Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Topic, Curriculum Concepts, Nature and Purpose Curriculum From Different Points of View
Uploaded by
Ana Hakura0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageThis document discusses the concepts, nature, and purpose of curriculum. It defines curriculum from both traditional and progressive points of view. Traditionally, curriculum was viewed as a set of subjects or body of knowledge prepared by teachers for students to learn. More progressively, curriculum came to be defined as the total set of learning experiences for an individual, both inside and outside the classroom, as defined by scholars like John Dewey. The document also notes there are many definitions of curriculum because of its complex and evolving nature.
Original Description:
TOPIC ,CURRICULUM CONCEPTS, NATURE AND PURPOSE CURRICULUM FROM DIFFERENT POINTS OF VIEW
Original Title
TOPIC ,CURRICULUM CONCEPTS, NATURE AND PURPOSE CURRICULUM FROM DIFFERENT POINTS OF VIEW
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses the concepts, nature, and purpose of curriculum. It defines curriculum from both traditional and progressive points of view. Traditionally, curriculum was viewed as a set of subjects or body of knowledge prepared by teachers for students to learn. More progressively, curriculum came to be defined as the total set of learning experiences for an individual, both inside and outside the classroom, as defined by scholars like John Dewey. The document also notes there are many definitions of curriculum because of its complex and evolving nature.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageTopic, Curriculum Concepts, Nature and Purpose Curriculum From Different Points of View
Uploaded by
Ana HakuraThis document discusses the concepts, nature, and purpose of curriculum. It defines curriculum from both traditional and progressive points of view. Traditionally, curriculum was viewed as a set of subjects or body of knowledge prepared by teachers for students to learn. More progressively, curriculum came to be defined as the total set of learning experiences for an individual, both inside and outside the classroom, as defined by scholars like John Dewey. The document also notes there are many definitions of curriculum because of its complex and evolving nature.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Module 2: CURRICULUM: CONCEPTS, NATURE AND PURPOSE
At the end of the lessons, the students will be able to:
1. Define curriculum.
2. Analyze the different types of curriculum.
3. Discuss different curriculum foundations.
4. Discuss different curriculum conceptions.
TOPIC: CURRICULUM: CONCEPTS, NATURE AND PURPOSE
CURRICULUM FROM DIFFERENT POINTS OF VIEW :
There are many definitions of curriculum. Because of this, the concept of curriculum Is sometimes
characterized as fragmentary, elusive and confusing. However, the Numerous definitions indicate
dynamism that connotes diverse interpretations of what Curriculum is all about.
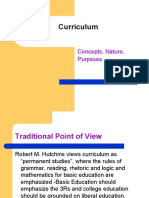
1. Traditional Points of View of Curriculum
a. In early years of 20th century, the traditional concepts of curriculum “curriculum is that is
a body of subjects or subject matter prepared by the Teachers for the students to
learn”.
b. Robert M. Hutchins views curriculum as “permanent studies” where the Rules of
grammar, reading, rhetoric and logic and mathematics for basic Education are
emphasized.
c. Arthur Bestor believes that the mission of the school should be intellectual Training,
d. Thus curriculum can be viewed as a field of study. It is made up of its Foundations
(philosophical, historical, psychological and social foundations); Domains of knowledge
well as its research and principles.
2. Progressive Points of View
a. Curriculum is defined as the total learning experiences of the individual. This Definition
is anchored on John Dewey’s definition of experience and Education.
b. Caswell and Campbell viewed curriculum as “all experiences children have Under the
guidance of teachers.
c. March and Willis on the other hand viewed the curriculum as all the “experiences in the
classroom which are planned and enacted by the Teacher, and also learned by the
students.
