Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Form 4 Amat Formulae and Note
Uploaded by
Johnny OhOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Form 4 Amat Formulae and Note
Uploaded by
Johnny OhCopyright:
Available Formats
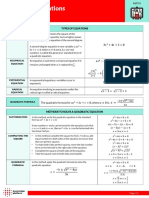
NOTES AND FORMULAE ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS FORM 4
1. QUADRATIC EQUATION (a) ax2 + bx + c = 0 x = The axis of symmetry is x p = 0 or x=p (c) Quadratic inequalities (x a)(x b) 0 Range x a, x b (x a)(x b) 0 Range a x b INDICES AND LOGARITHM x = an Index Form loga x = n Logarithm Form (c)
m A ( x1 , yP
P which divides AB in the ratio m : n
: ) n B
2(
b b 2 4ac 2a
Sum of roots: + =
x2
b a
Product of roots: =
3. (a)
P (d)
nx1 + mx 2 ny1 + my 2 , n+m n+m
c a
Gradient AB m=
(b)
y 2 y1 x 2 x1
y-intercept
Equation from the roots: x2 - (sum of roots)x + product of roots = 0
(b)
Logrithm Law 1. logaxy = logax + logay
2.
QUADRATIC FUNCTION (a) Types of roots b2 - 4ac > 0 2 real and distinct/different roots. b2- 4ac = 0 2 real and equal roots/two same roots. b2 - 4ac < 0 no real root. b2 - 4ac 0 got real roots.
y y
x 2. loga y = logax logay
3. loga xn = n logax 4. loga a = 1 5. loga 1 = 0 6. loga b = 7. loga b = 4.
(e)
m = x-intercept Equation of straight line (i) Given m and A(x1, y1) y y1 = m(x x1) Given A(x1, y1) and B(x2, y2)
(ii)
log c b log c a
1 log b a
(a)
y y1 y 2 y1 = x x1 x 2 x1
Area of polygon L=
0
2
x
2
b - 4ac > 0 (b)
b - 4ac = 0
b2 - 4ac < 0
COORDINATE GEOMETRY (a) Distance between A(x1, y1) and B(x2, y2) AB =
x1 1 x1 x 2 x3 ......... y1 2 y1 y 2 y 3
(g)
2
Completing the square y = a(x - p)2 + q a +ve minimum point (p, q) a ve maximum point(p, q)
( x 2 x1 ) + ( y 2 y1 )
2
Parallel lines m1 = m2 Perpendicular lines m1 m2 = -12.
(b)
Mid point AB M
(h)
x1 + x 2 y1 + y 2 , 2 2
5.
STATISTICS Measurement of Central Tendency
Prepared by Mr. Sim Kwang Yaw
(a)
Mean
C n
u l a
t i v e
r e q
e n
c y
x x =
n
x=
Ogive : C u m
l a
t i v e
f r e q
e n c y
For ungrouped data
For ungrouped data with frequency.
fx f
_n _ 2
_3 _ n 4
_ 1 n_ 4
x=
fx i f
e d U i ap n p
e r
o u
r y
(c)
For grouped data, xi = mid-point (b) Median The data in the centre when arranged in order (ascending or descending). Formula M=L+
Mode Date with the highest frequency By Histogram :
F r e q u e n c y
Interquartile range = Q3 Q1 (b) Variance, Standard Deviation Variance = (standard deviation)2
e r
u n
r y
=
=
( x x)
n
1 2
n F C fm
x
n
For ungrouped data
0 M o d eC l a s s b o u n d a r y
L = Lower boundary of median class. n = Total frequency F = cumulative frequency before the median class fm = frequency of median class C = class interval size By Ogive
Measurement of Dispersion (a) Interquartile Range Formula : 1 1 4 Q1 = 1 Q1 Q3 =
=
=
n F L + C f L3 +
3 4
f ( x x) f fx x f
2 2
For grouped data 6. CIRCULAR MEASURE (b) Radian Degree
n F3 C f Q3
Prepared by Mr. Sim Kwang Yaw
180
(c)
(d)
Degree Radian
o
d u v du u dv dx dx = 2 dx v v
rad (g) Differentiation of Composite Function
180
Length of arc s = j Area of sector L=
(e)
1 2 1 j = js 2 2
1 2 j ( 2
r
d (ax+b)n = an(ax+b)n-1 dx dy (h) Stationary point =0 dx
Maximum point:
(f)
Area of segment L= sin o)
dy d2y = 0 and <0 dx dx 2
Minimum point:
7.
