Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 1A Immuno
Uploaded by
nascha dump0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesOriginal Title
Chapter 1A immuno
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesChapter 1A Immuno
Uploaded by
nascha dumpCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
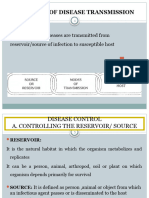
to eliminate the pathogen and prevent
ELEMENTS OF THE disease.
IMMUNE SYSTEM
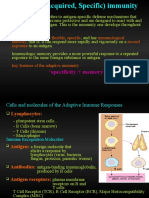
Definition of Terms • Immune recognition is remarkable for
“specificity”
Immunology – the study of the immune
system, including its responses to microbial
pathogens, and damaged tissues and its
role in disease. FUNCTIONS OF THE
Immune system – a biological structures IMMUNE SYSTEM
and processes within an organism that 1) To discriminate between self and non –
mediate resistance to infections by self
identifying and killing pathogens and tumor A. To protect from pathogens
cells. • Intracellular pathogens –
Immune response – collective and organisms that can grow and
coordinate response to the introduction of reproducing inside host cells
foreign substances in an individual • Extracellular pathogens – do not
mediated by the cells and molecules of the invade cells
immune system.
Immunity came from the Latin word
“’immunis’’ which means “’exempt’’ -
referring to protection against foreign
agents.
Definition:
The integration body system of
organs, tissues, cells and cell
products that differentiates self from
non – self and neutralizes potentially
pathogenic organisms
• Immune system is a remarkably versatile
defense system that has evolved to protect
animals from invading pathogenic
microorganisms and cancer. B. To eliminate modified or altered self
• A highly discriminatory immune system is
fundamental to survival. 2) Development of immunological
Immune Response can be divided into two memory as the basis for vaccine
related activities: efficacy
✓ Immunological memory is the ability
a) Recognition – for specificity of the immune system to quickly and
b) Response – effector and memory specifically recognize an antigen
that the body has previously
• Effector response – to eliminate or encountered and initiate a
neutralize the organism. corresponding Immune response
• Memory response - rapid and 3) Therapeutic intervention for immune
heightened immune reaction that serves based diseases
Lupus – Allergy - Rheumatoid arthritis
THE BAD AND UGLY SIDE challenge to clinicians who treat these
patients.
OF IMMUNE SYSTEM
Immunodeficiency and dysfunction as the
basis of disease Role of the Implications
Immune system
✓ Immunodeficiency diseases occurs
Defense against Deficient immunity
as the result of the absence
infections results in increased
(congenital or acquired) of one or
susceptibility to
more elements of the immune
infections;
system.
exemplified by
Immune dysfunction – occurs as a result of AIDS
improper regulation that allows the
immune system to either attack something Vaccination boosts
it shouldn’t or fail to attack something it immune defenses
should. and protects
against infections
➢ Most instances of immune dysfunction
Defense against Potential for
or failure fall into one of the following
tumors immunotherapy of
three broad categories:
cancer
a) Hypersensitivity (including allergy):
The immune Immune responses
overly zealous attacks on common
system can injure are the cause of
benign but foreign antigens
cells and induce allergic,
b) Autoimmune Disease – erroneous
pathologic autoimmune, and
targeting of self-proteins or tissues
inflammation other inflammatory
by immune cells
diseases
c) Immune Deficiency – insufficiency of
The immune Immune responses
the immune response to protect
system recognizes are barriers to
against infectious agents
and responds to transplantation and
d) Immune Imbalance – dysregulation
tissue grafts and gene therapy
in the immune system that leads to
newly introduced
aberrant activity of immune cells,
proteins
especially enhanced inflammation
and/or and reduced immune
inhibition
Cancer or Malignancy – occurs in host cells
when they begin to divide out of control.
Present unique challenges to clinicians,
because the healthy immune system
typically rejects or destroys non self-
proteins, such as those encountered in
most transplant situations, and tolerates
self-cells.
➢ The immune response renders “Tissue
transplantation” challenging.