You might also like
- M2 - Lesson 1 The School CurriculumDocument7 pagesM2 - Lesson 1 The School CurriculumJirk Jackson Esparcia89% (19)
- Module 1 - The Teacher and School CurriculumDocument17 pagesModule 1 - The Teacher and School CurriculumSienna Mae AgringoNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document18 pagesModule 2CHERRY MAE ALVARICO100% (1)
- Topic 1 Curriculum Definition Nature andDocument52 pagesTopic 1 Curriculum Definition Nature anddominguez margieNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Nature of The Curriculum: A. DefinitionDocument10 pagesUnit 1: Nature of The Curriculum: A. DefinitionMyrna Paras50% (2)
- CHAPTER 2 Lesson 1Document3 pagesCHAPTER 2 Lesson 1HeheNo ratings yet
- Module 2.1Document20 pagesModule 2.1Maila Calimpong AsimNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document11 pagesLesson 1Ryan JoaquinNo ratings yet
- Module 2 ED 5Document6 pagesModule 2 ED 5Karla Dao-ayNo ratings yet
- The Word: Curriculum: - Latin: Running Course - Scotland 1603: Carriage Way, RoadDocument41 pagesThe Word: Curriculum: - Latin: Running Course - Scotland 1603: Carriage Way, RoadRakhshanda Fawad100% (1)
- Introduction To CurriculumDocument54 pagesIntroduction To Curriculumsatiyavani darmalingam0% (1)
- The Teacher and CurriculumDocument11 pagesThe Teacher and CurriculumAudremie DuratoNo ratings yet
- The Teacher and School CurriculumDocument11 pagesThe Teacher and School CurriculumJohnlloyd CuanicoNo ratings yet
- EDUC2133 IntroductionToCurriculumDevelopment-Lesson1Document12 pagesEDUC2133 IntroductionToCurriculumDevelopment-Lesson1Wolfmystery OfficialNo ratings yet
- Curriculum PlanningDocument41 pagesCurriculum PlanningLOLITA GALAMITONNo ratings yet
- The Teacher As A Knower of CurriculumDocument48 pagesThe Teacher As A Knower of CurriculumLee Jay TesingNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Lesson1 and 2Document14 pagesUnit 2 Lesson1 and 2Analo Miranda AntigaNo ratings yet
- Module 27Document5 pagesModule 27Kel LumawanNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - The Teacher As A Knower of CurriculumDocument10 pagesModule 2 - The Teacher As A Knower of CurriculumVannessa LacsamanaNo ratings yet
- Learning Guide 1 in BPEd 71Document30 pagesLearning Guide 1 in BPEd 71Xyra V YponNo ratings yet
- MED5 Written Report PangGroupDocument5 pagesMED5 Written Report PangGroupRowelyn SisonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document2 pagesChapter 1Madelʚĭɞ Bernardo GatanNo ratings yet
- 4 The Teacher As A Knower of Curriculum - Lesson 1Document37 pages4 The Teacher As A Knower of Curriculum - Lesson 1jessalyn ilada85% (13)
- Module 2 Lesson 1Document26 pagesModule 2 Lesson 1novielyn bayangNo ratings yet
- EDUC 6 142 Module 2 Lesson 2.1Document16 pagesEDUC 6 142 Module 2 Lesson 2.1Jenkylyn CalmaNo ratings yet
- 1 Curriculum Definition NatureDocument17 pages1 Curriculum Definition NatureAngela Lomangaya CarmonaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3Document24 pagesLesson 3Rexson Dela Cruz TagubaNo ratings yet
- fs2 Group 1Document21 pagesfs2 Group 1Mella CañezoNo ratings yet
- ED 319 Lesson 1Document22 pagesED 319 Lesson 1Flordelez MacionNo ratings yet
- EDUC 15 Module 1 (Basic Concepts and Nature of The Curriculum)Document5 pagesEDUC 15 Module 1 (Basic Concepts and Nature of The Curriculum)Janine LucasNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Lesson 1Document4 pagesModule 2 Lesson 1Hector PonferradaNo ratings yet
- Module 2 The Teacher As A Knower of Curriculum - RheuDocument13 pagesModule 2 The Teacher As A Knower of Curriculum - Rheuqrhe30gswNo ratings yet
- School Curriculum ReportDocument20 pagesSchool Curriculum ReportJessa Laika CastardoNo ratings yet
- Curriculum - Theoretical DimensionsDocument46 pagesCurriculum - Theoretical DimensionsNuryani AhmadNo ratings yet
- Module 2 The Teacher As A Knower of CurriculumDocument10 pagesModule 2 The Teacher As A Knower of CurriculumJessa Mae RoneNo ratings yet
