo ratings yet
- Assignment EFE MATRIXDocument10 pagesAssignment EFE MATRIXabrarNo ratings yet