✓ The fact that the immune system will
attack and reject any transplanted
organ that is non-self, or not a genetic
match, raises a formidable barrier to
this potentially lifesaving treatment,
presenting a particularly unique
You might also like
- MicpLec 28week 429UpdatedCANVASJan2024HostResponsetoInfectionDocument11 pagesMicpLec 28week 429UpdatedCANVASJan2024HostResponsetoInfectionRaven Joyce LabayenNo ratings yet
- L07: The Immune System and The Diseases of The Immune SystemDocument10 pagesL07: The Immune System and The Diseases of The Immune Systemhstest842No ratings yet
- Introduction To ImmunityDocument43 pagesIntroduction To Immunityr.beqiraj22No ratings yet
- L1 - IntroductionDocument5 pagesL1 - IntroductionMiles NsgNo ratings yet
- Sworts Immunology - Introduction-To-Part-IDocument8 pagesSworts Immunology - Introduction-To-Part-IꕶᗋᏦᎥꕗNo ratings yet
- Adaptive ImmunityDocument101 pagesAdaptive ImmunityJames Carbonell Dela PeñaNo ratings yet
- Immunopharmacology - IntroductionDocument51 pagesImmunopharmacology - IntroductionIsrat Jahan Surovy 2225400672No ratings yet
- 4 Immunopathology (Page 131-168) .Kelik-2022Document38 pages4 Immunopathology (Page 131-168) .Kelik-2022Pola PhotographyNo ratings yet
- FinaDocument19 pagesFinaZabdiel Ann SavellanoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16Document5 pagesChapter 16Alanah JaneNo ratings yet
- Colorful Cute Playful Illustration Group Project PresentationDocument20 pagesColorful Cute Playful Illustration Group Project PresentationElaiza marie VenusNo ratings yet
- Immunogenecity and AntigenecityDocument18 pagesImmunogenecity and AntigenecitySujit GhoshNo ratings yet
- 1-How Immune System Works1 08 08Document63 pages1-How Immune System Works1 08 08all4one1983100% (1)
- Zoology6thSem PDFDocument88 pagesZoology6thSem PDFRouf MalikNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Properties and Overview of Immune ResponsesDocument45 pagesChapter 1 Properties and Overview of Immune Responses13701319477No ratings yet
- Task 1. Concept Analysis and DiagramDocument4 pagesTask 1. Concept Analysis and Diagramkristine keen buanNo ratings yet
- 2.0 Principles of Immunology and Immunization - April 20 2018Document13 pages2.0 Principles of Immunology and Immunization - April 20 2018Ranjan YadavNo ratings yet
- ImmunologyDocument1 pageImmunologyDr.2020No ratings yet
- MODULE 3 Infection and Host Resistance PDFDocument22 pagesMODULE 3 Infection and Host Resistance PDFVillanueva, AbegailNo ratings yet
- PAMPHLETS ImmunityDocument3 pagesPAMPHLETS ImmunityAlex CarnajeNo ratings yet
- Immunity: Presented By: DR - Reena Rani PG1 Year Pediatric and Preventive DentistryDocument137 pagesImmunity: Presented By: DR - Reena Rani PG1 Year Pediatric and Preventive DentistryReenaChauhanNo ratings yet
- Micp Lec (Week - 4) Host Response To InfectionDocument15 pagesMicp Lec (Week - 4) Host Response To Infectioncaitie miracleNo ratings yet
- Lec # 4 Body Defence SystemsDocument31 pagesLec # 4 Body Defence SystemssamotherlianNo ratings yet
- Acquired Imm and Infection - BPTDocument15 pagesAcquired Imm and Infection - BPTKathal 66No ratings yet
- NCM 119 - Rle (Prelim) Week 1: Immune Response Immunity: Natural and Acquired Immunity - Ma'am VAB Immune ResponseDocument13 pagesNCM 119 - Rle (Prelim) Week 1: Immune Response Immunity: Natural and Acquired Immunity - Ma'am VAB Immune ResponseJamaica Leslie Noveno100% (1)
- Immunology Lecturs 27Document27 pagesImmunology Lecturs 27Rolls SaeedNo ratings yet
- CH 1. Overview of The Immune SystemDocument23 pagesCH 1. Overview of The Immune SystemIbrahim MNo ratings yet