DIFFERENTIATION (a) Differentiation by First Principle
had y dy = x dx 0 x
dy d2y = 0 and >0 dx dx 2
(i) Rate of Change
(b) (c) (d) (e)
d (a) = 0 d x d n (x ) = nxn-1 d x d (axn) = anxn-1 d x
Differentiation of product
d y d y d x = d t d x d t
(j)
Small changes:
dy . x dx
d d v du (uv) = u +v d x d x dx
(f) Differentiation of Quotient
Prepared by Mr. Sim Kwang Yaw
You might also like
- TOP NINTENDO SWITCH GAMES - Docx (5 NOV 2021)Document14 pagesTOP NINTENDO SWITCH GAMES - Docx (5 NOV 2021)Johnny OhNo ratings yet
- Best Multi Region 3D Blu Ray Player (23 Feb 2021)Document16 pagesBest Multi Region 3D Blu Ray Player (23 Feb 2021)Johnny OhNo ratings yet
- Best Programs To Download Videos From YoutubeDocument3 pagesBest Programs To Download Videos From YoutubeJohnny OhNo ratings yet
- Carrom Rules (1 Feb 2021)Document10 pagesCarrom Rules (1 Feb 2021)Johnny Oh100% (1)
- The Sun Daily Final Edition 01-12-2020 CompleteDocument24 pagesThe Sun Daily Final Edition 01-12-2020 CompleteJohnny OhNo ratings yet
- LEAP 23 July 2012Document16 pagesLEAP 23 July 2012Johnny OhNo ratings yet
- BD Movie ListDocument1 pageBD Movie ListJohnny OhNo ratings yet
- Beware of Permanent Speed TrapsDocument2 pagesBeware of Permanent Speed TrapsJohnny OhNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- 2WAB0 BBK Week 1-2 AnnotatedDocument45 pages2WAB0 BBK Week 1-2 Annotatedxenia sastropawiroNo ratings yet
- Ial Spec Maths Issue 1 WebDocument112 pagesIal Spec Maths Issue 1 WebAku_AkramNo ratings yet
- Solving Quadratic Equation Using Quadratic FormulaDocument12 pagesSolving Quadratic Equation Using Quadratic FormulaJelliane grace RagoNo ratings yet
- Topic 8 Quadratic Equations PDFDocument38 pagesTopic 8 Quadratic Equations PDFHuong Dang0% (1)
- Name: - Date: - Grade Level and Section: - ScoreDocument2 pagesName: - Date: - Grade Level and Section: - ScoreJustine Antiojo CruzNo ratings yet
- Second Periodic Examination in Math Problem Solving: Main Campus - Level 11Document6 pagesSecond Periodic Examination in Math Problem Solving: Main Campus - Level 11Shanna Basallo AlentonNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet g10mt01 FinalDocument1 pageCheat Sheet g10mt01 FinalLobi RybgNo ratings yet
- Herbert Kreyszig, Erwin Kreyszig - Student Solutions Manual and Study Guide To Advanced Engineering Mathematics (Volume 1) - Wiley (2012)Document256 pagesHerbert Kreyszig, Erwin Kreyszig - Student Solutions Manual and Study Guide To Advanced Engineering Mathematics (Volume 1) - Wiley (2012)يوسف سعد محمودNo ratings yet
- GOA-Mathematics Sample Paper-1-Class 10 Question Paper (SA-I)Document6 pagesGOA-Mathematics Sample Paper-1-Class 10 Question Paper (SA-I)Firdosh KhanNo ratings yet
- A1 c9 Study Guide and Review Worked Out Solution KeyDocument31 pagesA1 c9 Study Guide and Review Worked Out Solution KeyLiezl CanlasNo ratings yet
- The Quadratic FormulaDocument14 pagesThe Quadratic FormulaAnie jane BentoyNo ratings yet
- (Bi) Modul 25 Add Math PDFDocument284 pages(Bi) Modul 25 Add Math PDFjosnih murniNo ratings yet
- Factorising Ax + BX + C: Quadratic Equations QuestionsDocument2 pagesFactorising Ax + BX + C: Quadratic Equations QuestionsHassan TauqeerNo ratings yet
- Class 10th Maths Basic SQP (CBSE 2022 - 23)Document8 pagesClass 10th Maths Basic SQP (CBSE 2022 - 23)Pareek EkuNo ratings yet
- Quadratic EquationDocument33 pagesQuadratic EquationBadal KumarNo ratings yet
- HP28S Math Apps Solution ManualDocument108 pagesHP28S Math Apps Solution Manualgnd100100% (3)
- 3.1 Quadratic Equations and Inequalities: X X X XDocument4 pages3.1 Quadratic Equations and Inequalities: X X X XClairNo ratings yet
- Algebra 1 Sec PDFDocument19 pagesAlgebra 1 Sec PDFAlanNo ratings yet
- 6.4 - Problem SolvingDocument35 pages6.4 - Problem SolvingDaRealTruthNo ratings yet
- Mtap 2018 Grade 9 Elim RoundDocument12 pagesMtap 2018 Grade 9 Elim Roundrmm0415No ratings yet
- Math 9, Quarter 1 Activity SheetsDocument5 pagesMath 9, Quarter 1 Activity SheetsNelson Maraguinot100% (1)
- Transformations Worksheet PDFDocument8 pagesTransformations Worksheet PDFmeanangel4No ratings yet
- Year 10 - Number and Algebra - Pre Victorian Curriculum Assessment - 9.5 11 - SampleDocument12 pagesYear 10 - Number and Algebra - Pre Victorian Curriculum Assessment - 9.5 11 - Samplelilly kitNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) FormatDocument3 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) FormatErwin B. NavarroNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Mathematics Lessons CoverageDocument3 pagesGrade 9 Mathematics Lessons CoverageBenigno BaluyutNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2:quadratic Expressions and Equations: M X + y - 3x + 5 7x - 3x - 2x + 3 5x - 4x + 7Document9 pagesChapter 2:quadratic Expressions and Equations: M X + y - 3x + 5 7x - 3x - 2x + 3 5x - 4x + 7Rita LauNo ratings yet
- Math 9 Q1 Week 9Document12 pagesMath 9 Q1 Week 9Zion Conrad FuentesNo ratings yet
- Math II Unit 2 PDFDocument79 pagesMath II Unit 2 PDFRoussel Palmaria0% (1)
- 1st Periodic Test - Math 7Document8 pages1st Periodic Test - Math 7MARCIAL ASADANo ratings yet
- Class 10 Sample Paper 8Document29 pagesClass 10 Sample Paper 823.Khushboo Singh IX-F DPSKNo ratings yet