- Course: Curriculum Development and Instruction (838) Semester: Spring, 2020 Level: M.A/M. Ed Assignment No.1Document16 pagesCourse: Curriculum Development and Instruction (838) Semester: Spring, 2020 Level: M.A/M. Ed Assignment No.1Masterclass MagicianNo ratings yet
- PROF ED 5 LectureDocument9 pagesPROF ED 5 LectureMelody CastroNo ratings yet
- Curriculum PlanningDocument29 pagesCurriculum PlanningChristian Bjorn R. CunananNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Curriculum DefinedDocument5 pagesLesson 1 Curriculum DefinedJosh Erick AlbaricoNo ratings yet
- Output No. 2 Nature of The CURRICULUMDocument19 pagesOutput No. 2 Nature of The CURRICULUMCherry Love AlcoverNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Development ThematicDocument15 pagesCurriculum Development ThematicKhimberly SupleoNo ratings yet
- The Teacher and The School Curriculum RepairedDocument103 pagesThe Teacher and The School Curriculum RepairedHoney MaeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Lesson 2.1 - Jovie Martinez, Jennifer Mercado - PolaDocument46 pagesChapter 1 - Lesson 2.1 - Jovie Martinez, Jennifer Mercado - PolaJovie MartinezNo ratings yet
- Module 2 The Teacher and The School CurriculumDocument14 pagesModule 2 The Teacher and The School CurriculumRoberto AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Deepen Module 2Document3 pagesDeepen Module 2Art TechNo ratings yet
- Reviewer 1.0 Ped 104Document23 pagesReviewer 1.0 Ped 104Michelle SalvadorNo ratings yet
- The School Curriculum - Definition, Nature and ScopeDocument31 pagesThe School Curriculum - Definition, Nature and Scopechazel mae ando100% (4)
- Educ 106Document34 pagesEduc 106Jay RicNo ratings yet
- B.edcourseCode403 CurriculumDevelopment AllUnitsDocument92 pagesB.edcourseCode403 CurriculumDevelopment AllUnitsSeema Gul0% (1)
- CurriculumDocument30 pagesCurriculumMarvin VinasNo ratings yet
- The Nature of CurriculumDocument21 pagesThe Nature of CurriculumPrince ZenNo ratings yet
- Study Guide Finally 123Document36 pagesStudy Guide Finally 123Krizza Aubrey Orias AmparadoNo ratings yet
- Ped 104 First LessonDocument6 pagesPed 104 First LessonMichelle SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Development Module 2 Lesson 1 and 2Document7 pagesCurriculum Development Module 2 Lesson 1 and 2Jireh Albay100% (1)
- Curriculum DevelopmentDocument27 pagesCurriculum DevelopmentAngie Bern LapizNo ratings yet
- CURRICULUM HandoutDocument2 pagesCURRICULUM HandoutMark Louie AguilarNo ratings yet
- College Teaching: Studies in Methods of Teaching in the CollegeFrom EverandCollege Teaching: Studies in Methods of Teaching in the CollegeNo ratings yet
- Learning to be Learners: A Mathegenical Approach to Theological EducationFrom EverandLearning to be Learners: A Mathegenical Approach to Theological EducationNo ratings yet
- Component 3 - Curriculum ExperiencesDocument3 pagesComponent 3 - Curriculum ExperiencesAna HakuraNo ratings yet
- Module 3 NATURE, CONCEPTS AND PURPOSE OF CURRICULUMDocument4 pagesModule 3 NATURE, CONCEPTS AND PURPOSE OF CURRICULUMAna HakuraNo ratings yet
- Major 17 - Finals ReviewerDocument2 pagesMajor 17 - Finals ReviewerAna HakuraNo ratings yet
- Points of View On Curriculum DevelopmentDocument3 pagesPoints of View On Curriculum DevelopmentAna HakuraNo ratings yet
- Educational System of SingaporeDocument3 pagesEducational System of SingaporeAna HakuraNo ratings yet
- Nano Technology ApplicationDocument3 pagesNano Technology ApplicationAna HakuraNo ratings yet
- Gabriel Imomotimi Okara (Born 24 April 1921)Document4 pagesGabriel Imomotimi Okara (Born 24 April 1921)Ana HakuraNo ratings yet
- Rizal's Life in AteneoDocument3 pagesRizal's Life in AteneoAna HakuraNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table Downloadable Version BookletDocument2 pagesPeriodic Table Downloadable Version BookletAna HakuraNo ratings yet
- REPORT IN CAMBODIA WPS Office-1Document18 pagesREPORT IN CAMBODIA WPS Office-1Ana HakuraNo ratings yet