- Immune Sys ReadingDocument67 pagesImmune Sys ReadingAar HNo ratings yet
- Basic Immunology For L200 PharmdDocument71 pagesBasic Immunology For L200 PharmdDei BenjaminNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Immunology and Immunopathology: Allergy, Asthma & Clinical ImmunologyDocument10 pagesAn Introduction To Immunology and Immunopathology: Allergy, Asthma & Clinical Immunologyhendra cahyaditaNo ratings yet
- Immune System (Inn & Adapt)Document53 pagesImmune System (Inn & Adapt)Bushra Khan100% (1)
- Control and Prevention of Communicable DiseasesDocument14 pagesControl and Prevention of Communicable DiseasesZabdiel Ann SavellanoNo ratings yet
- ImmunityDocument19 pagesImmunityKailash Nagar100% (1)
- Infection and Host ResistanceDocument9 pagesInfection and Host ResistanceDaren GocoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2. Infection and Host ResistanceDocument9 pagesLesson 2. Infection and Host ResistanceDaren GocoNo ratings yet
- Immunity Vaccination: Public HealthDocument41 pagesImmunity Vaccination: Public HealthBaraa AbosamraNo ratings yet
- Immunity 180603063305Document38 pagesImmunity 180603063305Musfira KhalidNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 16 MicroparaDocument46 pagesCHAPTER 16 MicroparaKathlyn LopeñaNo ratings yet
- Prelims - GMJ Lecture - Module 2 III DisorderDocument5 pagesPrelims - GMJ Lecture - Module 2 III DisorderjuiceNo ratings yet
- Diseases of Immune SystemDocument9 pagesDiseases of Immune SystemKhylle Camron LuzzieNo ratings yet
- 4 AntigensDocument37 pages4 AntigensRayNo ratings yet
- (OS201) E06 T02 Introduction To Basic Immunologic Principles Blood Coagulation and FibrinolysisDocument13 pages(OS201) E06 T02 Introduction To Basic Immunologic Principles Blood Coagulation and FibrinolysisJoe JoeNo ratings yet
- Invited Review: Principles of ImmunologyDocument10 pagesInvited Review: Principles of ImmunologyJoseNo ratings yet
- Vac UnasDocument6 pagesVac UnasromarismmariavNo ratings yet
- Lec 11مناعة الرشيدDocument7 pagesLec 11مناعة الرشيدتجربة أولىNo ratings yet
- Immune System and VaccinationDocument13 pagesImmune System and VaccinationSalihu MustaphaNo ratings yet
- Diseases of Immunity: I-Innate or Natural ImmunityDocument20 pagesDiseases of Immunity: I-Innate or Natural Immunitymano343No ratings yet
- A Presentation On Immunity - AjDocument59 pagesA Presentation On Immunity - Ajjsudarshan868No ratings yet
- ImmunityDocument29 pagesImmunitySHREE SWAMINARAYAN NURSING COLLEGE CHIKHLINo ratings yet
- Inmunidad Innata IIIDocument17 pagesInmunidad Innata IIIANDRÉS FELIPE ARDILA MURILLONo ratings yet
- Crawford Hes Lec Sas 10Document6 pagesCrawford Hes Lec Sas 10Divo SkyeNo ratings yet
- Micro Assignment Unit 3 Group BDocument12 pagesMicro Assignment Unit 3 Group Bnabeelpatras19No ratings yet
- A Gut Feeling For Immune Dysregulation & Neuroinflammation in Autism by Aristo Vojdani, PHD, MSC, MT and Jama LambertDocument9 pagesA Gut Feeling For Immune Dysregulation & Neuroinflammation in Autism by Aristo Vojdani, PHD, MSC, MT and Jama LambertautismoneNo ratings yet
- 9-3-23 Immunity, Epi, Disease Control, Delivered Lec by DR Shumaila Humayun, 09-03-23Document65 pages9-3-23 Immunity, Epi, Disease Control, Delivered Lec by DR Shumaila Humayun, 09-03-23Dr Sarah Bakhsh - Resident FCPS Community MedicineNo ratings yet
- Dasar Dasar Sistim Pertahanan Tubuh Sistem Imun (Imunologi Dasar)Document41 pagesDasar Dasar Sistim Pertahanan Tubuh Sistem Imun (Imunologi Dasar)Olivia NurudhiyaNo ratings yet
- Specificity + Memory': Flexible Specific Immunological Memory Second ExposureDocument12 pagesSpecificity + Memory': Flexible Specific Immunological Memory Second ExposureRakin Bin RaihanNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Immunology Systemicreview PDFDocument17 pagesAn Overview of Immunology Systemicreview PDFMohmed AttiaNo ratings yet
- Immunologic PharmaDocument20 pagesImmunologic PharmaAnnapril TasicNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ImmunologyDocument10 pagesIntroduction To ImmunologyArvi MandaweNo ratings yet
- Fly A Little HigherDocument14 pagesFly A Little Higherapi-314556221No ratings yet
- Vedic Astrology For Better HealthDocument27 pagesVedic Astrology For Better HealthJason MintNo ratings yet
- One Word Substitution: List 1Document11 pagesOne Word Substitution: List 1Malu SakthiNo ratings yet
- Upper Gastrointestinal SurgeryDocument74 pagesUpper Gastrointestinal SurgeryOstazNo ratings yet
- Usmle Hy Images: By: MeduploaderDocument62 pagesUsmle Hy Images: By: Meduploaderdamodarpatil100% (18)
- Facial NerveDocument45 pagesFacial NerveyudhafpNo ratings yet
- Psychological DisordersDocument21 pagesPsychological DisordersMark100% (2)
- Lesson Plan On Minor Disorders During Pregnancy Its Management 1Document20 pagesLesson Plan On Minor Disorders During Pregnancy Its Management 1Bhawna Joshi100% (6)
- Listening Sample Test 2 Audio ScriptDocument12 pagesListening Sample Test 2 Audio ScriptCCCAXANo ratings yet
- Extra Care Plus: Bajaj AllianzDocument18 pagesExtra Care Plus: Bajaj AllianzSushma SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Mice and RatsDocument12 pagesMice and RatssamfarghNo ratings yet
- DystociaDocument8 pagesDystociaCylin Dadural100% (1)
- Interpretation of Mmpi 2 Clinical ScalesDocument23 pagesInterpretation of Mmpi 2 Clinical ScalesJuan LopezNo ratings yet
- OBGYN Form 3 Qs SearchableDocument50 pagesOBGYN Form 3 Qs SearchableGrace75% (4)
- Hepatobilier Ultrasound: DR - Yanto Budiman, SP - Rad, M.Kes Bagian Radiologi FKUAJ / RSAJDocument65 pagesHepatobilier Ultrasound: DR - Yanto Budiman, SP - Rad, M.Kes Bagian Radiologi FKUAJ / RSAJResNo ratings yet
- Ijsetr Vol 3 Issue 1-94-99Document6 pagesIjsetr Vol 3 Issue 1-94-99Naveed KhanNo ratings yet
- Daftar PustakaDocument11 pagesDaftar PustakaRizky Dian PratiwiNo ratings yet
- Violence at WorkDocument20 pagesViolence at WorkNahmeshNo ratings yet
- Geriatric Radiography - Merrills Atlas of Radiographic Positioning and ProceduresDocument22 pagesGeriatric Radiography - Merrills Atlas of Radiographic Positioning and ProceduresJonald Pulgo IcoyNo ratings yet
- Annalyn S. Da-Anoy, M.D., R.M.T.Document88 pagesAnnalyn S. Da-Anoy, M.D., R.M.T.api-25914483No ratings yet
- LBM-Secrets of Black MarshDocument35 pagesLBM-Secrets of Black MarshSamuel SacherNo ratings yet
- Care Plan - Chronic PainDocument4 pagesCare Plan - Chronic Painapi-246639896No ratings yet
- How To Tap The Incredible Secret Powers of Your MindDocument218 pagesHow To Tap The Incredible Secret Powers of Your Mindfreeplump395% (22)
- Imunisasi HajiDocument89 pagesImunisasi HajiFakikha AditamiNo ratings yet
- SepsisDocument14 pagesSepsisyreshgemNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Case Study - LipidDocument3 pagesBiochemical Case Study - Lipidapi-309675337No ratings yet
- Liver Diseases in PregnancyDocument5 pagesLiver Diseases in PregnancyOana TimofteNo ratings yet
- Pulpotomy Pulpectomy PDFDocument1 pagePulpotomy Pulpectomy PDFShinta Syafe'iNo ratings yet
- Body LiceDocument2 pagesBody LiceCeline BrantegemNo ratings yet
- Altered Sensorium and Care of Unconscious PatientsDocument17 pagesAltered Sensorium and Care of Unconscious PatientsChhabilal BastolaNo ratings yet